Health, disease and the development of medicines
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/46
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
1
New cards
According to the WHO what is HEALTH?
Health as a state of complete physical, mental and
social well-being and not merely the absence of disease
social well-being and not merely the absence of disease

2
New cards
What is a communicable disease?
A disease that can be transmitted person to person, animal to person and insect to person
3
New cards
What is a non-communicable disease?
A disease that is NOT transmitted from one person to another. E.g. heart disease, diabetes,
4
New cards
What is periodontal disease and what can it lead to?
Gum disease and if the bacteria enter the blood they can travel to the heart and cause cardiovascular disease.
5
New cards
What is a pathogen?
A microorganism that causes disease

6
New cards
What are the different types of pathogens?
Bacteria, Virus, Fungus, Protists
7
New cards
What is cholera?
a communicable disease cause by bacteria. It affects the small intestine. Spread by infected water and causes severe vomiting and diarrhoea.
(BACTERIA)
(BACTERIA)

8
New cards
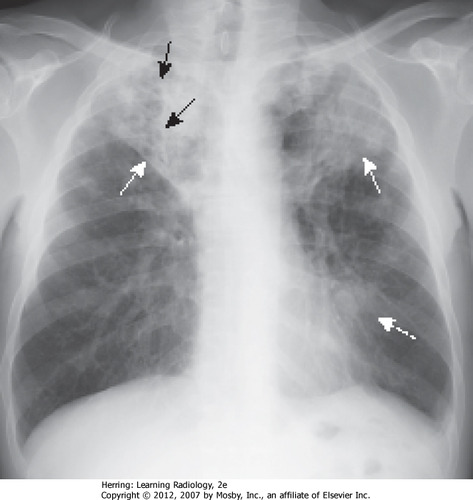
What is tuberculosis (TB)?
Bacterial infection of the lungs and is AIRBORNE
(TB for BACTERIA)
(TB for BACTERIA)
9
New cards
What is chalara ash dieback?
A fungus that infects ash trees and causes leaf loss and bark lesions
(FUNGI)
(FUNGI)

10
New cards
What is malaria?
Malaria affects the BLOOD AND LIVER. Spread by bites of infected mosquitoes
(PROTIST spread by the VECTOR mosquito)
(PROTIST spread by the VECTOR mosquito)

11
New cards
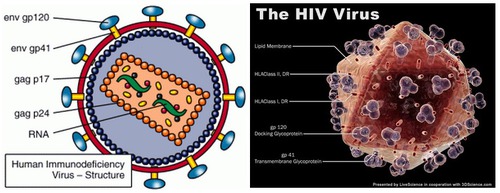
What is HIV?
VIRUS -
destroys white blood cells/immune system, leading to the onset of AIDS
destroys white blood cells/immune system, leading to the onset of AIDS
12
New cards
How is cholera bacteria spread?
contaminated water

13
New cards
How is tuberculosis bacteria spread?
airborne
14
New cards
How is chalara ash dieback fungi spread?
Carried through the air by wind and when diseased ash trees are moved between areas
15
New cards
How is malaria transmitted?
Animal vectors - mosquitos

16
New cards
What is an STI?
Sexually transmitted infection; caused by pathogens and spread through sexual contact.
17
New cards
What is chlamydia?
Most common bacterial STI. More than 1.2 million cases were reported in 2008.
18
New cards
How is chlamydia transmitted?
sexual contact
19
New cards
How can STIs be prevented?
Barrier method contraception
20
New cards
How can HIV be prevented?
do not share needles, use condoms, wear gloves if dealing with blood e.g. nurse
21
New cards
How is HIV spread?
Body fluids
22
New cards
Name 3 physical barriers to provide protection from pathogens in humans?
mucus, cilia and skin
23
New cards
Name two chemical defences to provide protection from pathogens in humans?
lysozymes (in tears breaks down cell wall of bacteria), hydrochloric acid (in stomach kills pathogens)
24
New cards
What is the immune system?
The body's defense against pathogens (white blood cells, lymphocytes, antibodies)

25
New cards
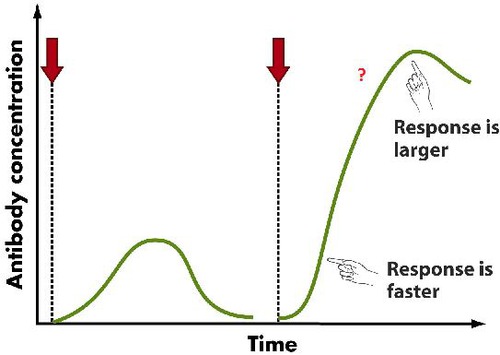
What is a memory lymphocyte?
A lymphocyte that remains in the blood for a long time after an infection or vaccination. On a second exposure to the pathogen they release MORE antibodies FASTER.
26
New cards
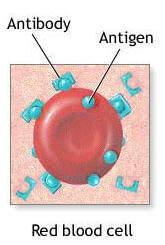
What is an antigen?
a toxin or other foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.
27
New cards
What do lymphocytes release?
antibodies
28
New cards
What is immunisation (vaccination)?
A 'safe' version of the pathogen is injected, lymphocytes release antibodies and memory lymphocytes. If the REAL pathogen then enters the body - the memory lymphocytes release MORE antibodies FASTER so that you are IMMUNE and do not get ill.
29
New cards
Explain the body's response to immunisation using an inactive form of a pathogen
The lymphocytes 'think' it is the real pathogen and start to attack with antibodies. (Memory lymphocytes are also produced)
30
New cards
What are antibiotics?
Drugs that kill or prevent the growth of bacteria without killing healthy body cells (They DO NOT work on VIRUSES)
31
New cards
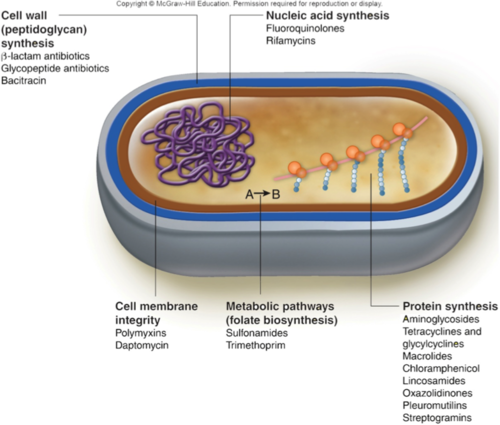
What do antibiotics target?
bacteria
32
New cards
What are antibiotics only used to treat bacterial infections?
Antibiotics can only be used to treat bacterial
infections because they inhibit cell processes in the bacterium but not the host organism.
infections because they inhibit cell processes in the bacterium but not the host organism.
33
New cards
What are stages of development of medicines?
Discovery,
Preclinical testing(on cells/tissues in a lab)
Animal testing
Small clinical trail (healthy people)
Large clinical trial (people with disease)
Preclinical testing(on cells/tissues in a lab)
Animal testing
Small clinical trail (healthy people)
Large clinical trial (people with disease)

34
New cards
What is a non-communicable disease?
non-communicable human diseases are caused by the interaction of a number of factors, including cardiovascular diseases, many forms of cancer, some lung and liver diseases and diseases influenced by nutrition - they are usually slow to develop and last a long time
35
New cards
Why does exercise help to lose weight?
It BURNS FAT for ENERGY
36
New cards
What is BMI?
Body Mass Index; a measure of body weight relative to height

37
New cards
How is BMI calculated?
MASS in kg/height in meters squared
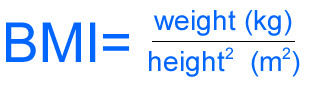
38
New cards
What is obesity?
excess body fat - BMI over 30

39
New cards
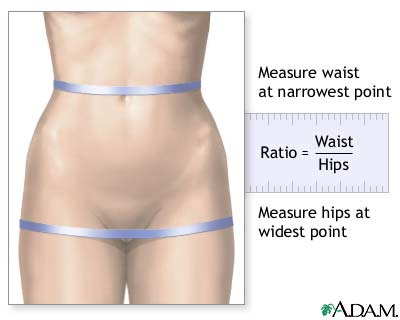
What is the waist to hip ratio?
circumference of the waist divided by the circumference of the hips
40
New cards
Why is waist to hip better than BMI?
Because a weightlifter can have their weight in their muscles and could have a BMI of over 30 but NOT be obese - waist to hip shows if they are ABDOMINALLY OBESE
41
New cards
What organ can alcohol damage?
The Liver (cirrhosis)
42
New cards
What is cardiovascular disease?
All the diseases and conditions of the heart and blood vessels.
43
New cards
What does smoking cause?
Disease of the heart, blood vessels and lungs
TAR causes cancer
Nicotine is addictive
TAR causes cancer
Nicotine is addictive
44
New cards
What are the types of treatment for cardiovascular disease?
life-long medication
surgical procedures
lifestyle changes
STENT
BYPASS
surgical procedures
lifestyle changes
STENT
BYPASS
45
New cards
What do we call a blockage of a blood vessel in the brain?
Stroke
46
New cards
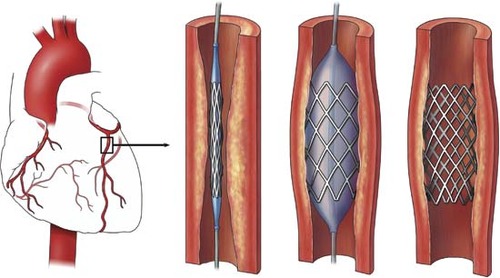
What is a stent?
A small object inserted into a blood vessel to open it up and keep it open.
47
New cards
What are lifestyle change treatment for cardiovascular disease?
Stop smoking, low sugar low carb diet, exercise, weight loss, reduce stress