M1L1 - Lipids & Membranes
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for the 7 questions in module 1, lesson 1 - contains images for reference
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is the name of a 1 carbon saturated fatty acid?
formic/methanoic acid
What is the name of a 2 carbon saturated fatty acid?
acetic acid
What is the name of a 3 carbon saturated fatty acid?
propionic acid
What is the name of a 4 carbon saturated fatty acid?
butyric acid
What is the name of a 5 carbon saturated fatty acid?
valeric acid
What is the name of a 6 carbon saturated fatty acid?
caproic acid
What is the name of an 8 carbon saturated fatty acid?
caprylic acid
What is the name of a 10 carbon saturated fatty acid?
capric acid
What is the name of a 12 carbon saturated fatty acid?
lauric acid
What is the name of a 14 carbon saturated fatty acid?
myristic acid
What is the name of a 16 carbon saturated fatty acid?
palmitic acid
What is the name of an 18 carbon saturated fatty acid?
stearic acid
What is the name of a 20 carbon saturated fatty acid?
arachidic acid
What is the name of a 16 carbon unsaturated fatty acid?
palmitoleic acid
What are the possible identities of an 18 carbon unsaturated fatty acid?
oleic, linoleic, or linolenic acid
What are the possible identities of a 20 carbon unsaturated fatty acid?
arachidonic acid or EPA
What is the name of a 22 carbon unsaturated fatty acid?
DHA
What is the identity of 18:1(9)?
oleic acid
What is the identity of 18:2(9,12)
linoleic acid
What is the identity of 18:3(9,12,15)?
linolenic acid
What is the identity of 20:4(5,8,11,14)?
arachidonic acid
What is the identity of 20:5(5,8,11,14,17)?
EPA
Is linoleic acid omega-3 or omega-6, given its identification is 18:2(9,12)?
omega-6
Is linolenic acid omega-3 or omega-6, given its identification is 18:3(9,12,15)?
omega-3
Is arachidonic acid omega-3 or omega-6, given its definition is 20:4(5,8,11,14)?
omega-6
Is EPA omega-3 or omega-6, given its identification is 20:5(5,8,11,14,17)?
omega-3
Is DHA omega-3 or omega-6, given its identification is 22:6(4,7,10,13,16,19)?
omega-3
Why is animal fat a solid at room temperature?
Animal fat has a HIGHER percentage of saturated fatty acyl groups connected to triacylglycerol and a LOWER percentage of unsaturated fatty acyl groups connected to triacylglycerol.
Why is plant oil a liquid at room temperature?
Plant oil has a HIGHER percentage of unsaturated fatty acyl groups connected to triacylglycerol and a LOWER percentage of saturated fatty acyl groups connected to triacylglycerol.
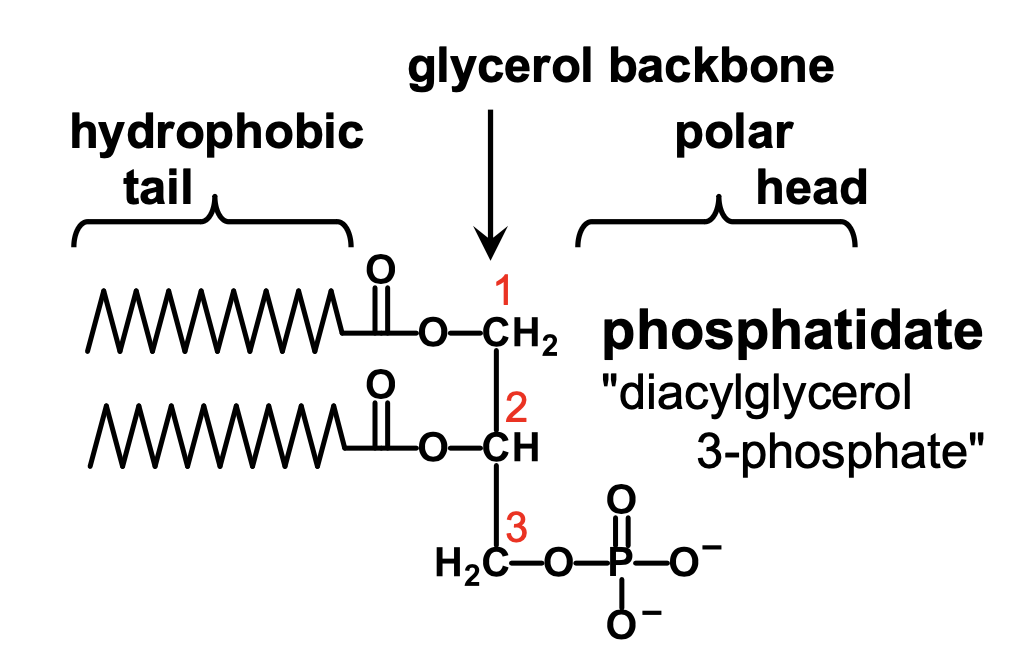
What is a glycerophospholipid?
Glycerophospholipids contain two fatty acyl groups connected to a glycerol backbone and a polar phosphate group attached to the end, which may have other groups attached
What is phosphatidate or phosphatidic acid?
diacylglycerol-3-phosphate
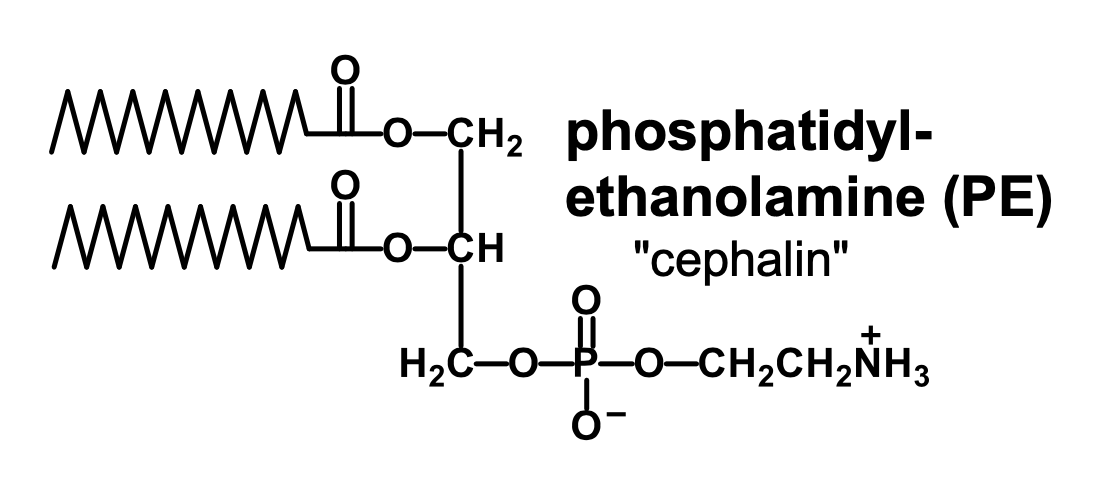
What is phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (PE)?
It is an ethanolamine connected to the phosphate group of phosphatidate
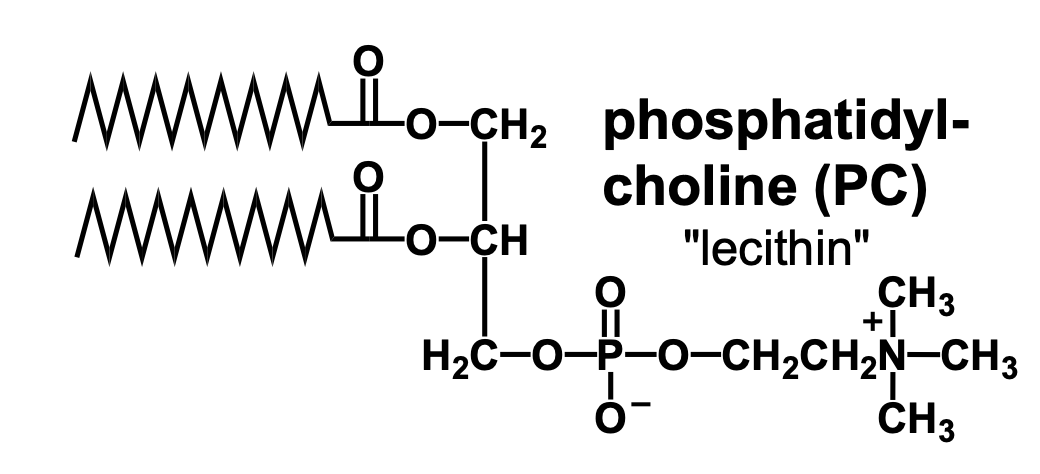
What is phosphatidyl-choline (PC)?
It is a choline connected to the phosphate group of phosphatidate
What is phosphatidyl-serine (PS)?
It is a serine connected to the phosphate group of phosphatidate
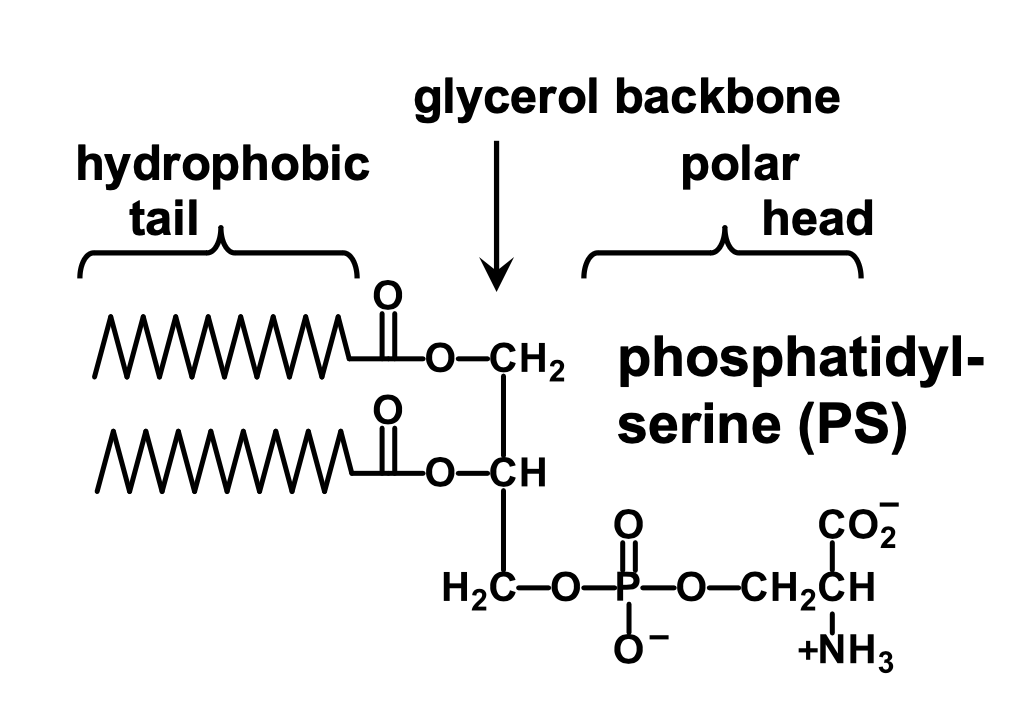
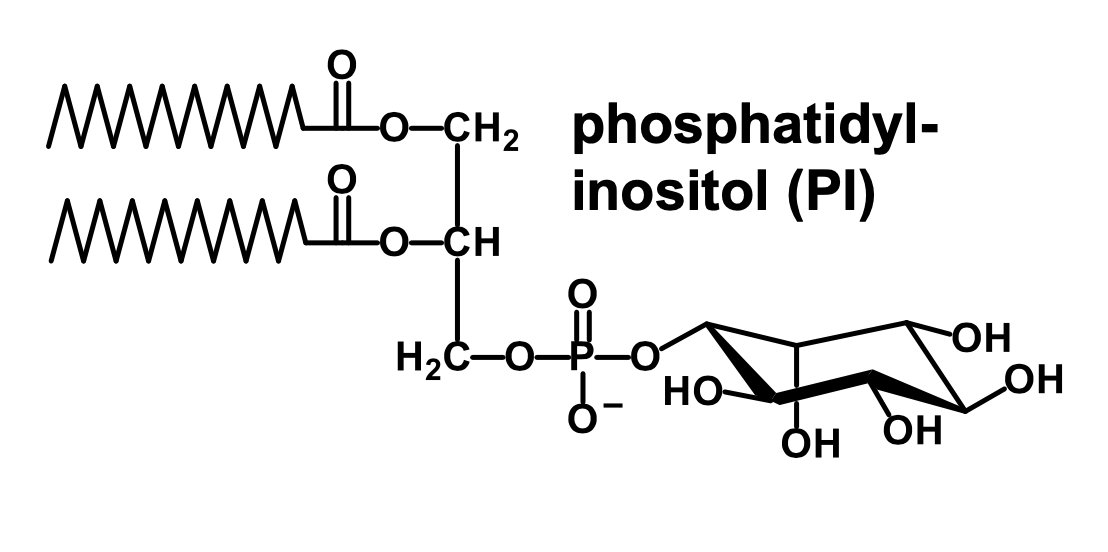
What is phosphatidyl-inositol?
It is an inositol connected to the phosphate group of phosphatidate
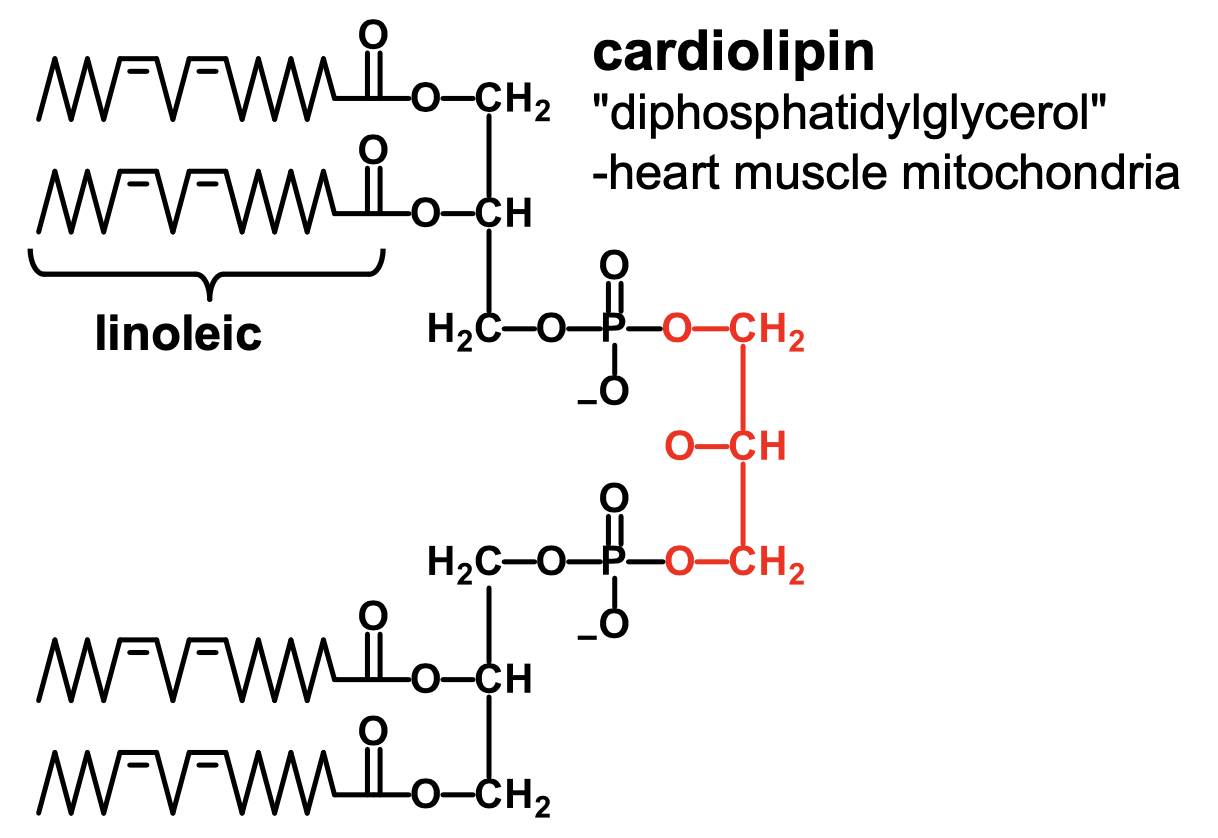
What is cardiolipin?
diphosphatidylglycerol
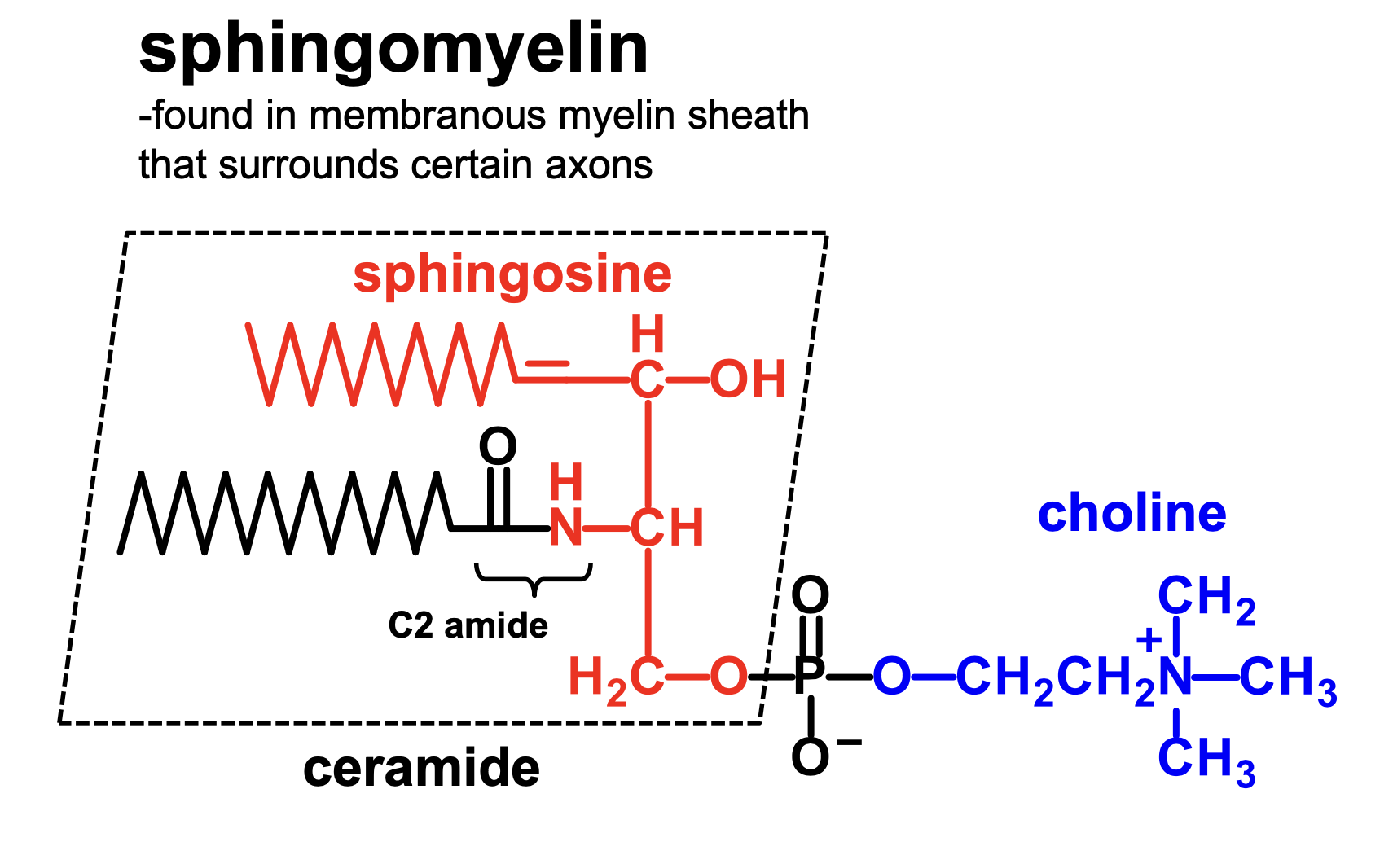
What is a sphingophospholipid?
sphingomyelin, which is a ceramide plus a phosphate plus a choline
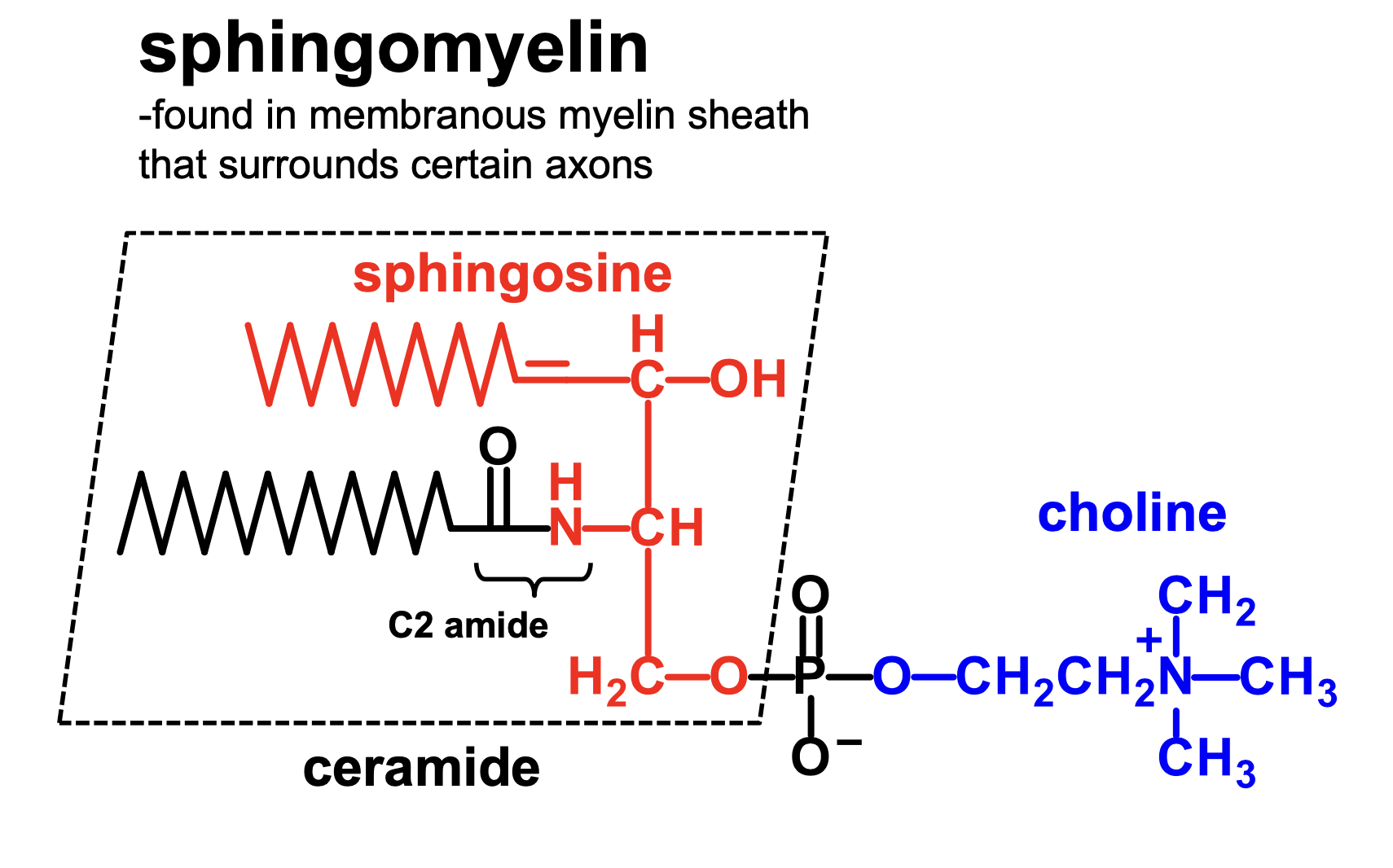
What is a ceramide?
a sphingosine plus a C2 amide
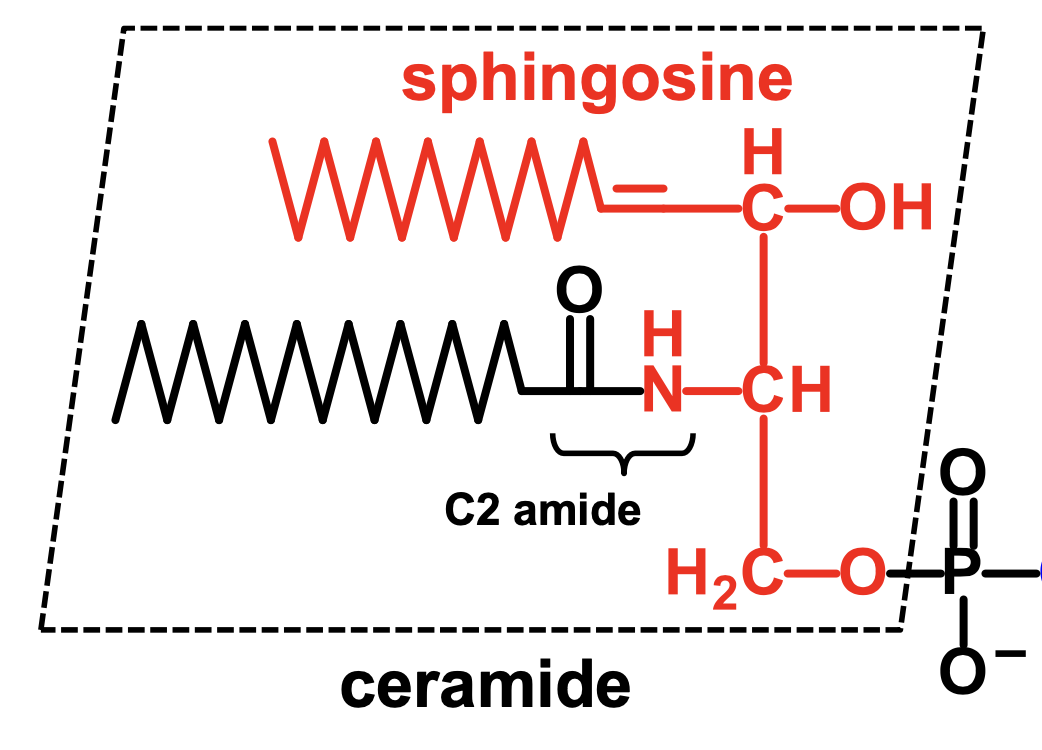
What is a glycosphingolipid?
a ceramide attached to one or more sugar molecules
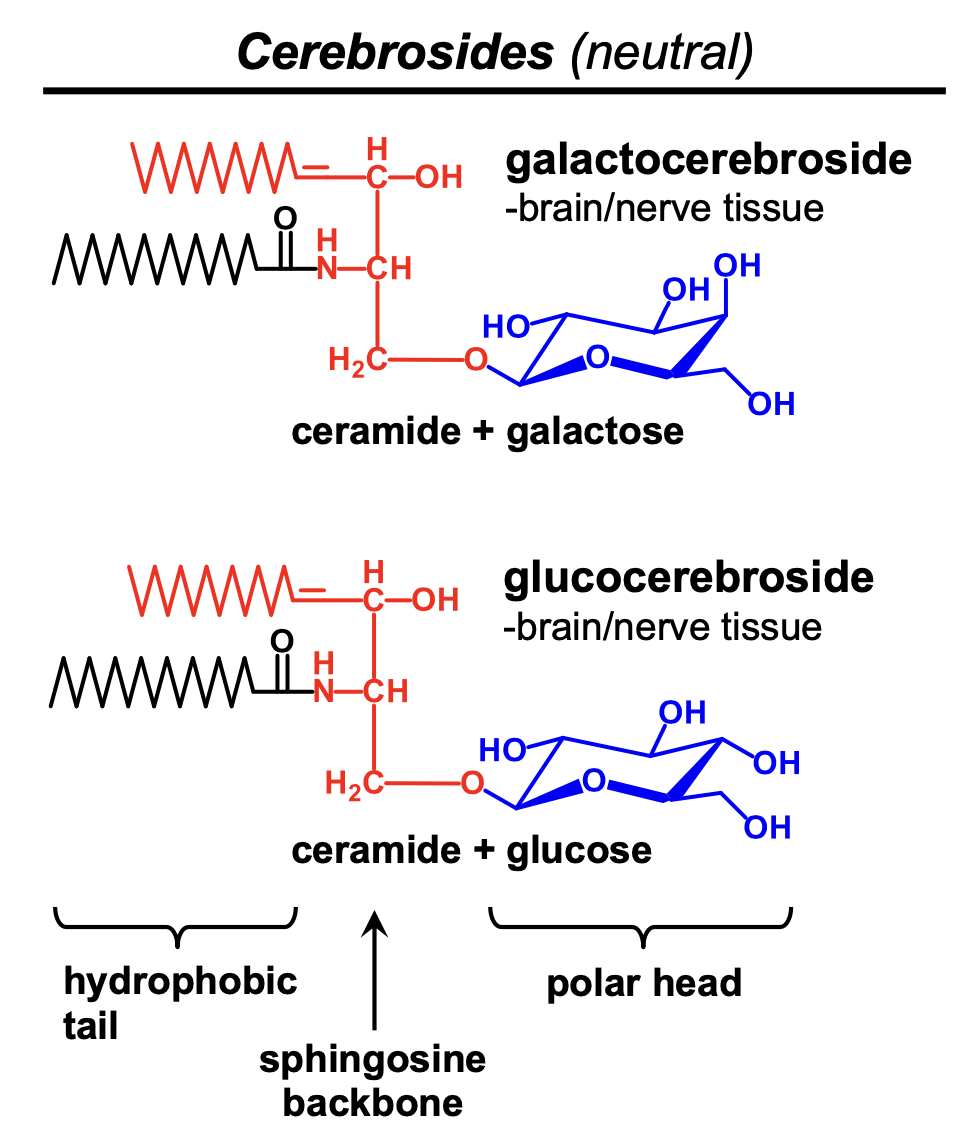
What is a cerebroside?
ceramide and sugar
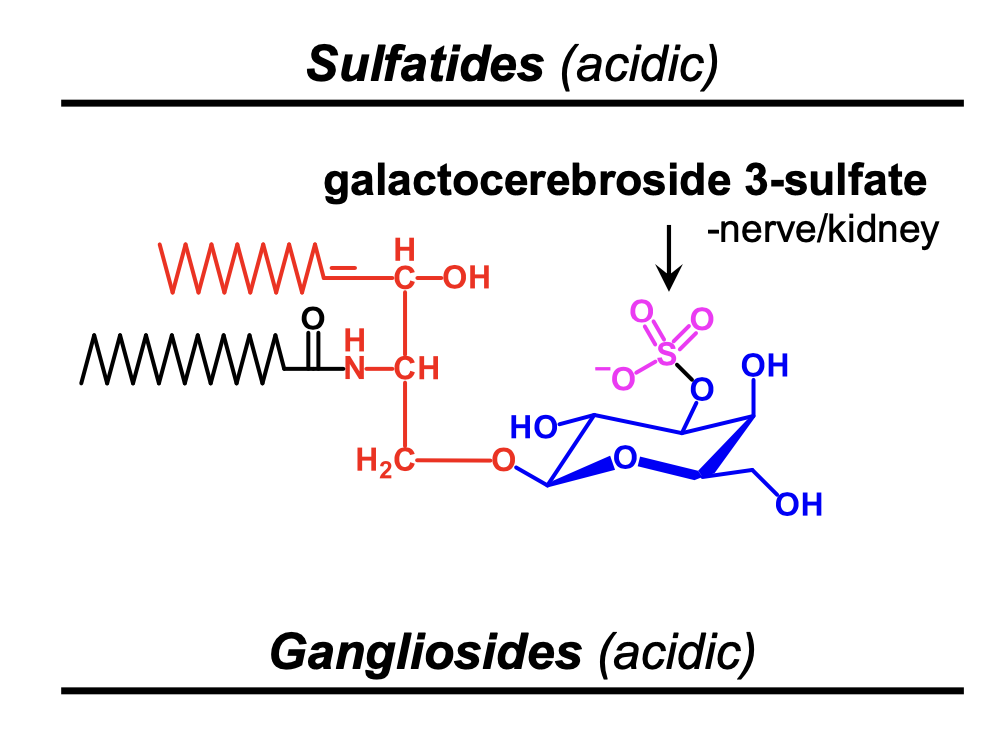
What is a sulfatide?
ceramide and sugar with a sulfate group
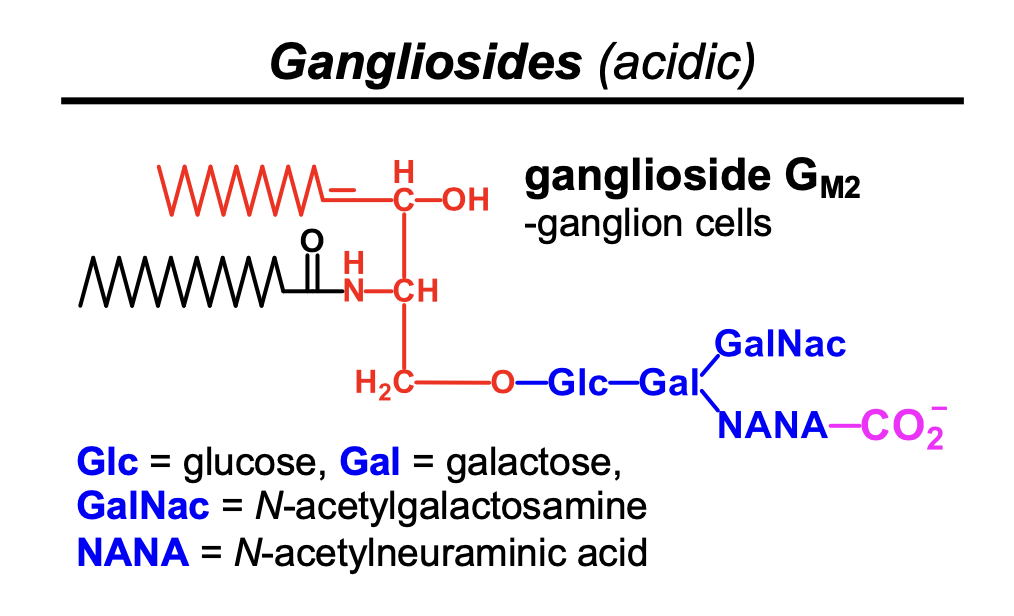
What is a ganglioside?
ceramide and multiple sugars where one sugar is oxidized
What is ceramide plus galactose?
galactocerebroside
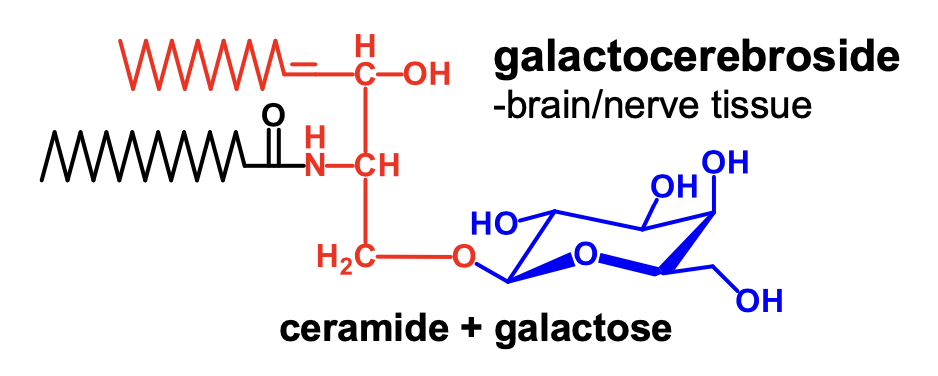
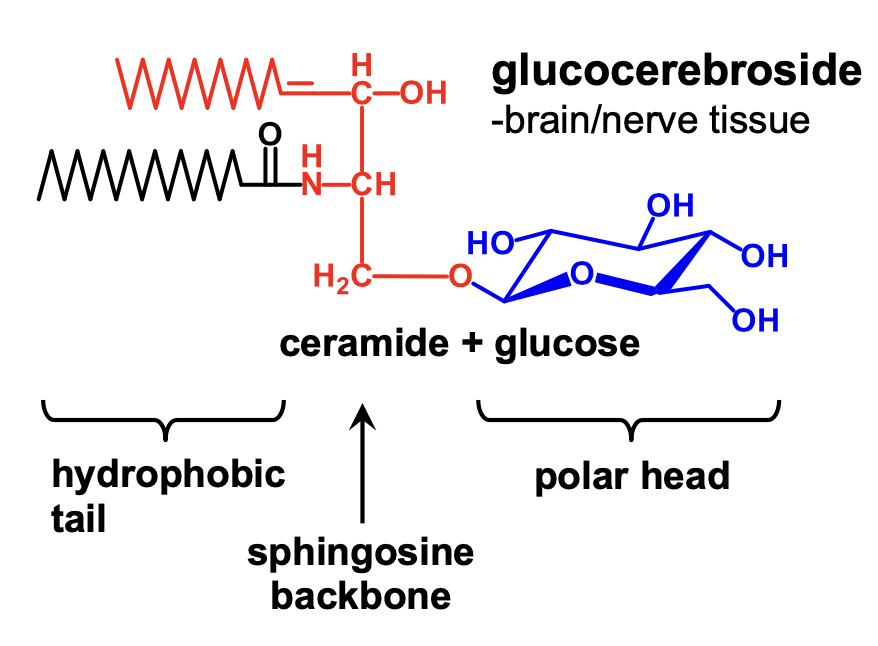
What is ceramide plus glucose?
glucocerebroside
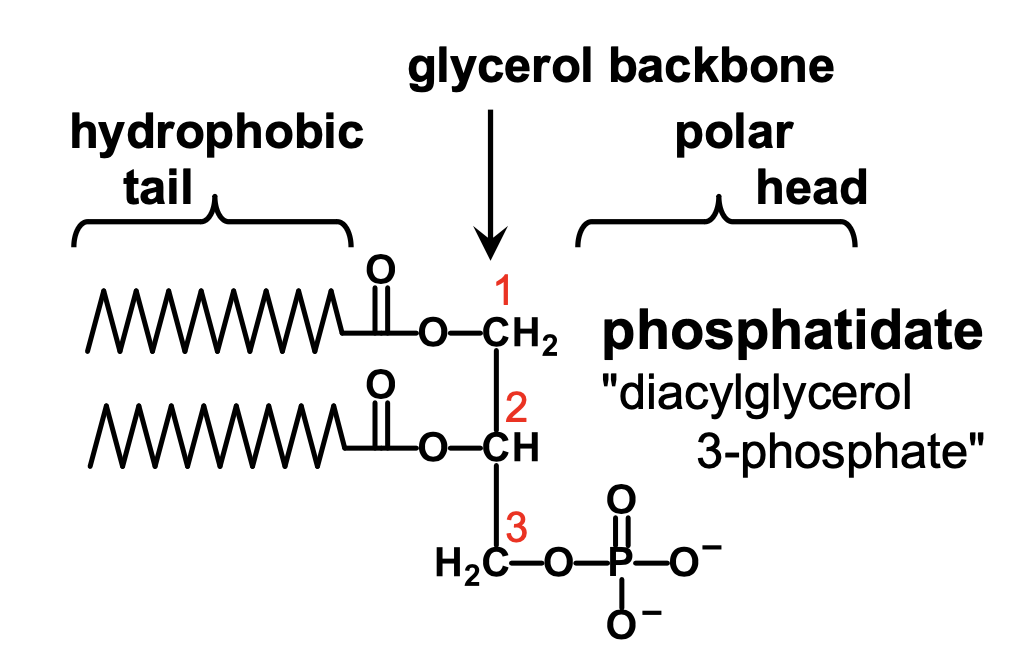
What is diacylglycerol-3-phosphate?
phosphotidate
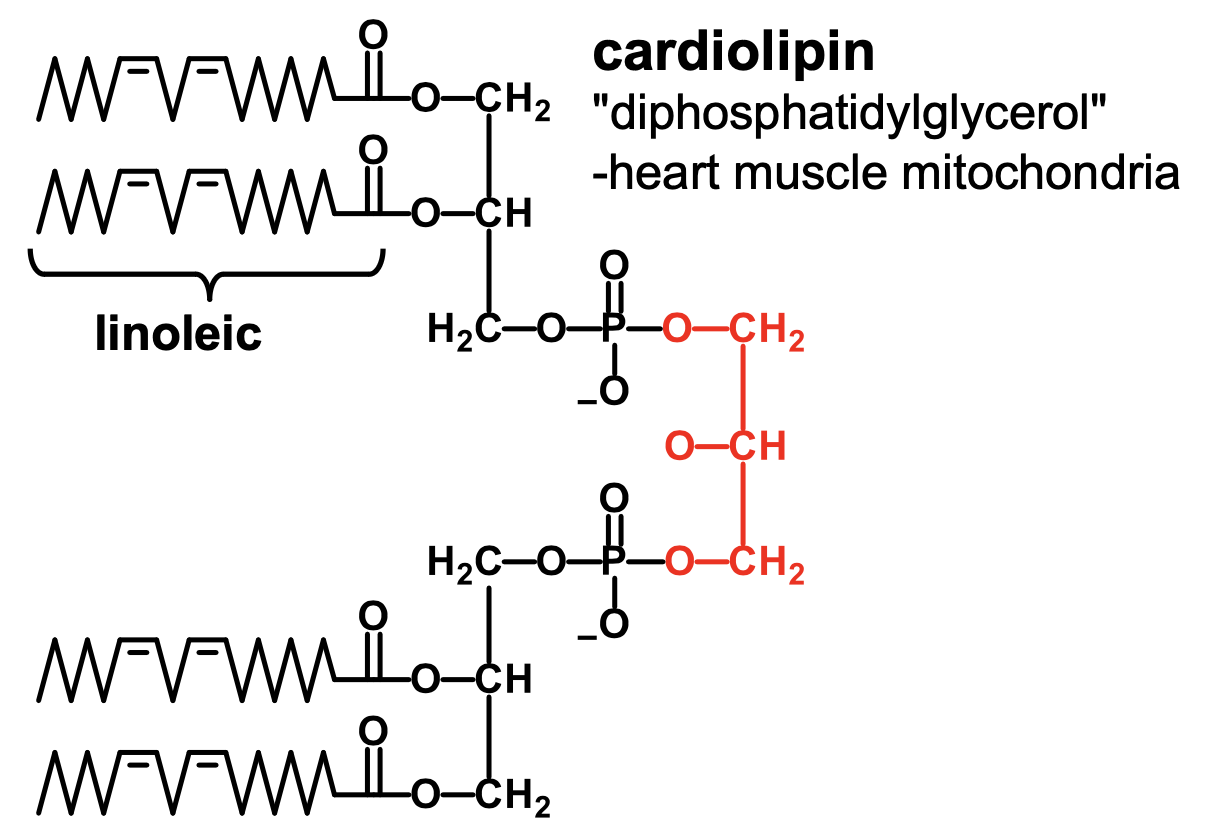
What is diphosphatidylglycerol?
cardiolipin
What is ceramide plus phosphate plus choline?
sphingomyelin
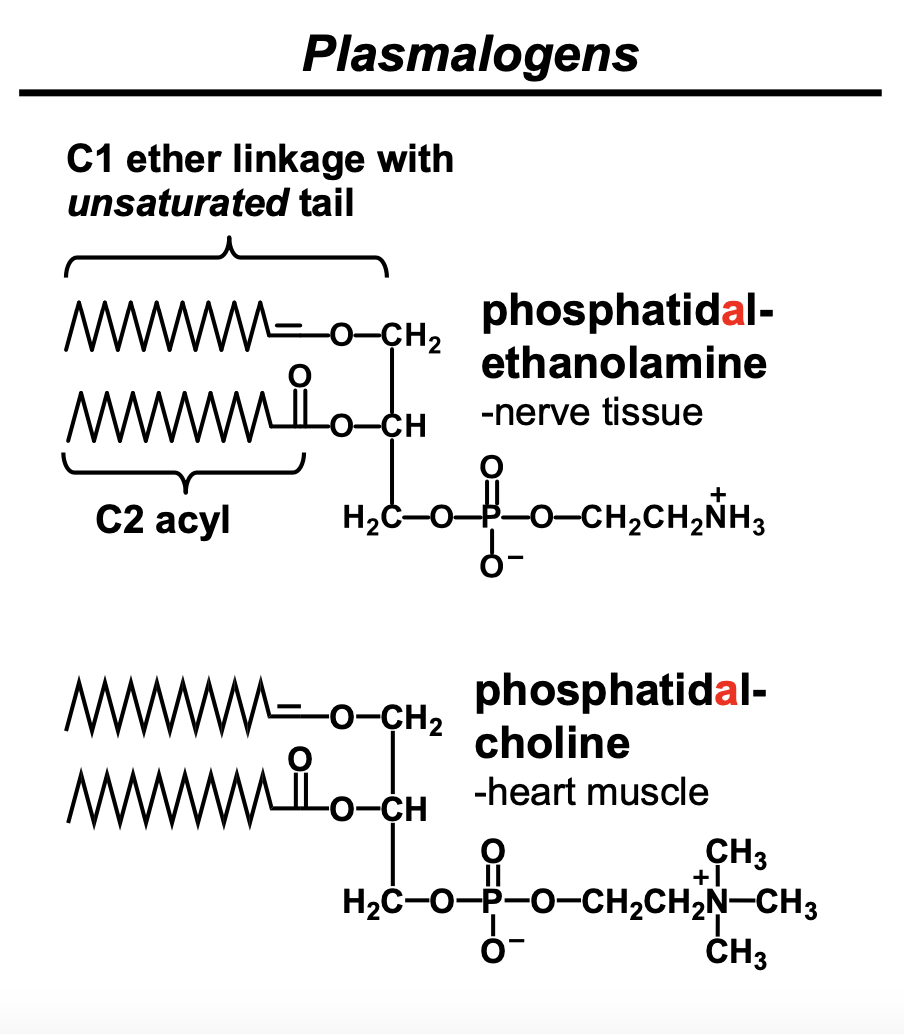
How can you recognize phosphatidal-ethanolamine and phosphatidal-choline?
The first acyl group has a C1 ether linkage with an unsaturated fatty acyl tail. They are called plasmalogens.
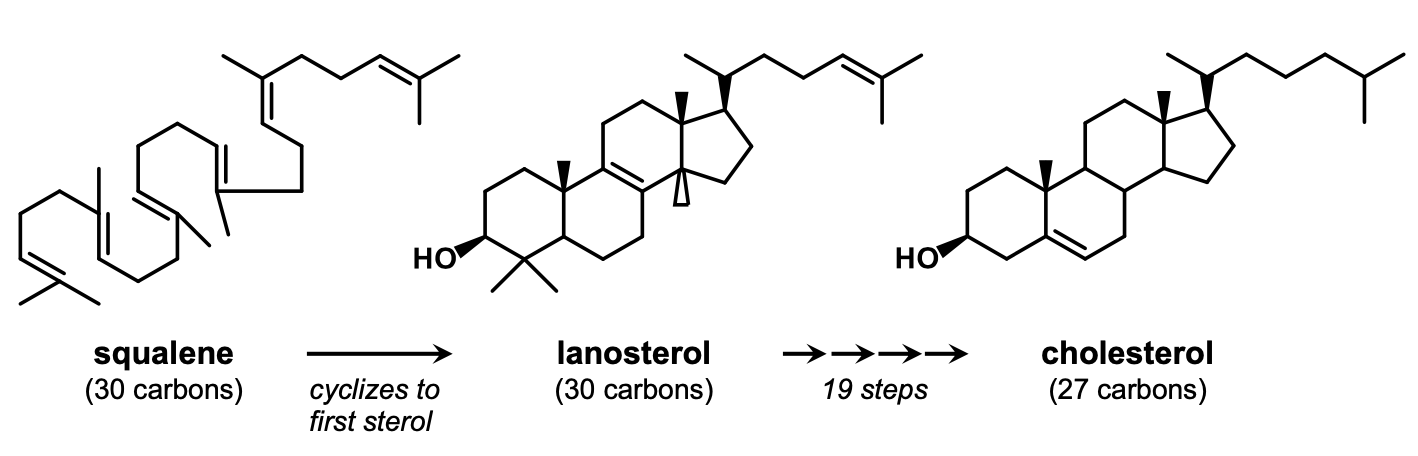
What is squalene?
Squalene is a triterpene (3 monoterpenes = 6 isoprenes = 30 carbons) and is the precursor to cholesterol in animal cells.
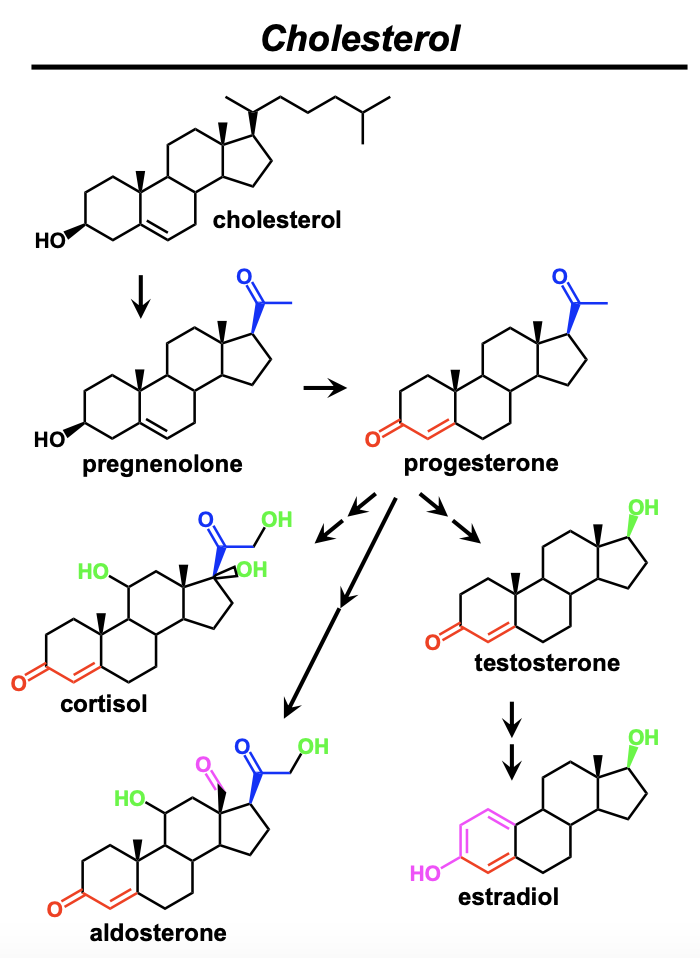
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a 27 carbon cyclic compound found in animal cells that is the precursor to many different hormones. It modulates fluidity of the plasma membrane.
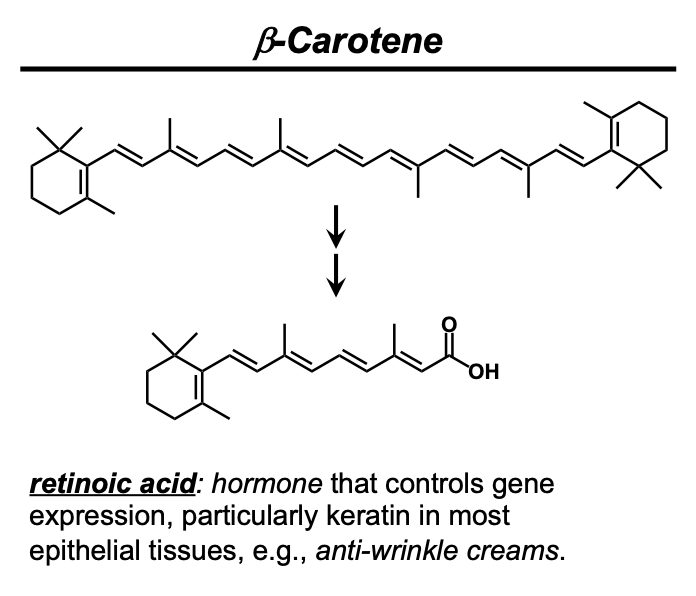
What is ß-carotene and why is it important?
ß-carotene is a tetraterpene (4 monoterpenes = 8 isoprenes = 40 carbons) and is the precursor to retinoic acid, which is Vitamin A