Dementia & AD- Miller
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is dementia?
defines the loss of cognitive functioning (thinking, remembering, reasoning) and behavioral abilities that interfere with a person’s daily life and activities
Does mild cognitive impairment (MCI) warrant a dementia diagnosis?
no! not everyone with MCI will develop dementia (about 15% do)
What is vascular dementia (VaD)?
how to reduce risk?
treatment?
refers to any dementia that is primarily caused by cerebrovascular disease or impaired cerebral blood flow
reduce risk—> antihypertensives, antithrombotic therapy
treatment—> cholinesterase inhibitors, memantine
What is frontal lobe dementia?
any current cure?
neuropathologically and clinically heterogeneous disorder characterized by focal degeneration of the frontal and/or temporal lobes
no current “cure”—> tx aimed at s/sx relief
What is the most common pathology of dementia and is defined as a gradual progressive dementia?
Alzheimer’s Disease
Early Onset Alzheimer Disease (EOAD) is age < ____.
Late Onset Alzheimer Disease (LOAD) is age ≥____.
EOAD is age <65
LOAD is age ≥65
What is the exact etiology of AD?
exact is not known!!! several genetic/environmental factors and hypothesizes
Which genes are most strongly associated with Alzheimer's disease risk, and what biological processes do they influence?
APOE and ABCA7—> most substantial heritable contributor to genetic risk
role: lipid metabolism
TREM2, CLU, and PICALM
role: implicated in amyloid plaque formation, tau pathology, neuroinflammation
What are the key genetic mutations associated with dominantly inherited Early-Onset Alzheimer's Disease (EOAD) and Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease (LOAD)
EOAD
dom inherited alterations in chromosomes 1,14, 21 that impact amyloid precursor protein (APP)
LOAD
APOE*4 allele (one copy/heterozygous less risk then two copies/homozygous)
What is Apolipoprotein E (APOE)?
fxn?
binds to what?
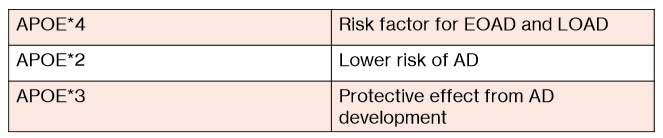
APOE*4 allele is associated with what?
Difference between APOE*4, APOE*3, APOE*2?
APOE—> a fat-soluble transporter
responsible for transporting cholesterol in the blood/brain and interacts with b-amyloid binds to NFTs
APOE*4 allele associated with modified clearance and increased deposition of Ab in AD
APOE*4- risk factor for EOAD and LOAD
APOE*2- lower risk of AD
APOE*3- protective effect from AD development
What is one gene that actually reduces the risk of AD/ EOAD development?
A673T (a rare APP mutation)
PRACTICE:
Genetic susceptibility to late-onset AD is primarily linked to which of the following?
a. apolipoprotein E4 genotype
b. presenilin gene mutations
c. amyloid precursor protein mutations
d. apolipoprotein E2 genotype
a.
T/F: the exact pathophysiologic mechanisms of AD are unknown.
true—> there are signature lesions made of amyloid plaques and NFTs in the brain’s cortical areas and medial temporal lobe structures tho
What is the amyloid cascade hypothesis of AD?
imbalance of what?
results in?
what’s unknown about it?
imbalance between the production and clearance of b-amyloid peptides
results in accumulation/aggregation—> plaque formation—> AD development
unknown if presence of ab is the primary pathology or changes are a marker of an alternate pathology
What are tau proteins?
What are NFTs?
How are NFTs correlated with dementia?
tau proteins provide structural support (to microtubules)
NFTs are composed of abnormally hyperphosphorylated tau proteins (microtubules now can’t fxn properly)
NFT density tends to correlate with severity of dementia
what is one of the most prominent neurotransmitter defects in AD?
cholinergic abnormalities (aka loss of acetyl choline)
What is the cholinergic hypothesis in AD?
BASICALLY—> a theory that loss of cholinergic neurons and neurotransmitter dysfunction (e.g., acetylcholine) contributes to cognitive/memory impairments in AD
What are the main limitations/flaws of the Cholinergic Hypothesis?
Cholinergic neurons are just one of many pathways damaged in AD.
cholinergic cell loss is a secondary consequence of AD pathology
What do cholinergic therapies do in AD?
minimize/ improve symptoms
Explain what the inflammatory mediator hypothesis for AD is.
BASICALLY—>proposes that chronic brain inflammation plays a key role in Alzheimer’s disease
β-amyloid has direct neurotoxicity AND triggers an immune response that indirectly damages neurons.
Inflammation represents a failed attempt to clear amyloid.
In addition to acetyl choline, what neurotransmitter abnormalities have been seen in AD?
glutamate
serotonin
There is a causal association between what disease and incidence of AD?
CV and vascular disease (ex: high cholesterol, HTN)
vascular disease may accelerate amyloid deposition and reduce clearance of amyloid b
With what stage of AD does functioning fluctuate from day to day?
a. mild
b. moderate
c. severe
b.
What are some cognitive symptoms of AD?
memory loss
aphasia (impaired communication)
circumlocution, anomia
apraxia (can’t sequence movements)
agnosia
disorientation
impaired executive fxn
What are some functional symptoms of AD?
inability to care
eating, toileting, bathing, dressing
What are some neuropsych symptoms of AD?
depression
hallucinations, delusions
behavioral disturbances
aggression
uncooperativeness
wander
repetitive manners
Screening for AD is done at what age regardless of symptoms?
mini-Cof or MoCA is rec at age 65 regardless of symptoms
What are the 4 screening assessments available for AD?
(idk how imp)
mini-mental state examination
montreal cognitive assessment
mini-cog
saint louis university mental status exam
What are the 2 categories of biomarkers in AD?
which is early changing versus late changing?
what do they help do? diagnose?
FYI: Biomarkers are measurable substances or processes in the body that indicate normal or abnormal conditions
Core 1 (early-changing)
includes b-amyloid and T1
help identify presence of AD
Core 2 (later-changing)
includes T2 biofluid and tau PET
help confirm AD diagnosis
What is the definitive diagnosis for AD?
is a clinical diagnosis!!!! (looks at symptoms, history, cognitive tests, imaging)
What is the goal of pharm therapy in AD?
tx cognitive difficulties symptomatically and preserve pt. function for as long as possible
Current AD treatments ______ seem to prolong life, cure AD, or halt/reverse processes of the disorder.
a. do
b. do not
b.
List all the pharm options for cognitive symptoms of AD:
just an overview, don’t memorize
cholinesterase inhibitors
Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine
NMDA receptor antagonists
Memantine
cholinesterase inhibitor + NMDA receptor antagonist
Donepezil + memantine
anti-amyloid monoclonal antibody (mAb)
Donanemab
Lecanemab
What is the indication of cholinesterase inhibitors?
1st line for mild-moderate AD
Name the cholinesterase inhibitors:
donepezil
rivastigmine
galantamine
What are the ADRs of cholinesterase inhibitors in general?
dizzy
syncope
bradycardia
atrial arrhythmias
sinoatrial and AV block
MI
n/v/d
anorexia
weight loss
ADRs specific to donepezil?
peptic ulcer disease
GI bleeding
insomnia
vivid dreams/ nightmares
ADRs and Counseling points with Rivastigmine?
ADR: allergic dermatitis
admin: take with food
MOA of each of the following:
donepezil
rivastigmine
galantamine
idk how imp
donepezil- specifically/reversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase
rivastigmine- psuedo-irreversible inhibitor of butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase
galantamine
ADR and counseling points of Galantamine?
ADR: serious skin reactions
admin: take with meals
MOA of Memantine:
uncompetitive antagonist of the NMDA glutamate receptor
ADRs and counseling points with Memantine (Namenda)?
ADRs: HA, confusion, dizzy, hallucinations, constipation
admin: can take w/ or w/out food, can open capsule and sprinkle contents on applesauce
Combination therapy is done for what kind of AD?
moderate-severe
Namzaric is a combination of what 2 drugs?
donepezil + memantine
What drugs are anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies used in AD?
Donanemab
Lecanemab
What is the main ADRs assoicated with Donanemab and Lecanemab?
ARIA (amyloid-related imaging abnormalities)
infusion related rxns
How often is each anti-amyloid mAb dosed?
Donanemab- q 4 weeks
Lecanemab- q 2 weeks
Contraindications to taking anti-amyloid mAbs?
homozygous for APOE e4 allele
When is pharm therapy for neuropsychiatric symptoms started?
is tx permanant or temporary?
when nonpharm has failed!!
temporary tx
If an antidepressant must be used in AD, what is the DOC? what antidepressant should be AVOIDED?
SSRIs (sertraline, citalopram) most common used in AD
AVOID Tricyclic antidepressants (anticholinergic activity)
What is the BBW on antipsychotics?
increased mortality in elderly patients with dementia related psychosis
What antipsychotics can be considered in AD?
aripriprazole
risperidone
olanzapine
quetiapine
Brexipiprazole is FDA approved for ________________________.
agitation with dementia
Suvorexant is approved in patients with mild-to-moderate AD for what?
insomnia