temporal lobes - ch 15
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What structures are found in the medial temporal cortex?
The amygdala, hippocampus, surrounding cortex (subiculum, entorhinal, perirhinal), and fusiform gyrus.
What are the primary functions of the temporal lobe?
Processing auditory input, visual object recognition, and long-term storage of information.
What is the role of the superior temporal sulcus?
It processes biological motion and is involved in social cognition, allowing us to infer others' intentions.
What is the significance of the fusiform gyrus?
It is functionally part of the lateral temporal cortex and is involved in face recognition.
What are the five distinct connections of the temporal cortex?
Hierarchical sensory pathway, dorsal auditory pathway, polymodal pathway, medial temporal projection, and frontal lobe projection.
What is the perforant pathway?
The major input pathway of the hippocampal formation, connecting auditory and visual association areas to the medial temporal lobe.
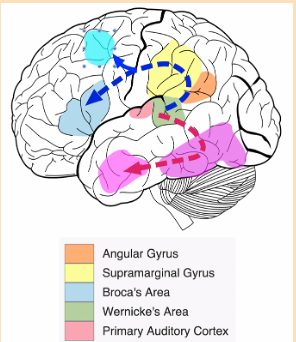
What is Wernicke's aphasia?
A patient has fluent but gibberish speech, and they have difficulty understanding spoken or written language, resulting from damage to the left temporal lobe.
What is Klüver-Bucy Syndrome?
A neuro-behavioral syndrome associated with bilateral lesions in the anterior temporal lobe, leading to visual agnosia, hypersexuality, and emotional changes.
What is the role of the left temporal lobe?
It is primarily involved in verbal memory and speech processing.
What is the role of the right temporal lobe?
It is primarily involved in nonverbal memory, musical processing, and facial recognition.
How does the temporal lobe contribute to memory?
It is crucial for long-term memory storage and retrieval, particularly through the hippocampus.
What is the function of the anterior temporal cortex?
It serves as an amodal semantic hub, integrating multimodal information to represent concepts and facts, including people, objects, actions, and sounds.
What is the impact of temporal lobe lesions on auditory processing?
They can lead to cortical deafness and impaired auditory processing, making it difficult to discriminate speech sounds.
What is the significance of the insula in the temporal lobe?
It contains the gustatory cortex and is involved in processing taste information.
What is the function of the dorsal auditory pathway?
It directs movement with respect to auditory information, connecting the auditory cortex to the posterior parietal cortex.
What are the symptoms of temporal-lobe lesions?
Auditory disturbances, visual perception disorders, long-term memory problems, and altered personality and affective behavior.
What is cross-modal matching?
The process of matching visual and auditory information, dependent on the cortex of the superior temporal sulcus.
What is the role of the temporal lobe in spatial navigation?
The hippocampus within the temporal lobe is essential for spatial memory and navigation.
What is the relationship between the corpus callosum and the temporal lobe?
The corpus callosum connects the lateral temporal cortices of the left and right hemispheres.
What is auditory association cortex?
It is involved in processing complex sounds and is located within the lateral fissure of the temporal lobe.
What is the role of the STS?
It helps in understanding biological motion , inferring intentions of others, and social cognition.
What are the effects of bilateral removal of the medial temporal lobes?
It results in anterograde amnesia, affecting the ability to form new memories.
What is the significance of the auditory association areas?
It interprets sounds and speech from the primary auditory cortex.
Hierarchical sensory pathway
incoming from primary & secondary auditory, and visual areas ; subserves stimulus recognition
polymodal pathway
from auditory & visual association areas to polymodal cortex in STS ; stimulus categorization
medial temporal projection
pathway is from auditory & visual association areas to medial temporal lobe ; forms the performant pathway
frontal lobe projection
auditory & visual information from temporal association areas to frontal lobe ; necessary for movement control, short-term memory, and affect