ECON 2110 - Clemson: Exam 1
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Absolute Advantage
The ability to produce a good using fewer inputs than another producer.
Comparative Advantage
The ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer.
True or False: It is impossible for a country to have an absolute advantage in both goods.
False.
True or False: It is impossible for a country to have a comparative advantage in both goods.
True.
If you have the opportunity cost of one good, how can you find the opportunity cost of the other?
The inverse of the first good.
Trade Off
The idea of having to sacrificing something for something else because of limits.
In order to have a higher overall production, a country should specialize in the good that it has a(n) (absolute/comparative) advantage in.
Comparative Advantage.
What makes everyone better off?
Trade
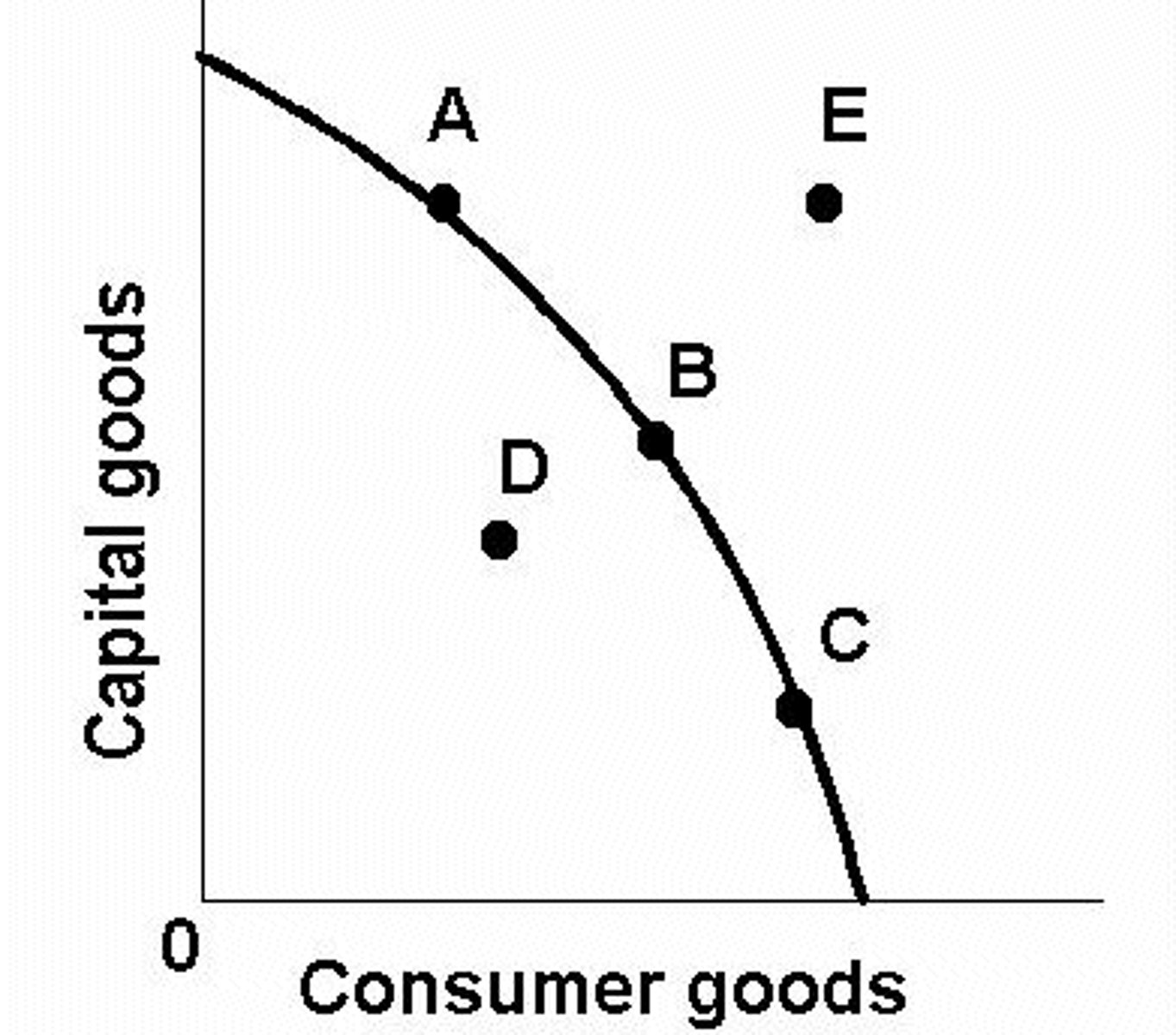
Production Possibility Frontier
A graph that shows the combination of two goods the economy can possibly produce given the available technology.
Point A, B, and C: Possible and Efficient
Point D: Possible but Inefficient
Point E: Not Possible (unless technology gets better)
Points A, B, and C are considered:
Point D is considered:
Point E is considered:
Opportunity Cost
What must be given up to obtain a different item.
From the PPF, how can you find the opportunity cost of one good?
The slope of the PPF
What two ways can shift the PPF outward?
1. Obtaining additional resources.
2. Improvement in technology.
What can cause the PPF to be bow-shaped?
When the opportunity cost of a good rises as more of the good is produced.
Microeconomics
The study of how households and firms make decisions and how they interact in markets.
Macroeconomics
The study of economy-wide phenomena, including inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
Interdependence
The idea that everyday, we rely on many people that we will never meet to provide us with the goods and services we enjoy.
Market
Group of buyers and sellers of a particular product.
Competitive Market
A market with many buyers and sellers, each with a negligible effect on price.
Quantity Demanded
The amount of the good that buyers are willing to and able to purchase.
Law of Demand
Other things equal, the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of a good rises.
Demand Schedule
A table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded.
Demand Shifter
Number of Buyers
Demand Shifter
Taste
Demand Shifter
Income
Demand for a (normal/inferior) good is (positively/negatively) related to income.
Normal - Positively
Inferior - Negatively
Demand Shifter
Expectations
Demand Shifter
Price of Related Goods
Complements
Two goods are considered this if a rise in price causes a fall in decrease in demand for the other.
Substitutes
Two goods are considered this if a rise in price causes a rise in demand for the other.
Quantity Supplied
The amount that sellers are willing and able to sell.
Law of Supply
Other things equal, the quantity supplied of a good rises when the prices of the good rises.
Supply Schedule
Table showing the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied.
Supply Shifter
Number of Sellers
Supply Shifter
Input Prices (Wages/Price for Raw Materials)
Supply Shifter
Technology
Supply Shifter
Expectations
Equilibrium
When quantity supplied equals quantity demanded.
Surplus
When quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded.
Shortage
When quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied.
3 Steps to Analyzing Changes in Equilibrium
1. Determine if events are shifting S or D curve, or both.
2. Decide which direction curves shifts.
3. Use Supply-Demand diagram to see how the shift changes equilibrium of Price and Quantity