Phase 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What do you call the end of a long bone
epiphysis
what do you call the area that provides longitudinal growth on a long bone
physis, growth plate, epiphyseal plate
junction between physis and metaphysis of a long bone with thin line of increased density
zone of provisional calcification
area where opposing cortices are not parallel
metaphysis
area where opposing cortices are parallel
diaphysis
area of most metabolic activity in long bone
metaphysis
normal secondary ossification center located on non-weight bearing portion
apophysis
densest, strongest portion of bone
cortex
internal cavity of bone
medulla
thin membrane around diaphysis and metaphysis
periosteum
between cortex and medullary space
endosteum
what imaging modality is best for deep internal structures
MRI
what imaging modality is best for fractures
CT
what imaging modality is best for superficial structures
ultrasound
Grashey view of shoulder is good for what
glenohumeral joint space
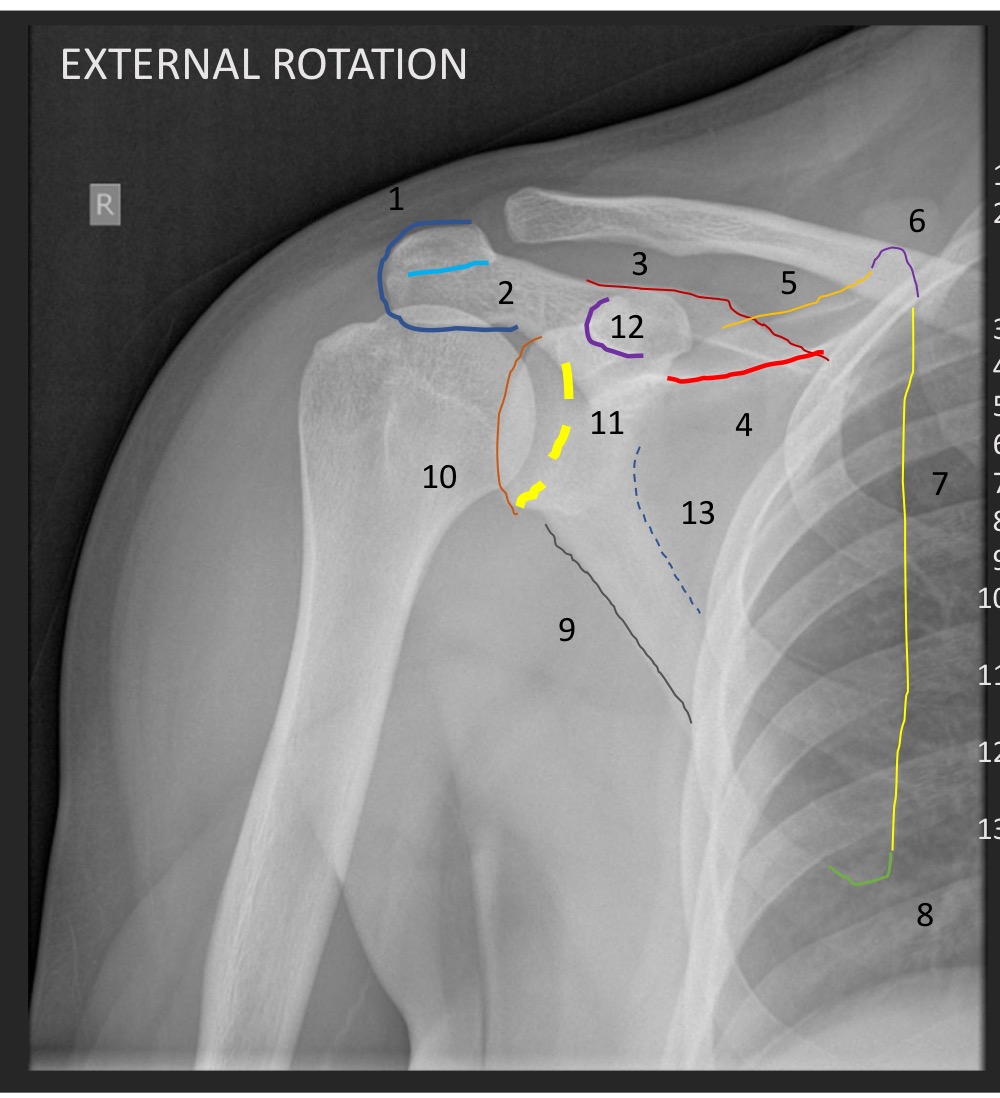
What type of view is this
external rotation AP shoulder
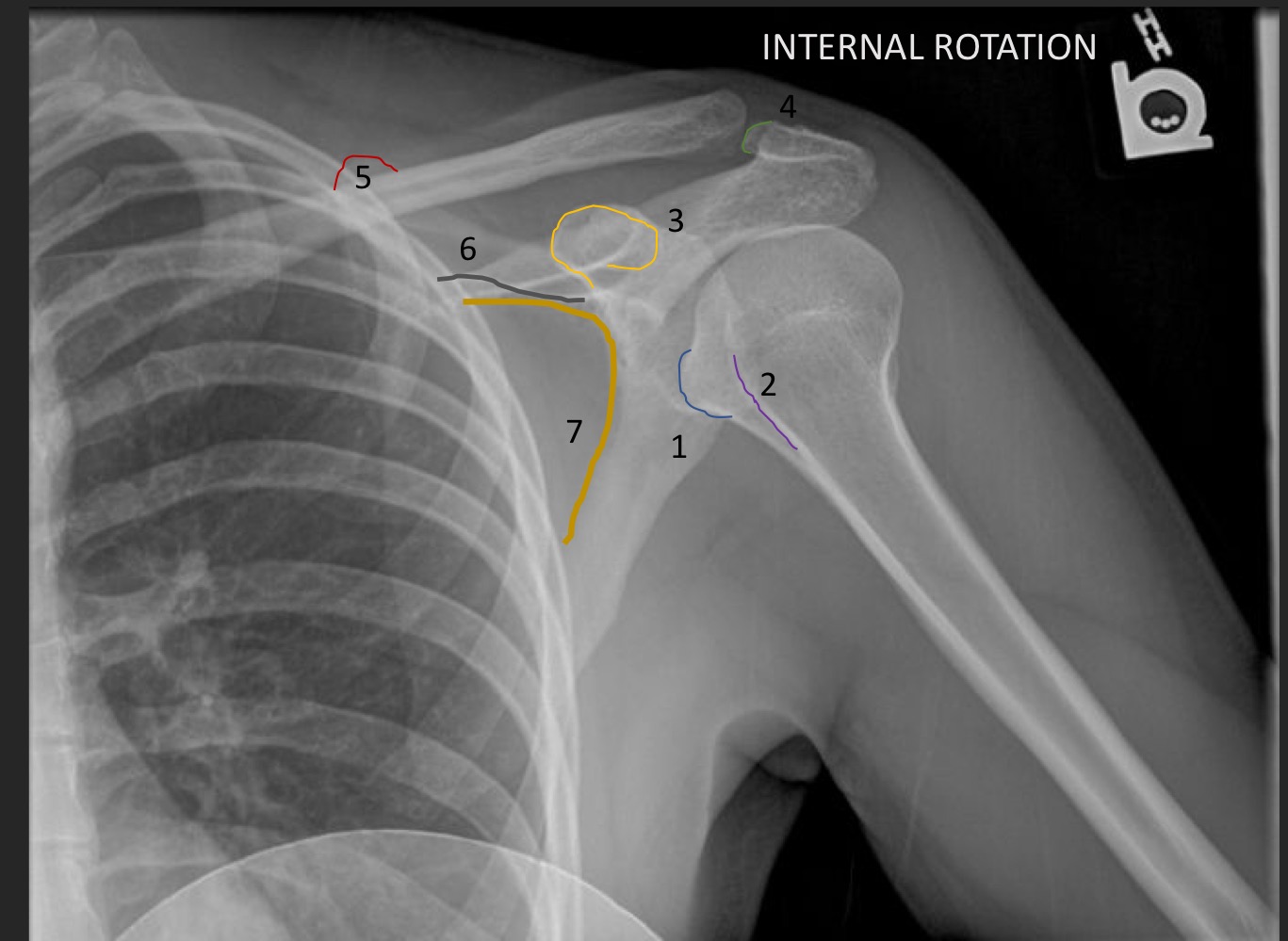
what type of view is this
AP internal rotation shoulder
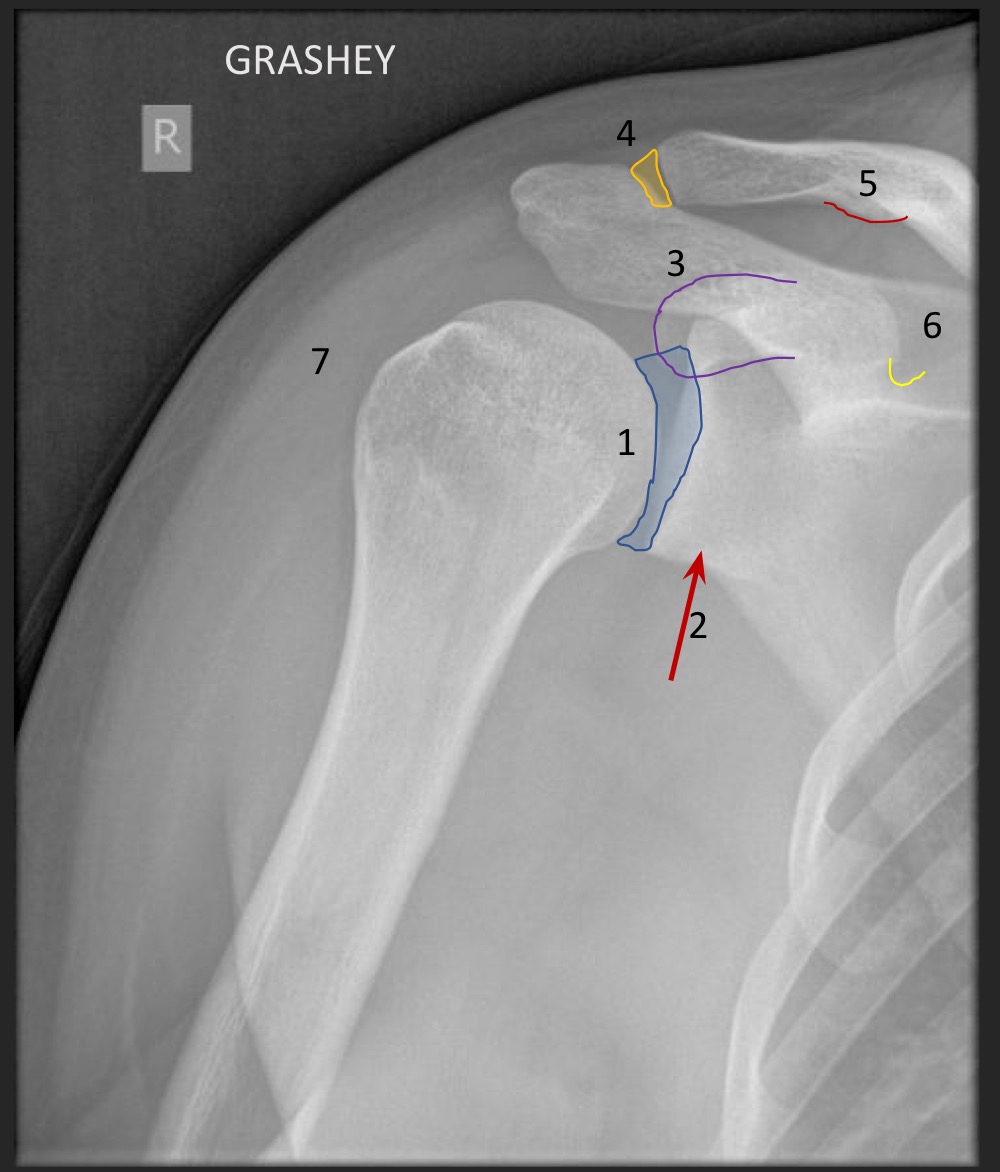
what type of view is this
grashey
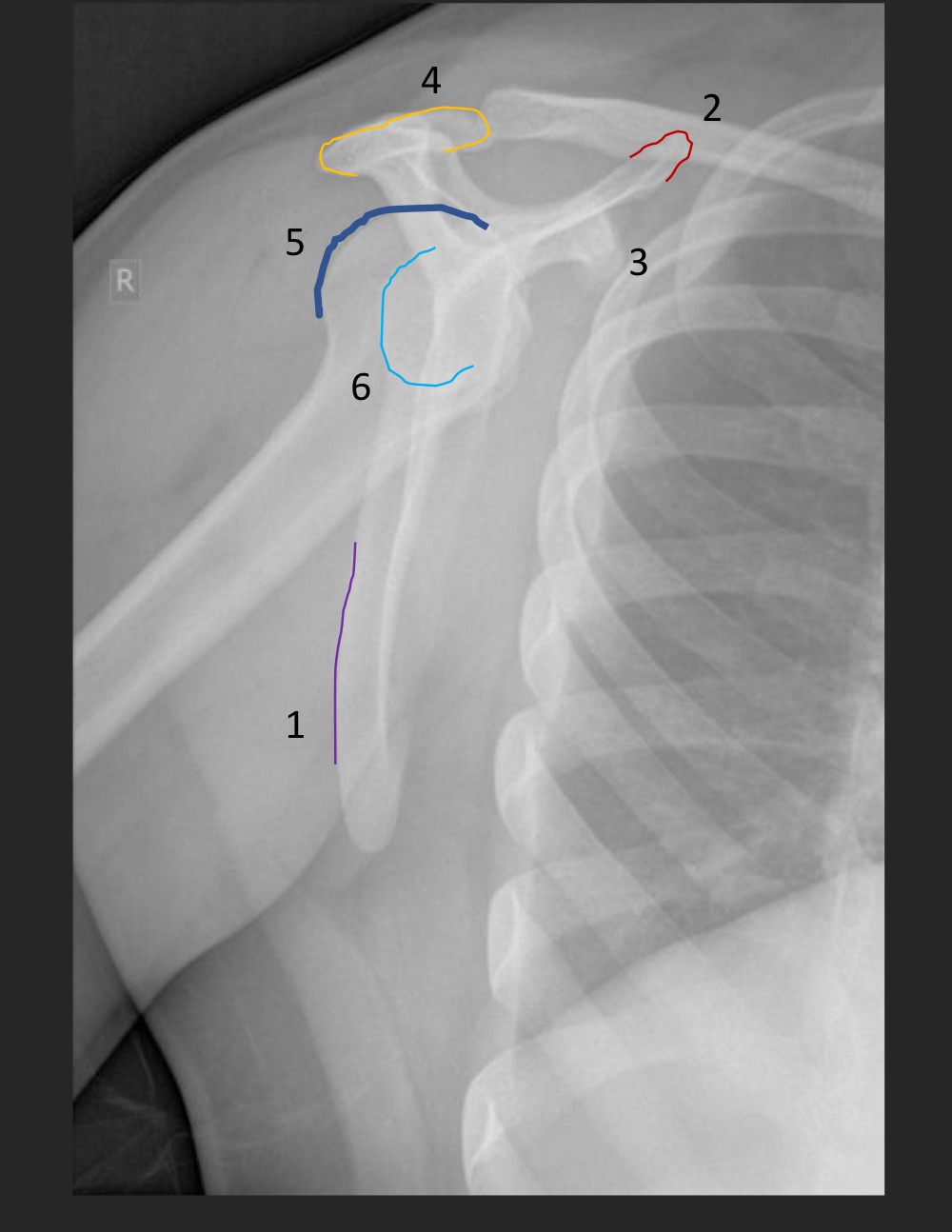
what type of view is this
Y view
What view is this
medial oblique elbow
what type of view is this
AP elbow
what type of view is this
lateral elbow
what type of view is this
PA wrist
what type of view is this
medial oblique wrist (intermetacarpal spaces are uneven)
what type of view is this
lateral wrist (metacarpals are stacked)
what type of view is this
PA wrist
what type of view is this?
PA hand
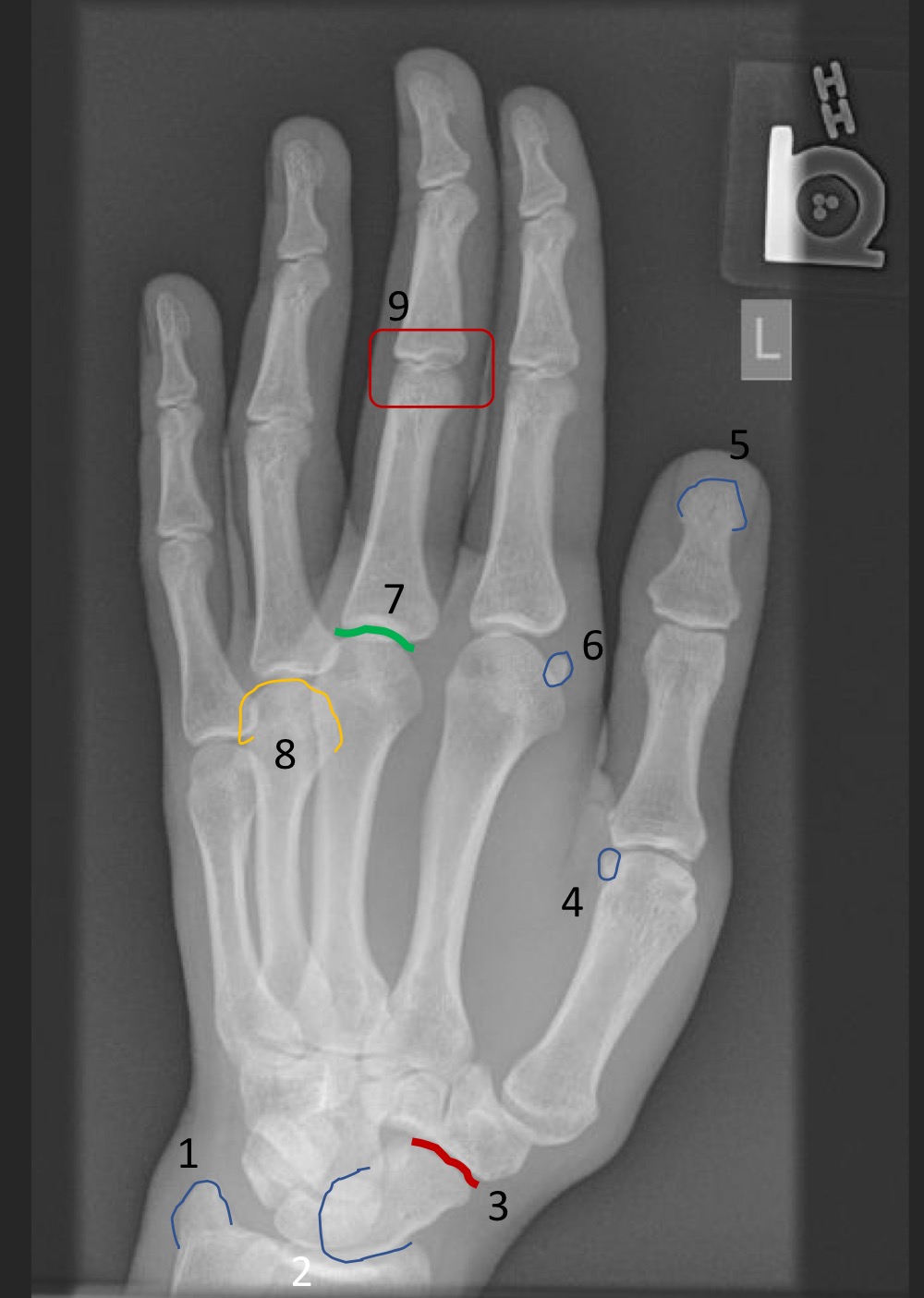
what type of view is this
medial oblique hand (digits included and intermetacarpal spaces are uneven)
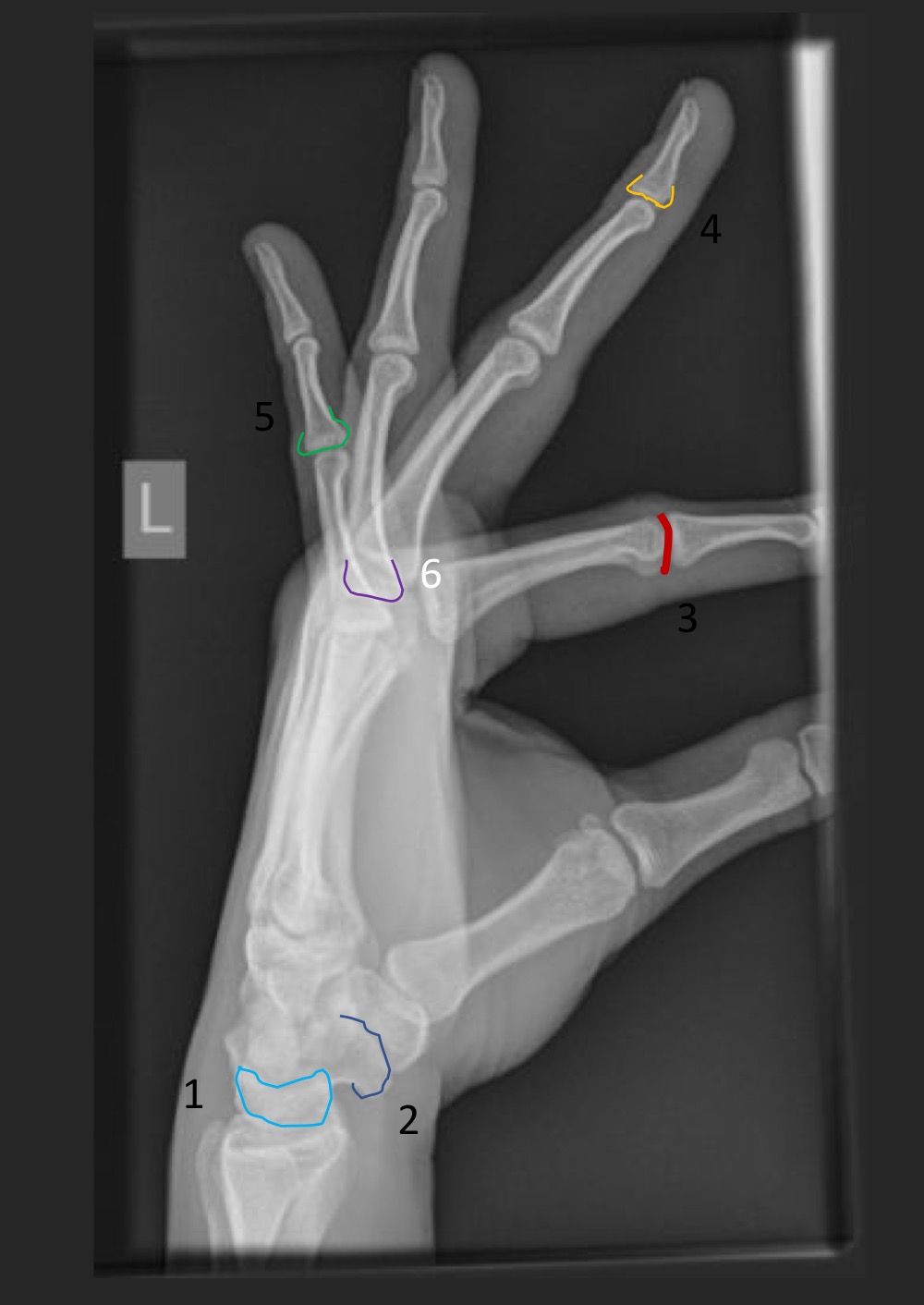
what type of view is this
lateral hand
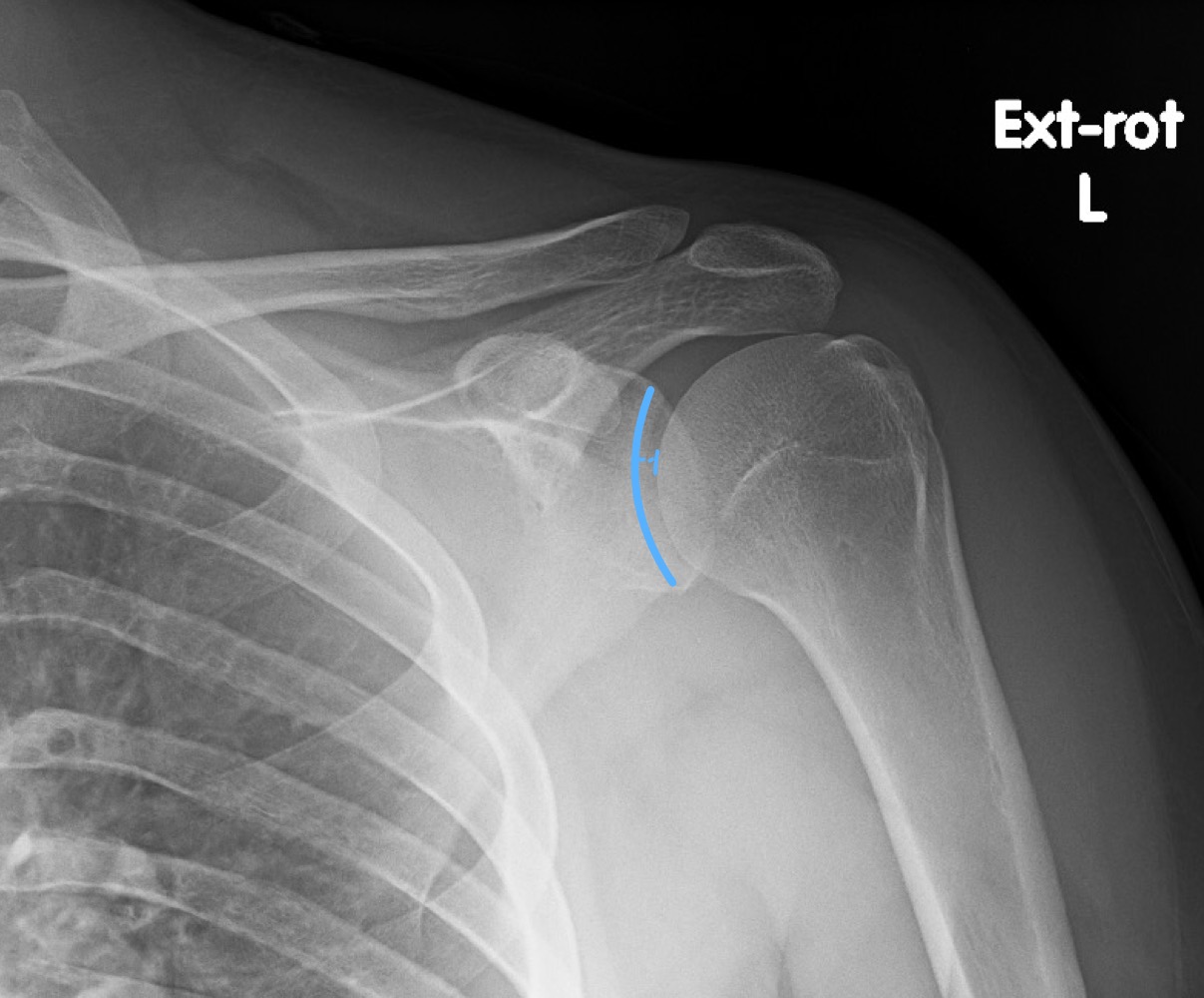
what is this measurement called and what are the normal limits
glenohumeral joint space
4-5mm
what is a decreased glenohumeral joint space suggestive of
arthritic conditions wha
what is an increased glenohumeral joint space measurement suggestive of
joint effusion, posterior shoulder dislocation, acromegaly
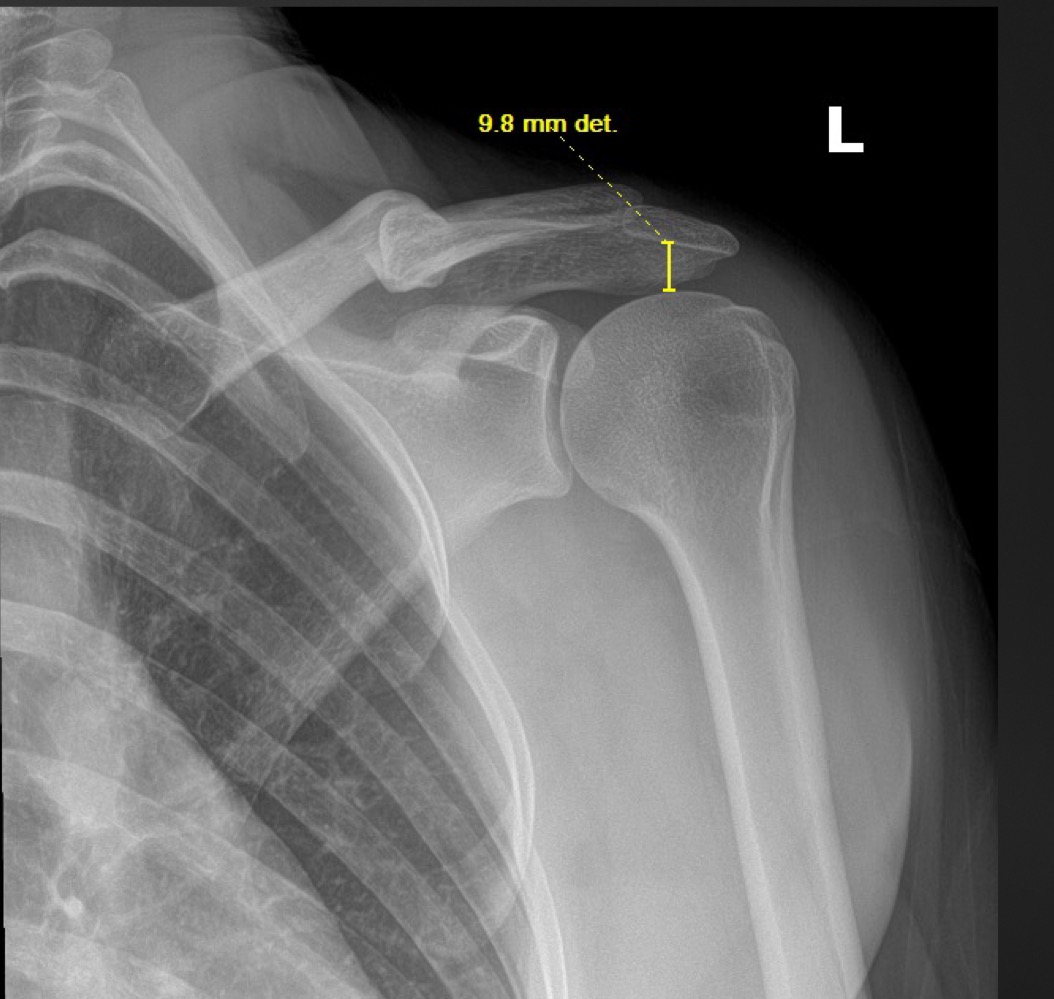
what measurement is this called and what are the normal limits?
acriohumeral space
7-11mm
what is a decreased acromiohumeral joint space suggestive of
rotator cuf injury or degeneration
what is an increased acriohumeral space suggestive of
subluxation, joint effusion, stroke, brachial lesion
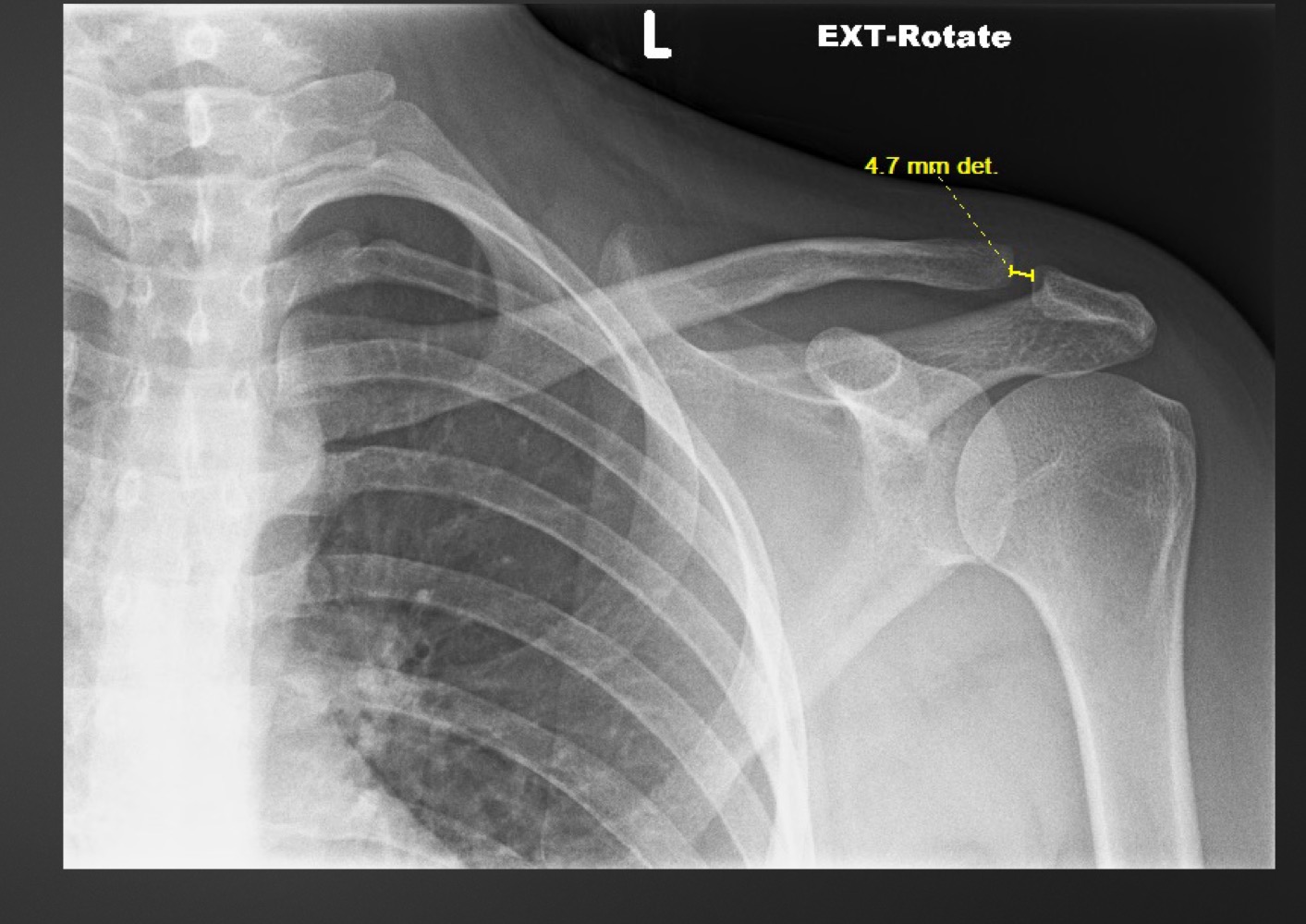
what measurement is this called and what are the normal ranges
acromioclavicular joint space
3 mm/no more than 2-3 mm difference between sides
what is a decreased acromioclavicular joint space suggestive of
degeneration
what is an increased acromioclavicular joint space suggestive of
traumatic separation, osteolysis, inflammatory conditions
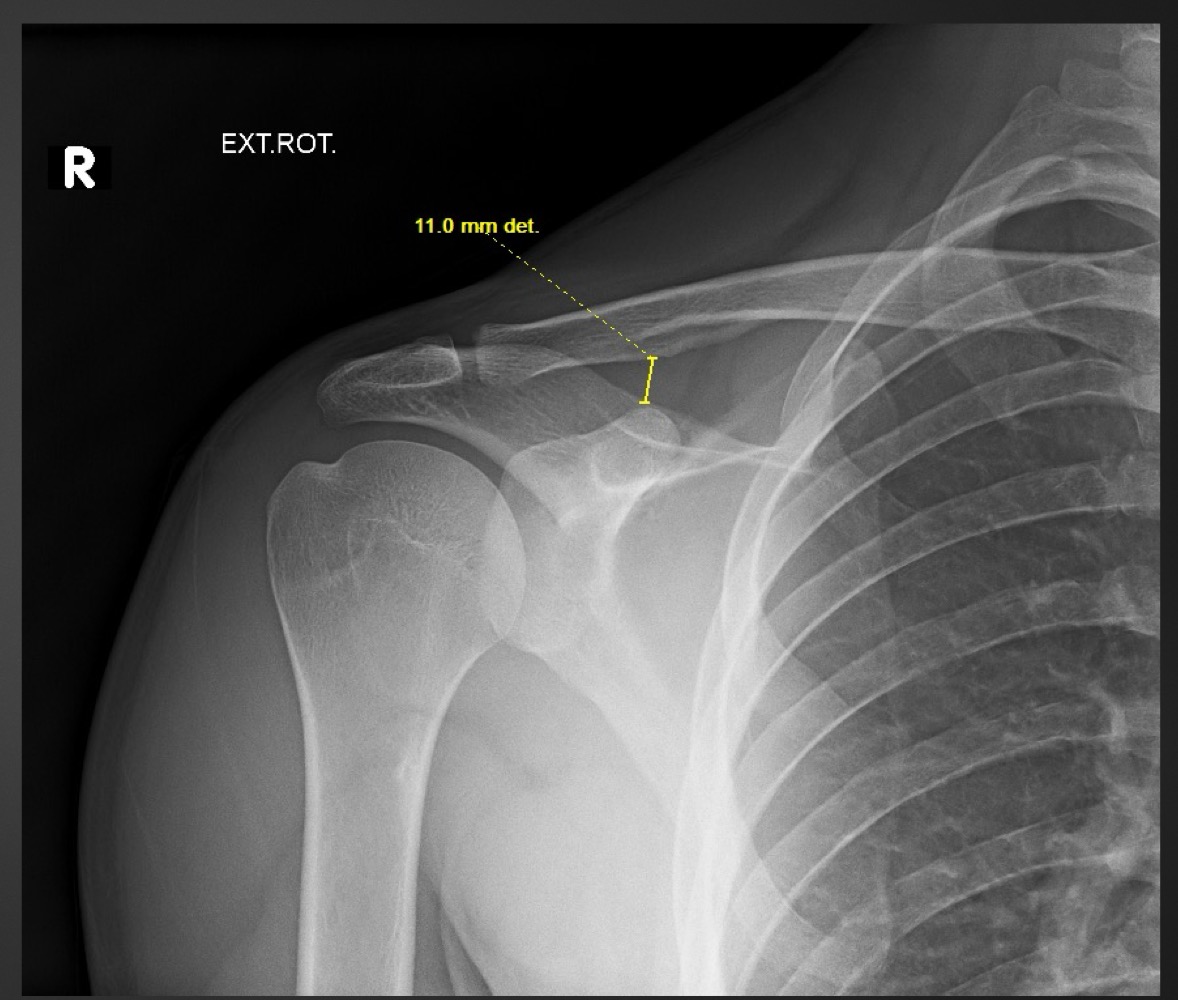
what is this measurement called and what are the normal ranges
coraclavicular distance
11-13 mm/no more than 5mm difference between sides
what is the coracoclavicular distance used for
determining degree of Rockwood type of AC joint injury
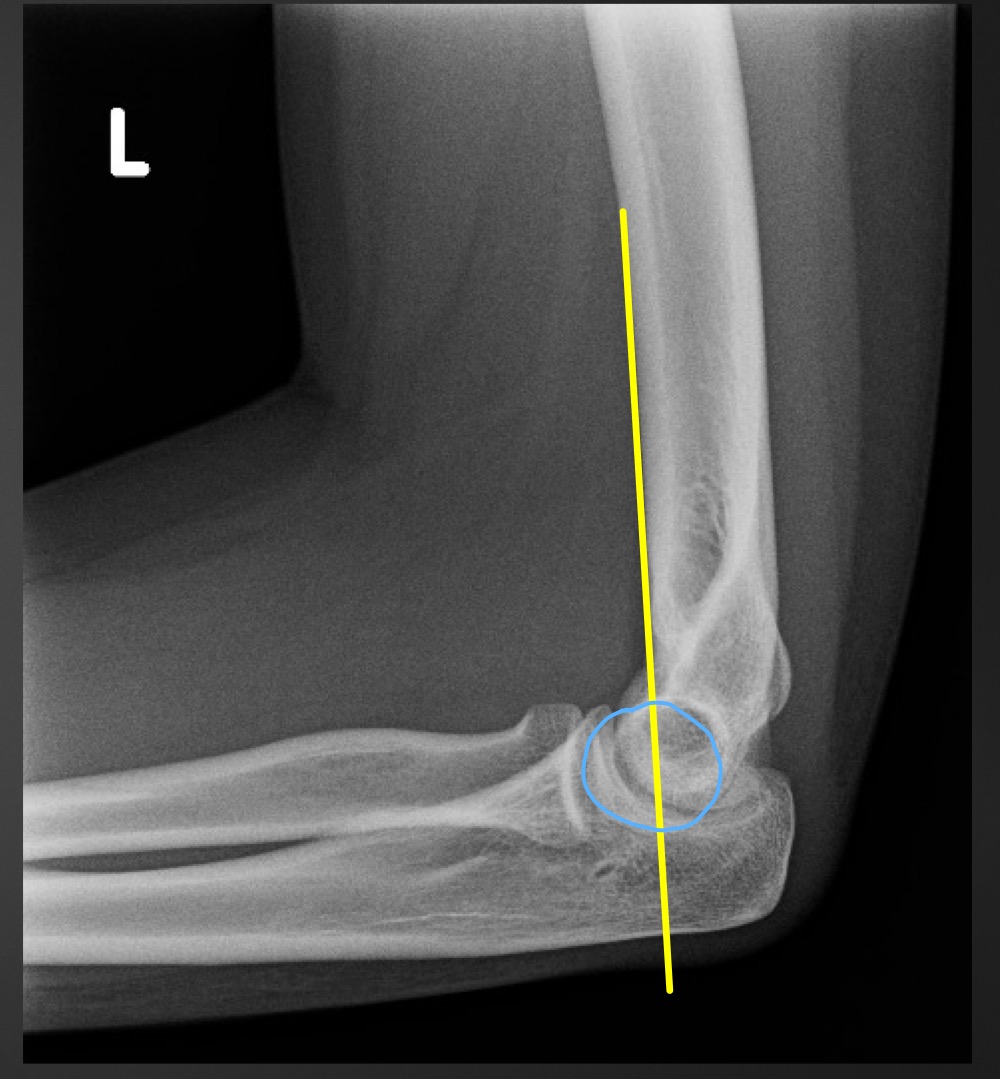
what is this measurement called and what are the normal ranges
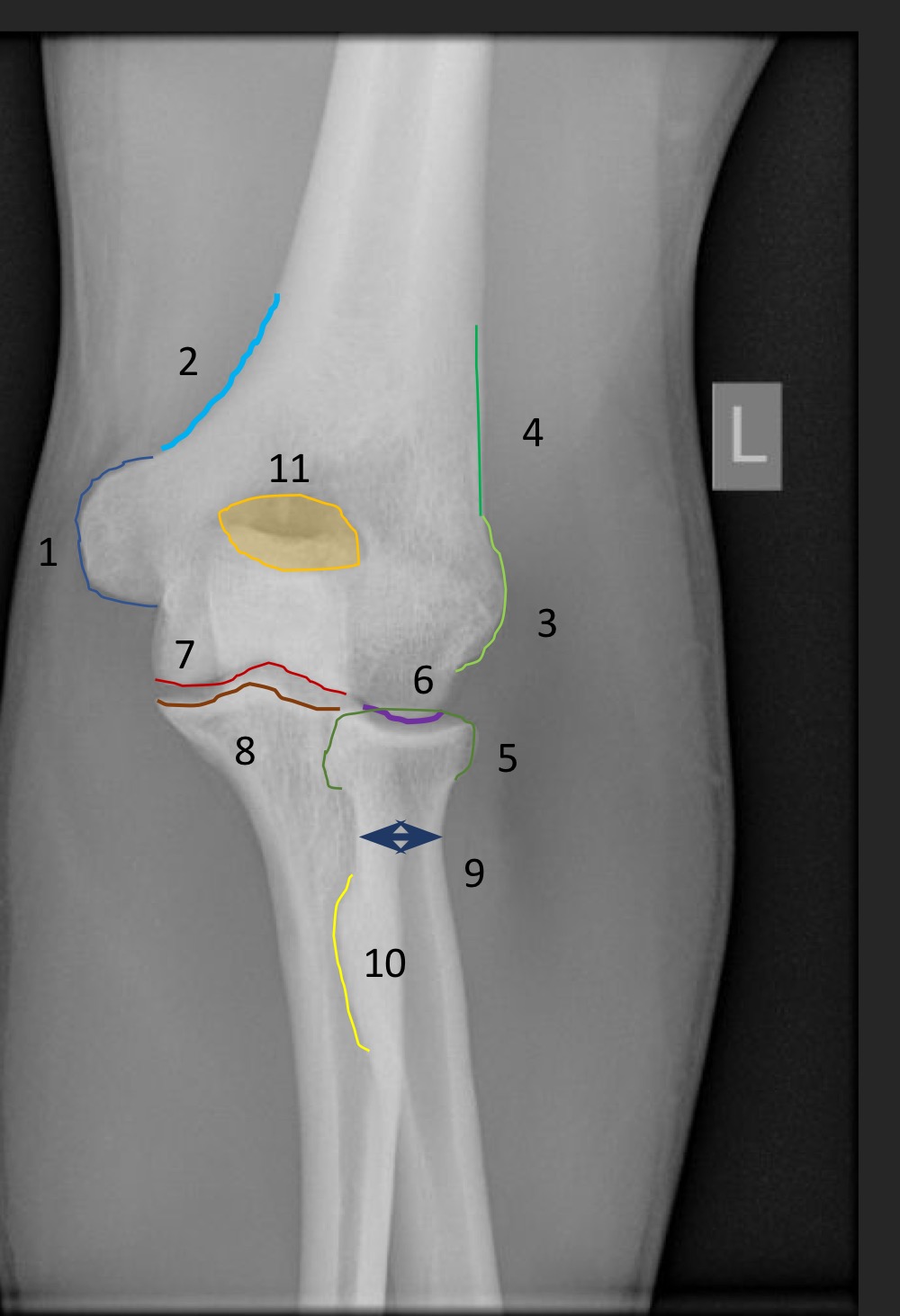
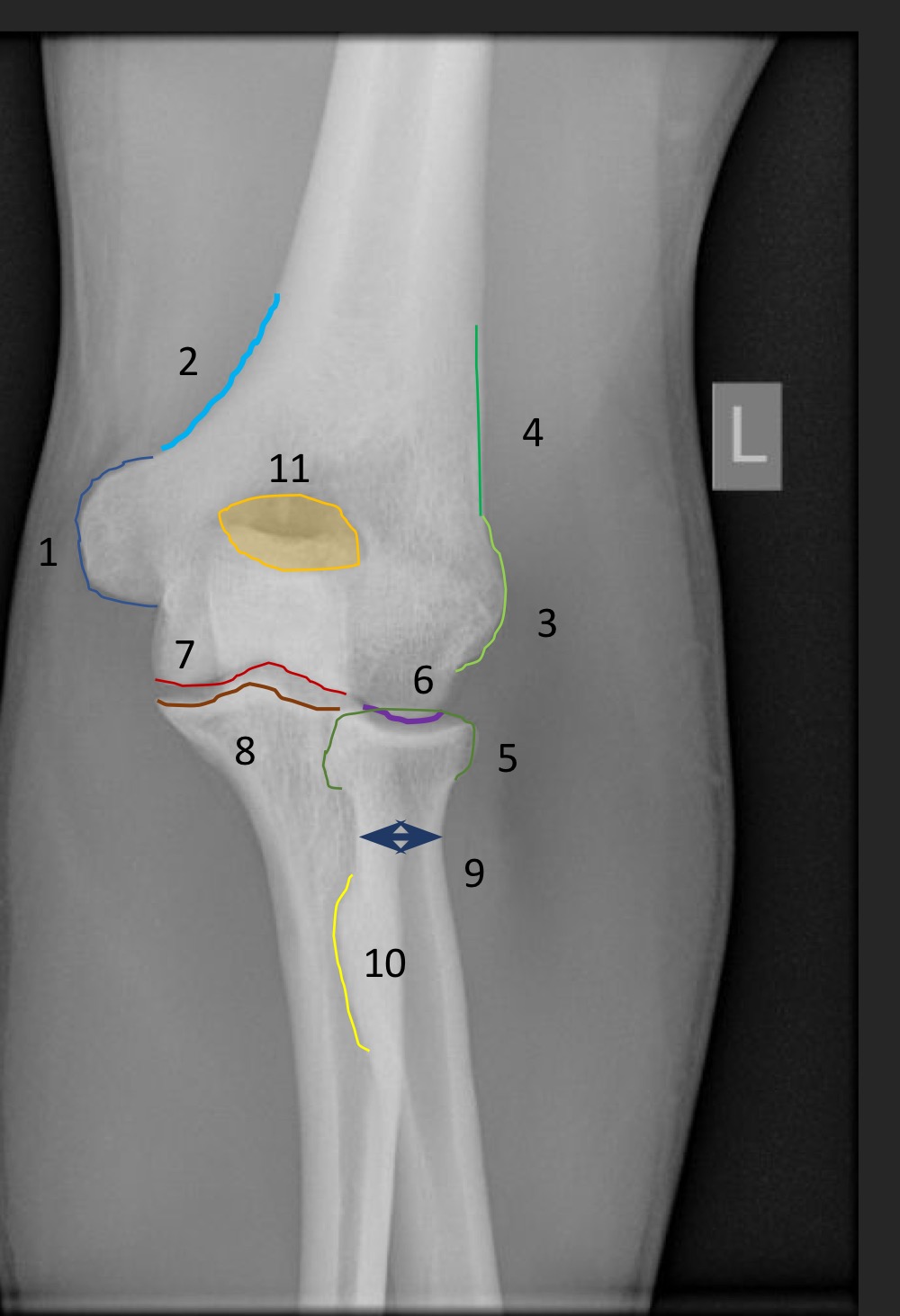
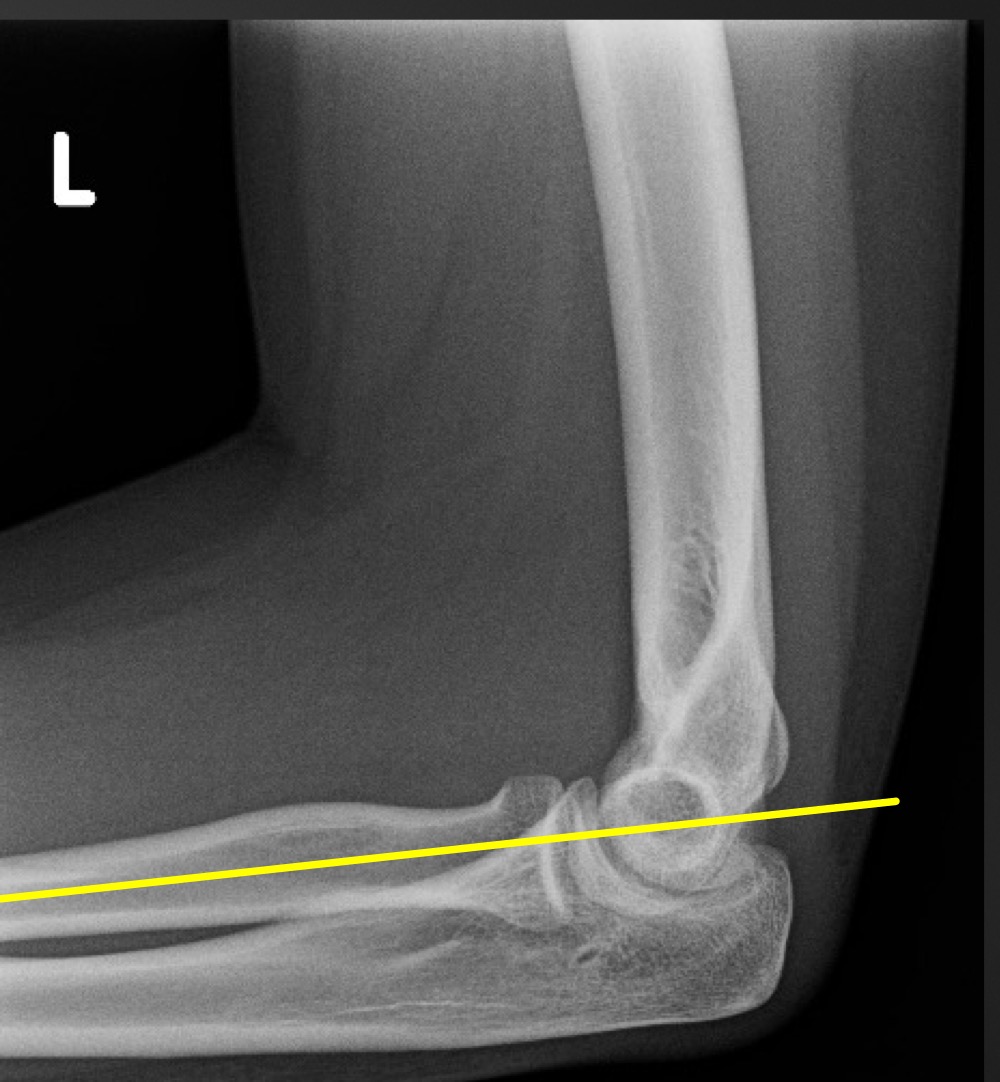
anterior humeral line
line hsould intersect the middle third of the capitellum
if anterior humeral line is abnormal what is implied
fracture through supracondylar portion of distal humerus
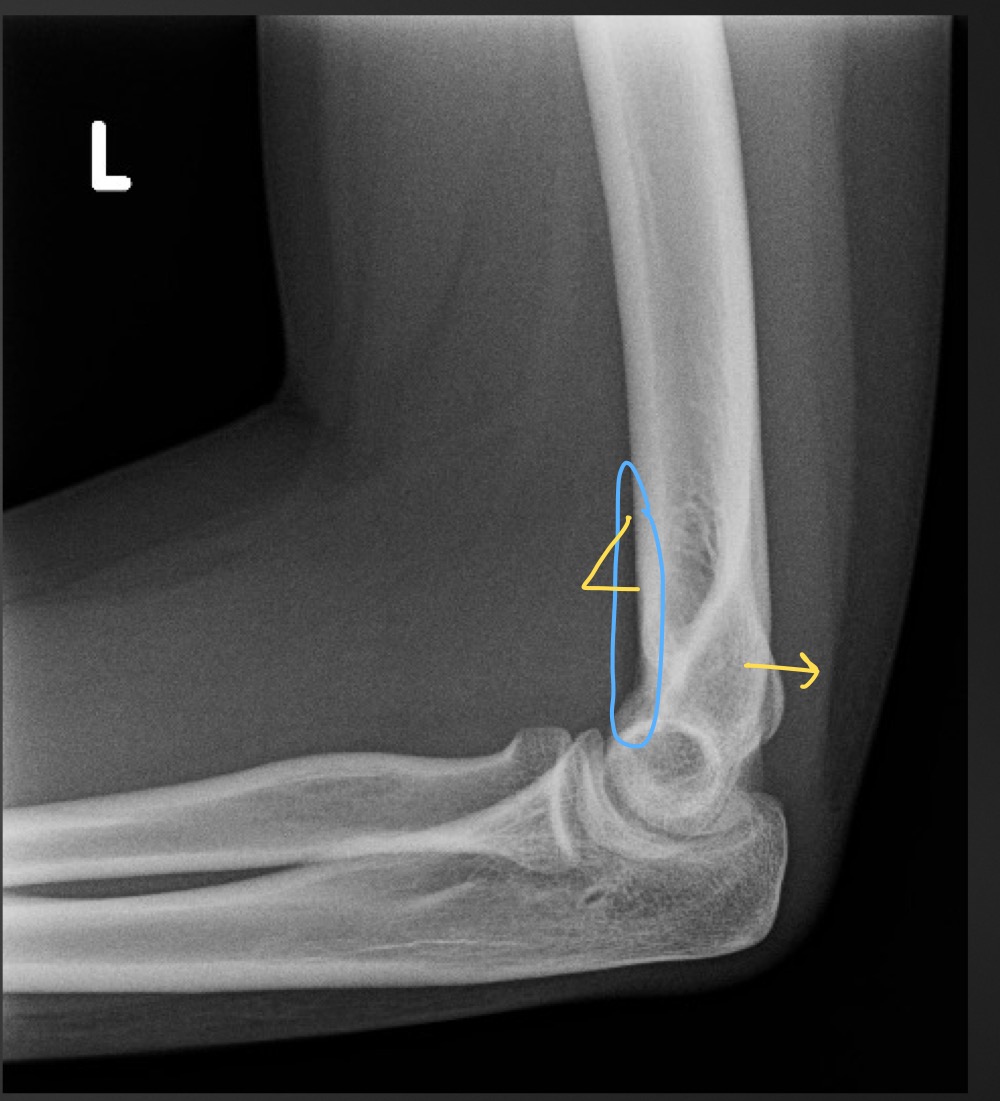
what is this measurement called and what is the normal range
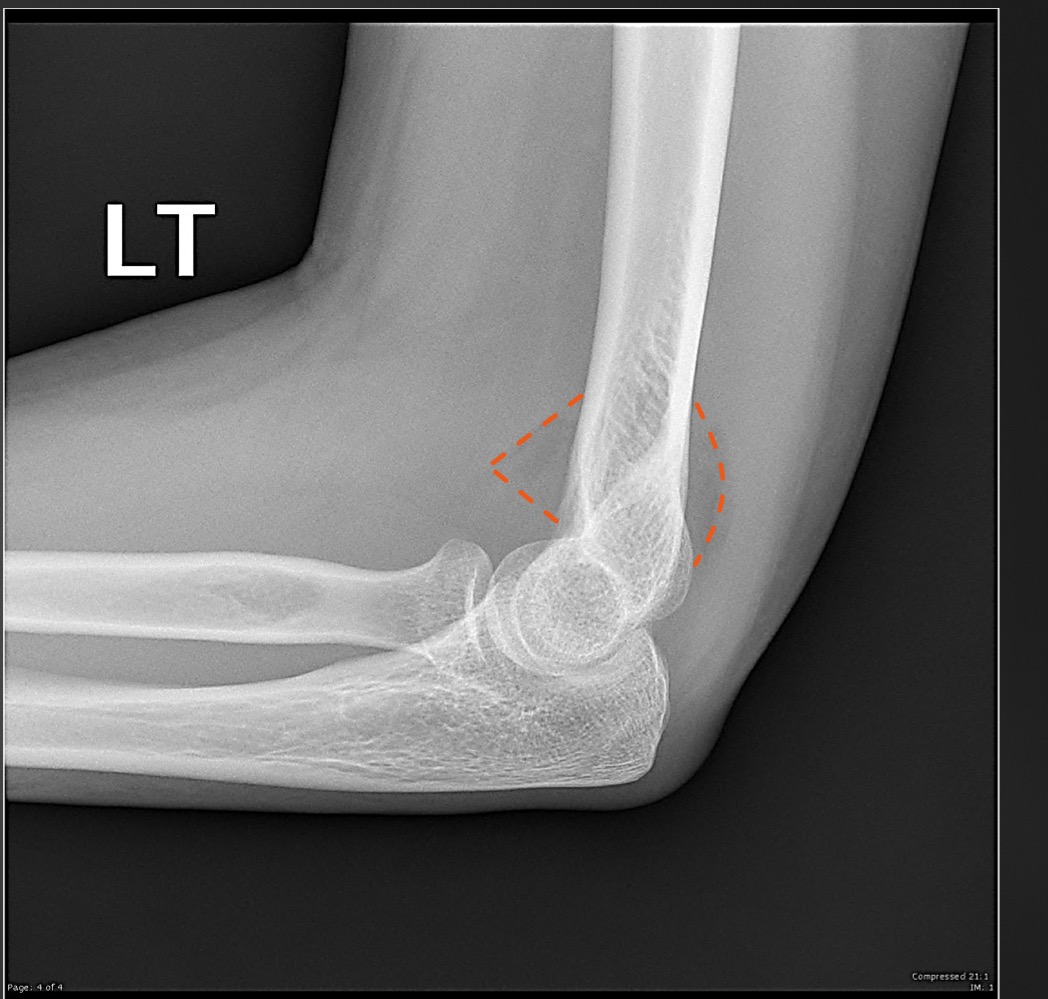
fat pad assessment
anterior fat pad is slim, no posterior fat pad
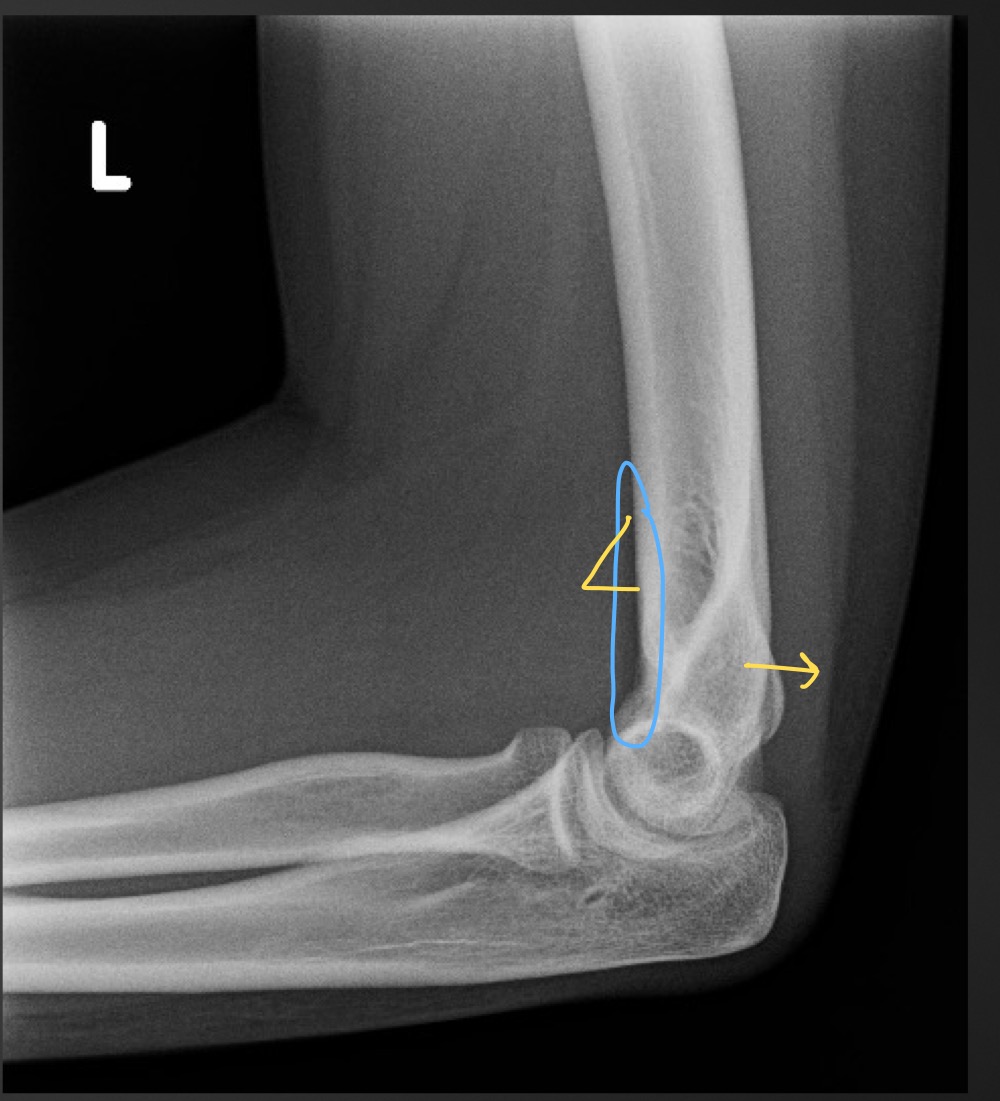
if the anterior fat pad is raised what is that sign called
sail sign
what is indicated if the posterior fat pad is present
joint effusion due to an occult fracture
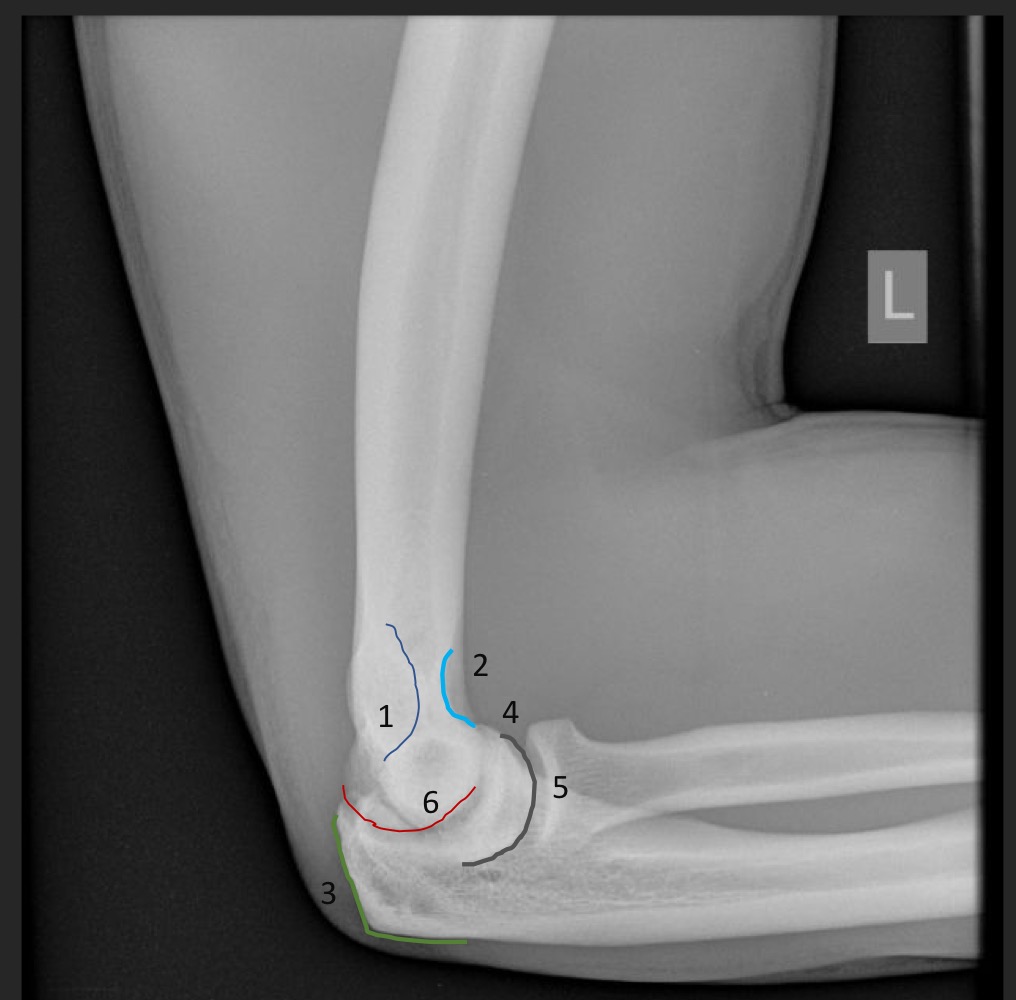
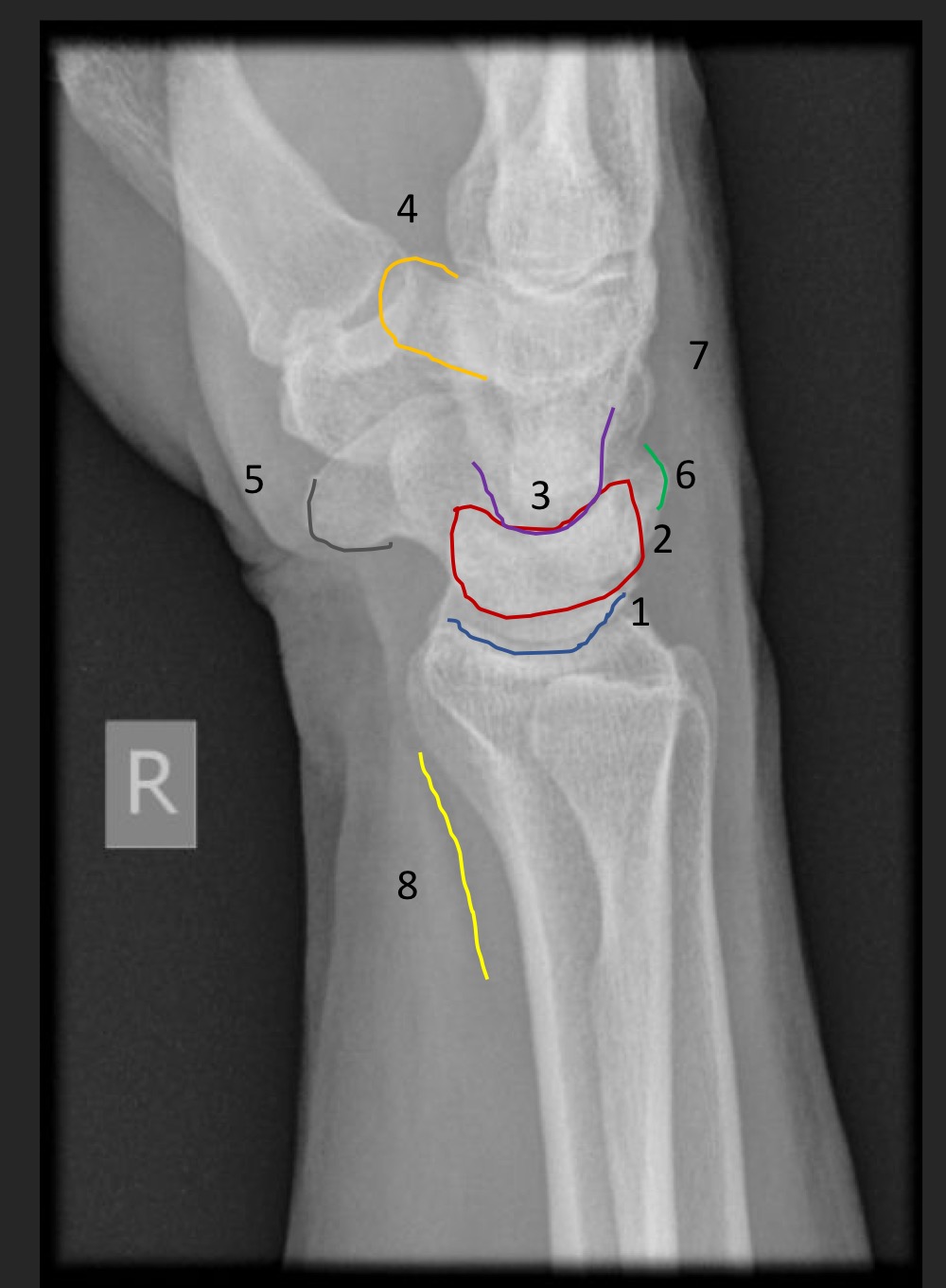
what is this measurement called and what are the normal ranges
radiocapitellar line
line from neck of radius toward elbow joint should intersect the capitellum
if the radiocapitellar line does not intersect the capitellum what is suggested?
radial head dislocation/subluxation
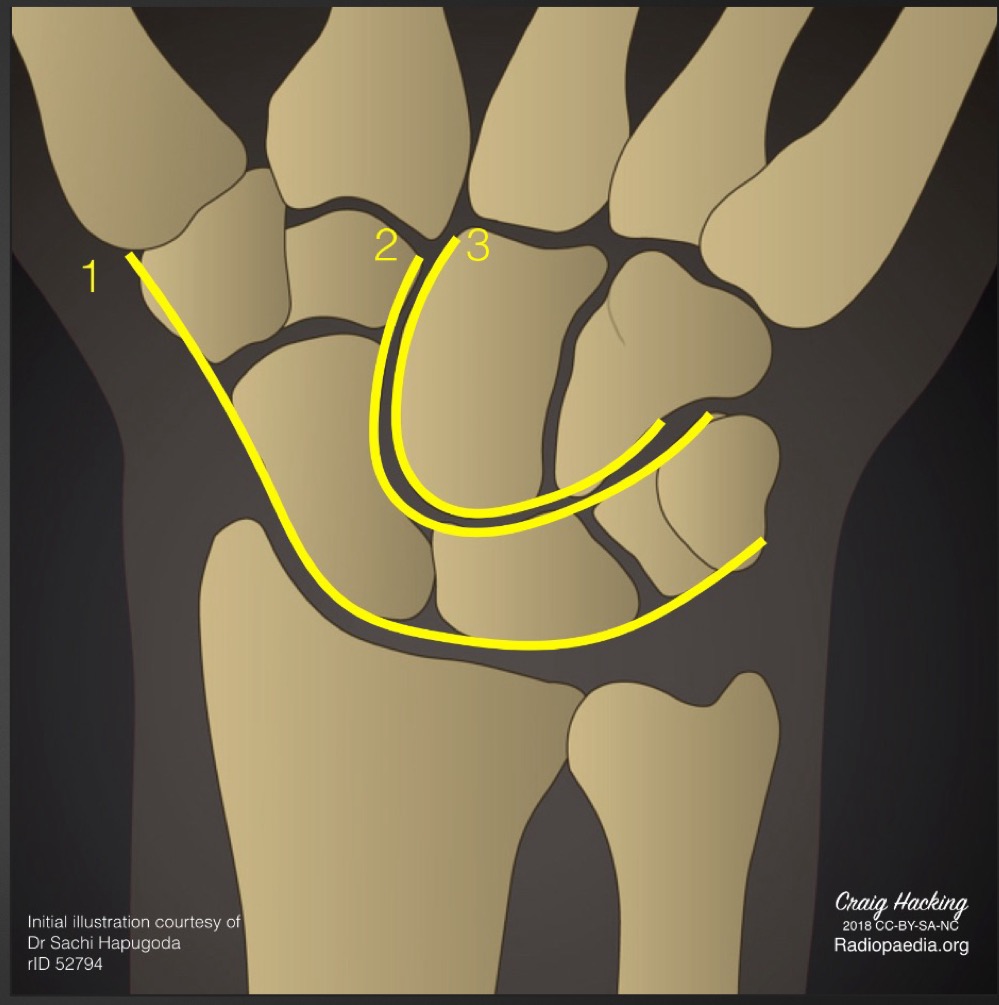
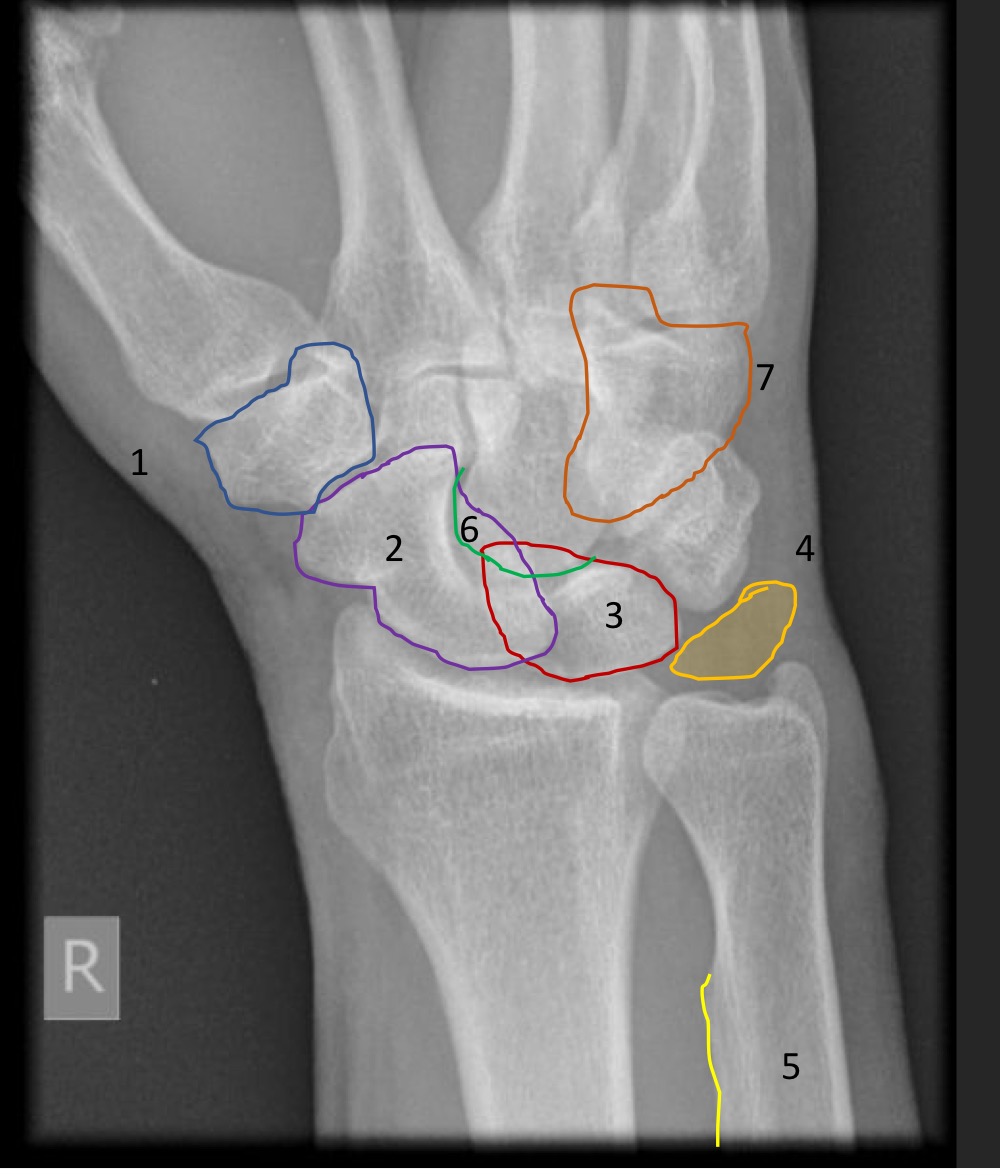
what is this measurement called and what is considered normal
carpal arcs
smooth lines from all 3 arcs
what is indicated if the carpal arcs are uneven
ligamentous laxity or fracture
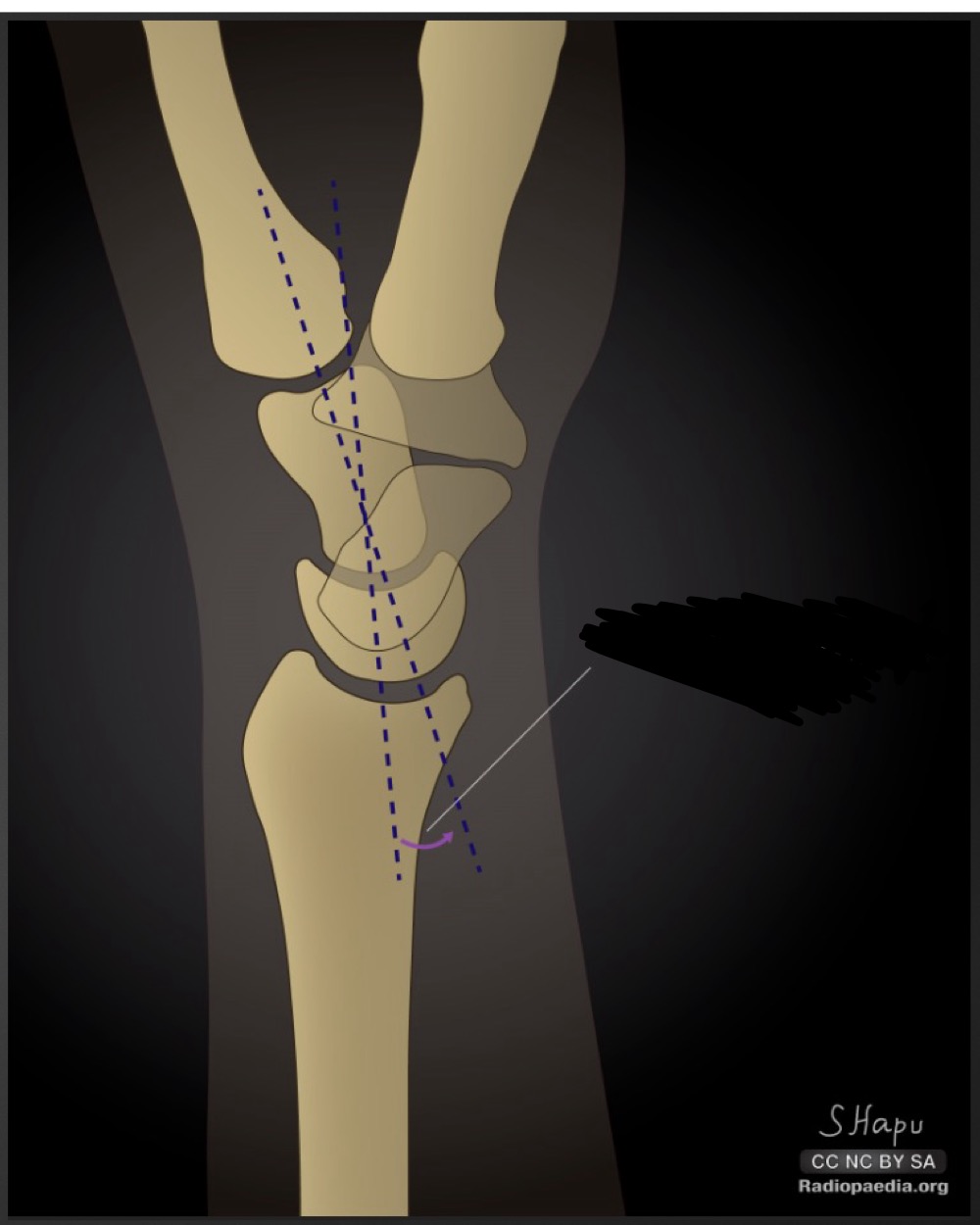
what is this measurement called and what are the normal ranges
captiolunate angle
less than 30 degrees
what is the significance of an increased captiolunate angle
increased dorsal or volar intercalated segment instability
how do you determine whether an increased capitolunate angle is due to dorsal or volar intercalated segment instability
take scapholunate angle
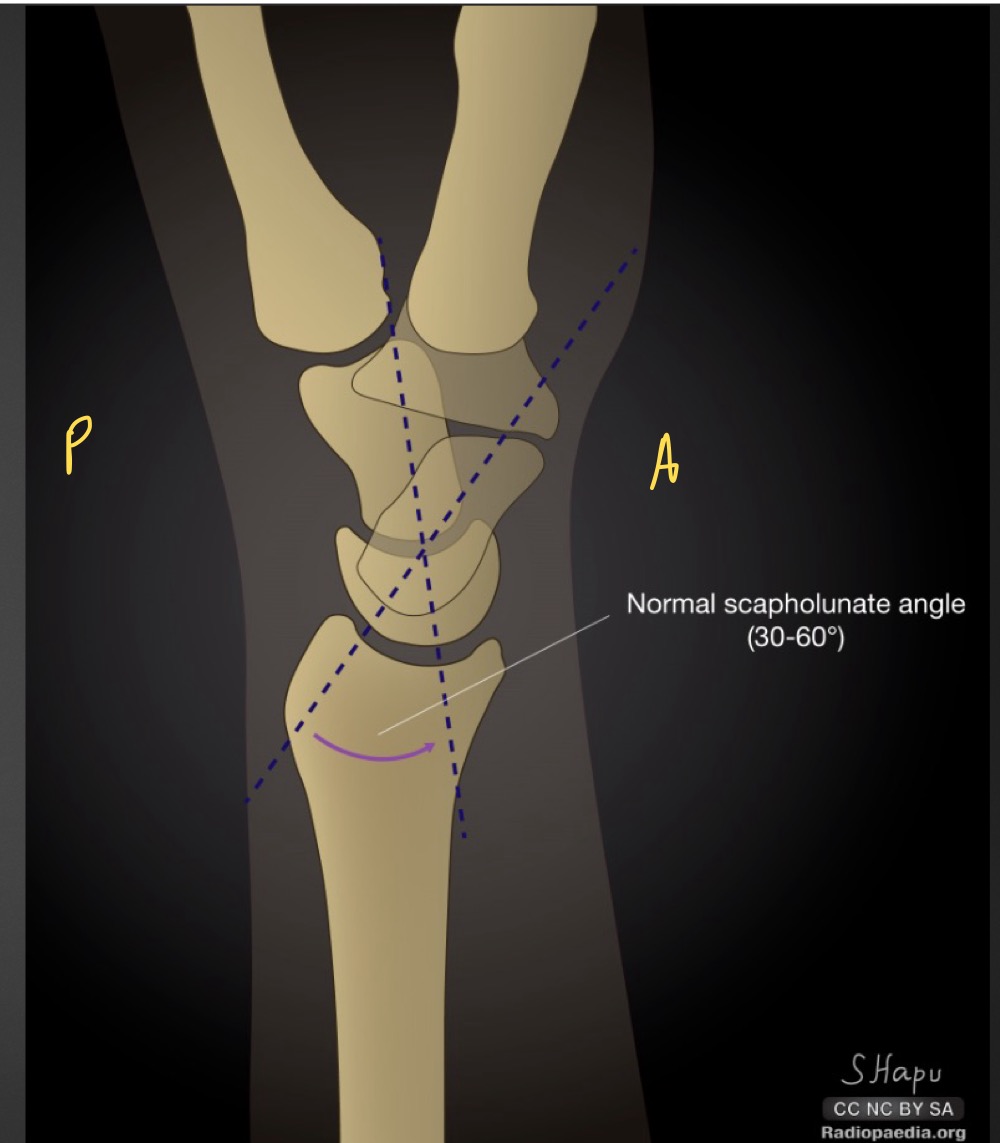
what is this measurement and what is considered normal
scapholunate angle
30-60 degrees
if scapholunate angle is increased what is implied
dorsal intercalated segment instablity
if scapholunate angle is decreased what is implied
volar intercalated segmental instability
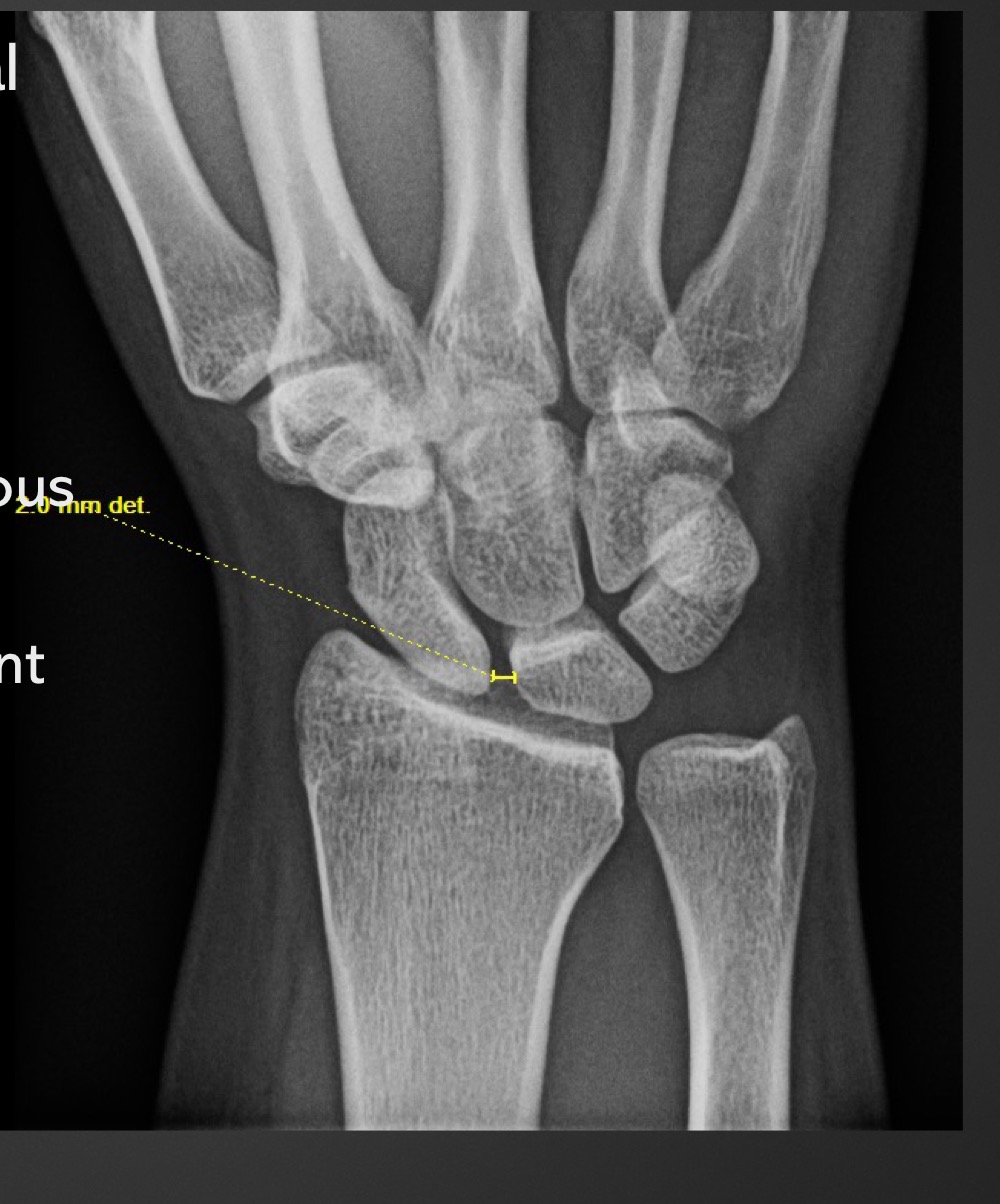
what is this measurement and what is considered normal
intercarpal joint space
1-2 mm, all should be about equal
if intercarpal joint space is increased what is suggested
ligamentous laxity or injury
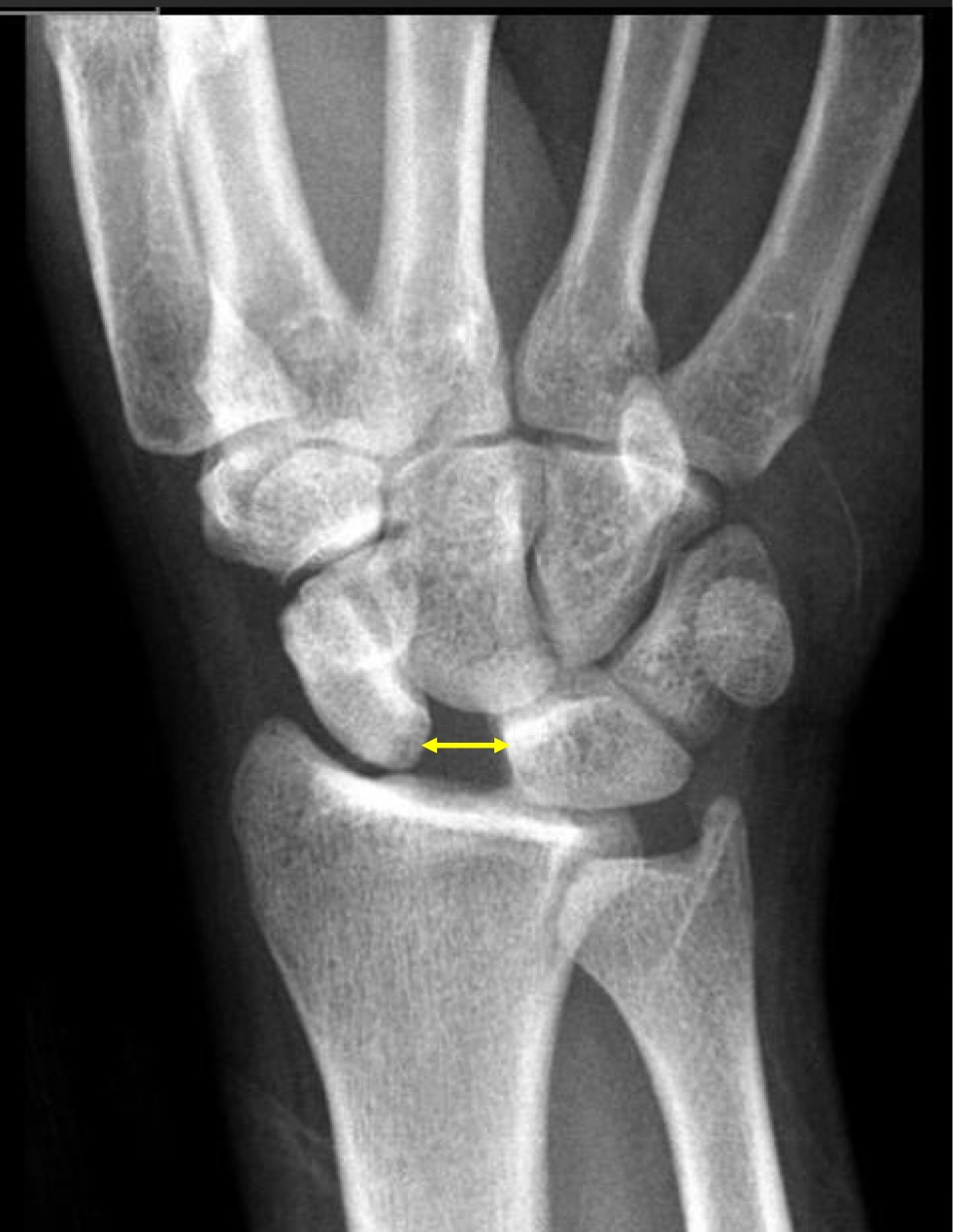
what is the scapholunate interval called and what does it mean
terry thomas sign
greater than 2mm between scaphoid and lunate
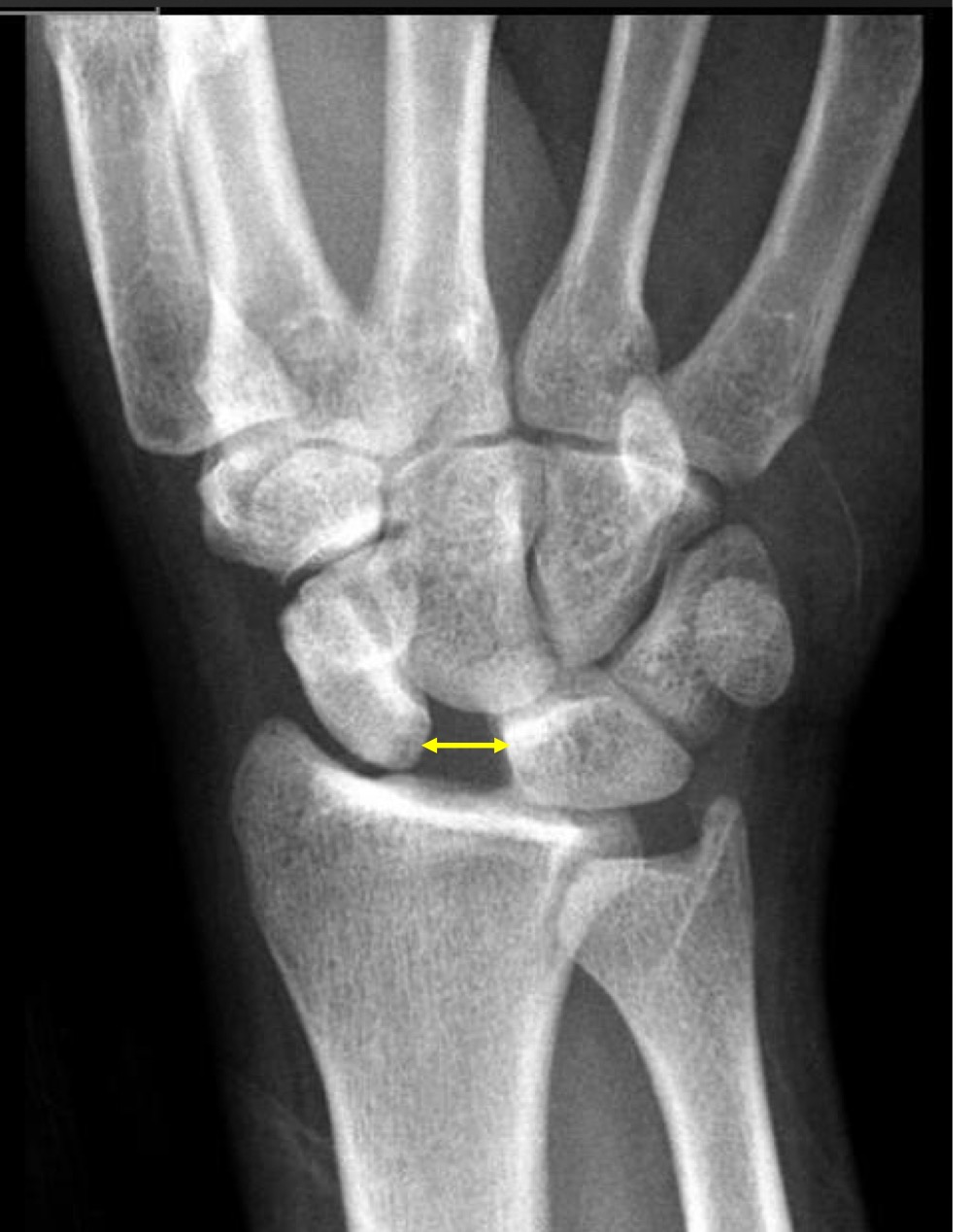
what are the limits for the scapholunate interval
2mm is suspicious
4mm is definitely abnormal
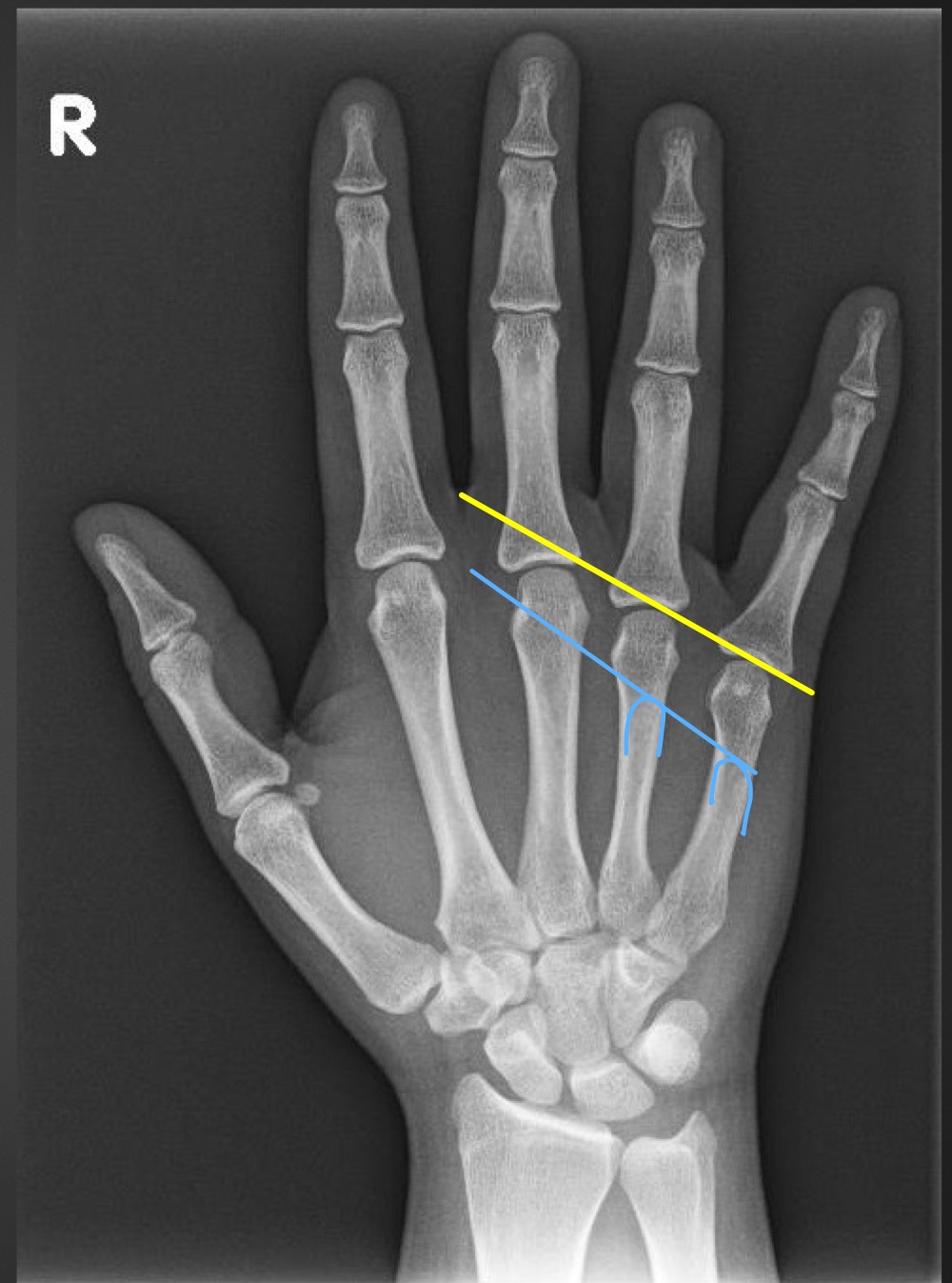
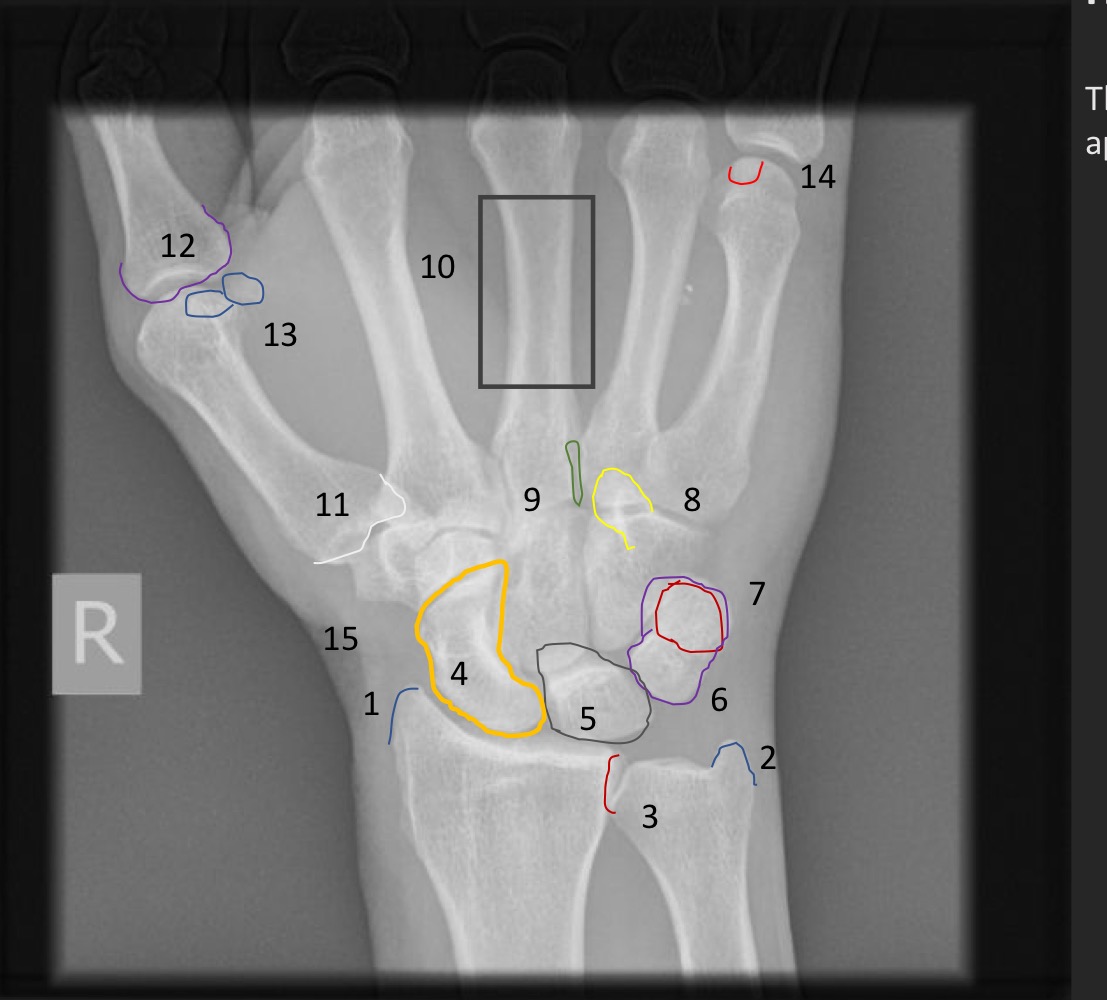
what is this measurement and what is considered normal
metacarpal sign
line through the distal articular surfaces of the fourth and fifth metacarpals should be distal to the third metacarpal head
what is indicated if the line through the 4th and 5th metacarpal heads passes through the third metacarapal head
gonadal dysgenesis (Turner’s syndrome) or fracture deformity
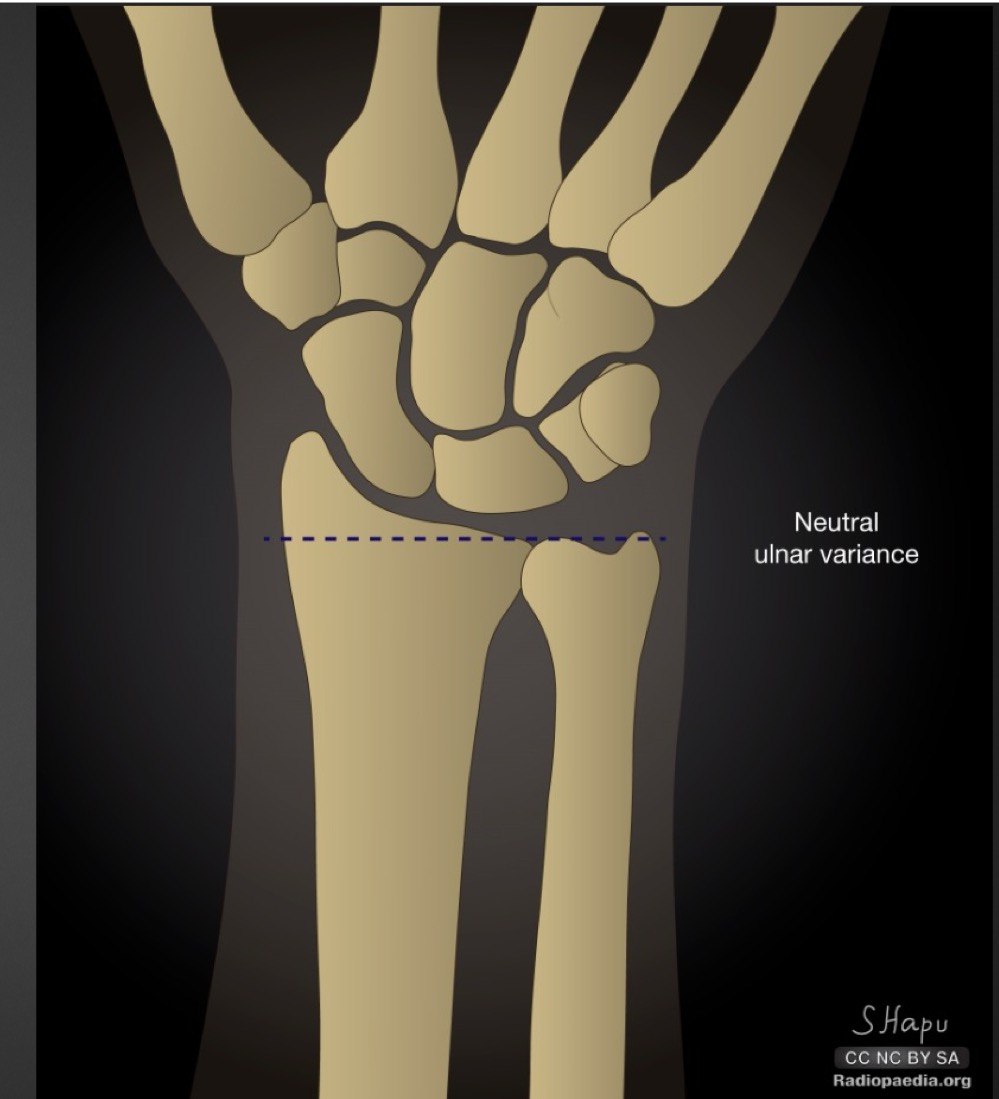
what is this measurement and what is considered normal
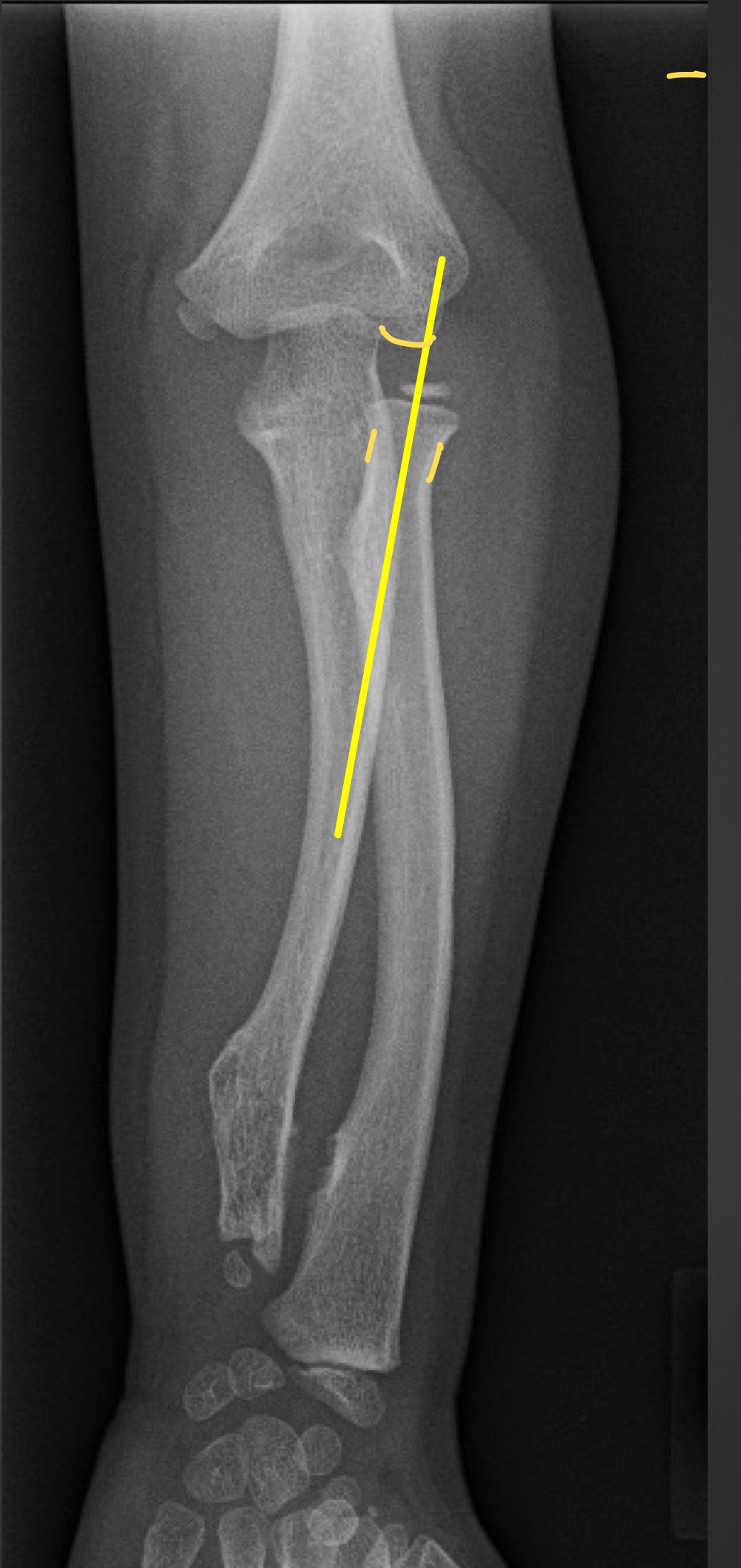
radioulnar variance
distal ulnar and radial surfaces should align with each other
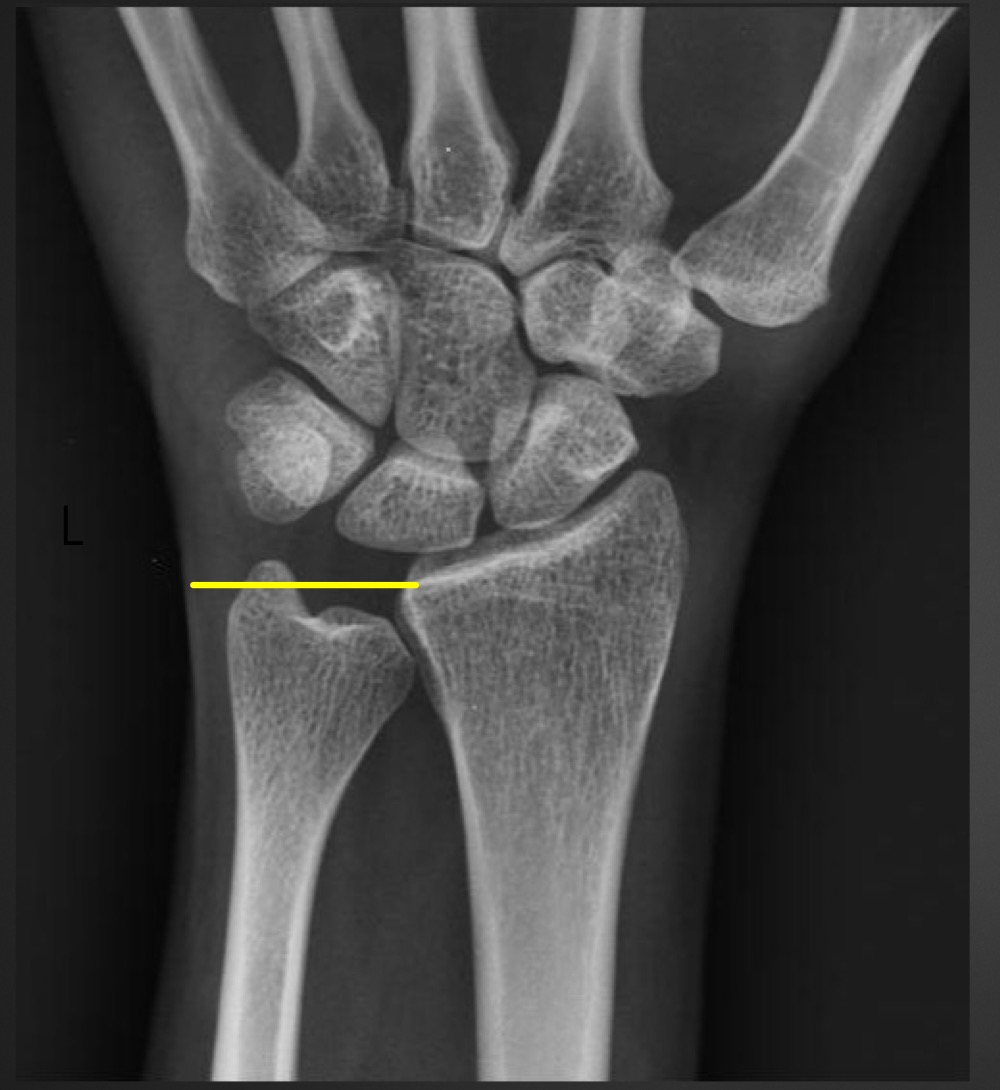
what is a short ulna called and what are the ramifications
negative ulnar variance
avascular necrossis of lunate (Kienbock’s disease)
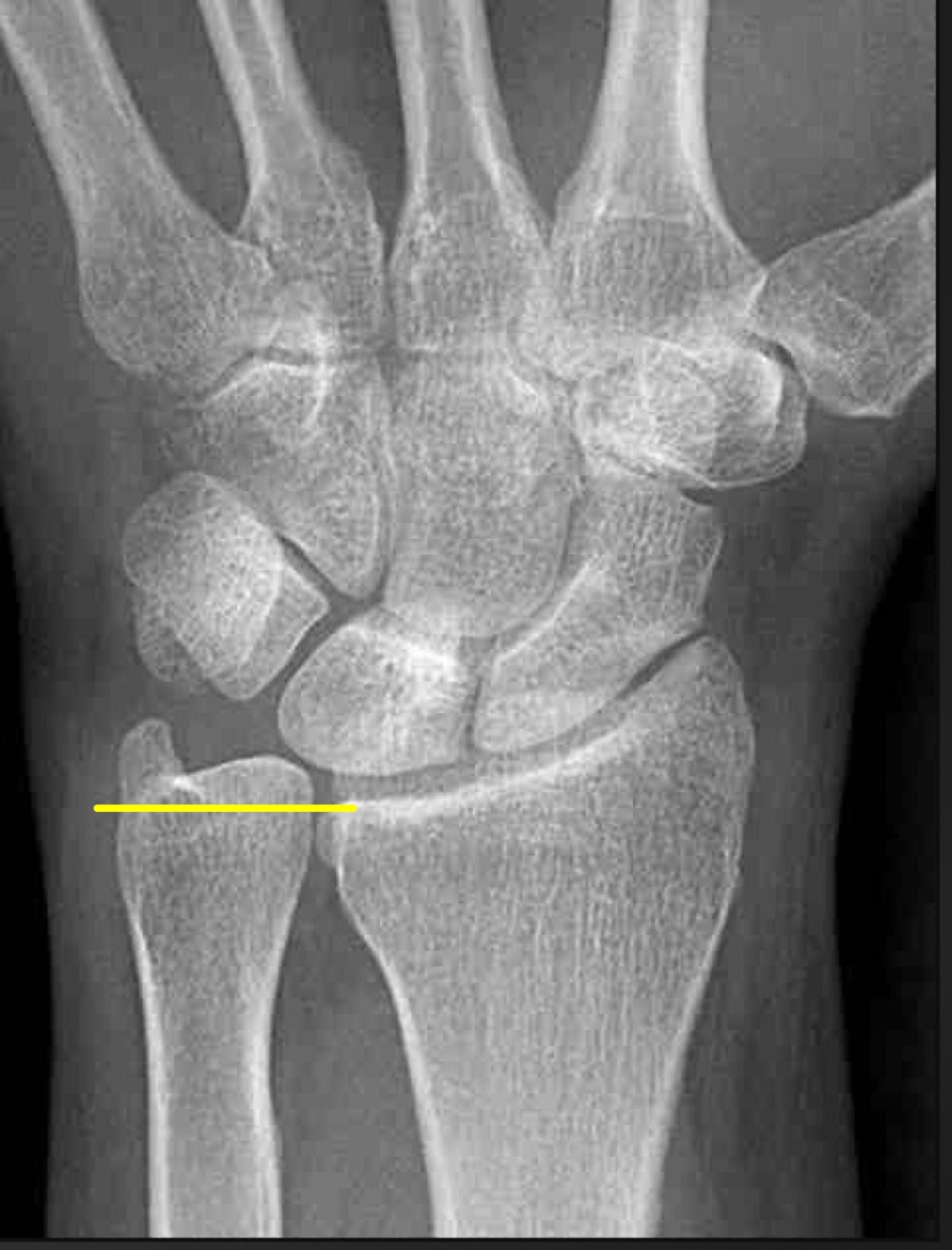
what is a long ulna called and what are the ramifications
positive ulnar variance
mechanical impingement of triangular fibrocartilage coplex (TFCC) and/or lunate and triquetral bones
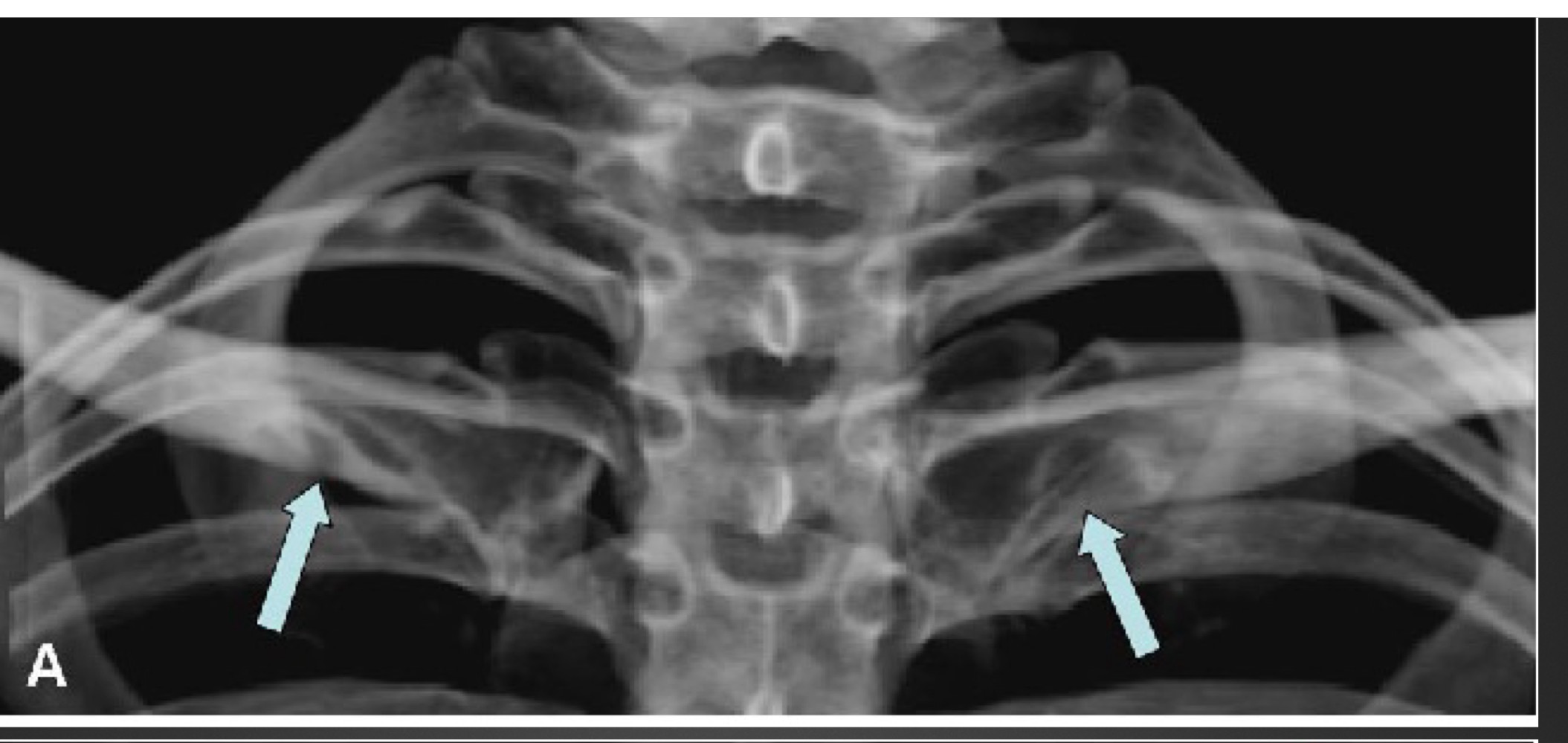
what is this anomaly called
rhomboid fossa
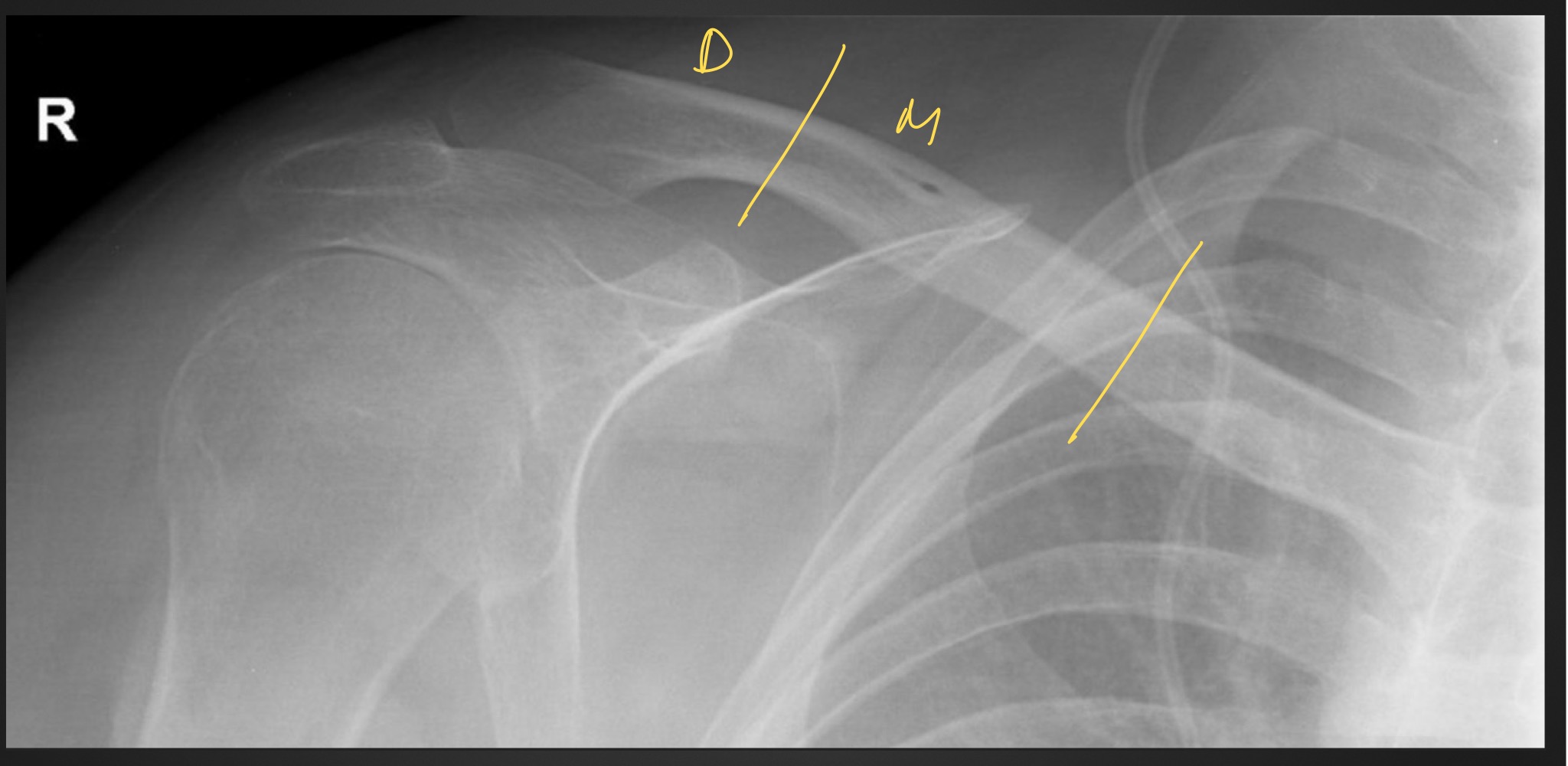
what is this anomaly called
supraclavicular foramen
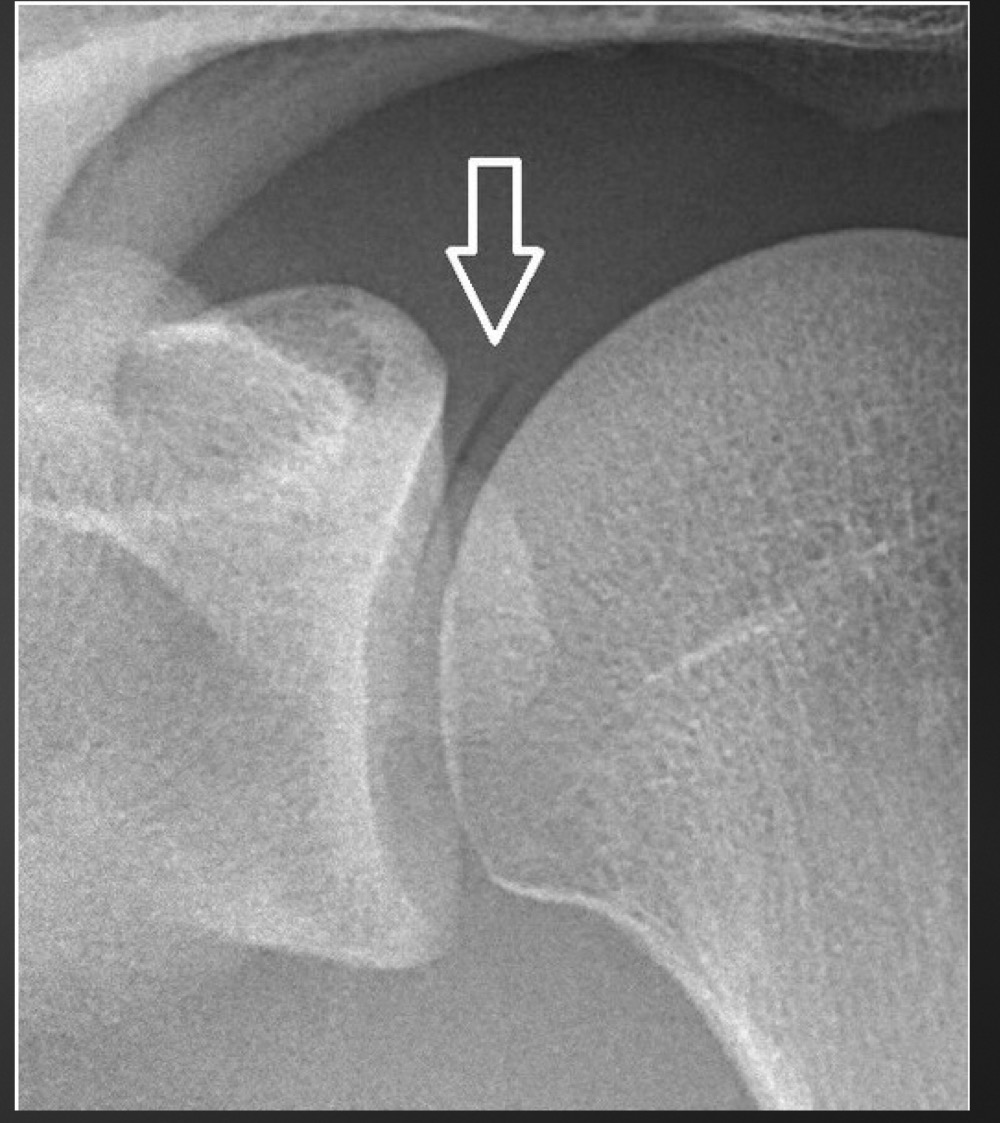
what is this anomaly called
vacuum phenomenon
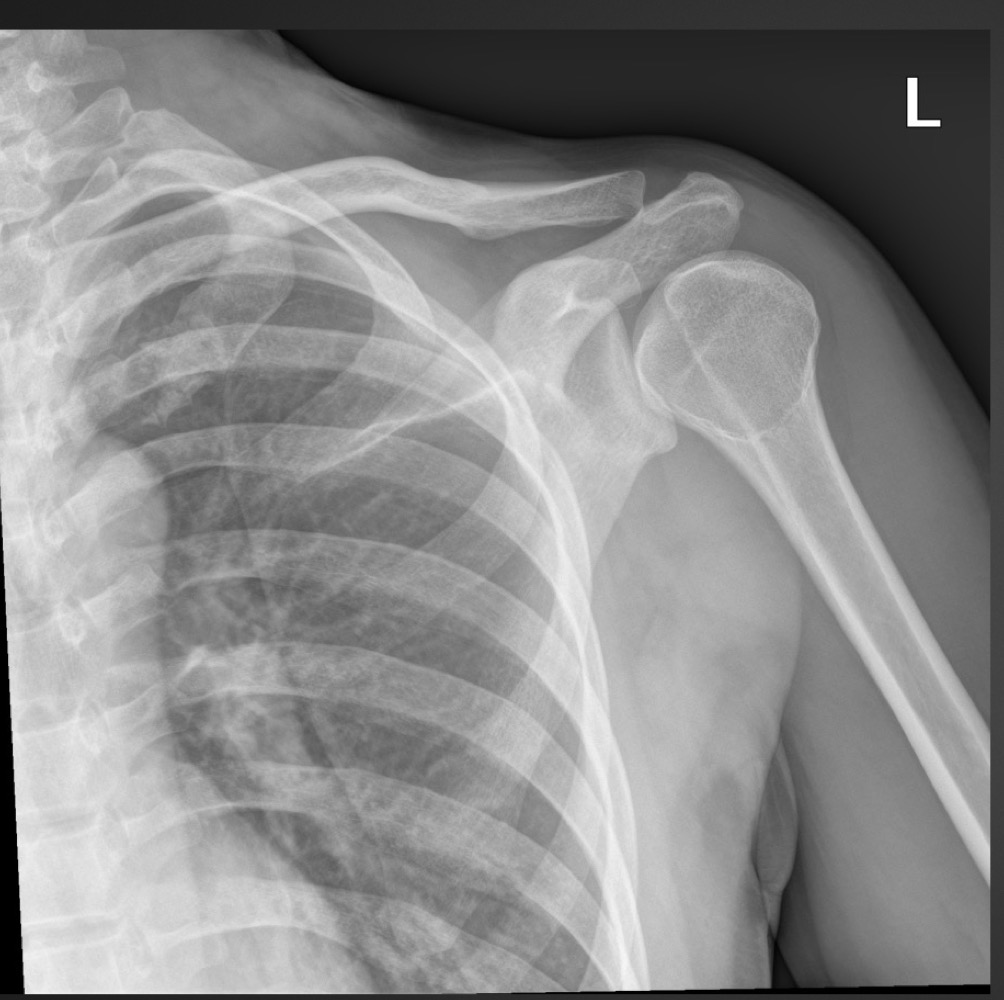
what is this anomaly called
os acromiale
what is this anomaly called
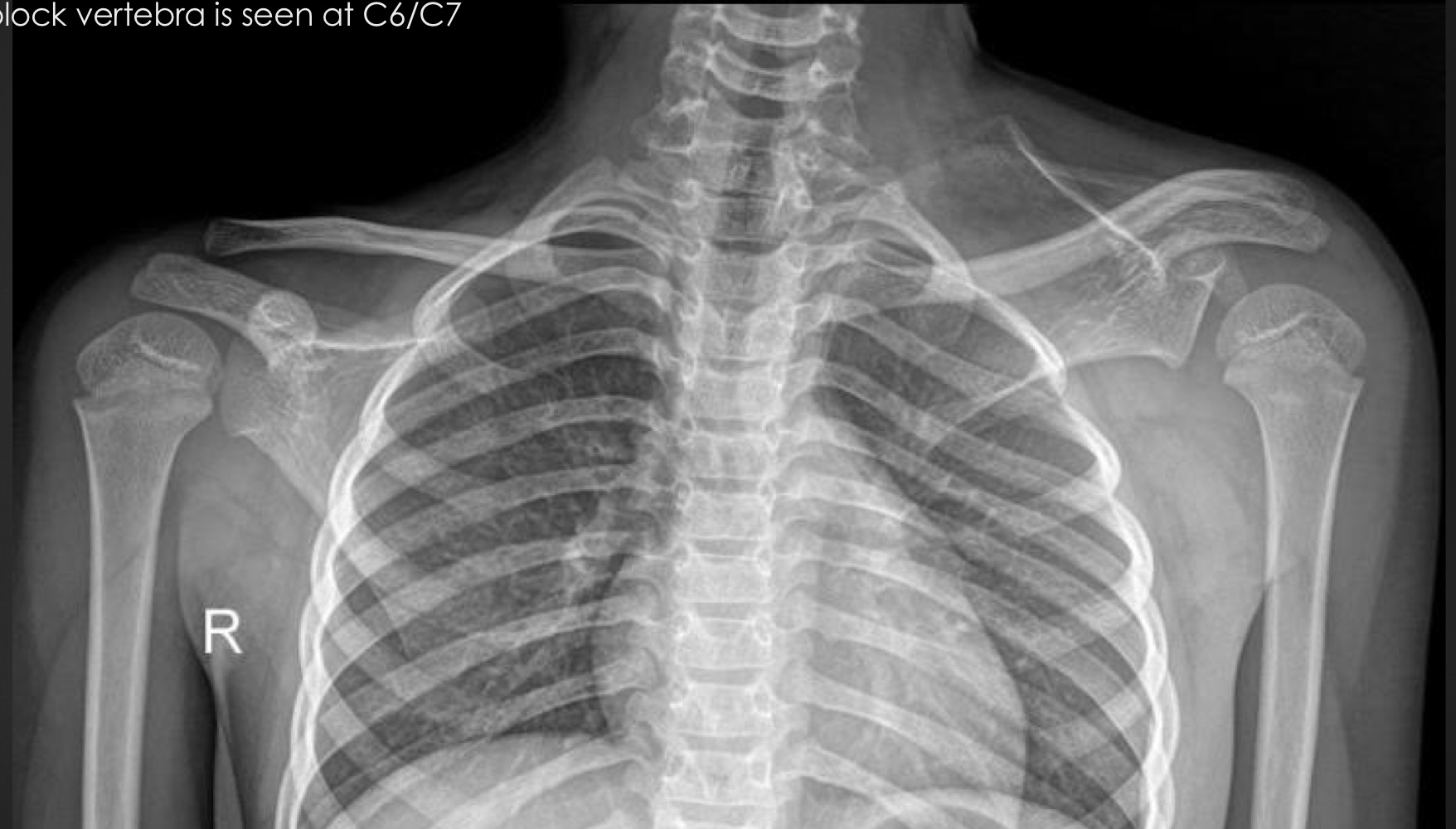
what syndrome is it often associated with when other factors are present
Sprengel’s deformity
Klippel Feil Syndrome
what other factors must be present with a sprengel’s deformity to diagnose klippel fiel syndrome
omovertebra
multiple block vertebra
spina bifida oculta
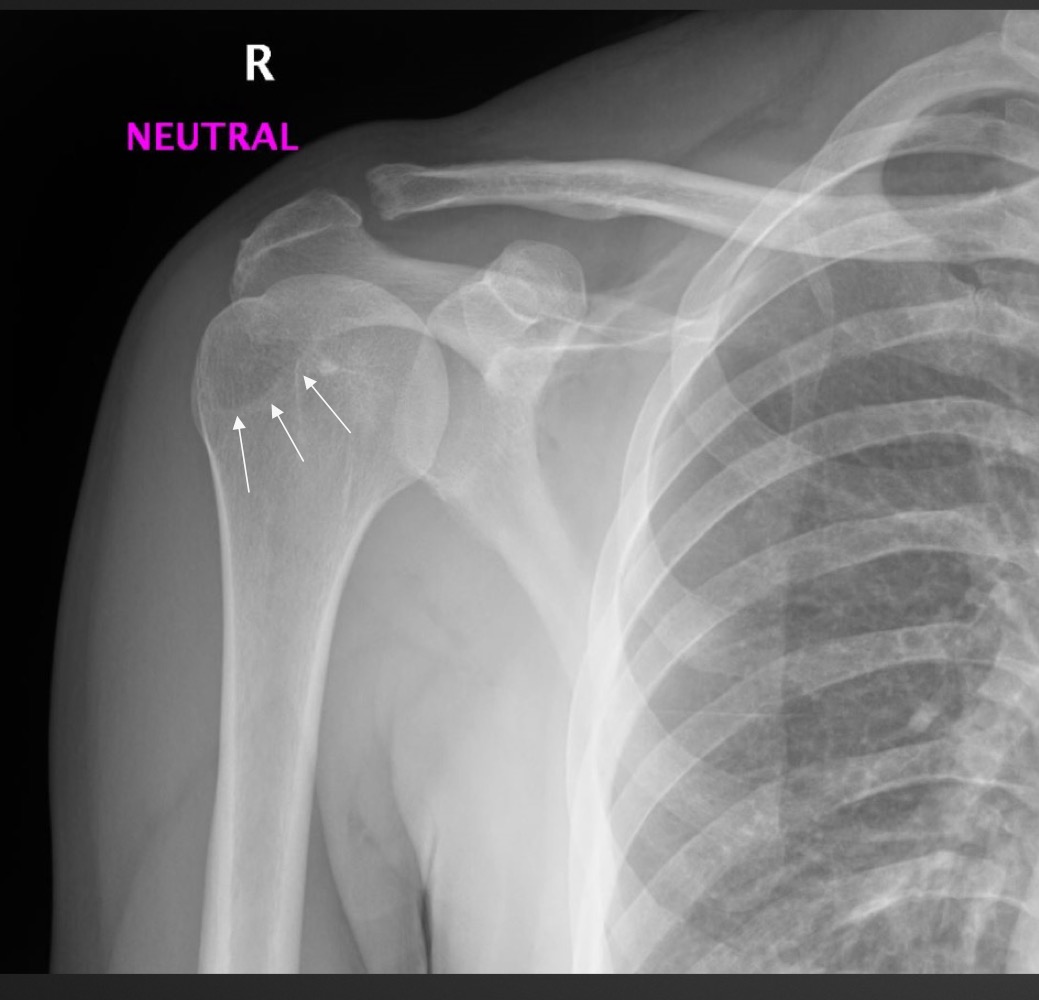
what is this anomaly called
pseudotumor/pseudocyst of humerus
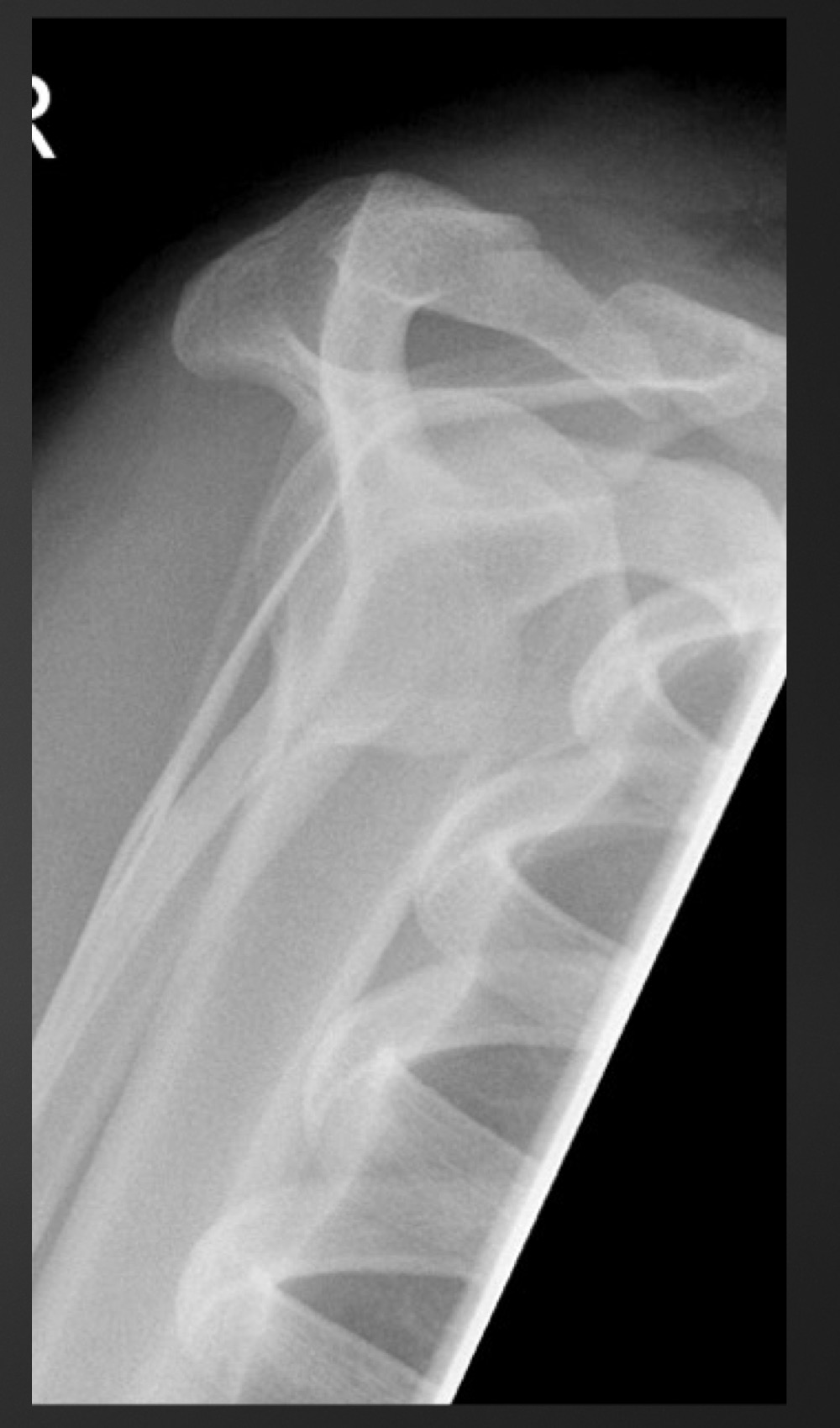
what is this anomaly called
pseudotumor/pseudocyst of humerus
what is this anomaly called
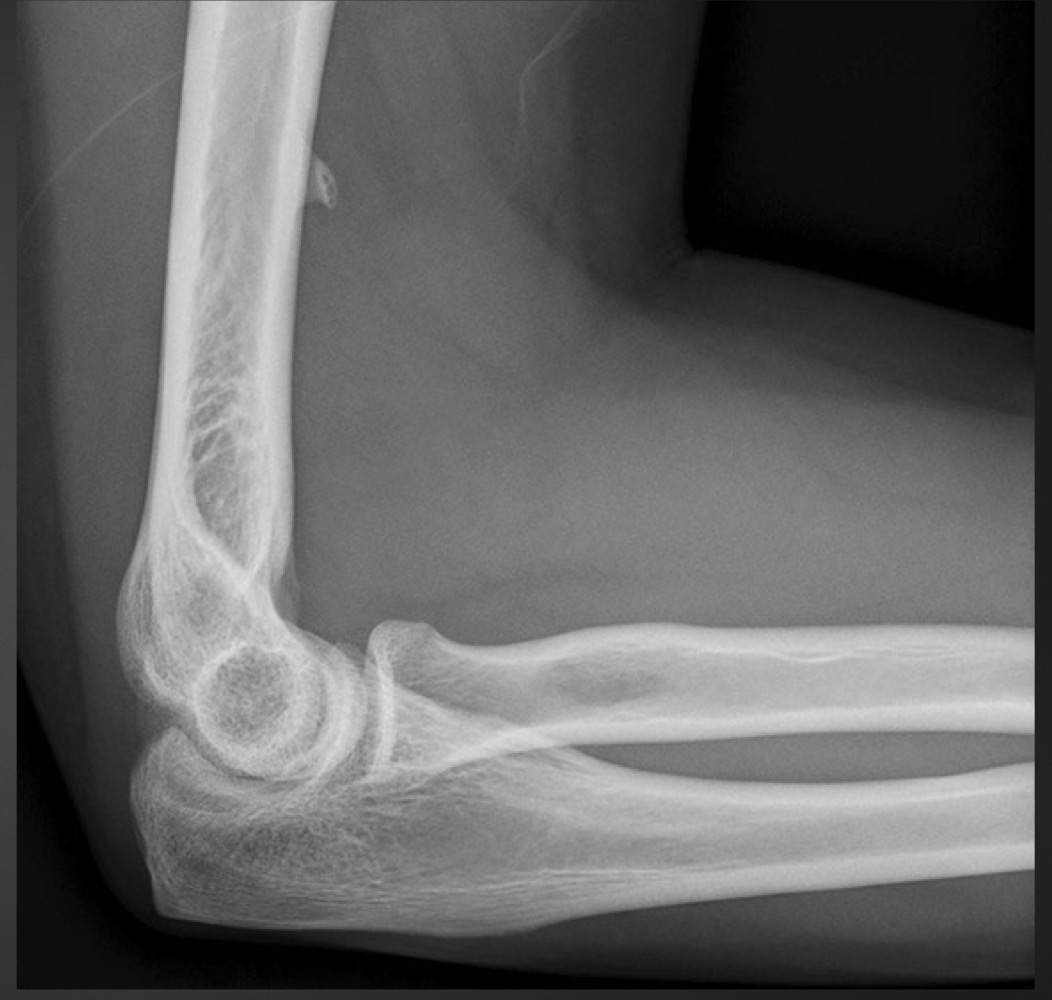
supracondylar process
what is this anomaly called
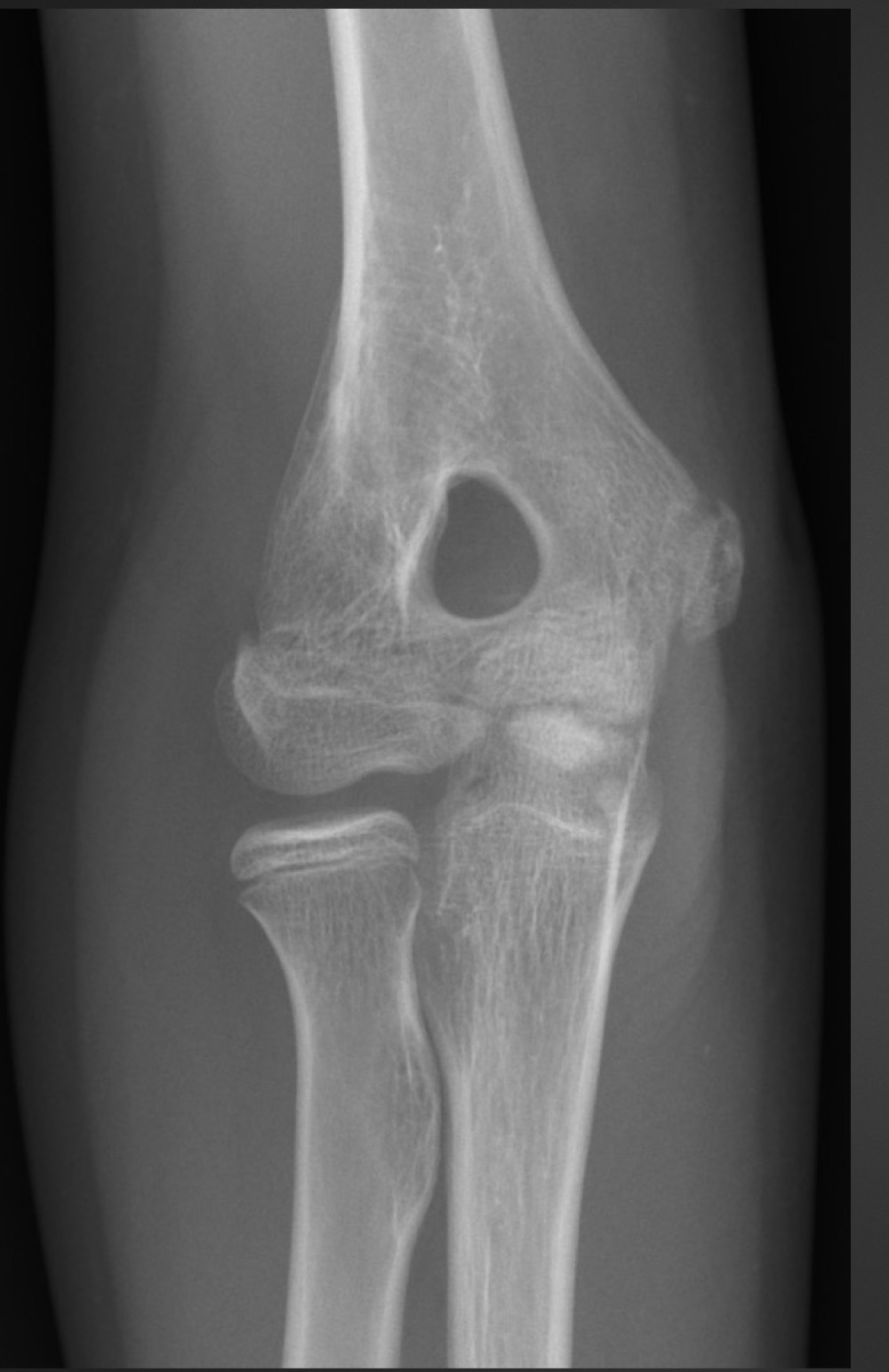
olecranon foramen
what might a supracondylar process cause
neurovascular compression of struther’s ligament, median nerve, and brachial artery
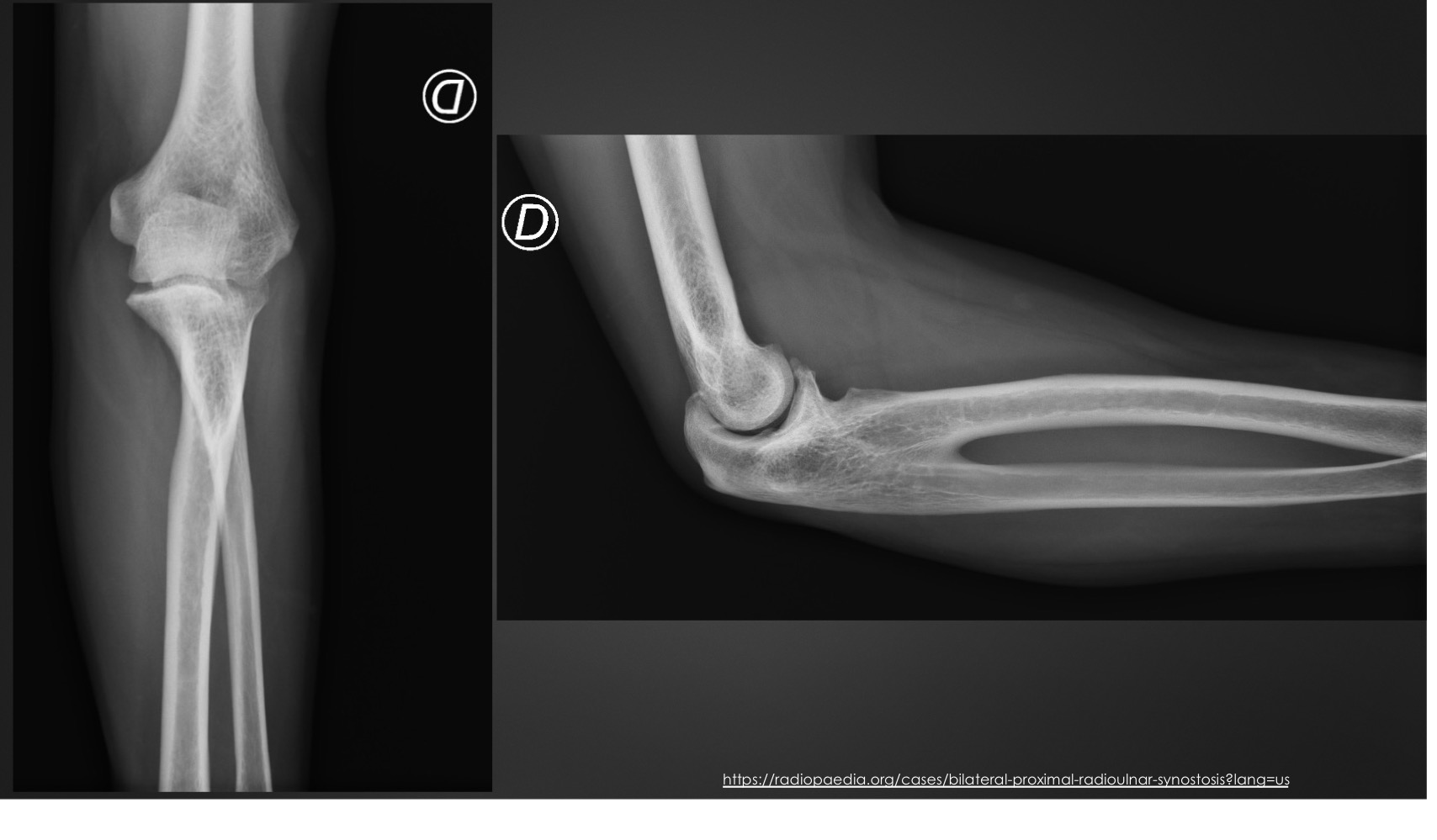
what is this anomaly called
radioulnar synostosis
what might a radioulnar synostosis cause
limited pronation/supination
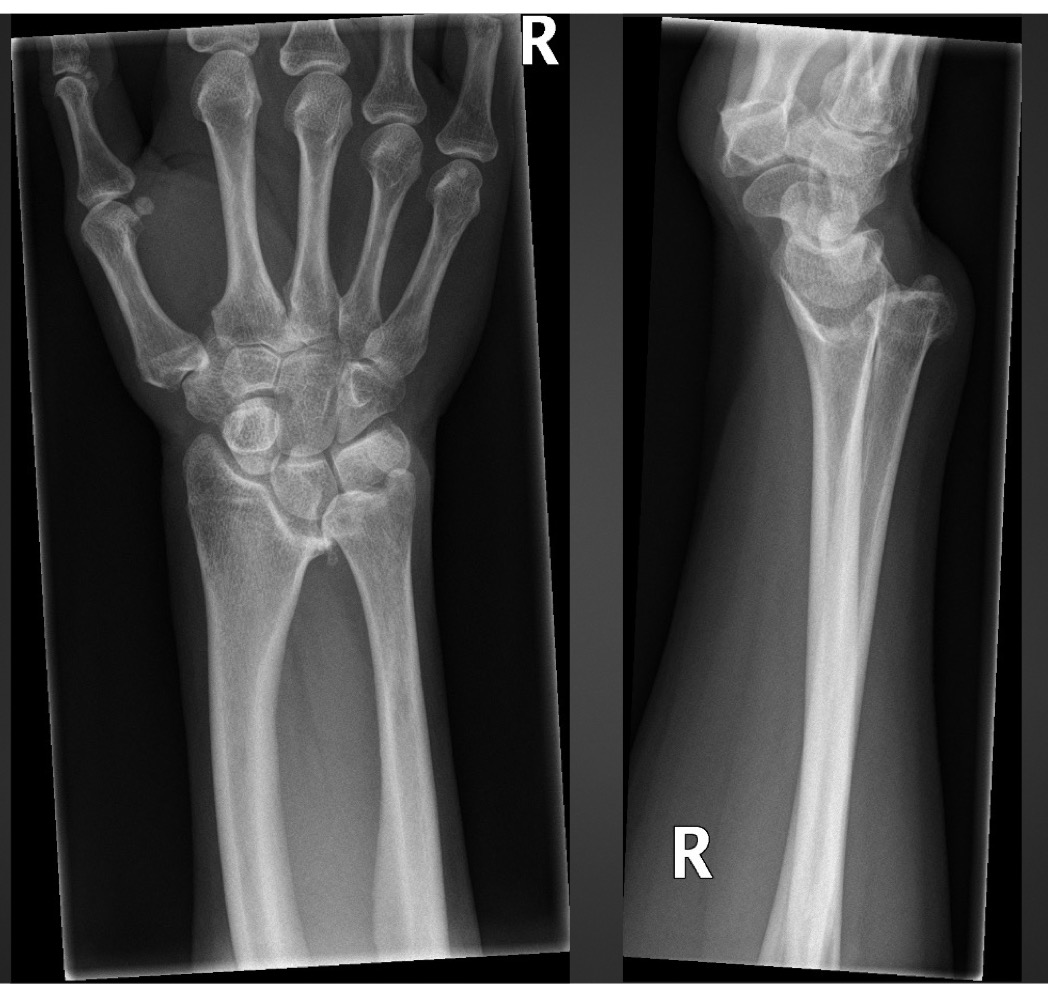
what is this anomaly called
Madelung’s deformity
what is madelung’s deformity characterized by
short, bowed radius angled toward ulna
v shape configuration of the carpus
widening of distal radioulnar joint
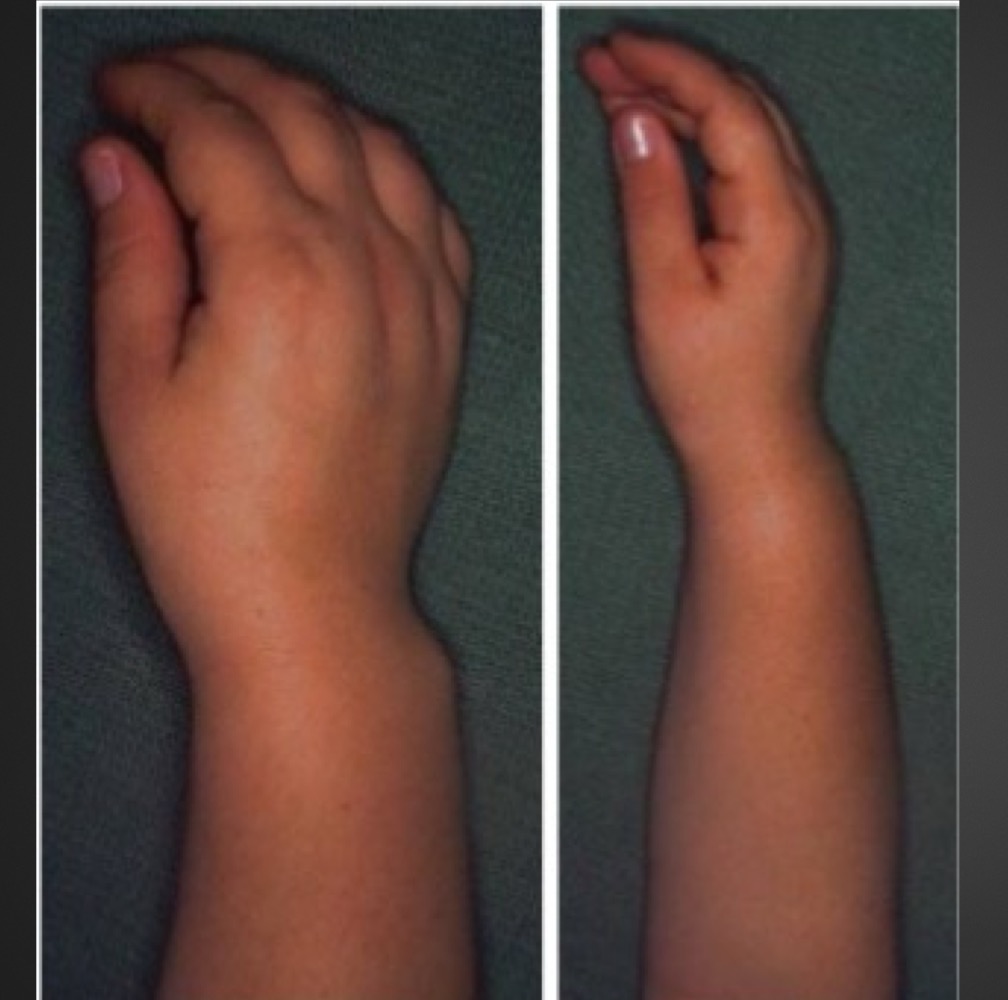
this physical appearance is characteristic of what?
Madelung’s deformity
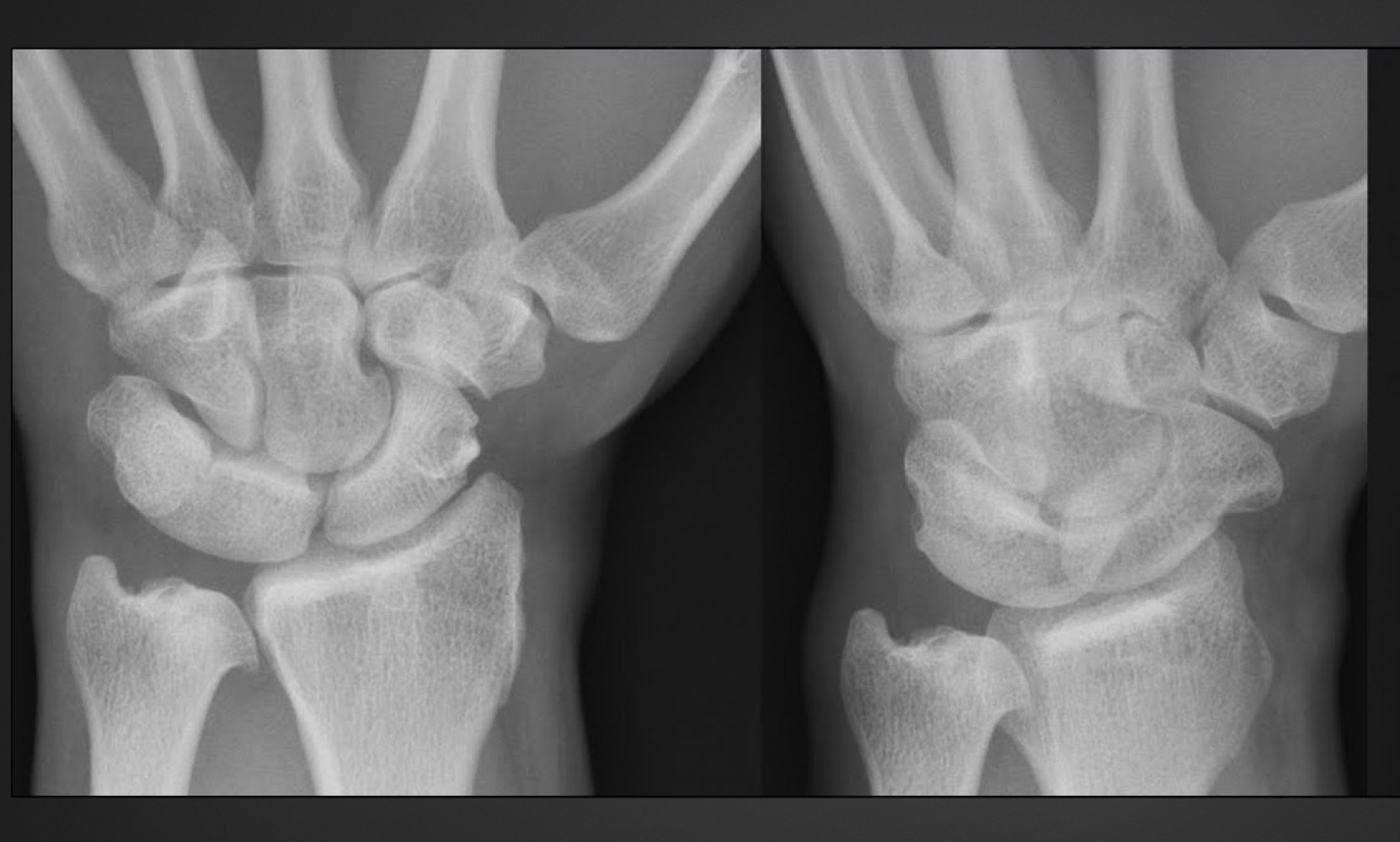
what is this anomaly called
carpal coalition (of triquetrum and lunate)
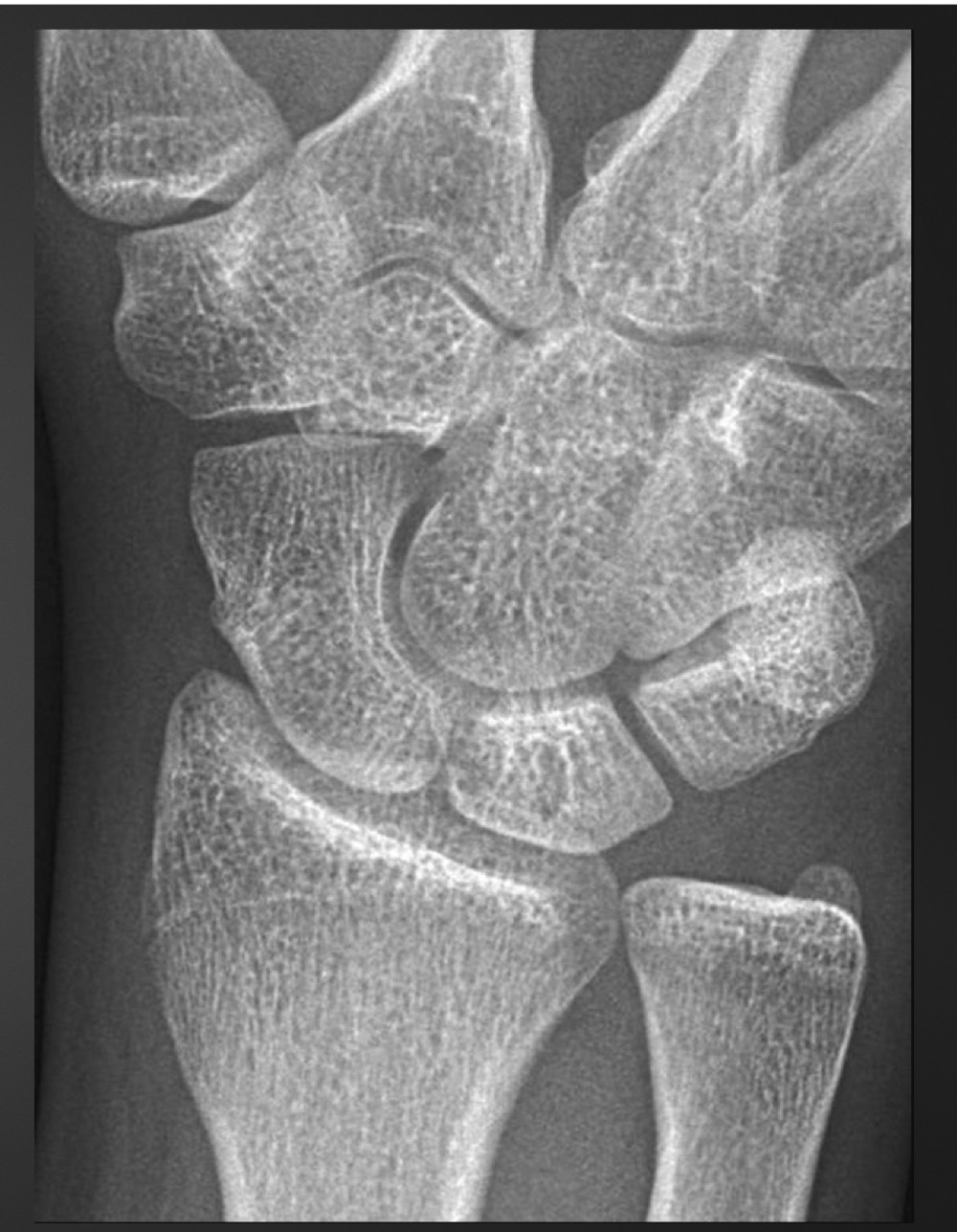
what is this anomaly called
carpal coalition of capitate and hamate
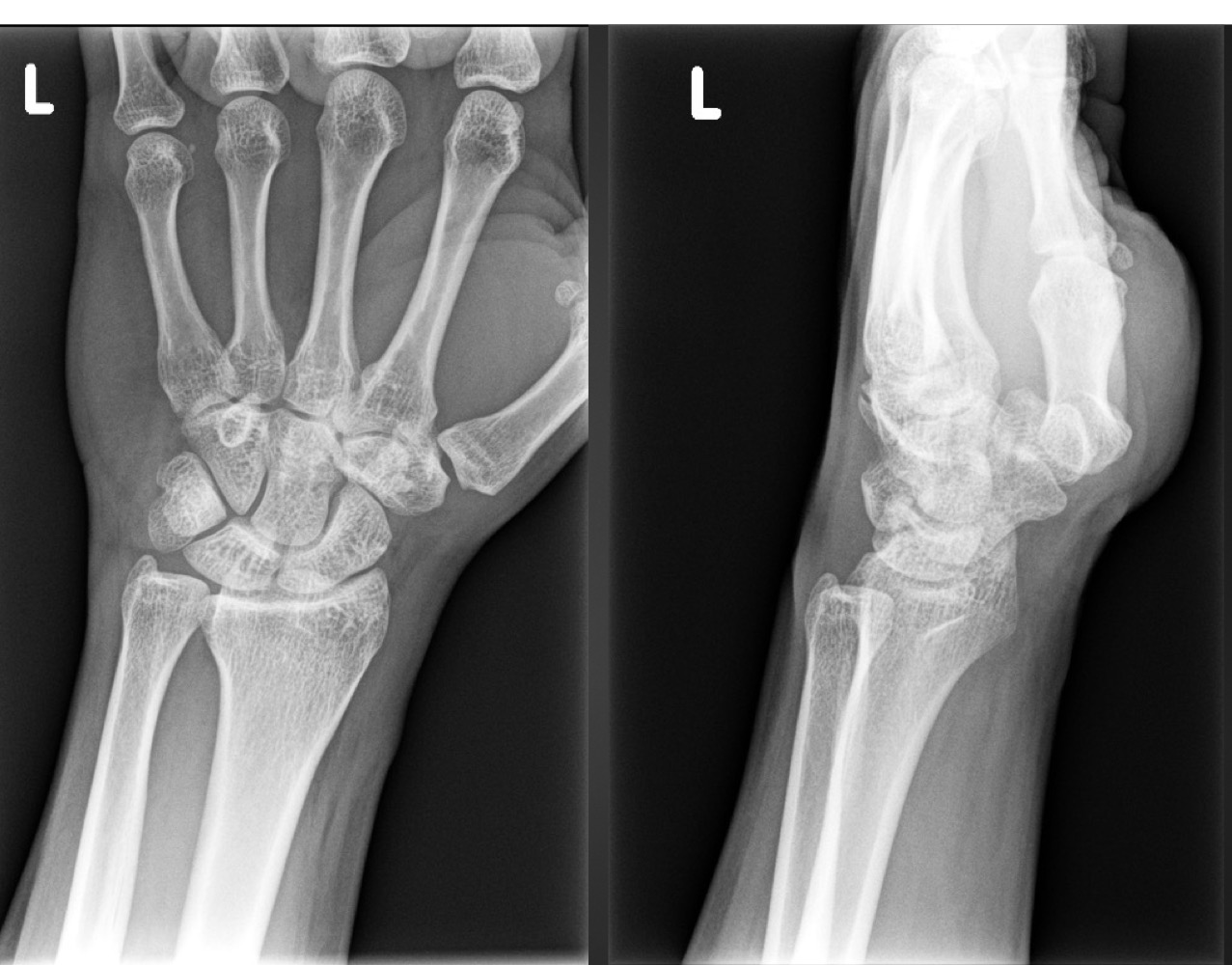
what is this anomaly called and what action might cause this patient pain
carpal boss
extension
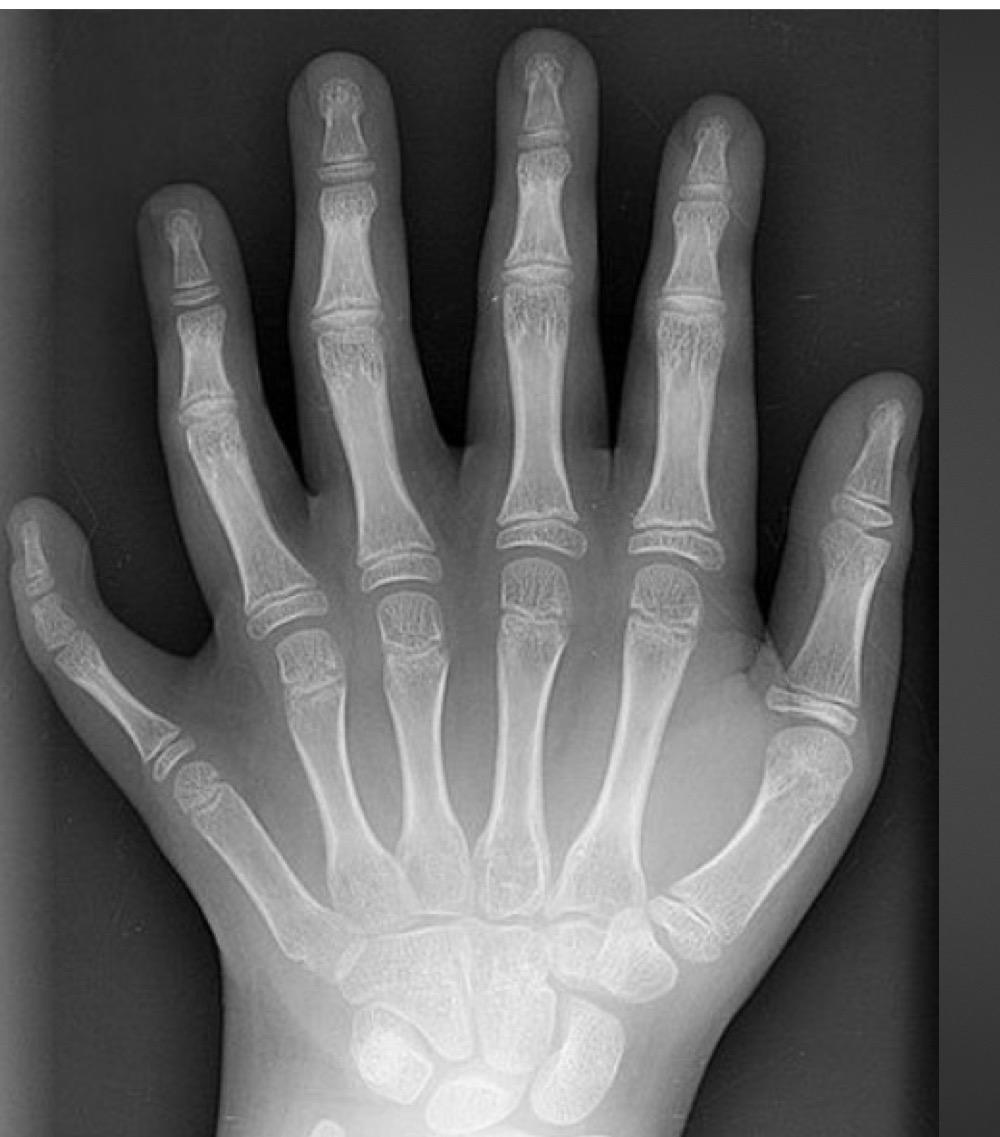
what is this anomaly called
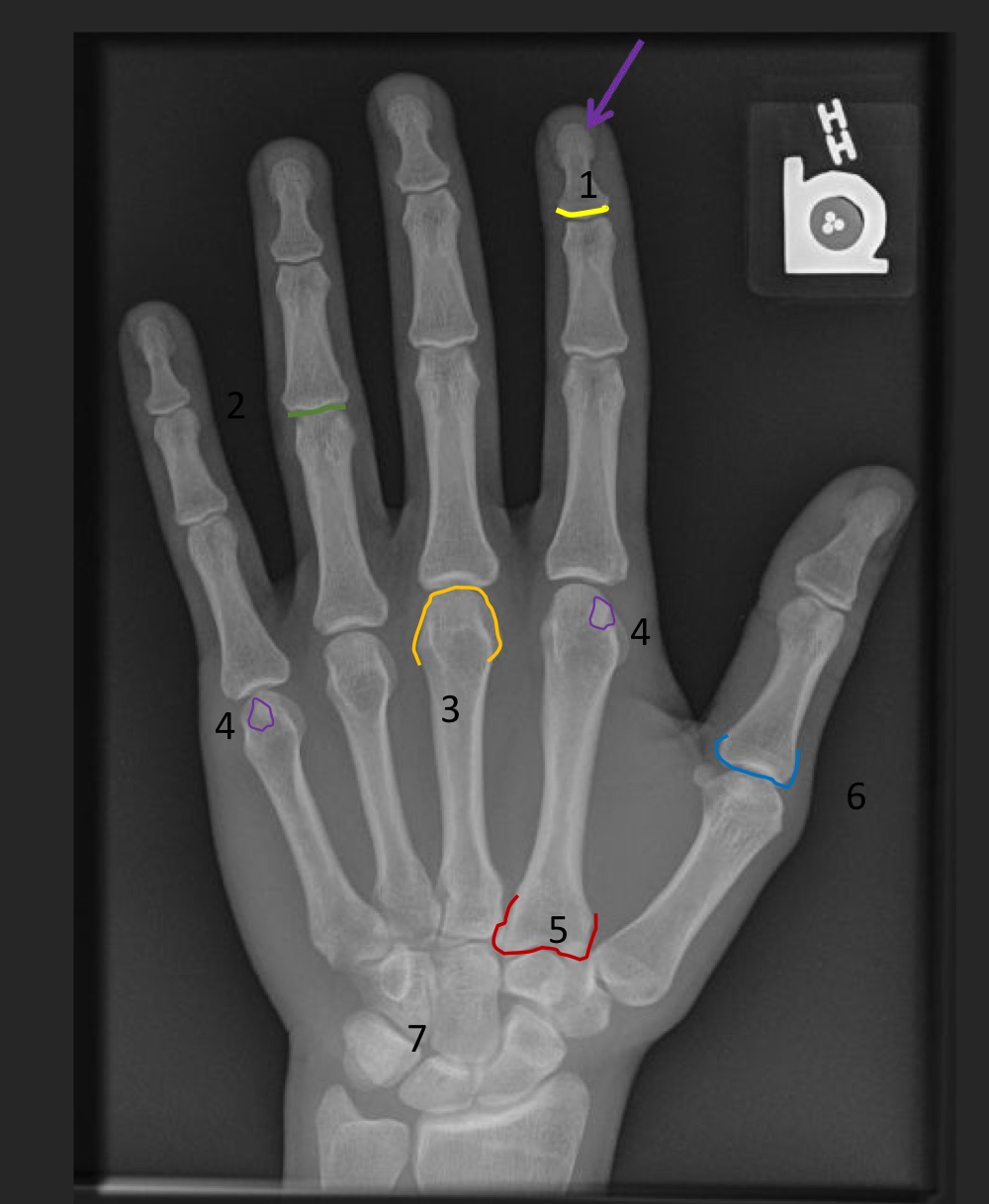
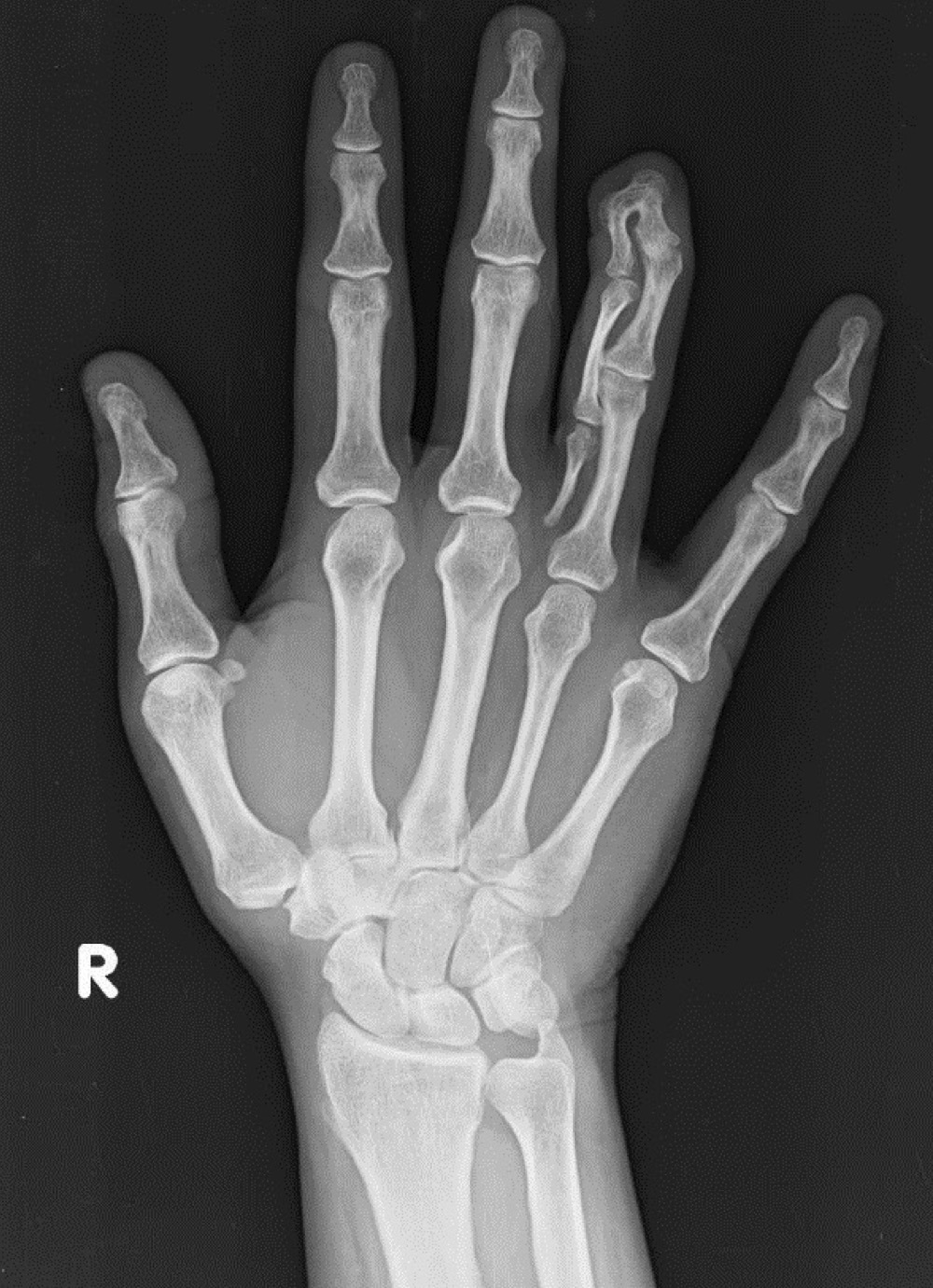
central polydactyly
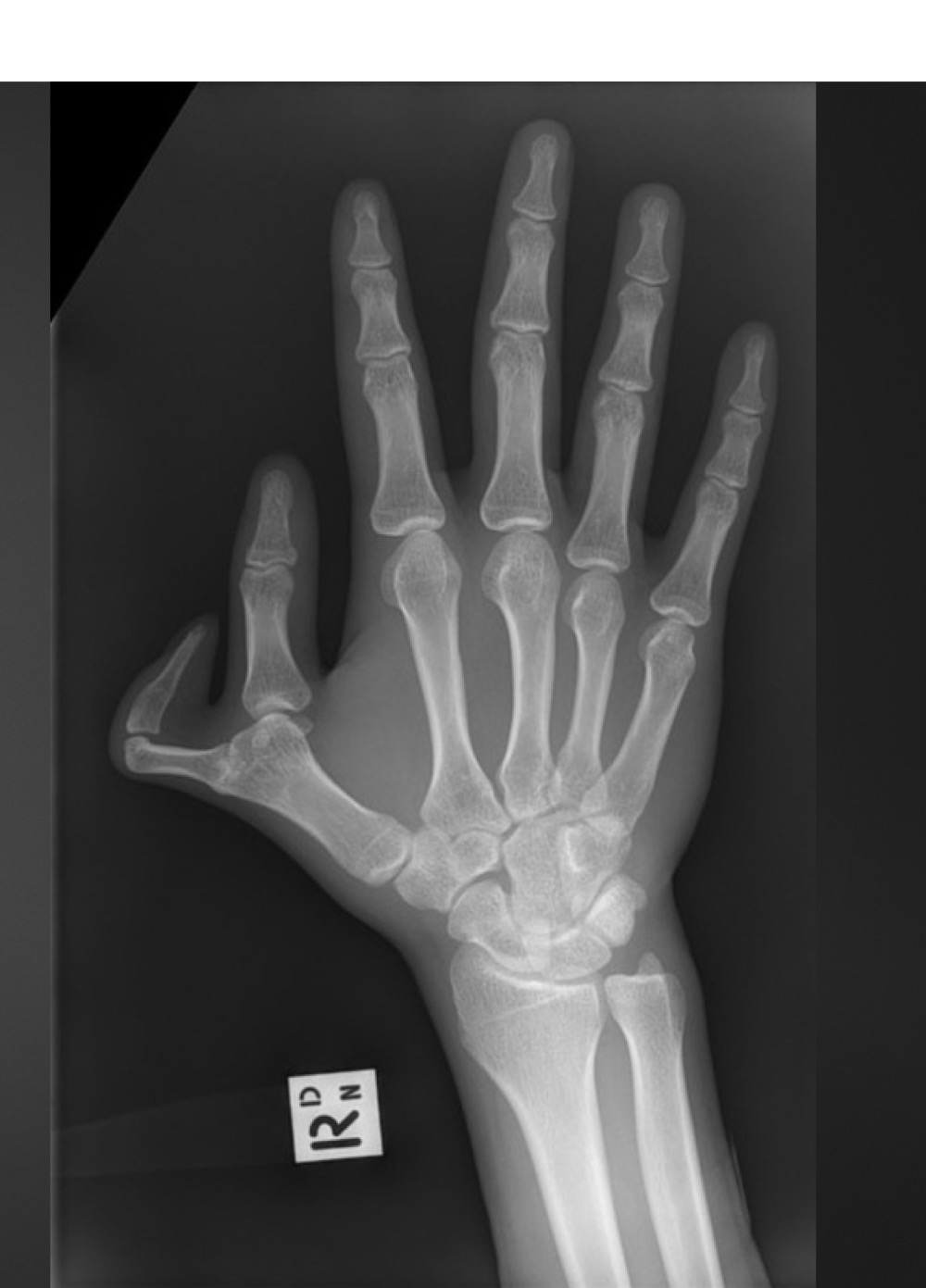
what is this anomaly called
pre-axial polydactyly
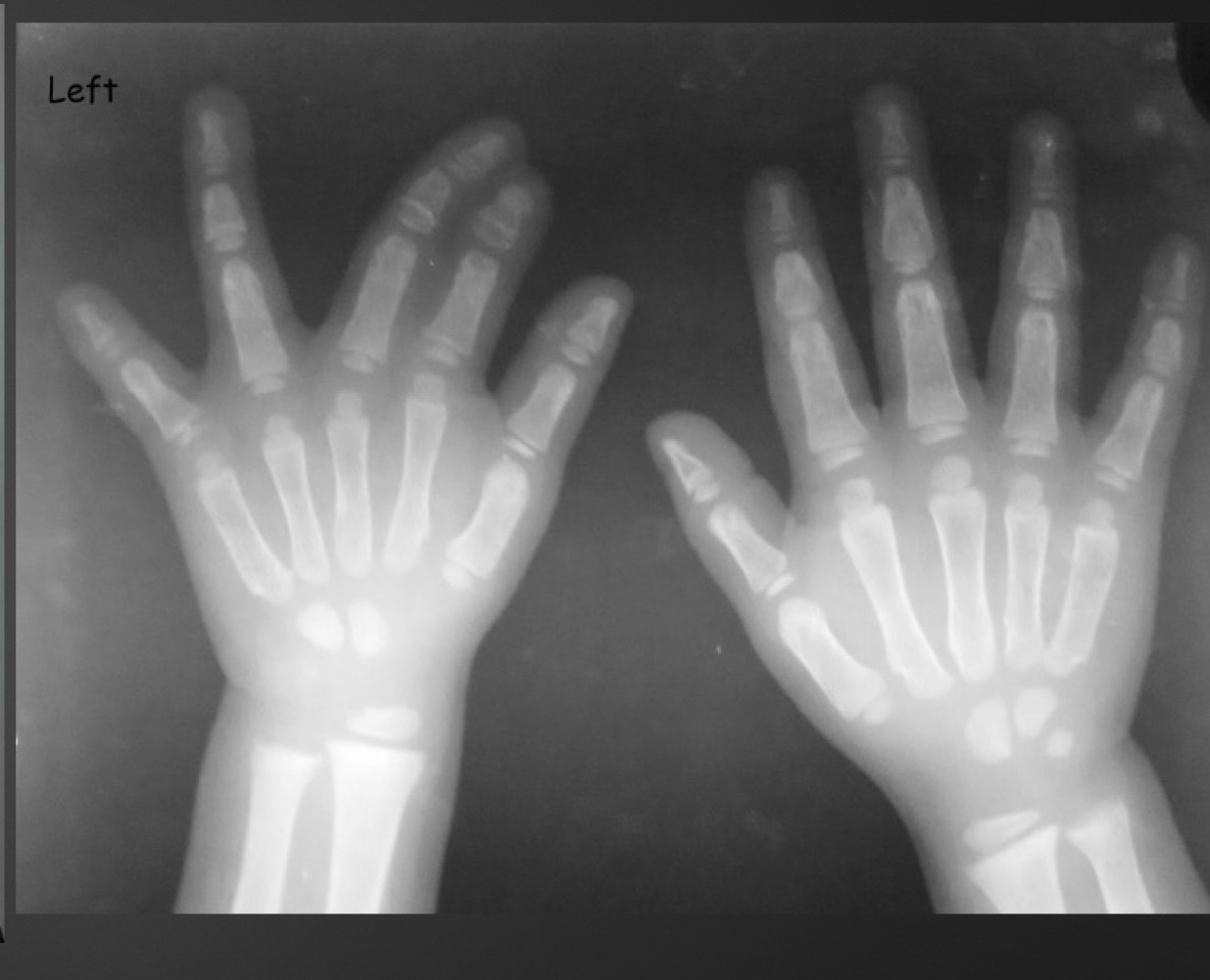
what is this anomaly called
syndactyly
where is syndactyly most common?
thrid and fourth digits or second and third
syndactyly occurs due to what
defect in mesenchymal organization
what is the most common developmental anomaly of the hand
syndactyly
what is this anomaly called
polysyndactyly (combo of polydactyly and syndactyly)
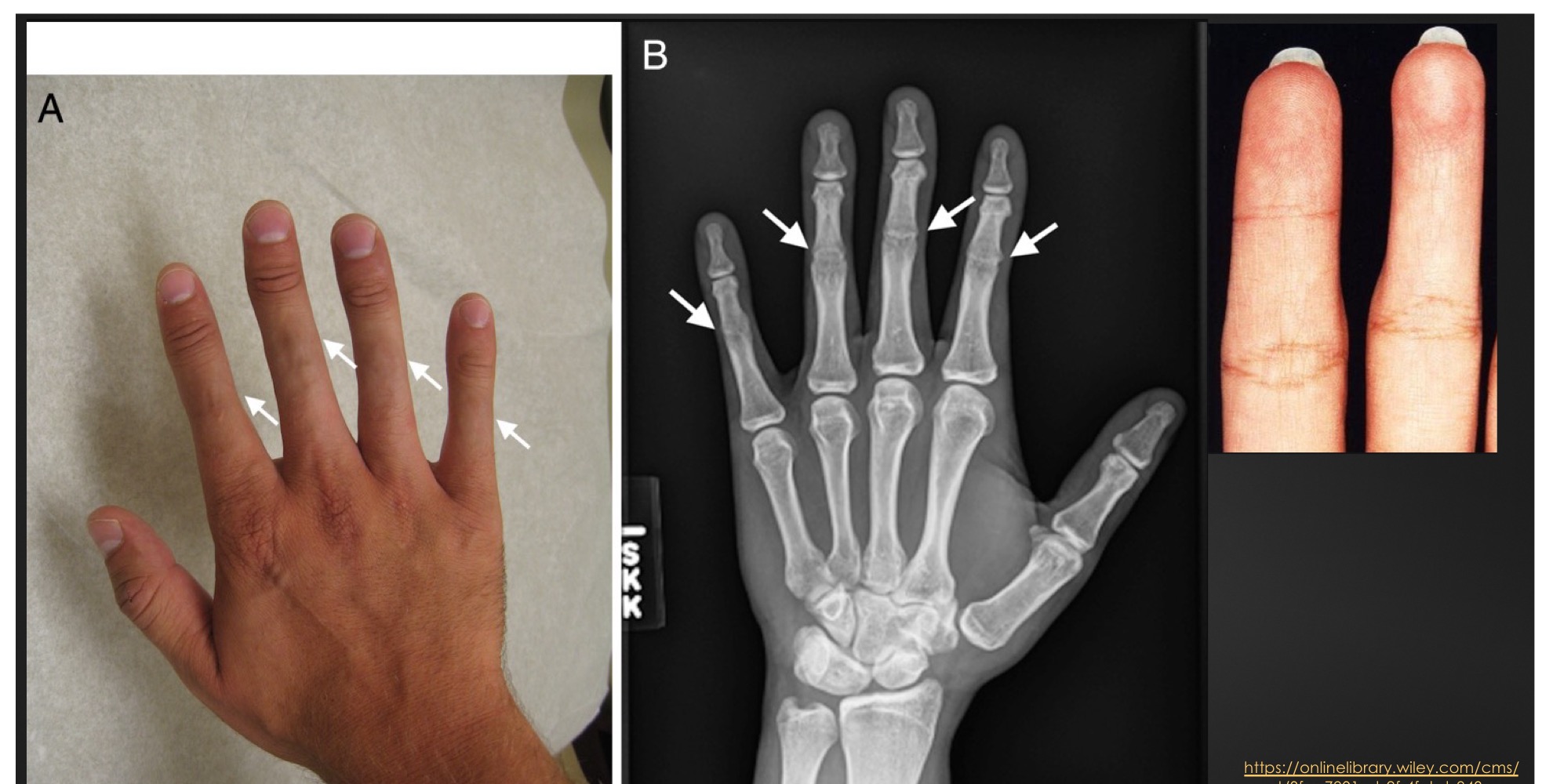
what is this anomaly called
symphalangism
what might symphalangism cause
stiffness, lack of volar skin folds at knuckles, reduced range of motion
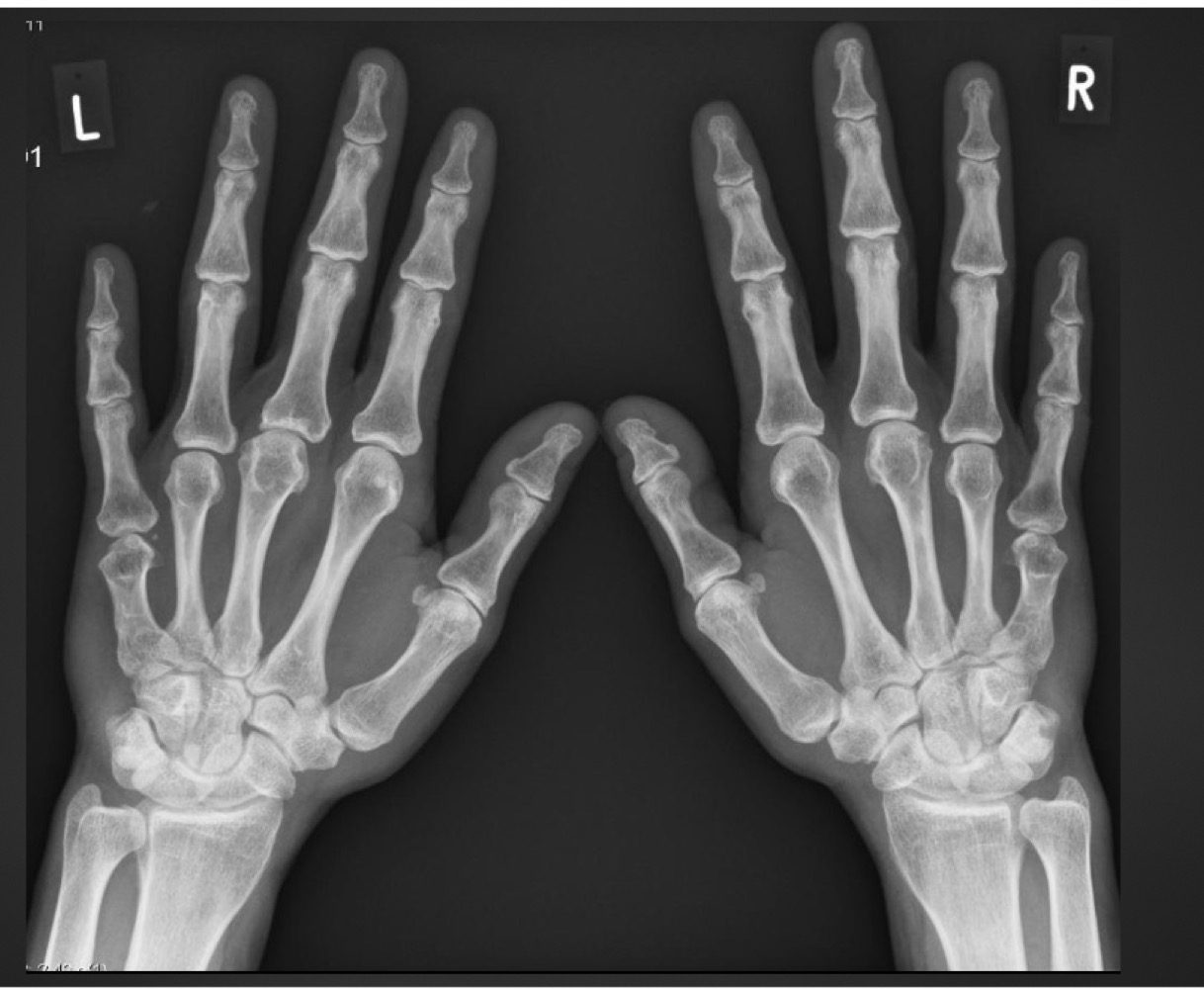
what is this anomaly called and what does it mean
brachydactyly
disproportionately short fingers and toes
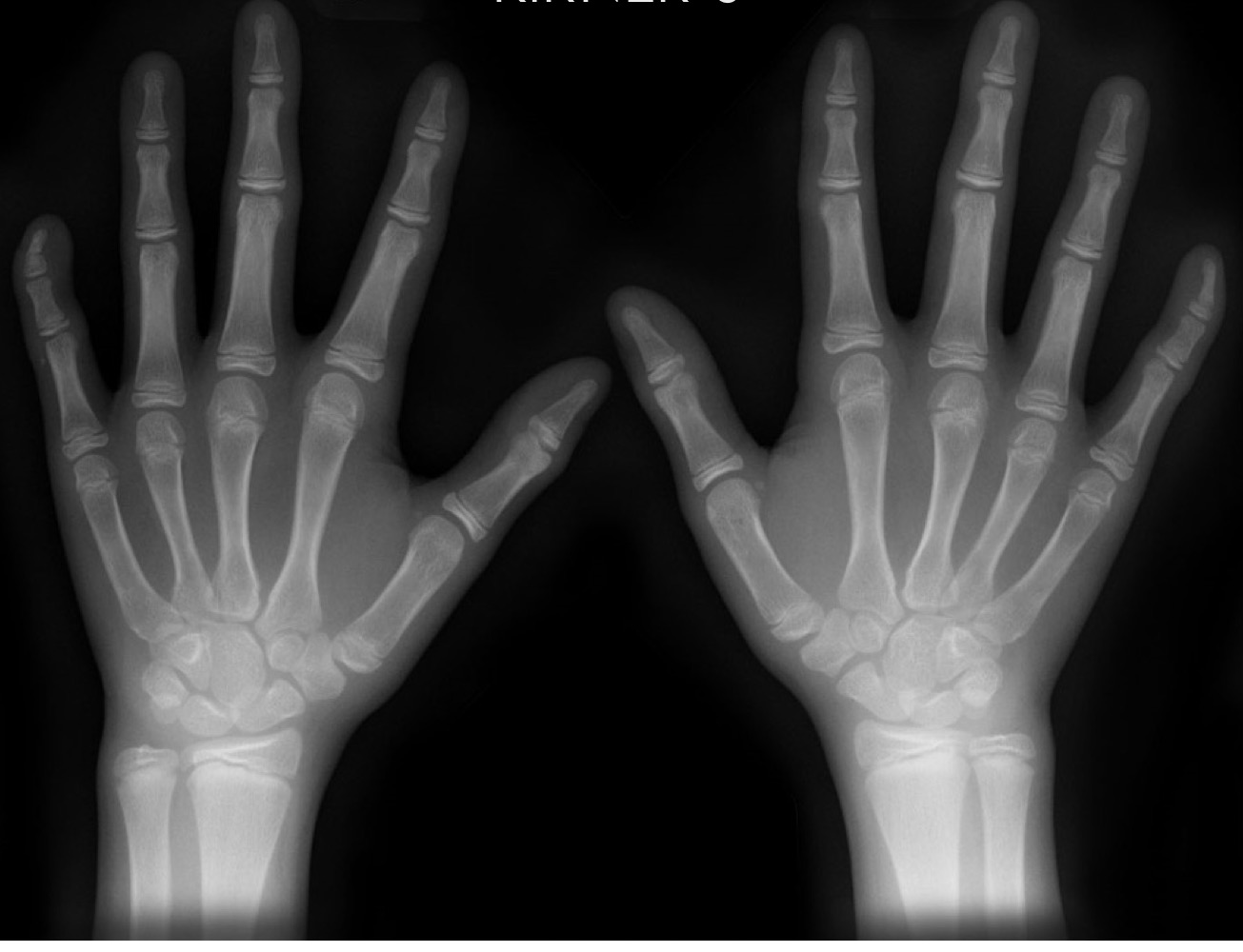
what is this anomaly called
Kirner’s deformity
Kirner’s deformity typically affects what digit and causes curvature in what direction(s)
5th
palmar AND radial
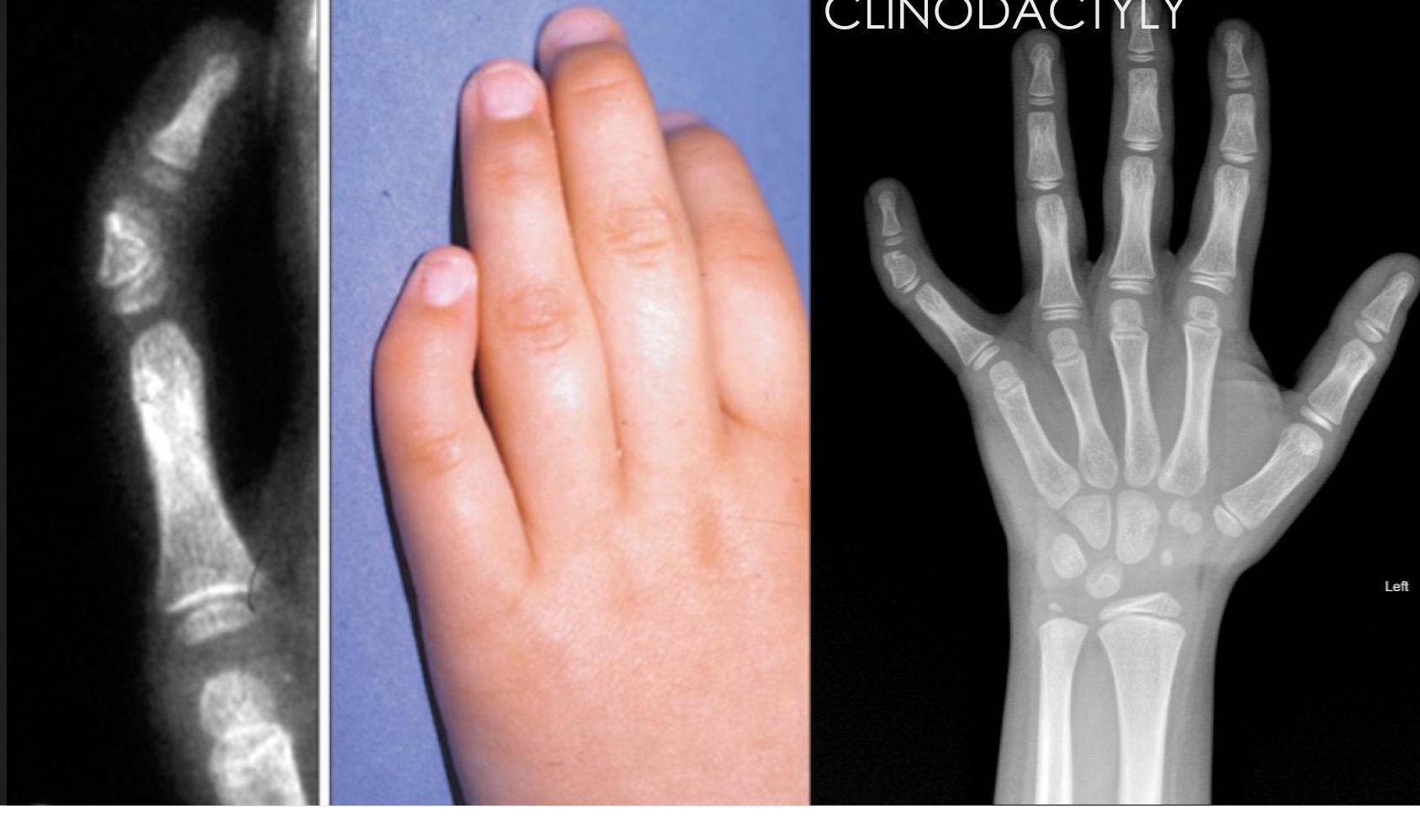
what is this anomaly called
clinodactyly
clinodactyly is typically found at what digit and caused angulation in what direction(s)
5th
radial OR palmar
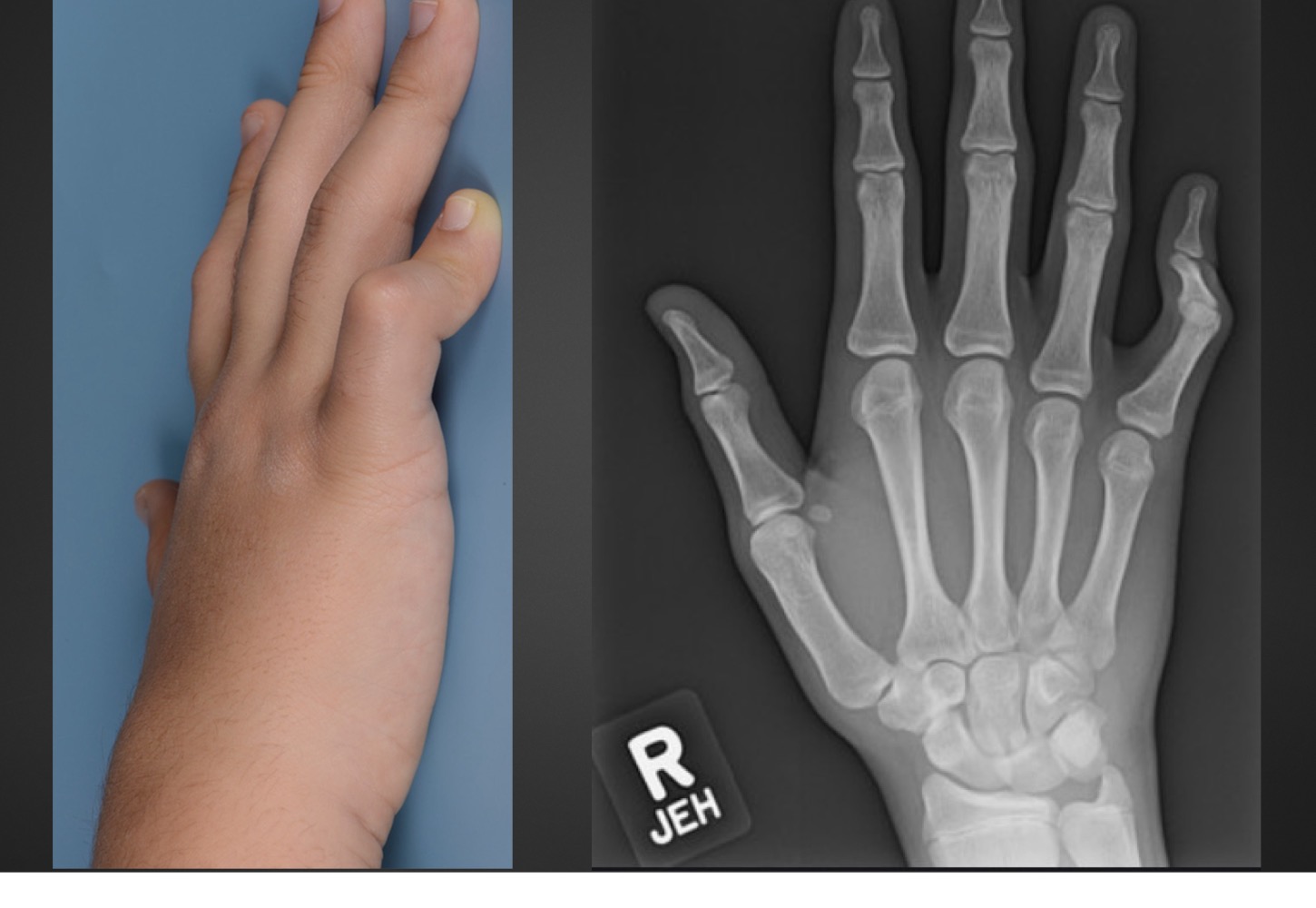
what is this anomaly called
campodactyly
campodactyly is characterized by what
permanent flexion of digit usually at proximal interphalangeal joint
(permanent extension in distal interphalangeal joint in response)
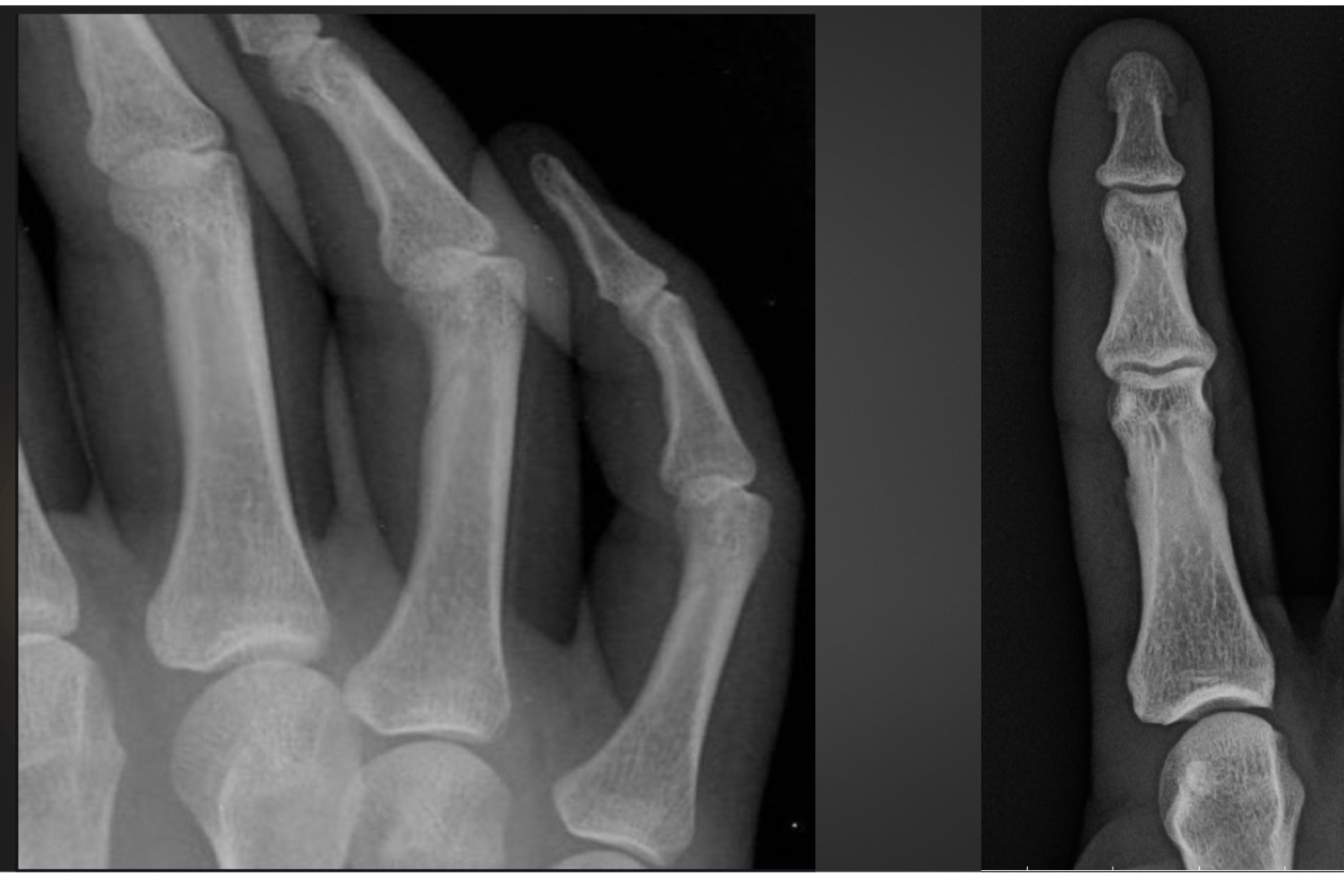
what is this anomaly called
nutrient foramen