Drug metabolism
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Drug Metabolism
Transformation of drug molecules into more polar compounds to facilitate elimination
Active Metabolite
A metabolite that retains pharmacologic activity (e.g., diazepam → oxazepam) following metabolism
Prodrug
A medication administered in inactive form that is metabolized to an active form (e.g., codeine → morphine)
Bioactivation
Conversion of a drug into a toxic or reactive metabolite (e.g., acetaminophen → NAPQI)
Major Sites of Metabolism
Primarily liver; also lung, kidney, intestine, skin, placenta, testes, adrenals
Phase I Metabolism
Functionalization reactions introducing/unmasking functional groups (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, cyclization, decyclization)
Phase II Metabolism
Conjugation reactions adding polar groups to increase solubility for excretion
Cytochrome P450 Enzymes (CYPs)
Major metabolic enzymes responsible for ~60% of drug metabolism (most commonly hydroxylation)
CYP Nomenclature
System identifying family (number), subfamily (letter), and isoform (number)
CYP3A4
Most abundant hepatic CYP; responsible for metabolism of most drugs
CYP2D6
Key polymorphic enzyme involved in metabolism of opioids like codeine (converts to active form morphine) and tramadol
FMO (Flavin-containing Monooxygenase)
Phase I enzyme metabolizing amines and thiols, phase 1
Alcohol Dehydrogenase
Converts alcohols to aldehydes (cytosolic), type 1 enzyme
Aldehyde Dehydrogenase
Converts aldehydes to carboxylic acids (mitochondrial); inhibited by disulfiram, phase 1 enzyme
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO)
Metabolizes neurotransmitters; located in mitochondrial outer membrane, phase 1 enzyme
Xanthine Oxidase
Purine metabolism enzyme present in liver and intestine, phase 1 enzyme
Esterases
Phase I enzymes catalyzing hydrolysis (e.g., lidocaine, procaine)
Phase II Conjugation Reactions
Conjugation (make hydrophobic by using functional groups, increases polarity for excretion), reactions catalyzed by transferases
P-glycoprotein (P-gp)
Major efflux transporter (ABC/ATP-binding casette family) reducing drug absorption and increasing elimination
ABC Transporters
ATP-dependent efflux proteins that pump drugs out of cells
Influx/uptake proteins
Help drug enter cell, example= OATP (organic anion transport protein 1 and 2, controls cholesterol/statin synthesis)
Polymorphic CYPs
CYP2D6 (Codeine/opioids, overactive= toxic, underactive= won’t activate drug), CYP2C9 (Warfarin, anticoagulant), and CYP2C19 (omeprazole), expression determines effectivity and toxic levels
CYP2D6 Metabolizer Phenotypes
UM (ultrarapid metabolizers), NM (normal metabolizers), IM (intermediate metabolizers), PM (poor metabolizers)
Factors Affecting Drug Metabolism
Age, sex, nutrition, disease states, PK (dose, frequency, route), exposure to xenobiotics
Drug-Drug Interaction
A measurable modification of one drug’s action by another taken previously or concurrently
Pharmaceutical Interaction
Drug incompatibility outside the body (oxidation, drug mixing, etc)
Pharmacokinetic Interaction
Effects on absorption, protein binding, metabolism, transport, or renal excretion
Pharmacodynamic Interaction
Interactions at receptor sites causing antagonism or potentiation
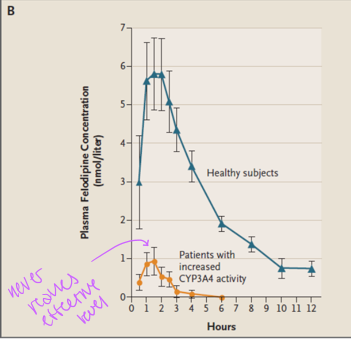
Enzyme Inhibition
Reduction in metabolic activity → increased drug exposure
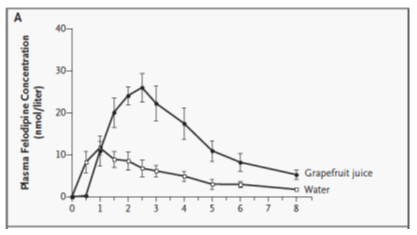
Enzyme Induction
Increased metabolic enzyme expression → decreased drug exposure
CYP Inhibitors
Examples: grapefruit juice, ketoconazole, fluconazole, clarithromycin
CYP Inducers
Examples: St. John’s wort, rifampicin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, cigarette smoke