EM Waves & General Wave basics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Waves transfer energy in the direction…
that they are travelling
amplitude means
the maximum displacement of a point on the wave from its undisturbed position.
Wavelength means
distance between the same point on 2 adjacent waves
Frequency means
and is measured in
number of complete waves passing a certain point per second. 1 Hz = 1 wave / second
The period of a wave means
the amount of time it takes for a full cycle of the wave to pass a point.
Formula for period of a wave
t = 1/f
t is period in seconds
f is frequency in Hz
Transverse waves have __ vibrations
the oscillations are __ to the direction of energy transfer
perpendicular
perpendicular
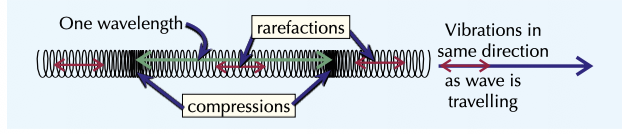
Longitudinal waves have __ vibrations
the oscillations are __ to the direction of energy transfer
parallel
parallel
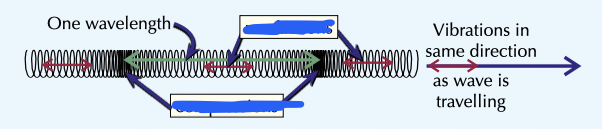
Complete the longitudinal diagram
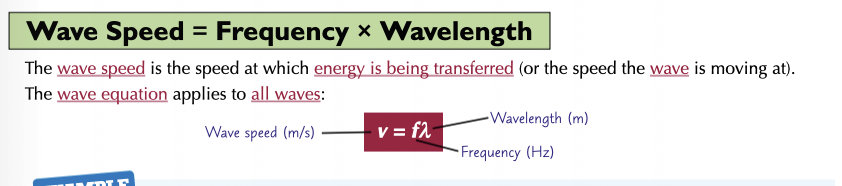
The important equation:
wavespeed (define this too)
wavelength
frequency
with units!
3 wave experiments using the equation
Sound: a speaker attached to signal generator. 2 microphones attached to an oscilloscope. move microphones in relation to each other until the 2 waves line up on oscilloscope. measure distance between microphones for wavelength
2. Ripple tank
String: signal generator attached to vibration transducer attached to string with pulley with masses on at end. measure nodes
EM Radiation:
As you go down from Radio to Gamma,
frequency __
and wavelength __
(increase/decrease)
frequency up
wavelength down
Radio waves uses
long range communication
short wave signals reflect off the ionosphere, so bounce around the earth and off its atmosphere
long wave signals bend around the earth
TV and FM radio would be very short wavelength radio waves, because to get signal you must be in direct sight of transmitter. Signal doesn't bend or travel far through buildings.
2 uses of microwaves
satellite comms. Micro is best for passing easily through earth’s watery atmosphere
2 . microwave ovens, where water molecules absorb microwaves which have penetrated a few cm into the food. they then quickly spread this absorbed energy to the rest of the food.
Infrared is used for
monitoring temperature.
It is given off by everything, more if the object is hot, less if cold. IR cameras can show the IR being given off, red for more, green for less.
used by police and nature ppl
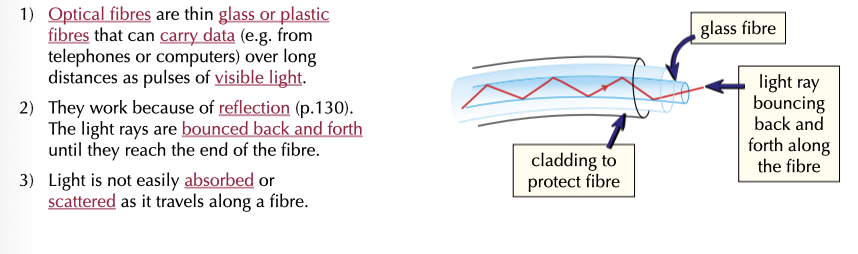
Fibre optic cables can be used for
they use which type of wave?
using visible light to transmit data
UV uses
suntanning
fluorescence: Chemicals absorb UV and emit visible light. Used in hi-vis jackets, security pens, detecting forgery
X- Rays and Gamma Rays in medicine: talk about the uses
X-rays pass easily through flesh, but not bones, so we can see bones on the image clearly because they absorb the waves.
X and gamma can be targeted at cancer cells to kill all cells in the area, but it’s risky.
Risk: radiation dose is measured in
Sieverts
Sv
higher frequency waves usually more dangerous