Anatomy and Physiology Ch. 3
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
184 Terms
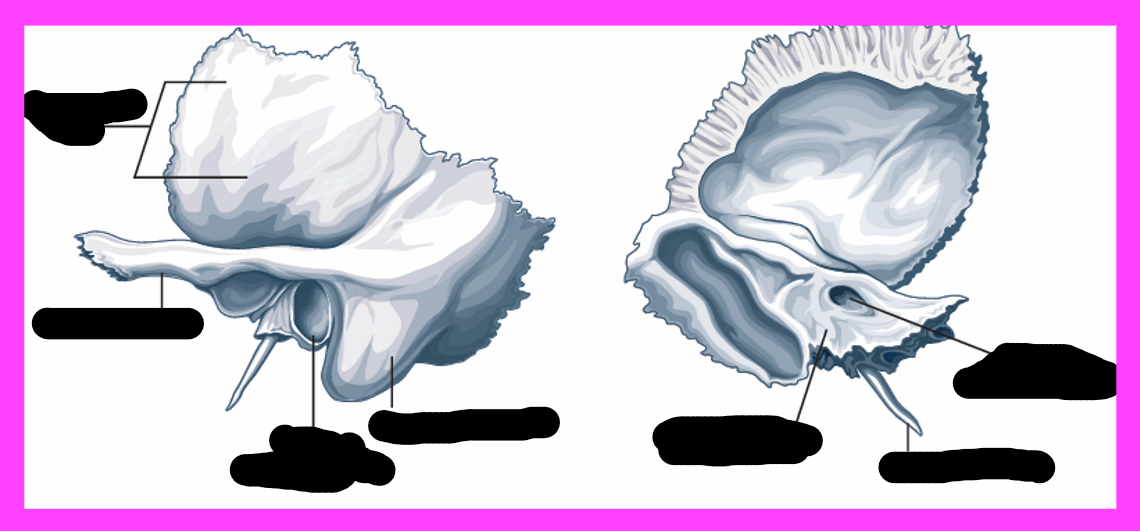
temporal bone
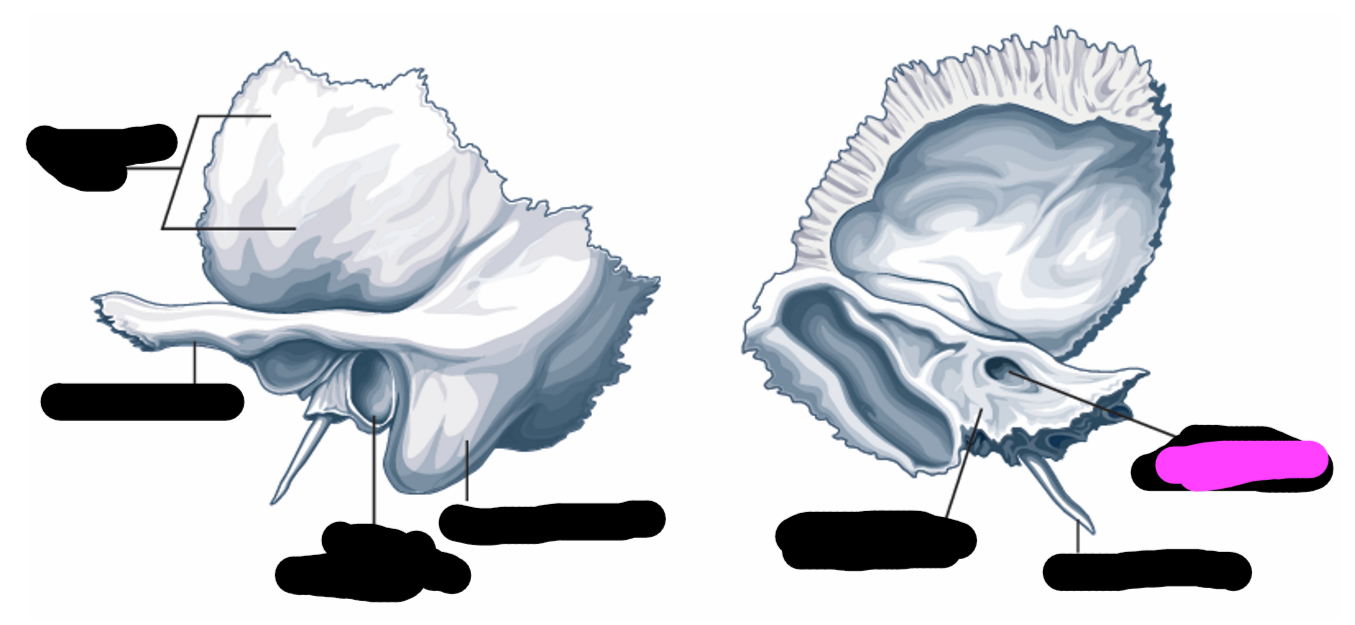
internal auditory meatus
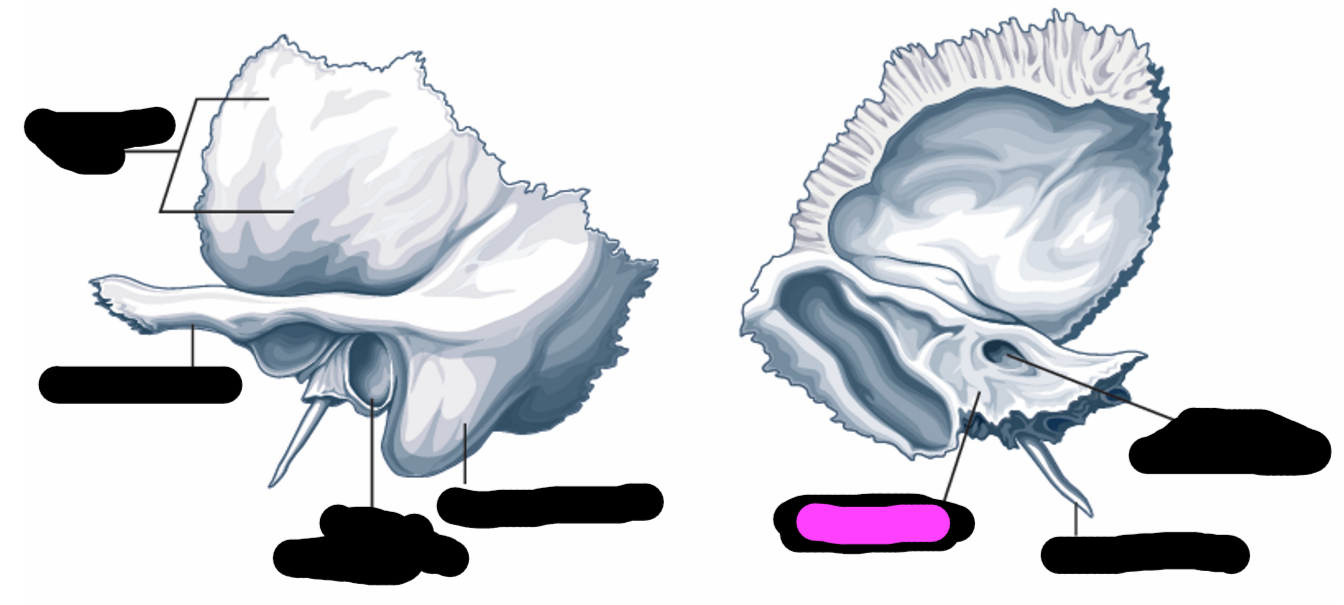
petrous portion
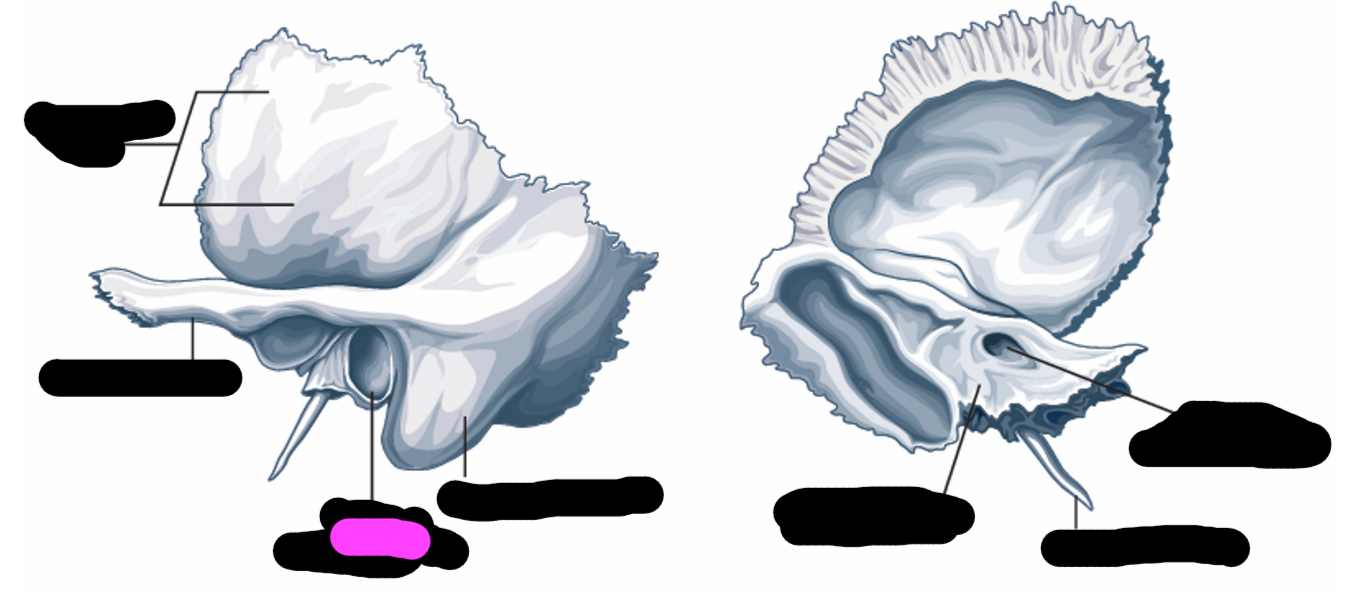
external auditory meatus
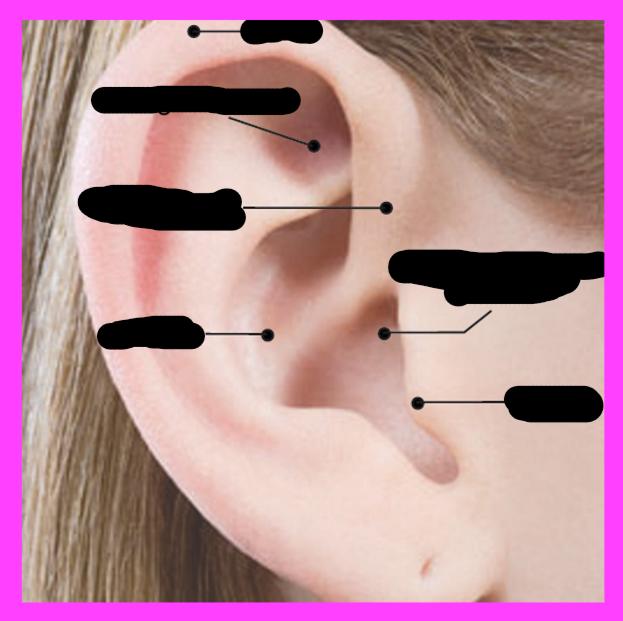
pinna/auricle
concha
external auditory meatus
tympanic membrane
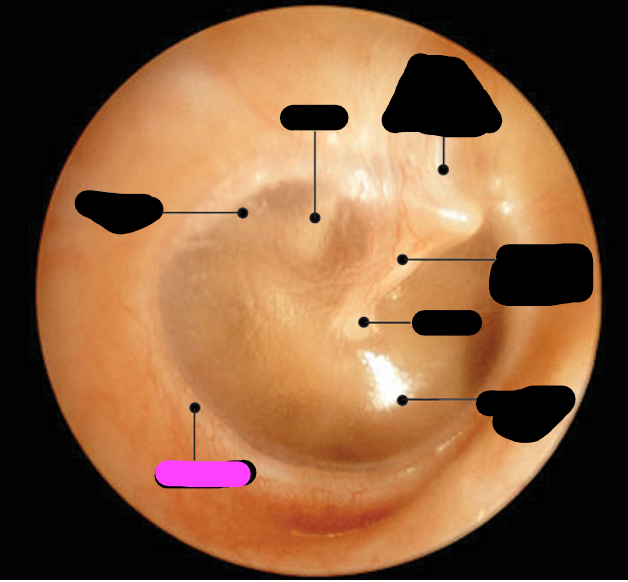
annulus
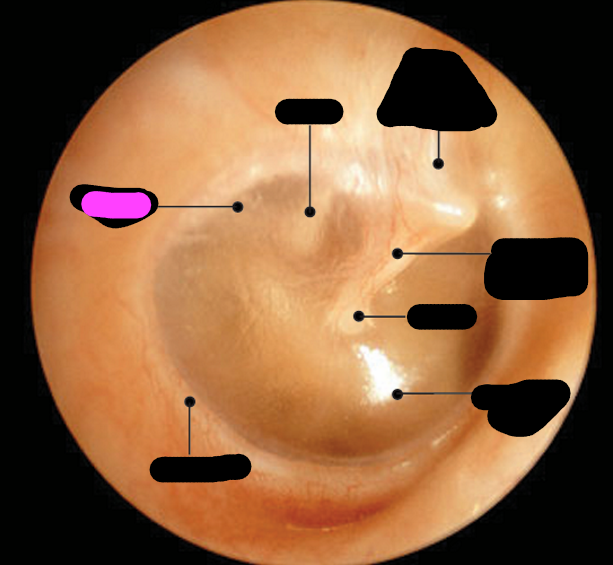
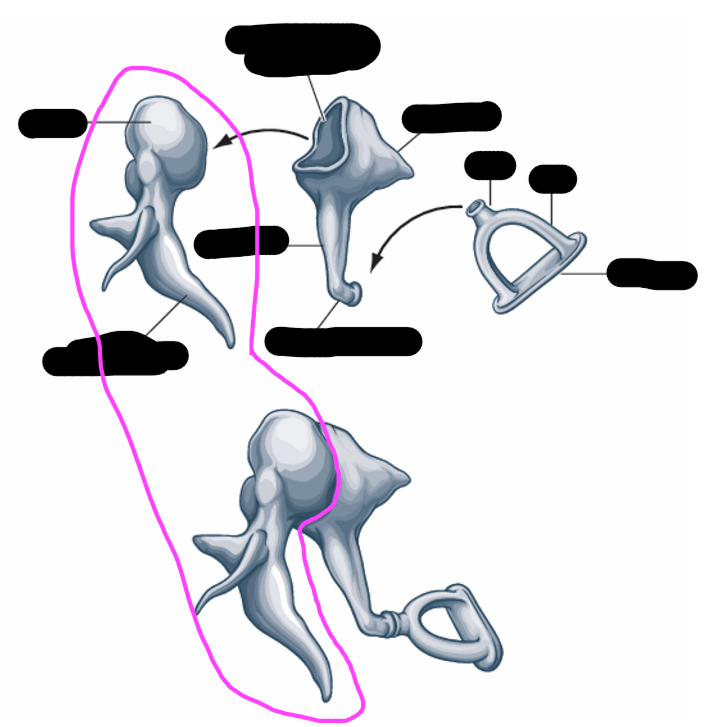
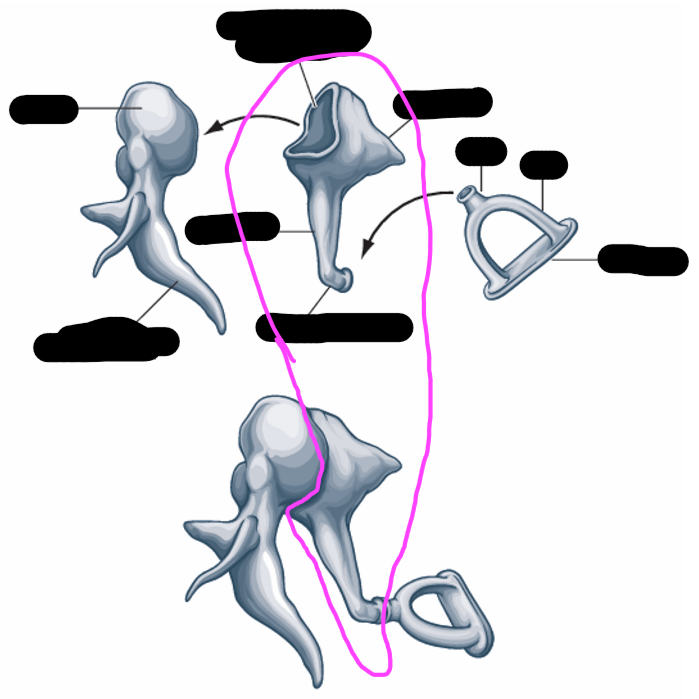
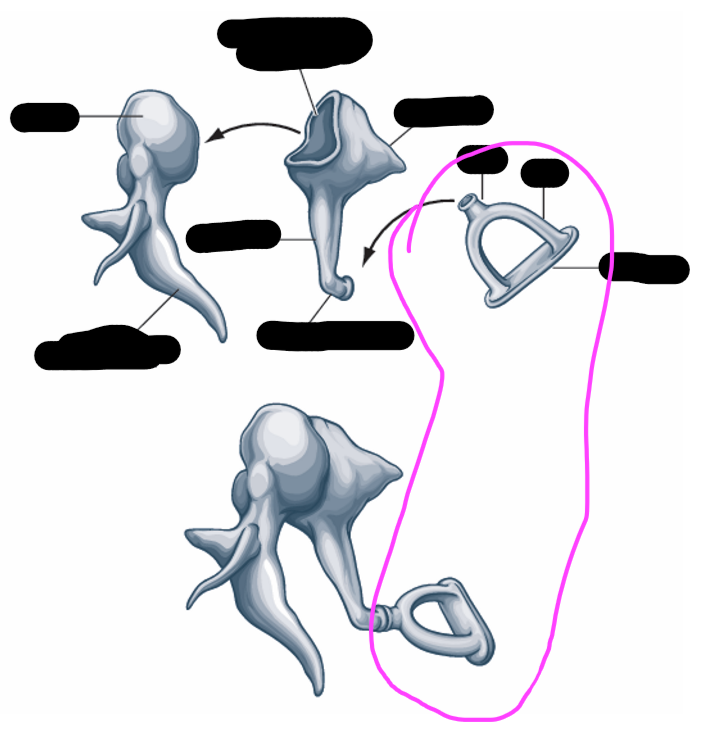
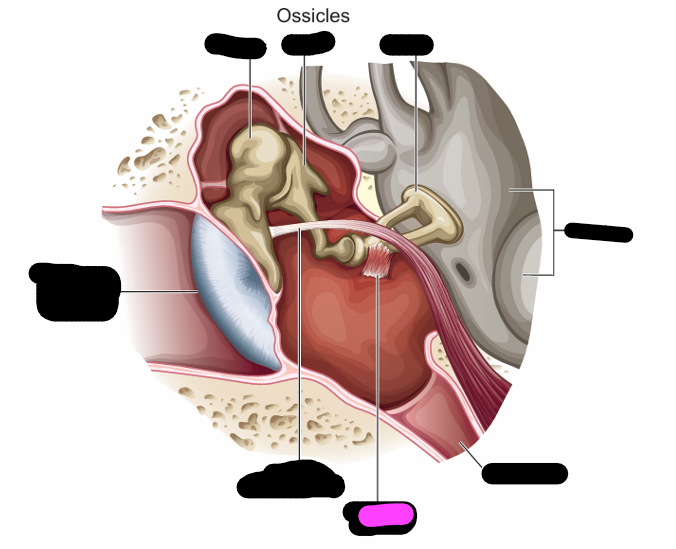
stapes
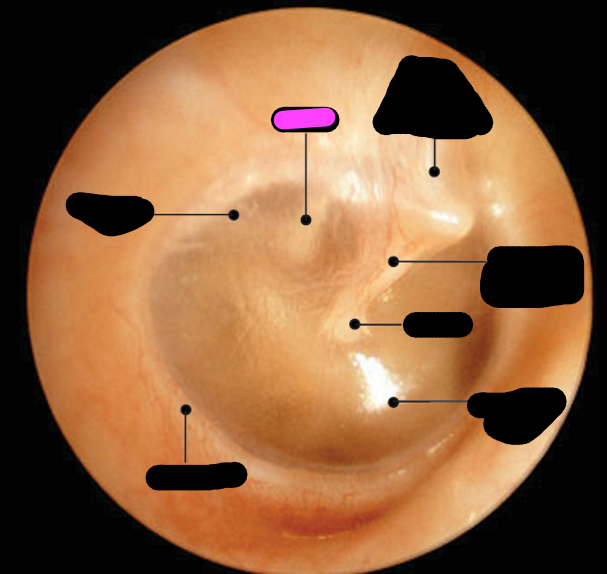
incus
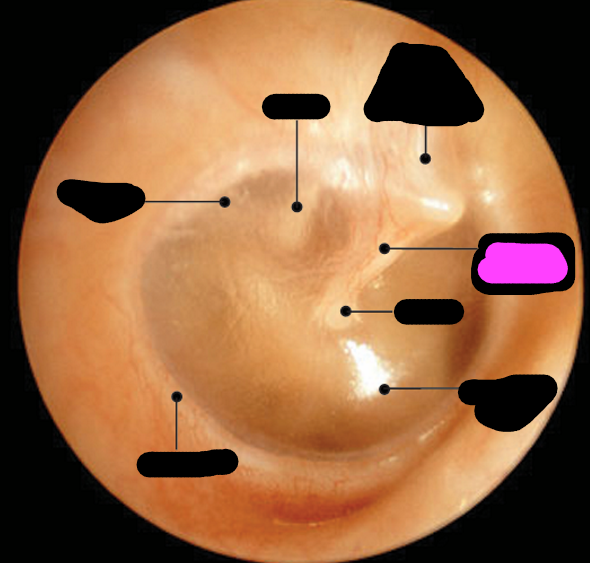
malleus
malleus
incus
stapes
what bones share a border with the temporal bone
sphenoid bone, parietal bone, occipital bone
structures of the middle ear and inner ear are contained in the _____
temporal bone
External auditory meatus (temporal bone)
bony part of the ear canal
Internal auditory meatus
opening for the auditory nerve to pass through
Petrous portion
contains the inner ear structures
Selected features of the outer ear
-pinna/auricle
-concha
-external auditory meatus
Pinna/auricle function
sound-gathering
concha fuction
collects sound and directs to the external auditory meatus
External auditory meatus (ear canal) contents
pathway and tympanic membrane
What does the external auditory meatus (er canal) contain
-cerumen glands (secrete cerumen to lubricate and trap debris)
-contains cilia to clear cerumen
What does the external auditory meatus do in relation to resonating sounds
it maximally resonates sounds that are around 3300 Hz (determined by length of tube)
sound in the external auditory meatus vs entrance of ear canal
sounds in the EAM range will be 2-4x greater than level at enterance
What is the tympanic membrane
-boundary btwn outer and middle ear
-fibrous membrane attached to bony wall of canal by the annulus
annulus
ring shaped cartilage
tympanic membrane shape
cone shaped (conical)
tympanic membrane look
somewhat translucent; can see parts of the ossicles through the membrane
Role of TM
along with the ossicles of the middle ears, the TM is important for transforming energy from sound waves (vibrating air) eventually into fluid waves in the cochlea
vibration/movement of TM
-vibrates when sound waves strike it
-vibration is transmitted to ossicles
-the stapes pushes into the fluid of the cochlea
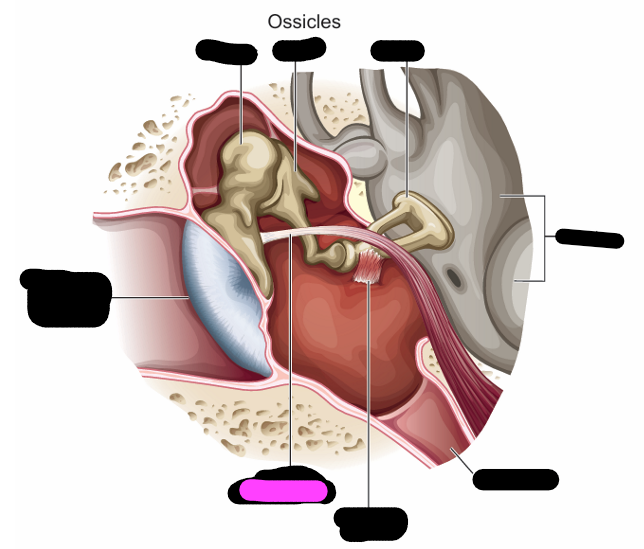
what are the smallest bones in the body
ossicles
ossicles location
extends from medial surface of TM to oval window
malleus shape
hammer
malleus attachment
handle/manubrium attaches to TM
incus shape
anvil- long and short limbs
stapes shape
stirrup
stapes attachment
-footplate fits into the oval window of the cochlea
-held in the window by the annular ligament
ossicles transmission
transmit vibrations from the TM to inner ear
tensor tympani
stapedius
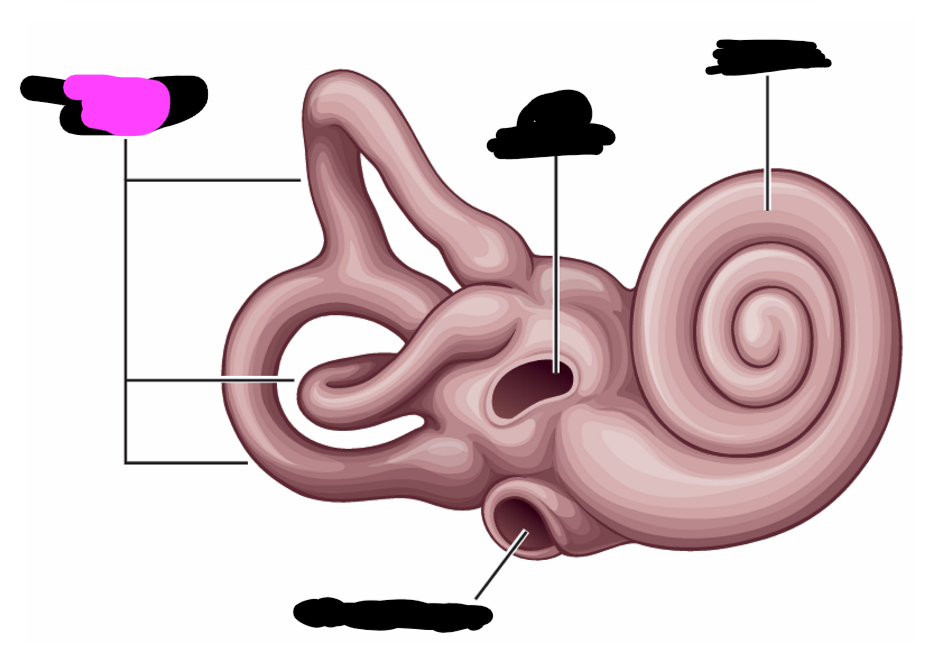
semi-circular canals
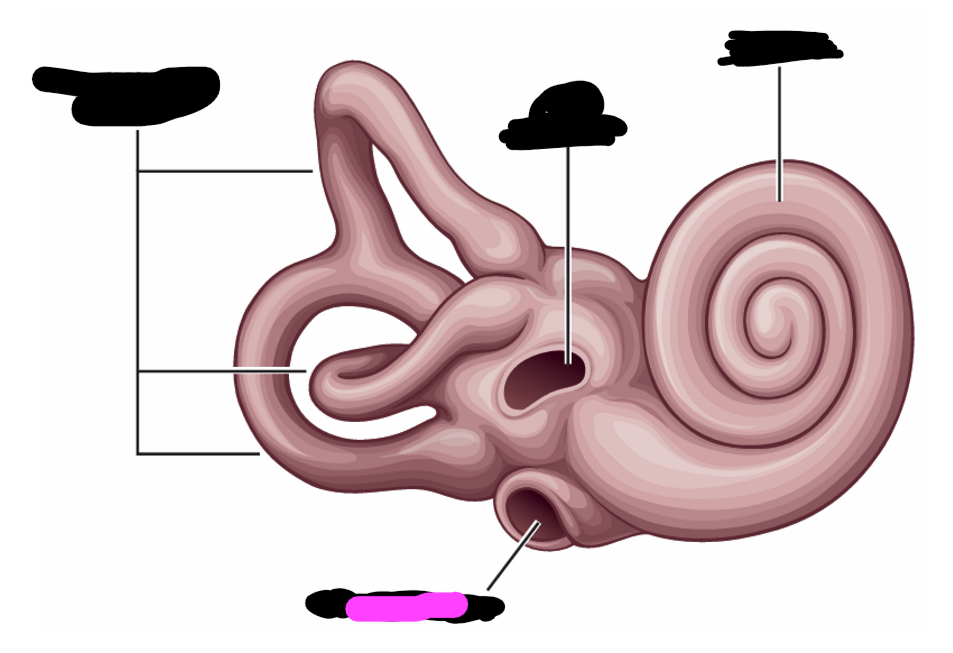
round window
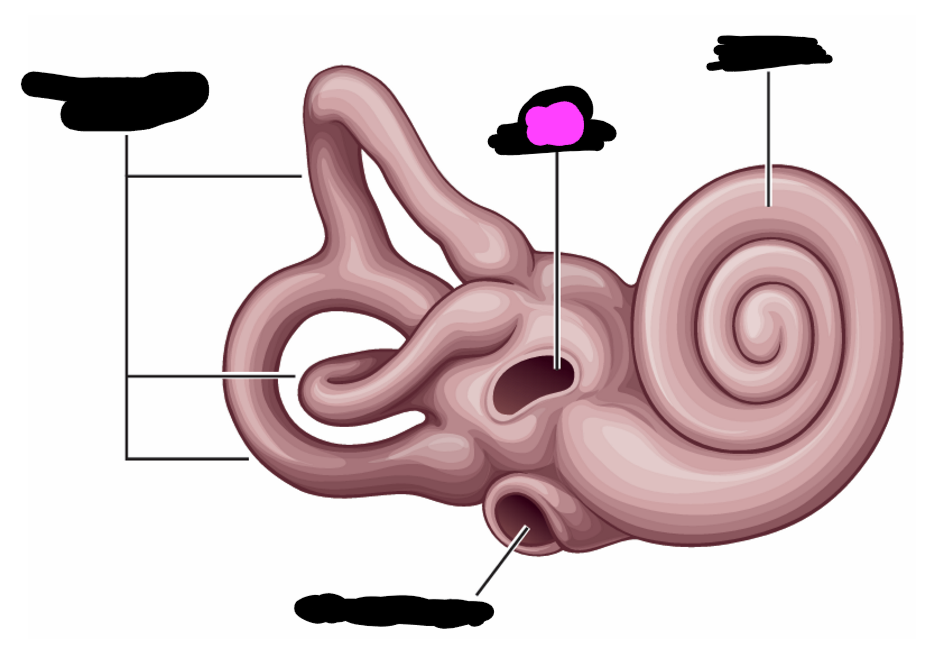
oval window
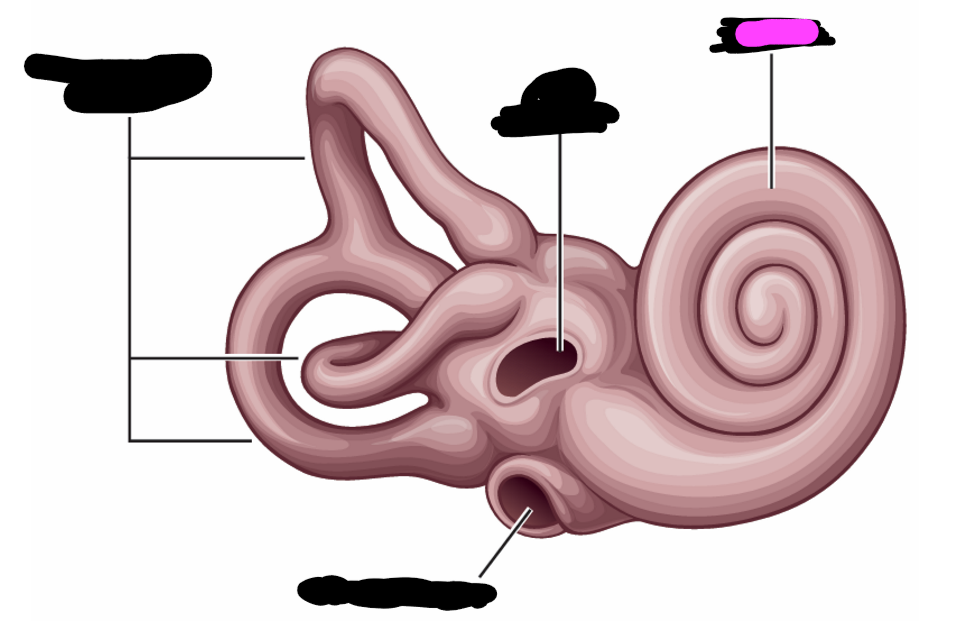
cochlea
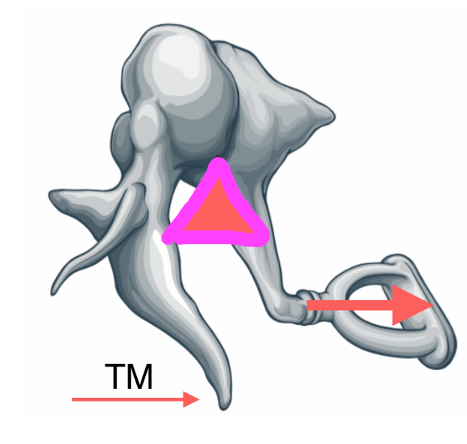
What does this triangle represent
fulcrum
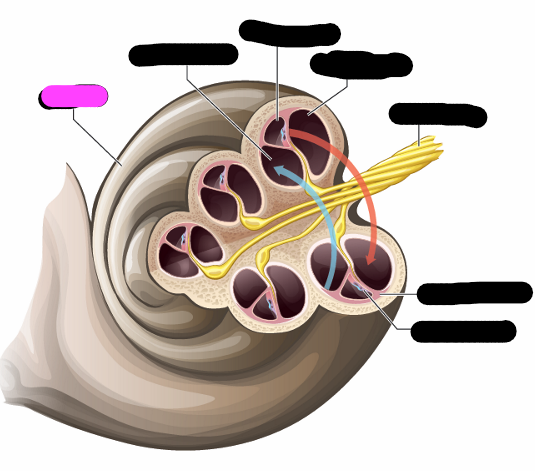
cochlea
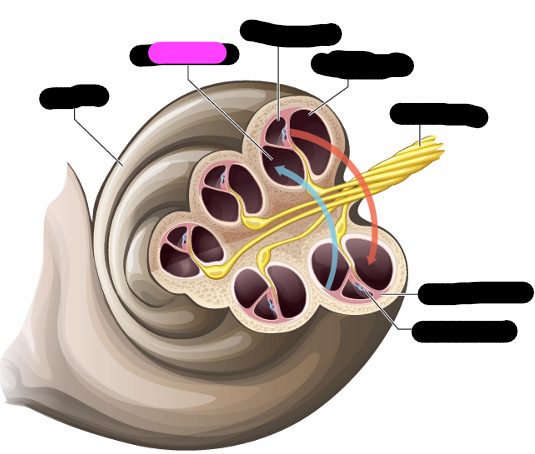
vestibular canal
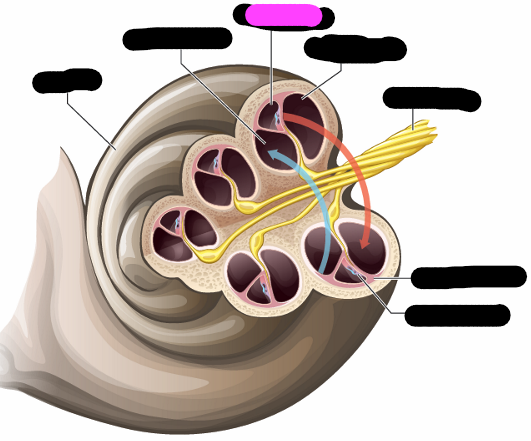
cochlea duct
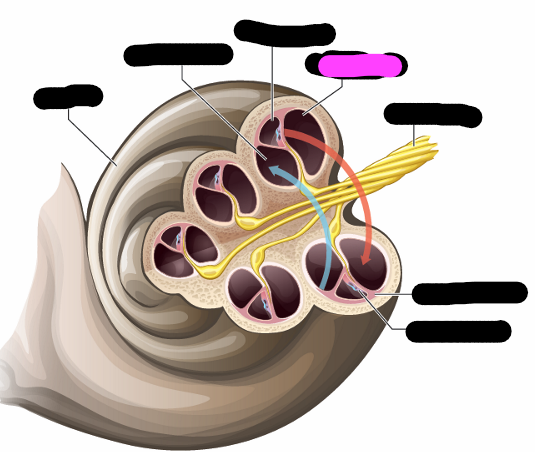
tympanic canal
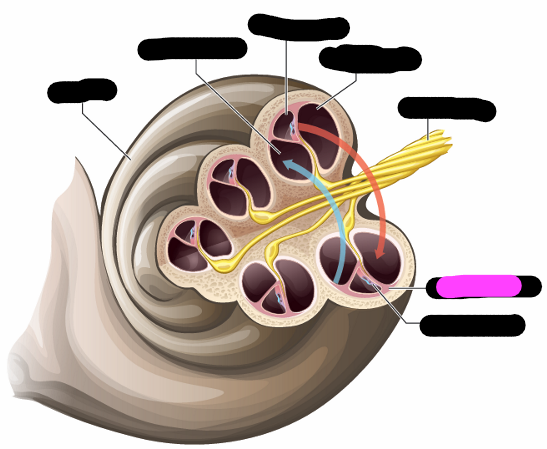
basilar membrane
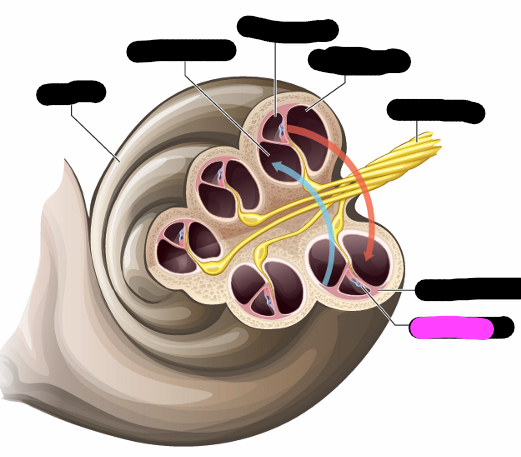
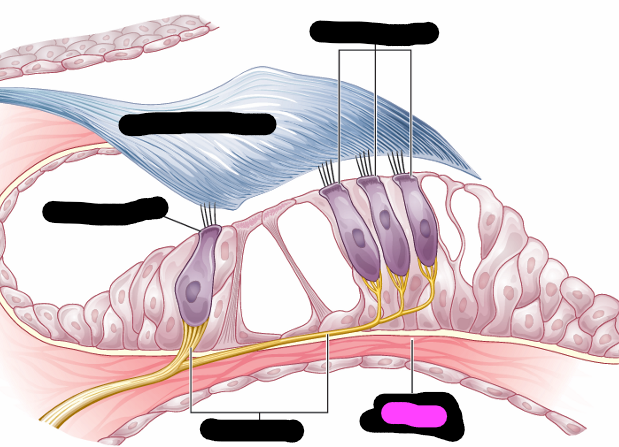
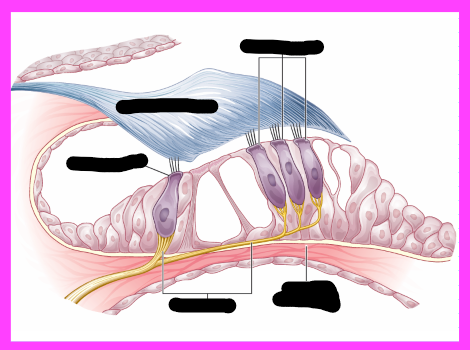
organ of corti
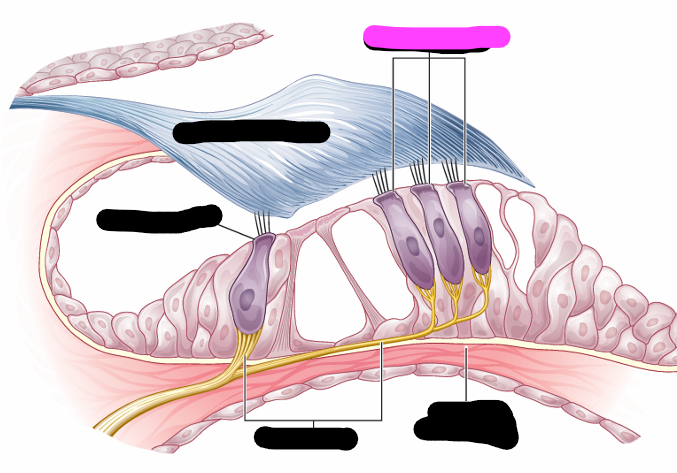
outer hair cells
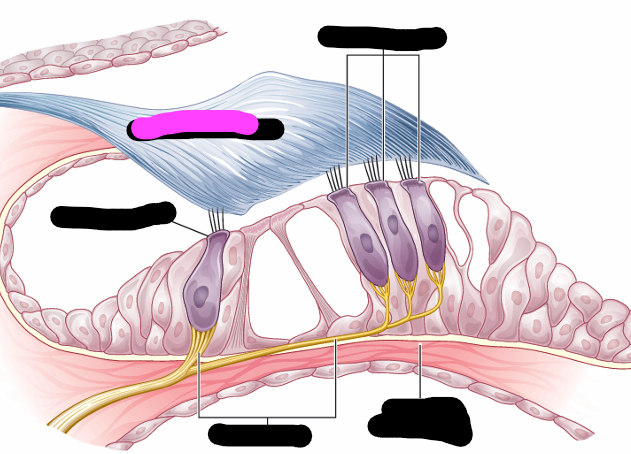
tectorial membrane
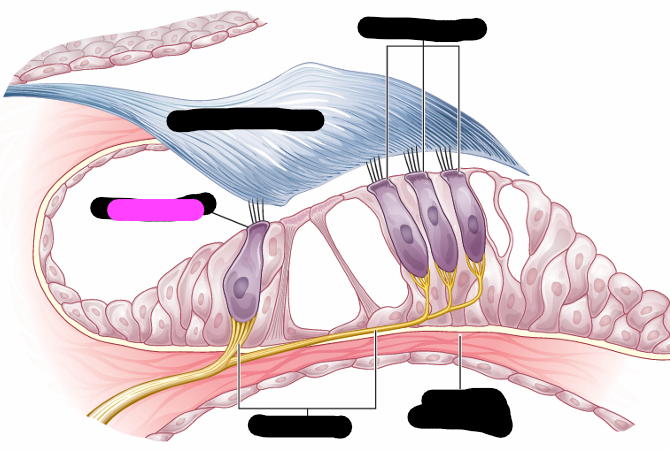
inner hair cell
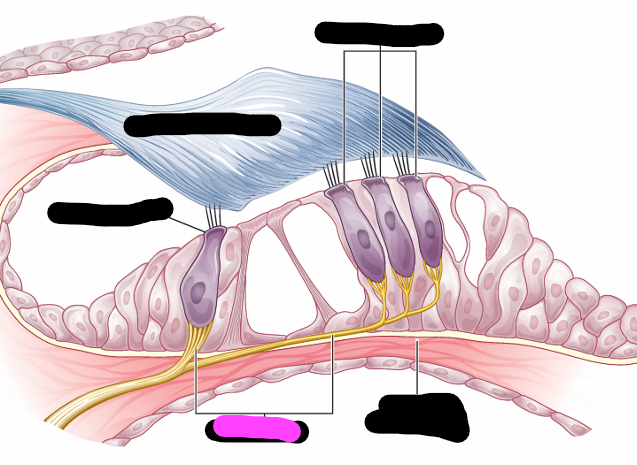
nerve fiber
basilar membrane
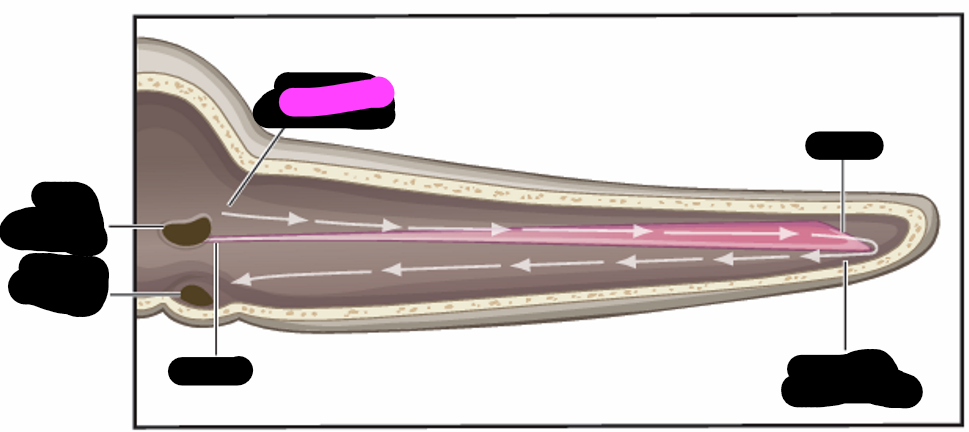
highest frequencies
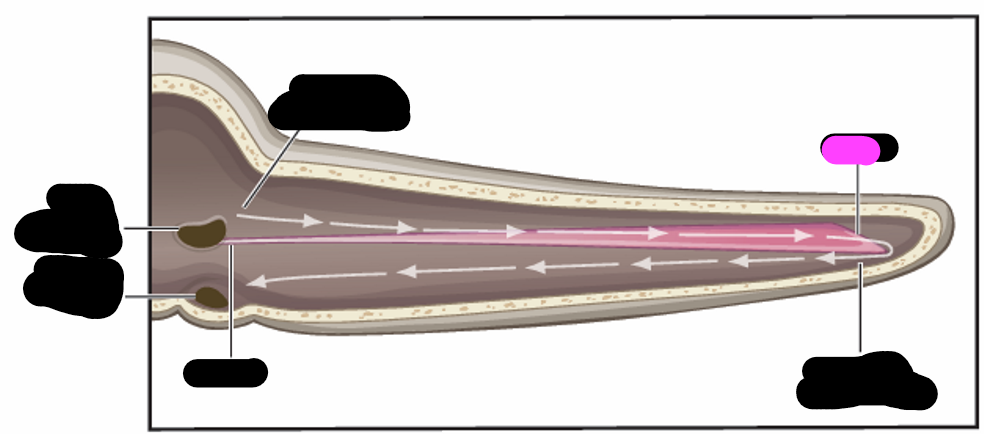
apex
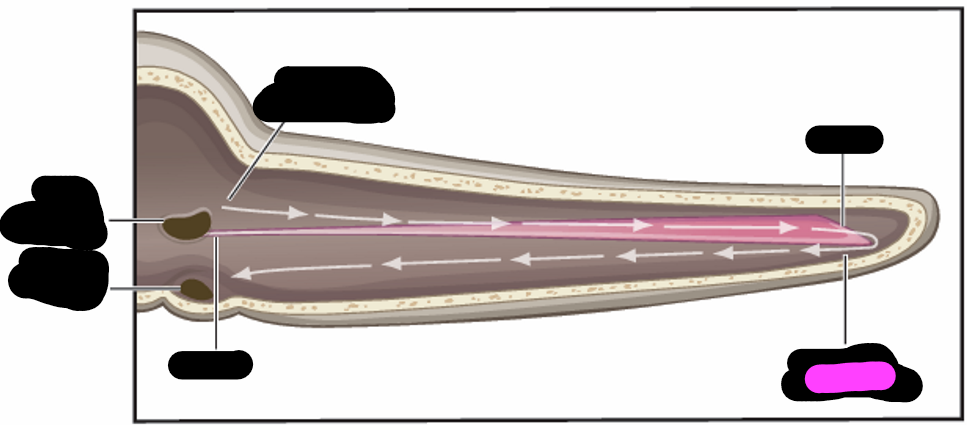
lowest frequencies
base
organ of Corti
Muscles of the middle ear
-tensor tympani
-stapedius
tensor tympany origin/ insertion
originates in bony canal/temporal tube in the from wall of the middle ear cavity and inserts into the handle of the malleus
tensor tympani contraction
pulls the handle of the malleus inward to stiffen the TM and ossicular chain
stapedius origin/ insertion
originates in a hole in the back wall of the cavity and inserts into the stapes
stapedius contraction
contraction draws stapes away from oval window and stiffens the ossicular chain
what muscles protect hearing
-tensor tympani
-stapedius
Eustachian tube location
runs from middle ear to the nasopharynx
eustachian tube purpose
provides means of pressure equalization
how does the eustachian tube equalize pressure
-swallow/ yawn contracts tensor palatini which opens the lip of the tube
-atmospheric pressure flows into middle ear space
-TM is free to vibrate due to equal air pressure on either side of it
impedance mismatch
-sound waves are vibrating air
-inner ear must be stimulated, but its filled with fluid
-sound transmission would be impeded (impedance mismatch)
TM and ossicles amplify and transform sound into
mechanical energy
Amplification can be accomplished in several ways
-TM is 20x larger than footplate of stapes and the energy is concentrated onto the small footplate
-leverage and fulcrum arrangement of ossicles
-resonating characteristic of ear canal and ossicular chain combine to amplify sounds between 1000-3500 Hz
Transmission of sound
-impedance mismatch
-TM and ossicles amplify and transform sound
-amplification is accomplished in multiple ways
-all of the above helps overcome the impedance mismatch
what are the structures of the inner ear contained in
bony labyrinth
oval window
a hole in the bony labyrinth in which the footplate of the stapes is embedded
round window
covered with a membrane that displaces to accommodate fluid waves
bony labyrinth contains 3 _____
semicircular canals at various angles
semicircular canals/ inner ear info
-filled with perilymph; they also contain an inner duct system (membranous labyrinth) filled with endolymph
-leverage from the fulcrum arrangement of ossicles
-head movements displace the endolymph, which bends hair cells (encodes movement)
vestibule
contains the utricle and saccule which contain hair cells that sense movement of head
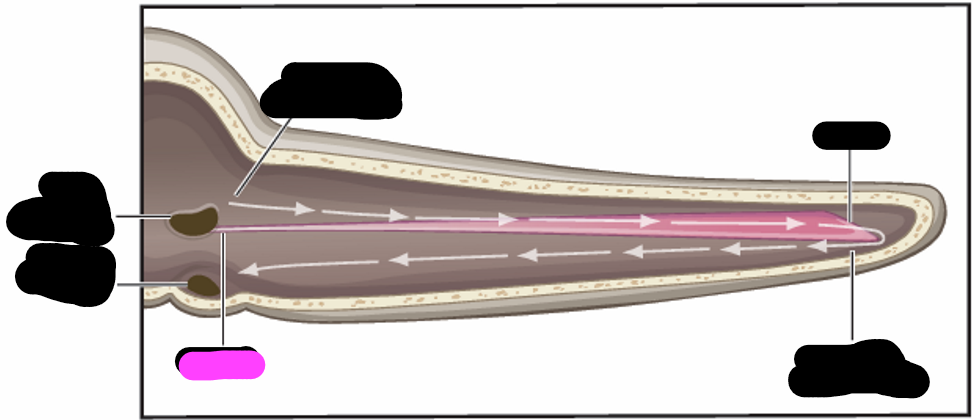
the cochlea is ___
a coiled structure with chambers
Scala vestibuli/ vestibular canal contains ____
perilymph
Scala media (cochlea duct) contains____
endolymph
Scala tympani/ tympanic canal contains___
perilymph
the chambers of the cochlea are separated by _____
Reissner’s membrane and basilar membrane (organ of corti is situated on the basilar membrane)
basilar membrane location
stretches between bony wall and bony core
where is the organ of corti
rests on basilar membrane
what does the organ of Corti do
converts fluid waves into bioelectric energy
organ of corti hair cells info
-one row of inner hair cells
-three rows of outer hair cells
-deformed by tectorial membrane and fluid waves traveling though scala media
-convert hydraulic motion into electrical impulses that are sent to brain via auditory pathway
basilar membrane hair cells location
the entire length of the basilar membrane
hair cells in relation to frequency
where a hair cell is located along the membrane determines its frequency sensitivity
base end of BM
-narrow and stiff
-responsive to highest frequencies
-aka vestibule end
apex end BM
-wide and lax
-responsive to lowest frequencies
middle portion of BM
-intermediate width and stiffness
-responsive to mid frequencies
chochlear fluid movement
fluid in cochlea moves in phase with the footplate of stapes
vibration is transmitted along BM as a ____
traveling wave
shape of wave development over time
-build to a crest where most of its energy is spent
-quickly dissipate after crest