PoR 4B: Logical Positivism and A.J Ayer's Verificationism
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is Cognitive Language?
statements that are truth-apt, and thus attempt to describe the world, even if they are false.
What is an example of Cognitive Language?
The grass is green

What is non-cognitive language?
Language that is not empirically verifiable or falsifiable because it does not attempt to make a truth-apt statement about the condition of the world.
What is an example of non-cognitive language?
"Ouch"

What was the name given to the group of philosophers who are now believed to have been the principle proponents of Logical Positivism?
The Vienna Circle
Which member of the Vienna Circle was particularly instrumental in the development of LP?
Rudolf Carnap
According to the Vienna Circle, the meaningfulness of a statement was grounded in what?
Empirical Observation and Experience
As a result of the original Vienna Circle's criterion of meaning, what statements were considered to meaningless?
Religious, metaphysical, aesthetic and ethical statements
Logical Positivism is above all, what? (For the Vienna Circle)
Anti-Metaphysical
According to the Logical Positivists, held that the world could only be understood by means of what?
Empirical Sciences
In its positive form, how did the Logical Positivists believe that the meaning of a statement could be demonstrated?
Through verification of a statement's truth or falsity.
In its negative form, what did the Criterion of Meaning mean for Religious and Metaphysical statements?
No statement can be seen as meaningful unless there is some form of verification attached to it.
Why are metaphysical statements considered meaningless by the Logical Positivists?
Because there are no methods to prove that such statements are verifiable in truth or falsity.
What is an example of a Religious Statement that the Logical Positivists believed was meaningless?
"God Exists"
Metaphysical statements use what type of language?
Non-cognitive
Using the Verification Principle, the Vienna Circle believed that they had proved a great deal of language to essentially be meaningless. However, what was an area of philosophy that was still perceived to be meaningful, even in the absence of empirical science?
Maths and Logic
Why are the disciplines of Mathematics and Logic still considered to be meaningful, even in the absence of empirical science?
Because their verification lies in a priori reasoning alone.
How did Wittgenstein define the verifiability of logical and mathematic statements?
Because the statement is consistent with the meanings underpinned by the signs or symbols involved.
What is the name of the English Philosopher who developed Logical Positivism into Verificationism?
A.J Ayer
Verification attempts to discern what type of meaningful statements?
COGNITIVELY MEANINGUL.
What does Verificationism continue to hold about non-cognitive statements?
That they may be useful and important in describing emotions and influencing feelings, but make no relevant influence on truth value of describing the world.
Ayer proposed that a statement can be considered meaningful if it is able to be verified in two ways. What are the two methods?
Analytical Verification and Empirical Verification
What does Empirical Verification involve?
Repeatedly using sense data and experimentation to prove a statement through observation.
What does Analytical Verification involve?
Considering the meanings of the signs and symbols used to distinguish if a statement is verifiable by means a priori.
What is an example of an Empirically Verifiable statement?
"Not all ladybirds have 5 spots"

What is an example of an Analytically Verifiable statement?
x=y or x≠y
An analytically verifiable statement that is correct in all interpretations is called what?
Tautology
Ayer drew a distinction between two methods of verifying statements. What was the first?
Practical Verification
What does Practical Verification involve?
Continued and prolonged empirical investigation to find out whether a statement provides a cognitively meaningful description of the world.
What is the second form of verification described by Ayer?
Verifiability in Principle
What is meant by "Verifiability in Principle"?
Things that are not practically verifiable currently, but may be in the future. For example, the statement that there is life on other planets.
According to Ayer, Verification can be both strong and weak. What makes for a strong verification?
Repeatable and conclusive evidence
What makes for a weak verification, according to Ayer?
Unclear, or inconclusive evidence that is not necessarily repeatable.
Why do Historical Events present an issue for Ayer's theory?
Because they can neither be proven empirically or analytically. One cannot time travel, and it is not in the essential nature of a specific timeframe to say that one event must have occurred within that window. For example, it is not factually meaningful for the Battle of Hastings to have occurred in 1066, because it is not in the definition of the year 1066 for the Battle to have occurred in it.
How may Ayer have argued that Historical Events can be verified?
- The great deal of evidence we have to suggest that a certain event occurred in a certain manner means that it is verifiable in principle.
- It just happens that historical events are only WEAKLY verifiable, not completely as we may expect.
How do Practical and Scientific Laws cause an issue for Ayer's Theory?
- One may take a law that "All water boils at 100 degrees", but it is impossible to test every water molecule to see if this is factually meaningful.
- Thus, either practical laws are only weakly verifiable or Ayer is excluding a great deal of human knowledge from his theory.
How does Ayer see general scientific rules and practical laws in regards to his own theory?
They are verifiable in principle.
What was the name of the Theologian who argued against Ayer's assertion that God-Talk was meaningless?
John Hick
What parable did Hick use to illustrate his retort to Verificationism?
The Celestial City
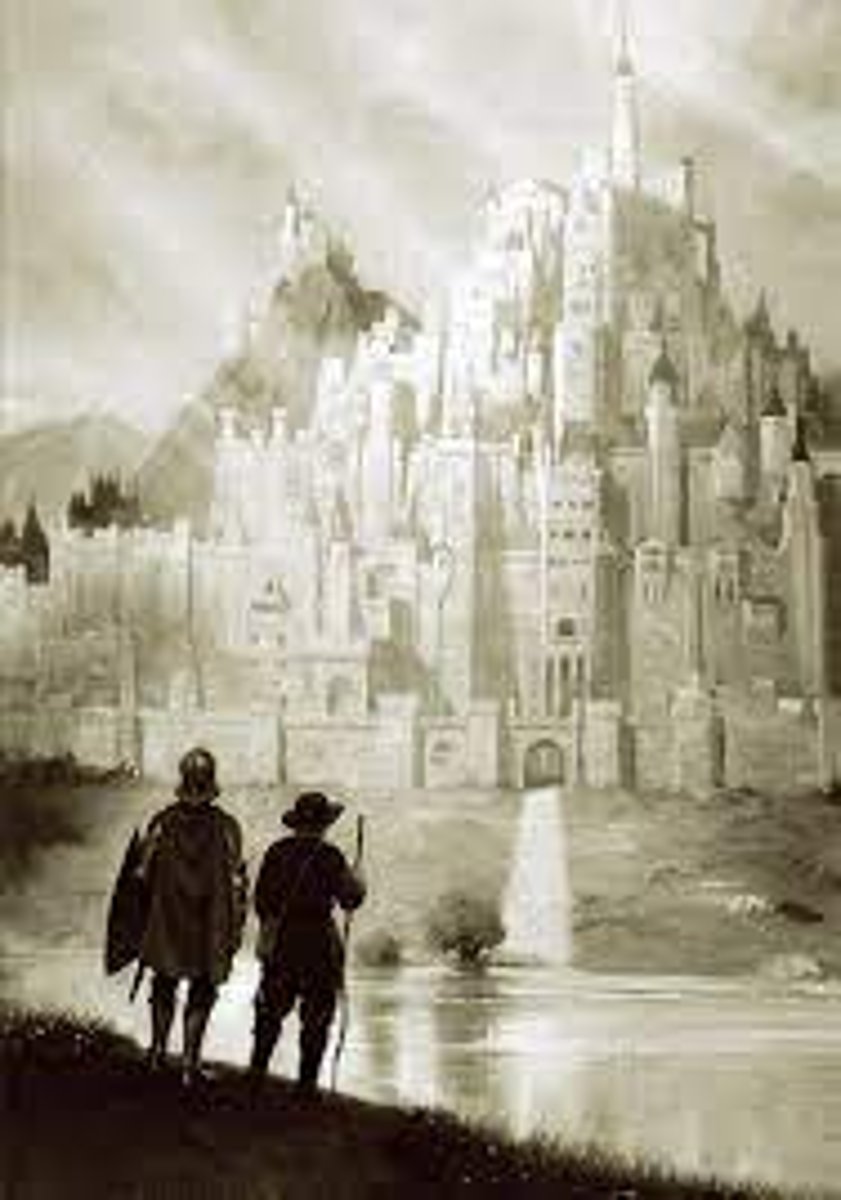

How is the Celestial City supposed to illustrate the verifiability of religious statements such as "there is a god"?
- Hick accepts the premise of verifiability in principle, but edits it to conform with the theist assertion.
- The two travellers represent a believer and a non-believer travelling towards the city, only one is factually meaningful in their statement that it exists; whilst the other is wrong.
- Who is right and who is wrong is only revealed when they reach the destination.
- Thus, Hick draws an analogy between the theist and atheist going into the afterlife. Religious statements are verifiable, but only after we die and revelation is given.
What term does Hick use to describe the verification of religious statements?
Eschatological Verification
By its own logic, the Verification Principle is what? (Criticism)
Meaningless
Which quote from Hick describes the factual meaningfulness of religious statements
"the theistic assertion is indeed true of false - a genuinely factual assertion"
Why can the Principle of Verification itself be seen as meaningless?
Because the framework of the theory cannot be empirically verified, nor is it a tautology.
Why have some scholars criticised Ayer's selective approach to evidence worthy of use for verification?
There appears to be an inconsistency with Ayer considers adequate evidence. General scientific rules are considered verifiable in principle, but countless religious records not.