Amino acids and Primary Structure
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Amino acids and Primary Structure
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is a di/polypeptide
When two/multiple amino acids join to form a chain
How does a peptide bond form
The carboxyl group of on acid reacts with the amine group of another in a condensation reaction forming a covalent bond
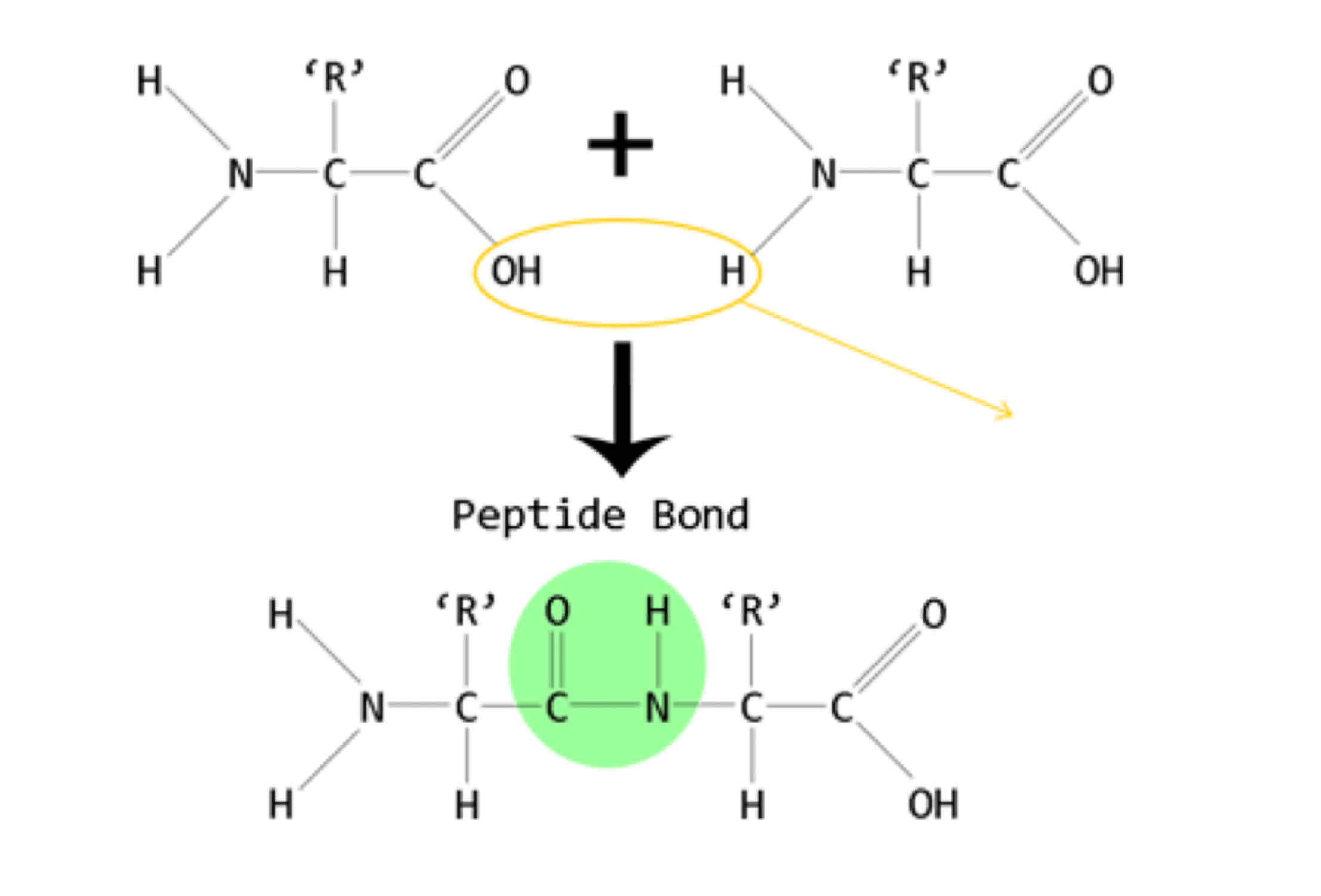
How can a peptide bond be broken
Hydrolysis reaction (add water)
How can a hydrolysis reaction be catalysed
Protease enzyme
Define the primary structure of a protein
The linear sequence of the amino acid within a polypeptide chain (only peptide bonds involved in this level)
How is the sequences of amino acids coded
By a gene, each three bases codes for one amino acid
Give the structure of a protein
Macromolecules
Polymers made of multiple amino acids linked together
Containing hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, (sulfur)
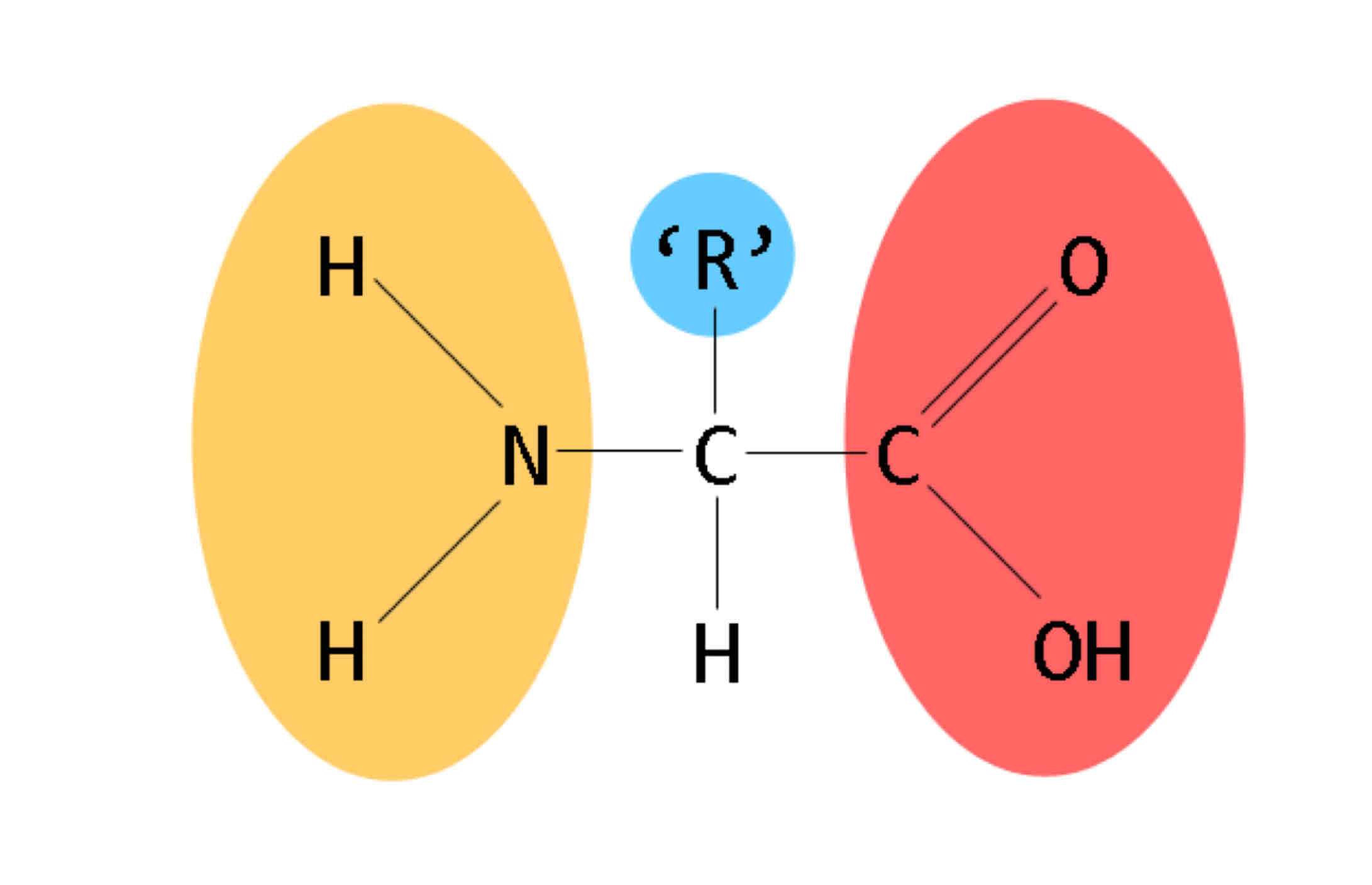
Give the structure of an amino acid
Central carbon
Hydrogen atom
Carboxyl group
Amine group
Residual group
Draw a general amino acid
Which group is responsible for variation in amino acids
R groups
What is the R group for Glycine
-H
What is the R group for cysteine
- CH3-SH