LSU GEOL 1003 Luther Exam 2 Spring 2025
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Hadean Eon
- Hades
- magma ocean boiling at the surface
- oldest time period
Events that shape the Hadean
1. Differentiation of Earth's interior
2. Formation of the crust
3. Differentiation changes composition of crust
Accretion
- the process of adding material to a tectonic plate or landmass
- heavy (dense) sinks and lighter rises
Differentiation
- materials separate into distinct layers or compositions
- occurs over tens of millions of years
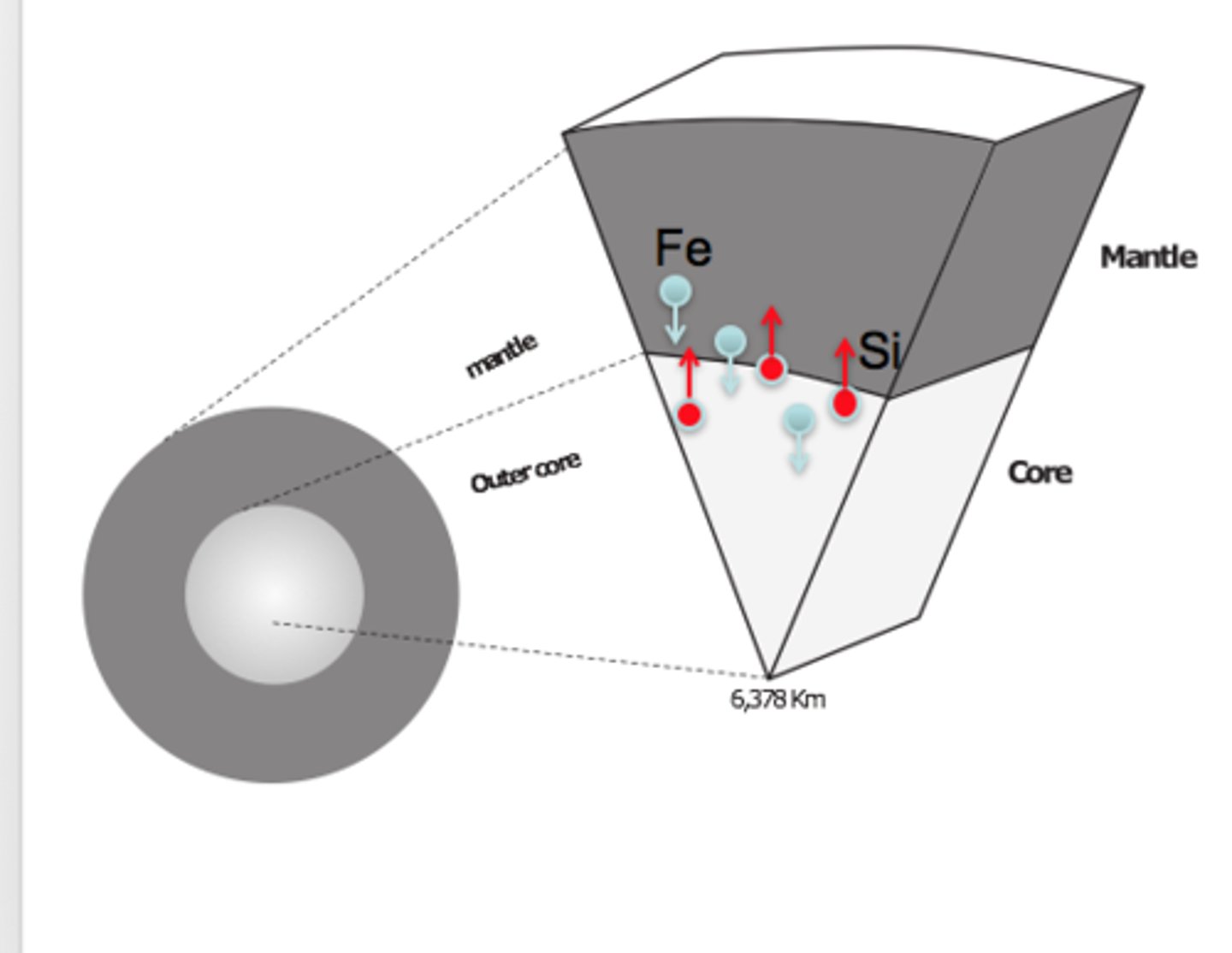
Earth's layers- seismic wave analyses
- increase in density > increase in wave velocity
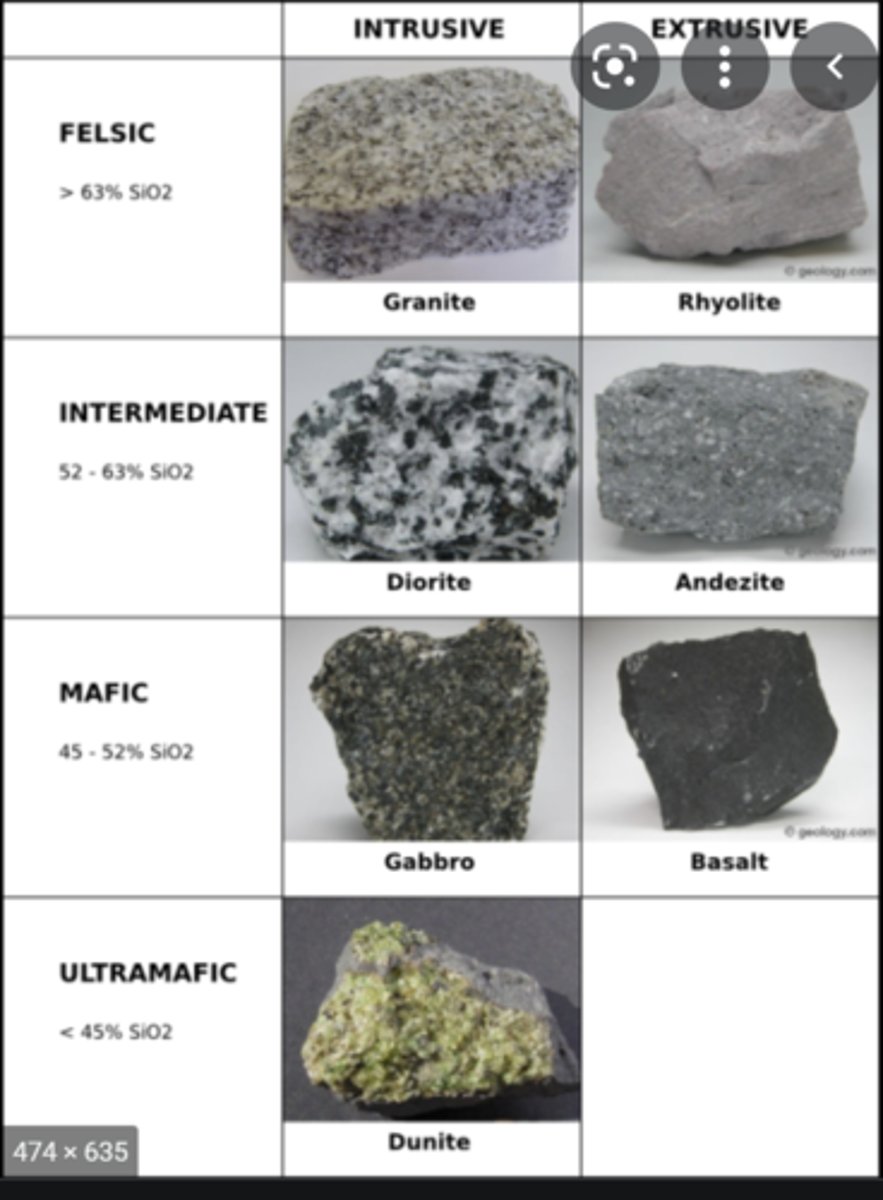
Earliest crust
- earliest crust forms
- made of komatiite- ultramafic
- very rare and fine grained
- peridotite: ultramafic
- oceanic crust- basalt
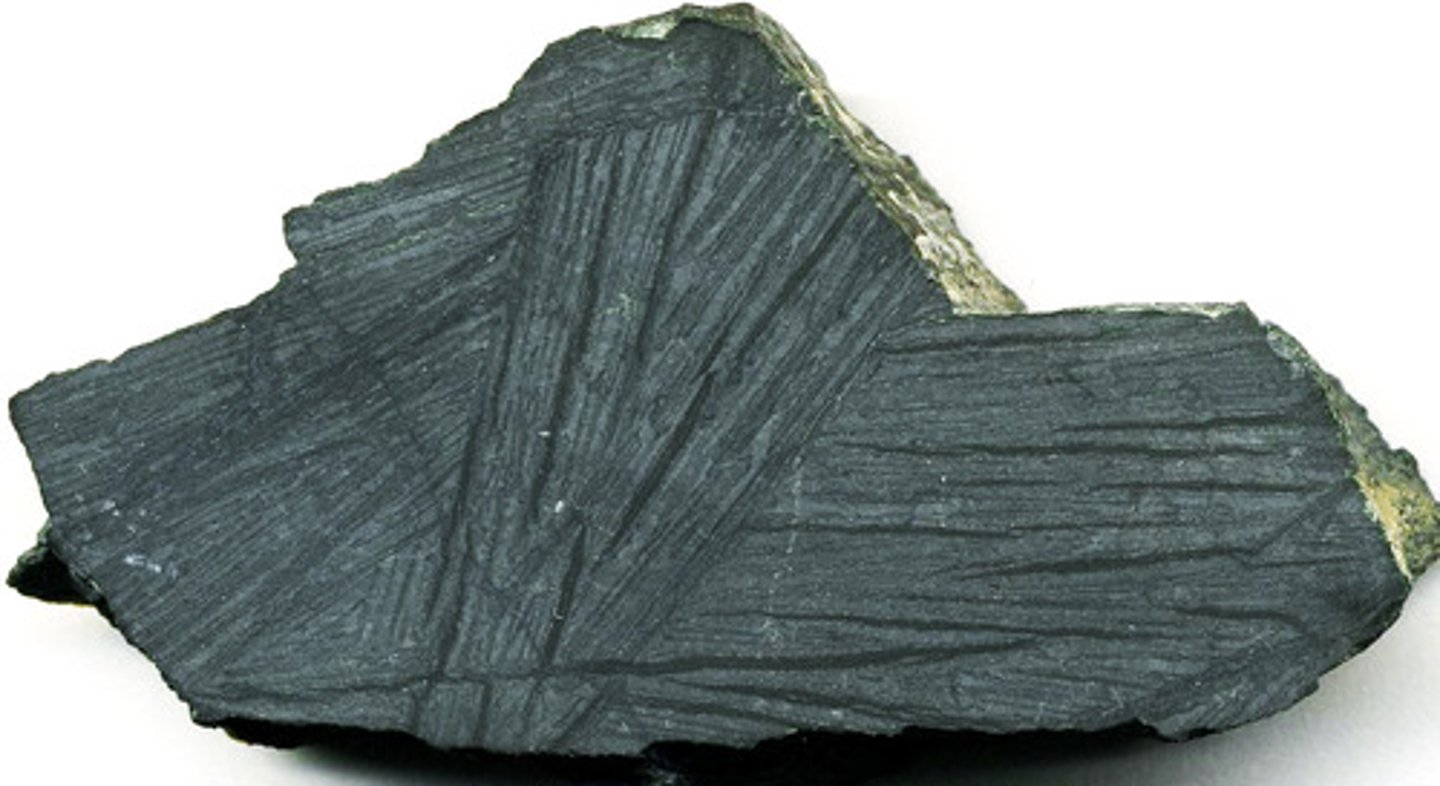

Earliest composition of Earth
- felsic: continental crust
- mafic: current oceanic crust

Earth's oldest rocks
1. Jack Hill's zircon: oldest mineral
2. Acasta Gneiss Complex: oldest presumed rock- 4 billion years old
3. The Nuvvuagittuq Greenstone Belt
Jack Hill's Zircon
- oldest mineral
- 4.404 Ga
- commonly form in granite
- found in a sedimentary rock
- 150 my > crust differentiates
- oxygen isotopes
- heavy and cool enough for oceans to be present
Acasta Gneiss- Slave Craton
- craton: stable interior of continent > no tectonism for 1 Ga
- shield: exposed craton
- platform: craton covered with sediments
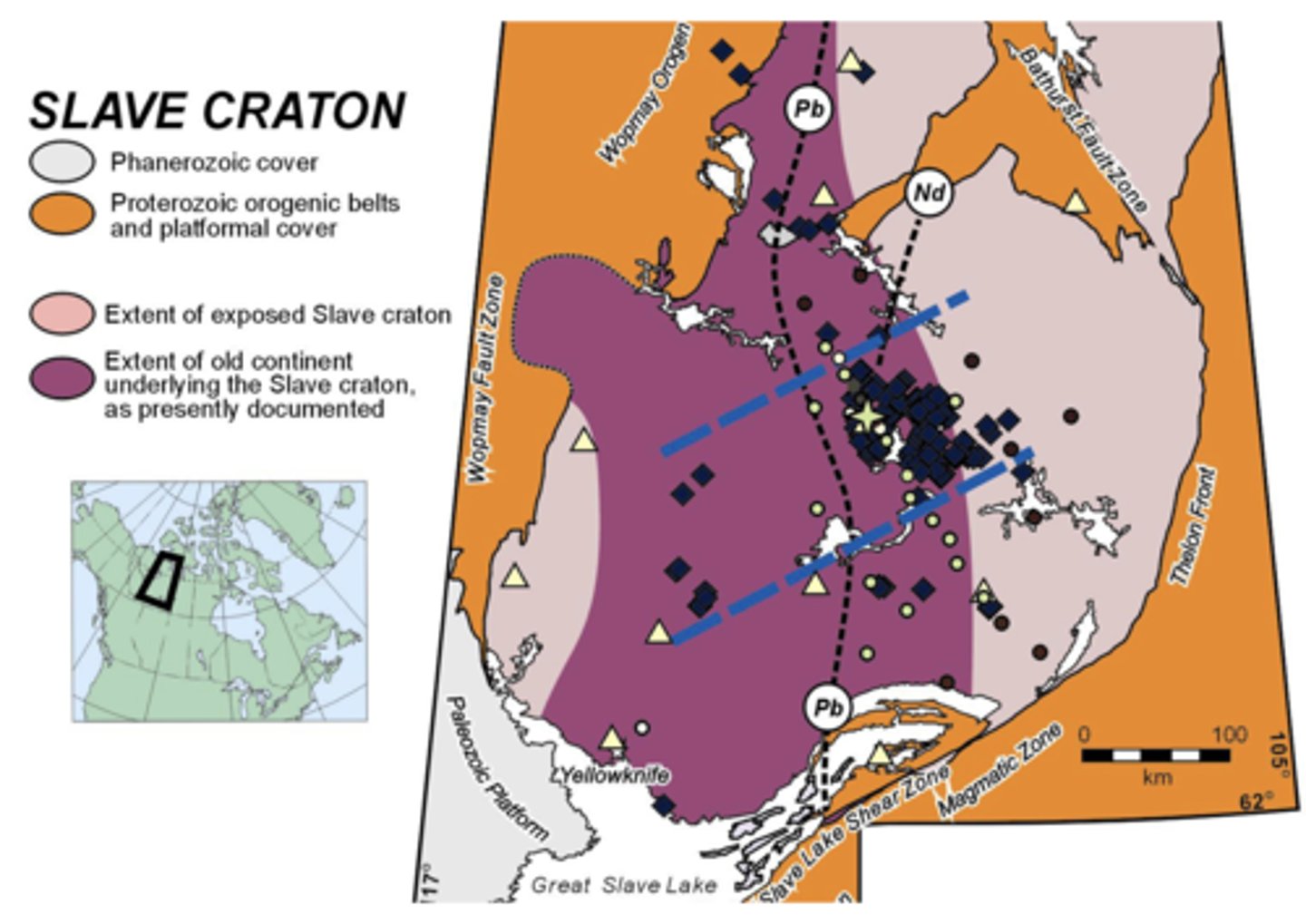
Acasta Gneiss
- oldest rock
- gneiss is an igneous rock
- 3.92-4.02 Ga
- crust must exist for this to intrude
The Nuvvuagittuq Greenstone Belt
- oldest oceanic crust
- mafic and ultramafic volcanic rocks
- erupted in an ancient ocean- presence of lava pillows
- cut by 3.77 Ga rocks- actual age unknown
Earth's oldest fossils?
- also found in NGB
- 2017 traces of life found in seds of the NGB
- microscopic small tubes made of the iron mineral hematite
- same shape and size of those made by bacteria in modern hydrothermal vent environments
- discovered the mineral graohite composed entirely of carbon
- formed by metamorphism of organic material
O2 in the atmosphere
- earth cooled: atmosphere formed mainly from gases spewed from volcanoes
- hydrogen sulfide, methane, and ten to two hundred times as much carbon dioxide as today's atmosphere
- after about half a million years, Earth's surface cooled and solidified enough for water to collect on it
Miller and Urey Experiment (1953)
- demonstrated that organic compounds could be made by simulating conditions on early Earth
- methane, ammonia, water vapor and hydrogen- no oxugen
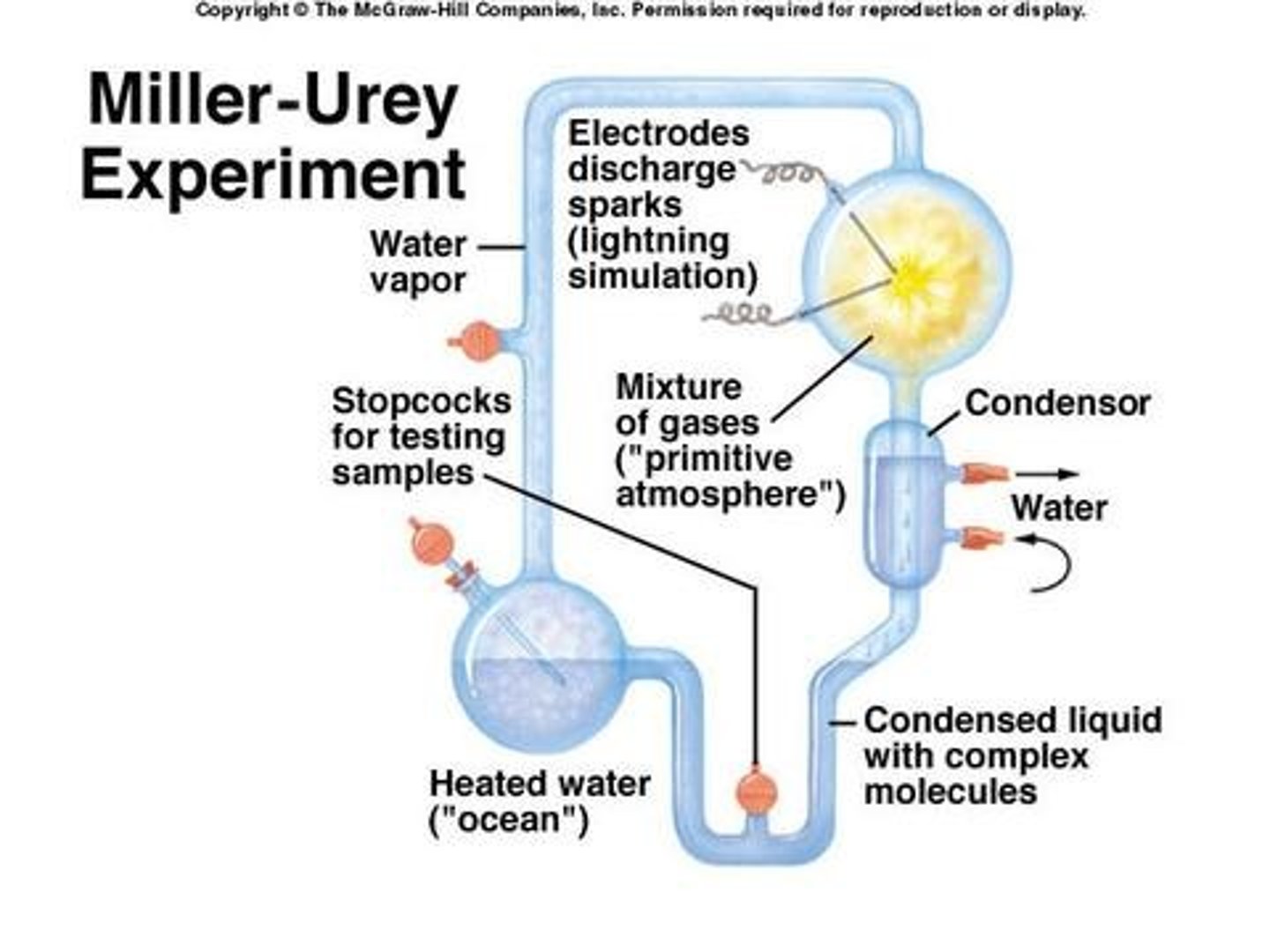
Formation of the oceans
- origin of water still up for debate
- most astronomers believe water came from comets
- salt > free
- salt comes from weathering of rocks
- Earth reached current salinity by the end of the Archean
Major Proterozoic events
- increase in atmospheric oxygen
- BIF's stop forming and red beds begin
Onset of typical plate tectonics
- arcuate belts of tectonic activity
Proterozoic Supercontinents
- Rodinia: formed at 1.6 bya and broke up at 1 bya
- Grenville orogenic belt: an arcuate orogenic region, 1.3 to 1.0 Ga, extensive area of present-day North America and adjacent regions
Supercontinent cycles
- a tectonically driven cycle defined by the assembly of a supercontinent and later fragmentation and dispersal of its pieces
- begins with the collision and welding of tectonic plates to form an enormous mass of continental crust
- ends with the breakup and dispersal of fragments of the supercontinent
- proterozoic eon witnessed at least 2 cycles
Gondwana
- late Paleozoic continent that formed the southern portion of Pangaea, consisting of all or parts of present-day South America, Africa, Australia, India, and Antarctica
Late proterozoic sea level related to plate tectonics
- breakup of supercontinent near the end of proterozoic
- high rifting rates: large volume of warm expanded oceanic lithosphere
- high sea levels lasted until the Cambrian
Snowball Earth
- entire Earth frozen
- 3 different events Neo (720-660)(645-640)(580)my
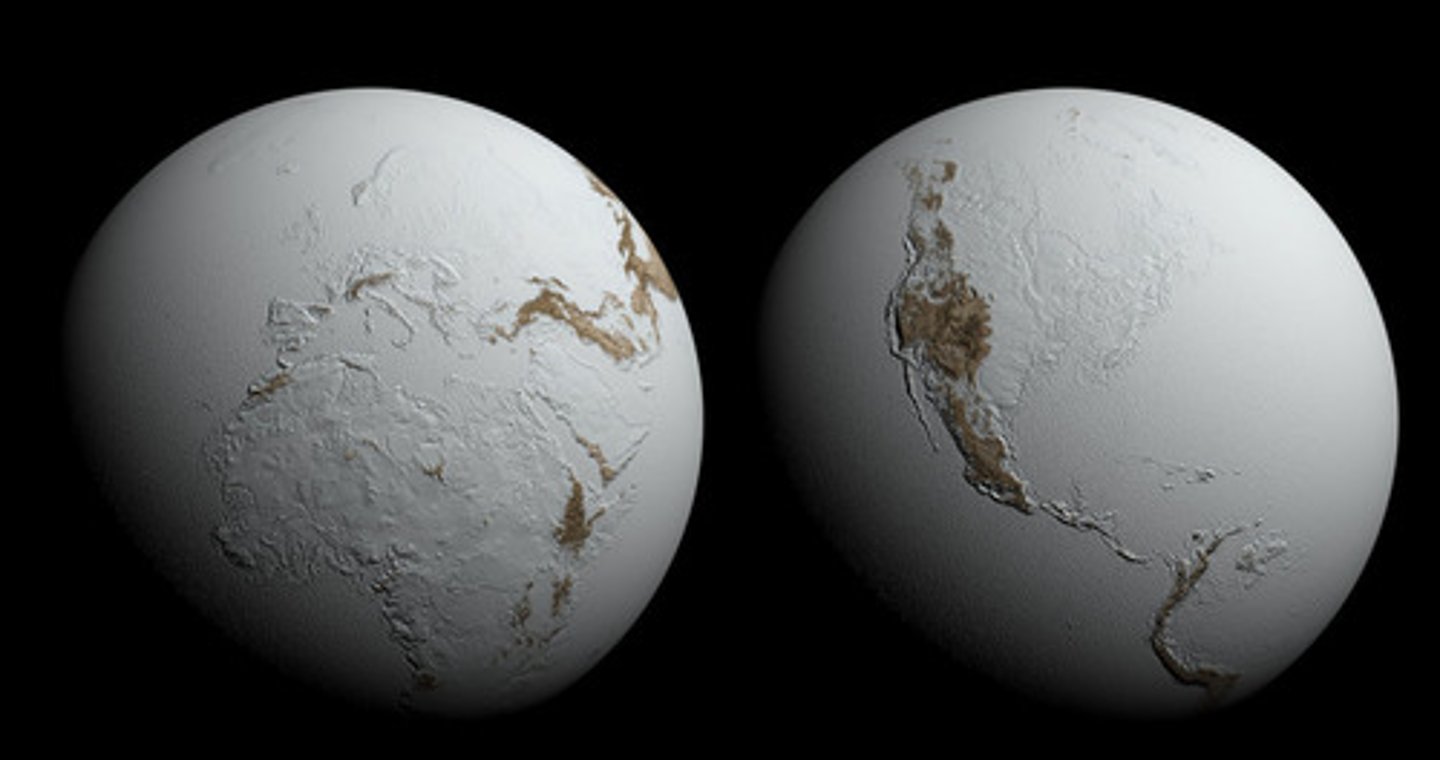
Evidence for snowball Earth
- glacial striations: tilites- sediment in ice melted
- tillites (rocks with glacial sediment) and diamictites
- dropstones
Why scientists believe snowball Earth was global
- glaciers at low altitudes
- paleomagnetism: past magnetic field and determines rock location at time
Snowball Earth stage one
- continents near equator develop large carbonate deposits along their continental shelves
- this may have increased when Rodinia began to split up
- carbon dioxide levels drop and greenhouse reduced > Earth cools
Snowball Earth stage two
- cooling Earth develops sea ice cover and continental glaciers
- increased albedo reflects sunlight, enhances cooling
- formation of carbonate stops
- CO2 no longer removed from atmosphere
Snowball Earth stage three
- Earth completely covered in ice
- surface temperature from 0 to negative forty degrees C
- volcanoes continue to erupt
- CO2 levels rise in the atmosphere but biological activity takes time to recover
Snowball Earth stage four
- lag in biological production of limestone and removal of CO2
- CO2 reaches 100 times normal level to form greenhouse
- glaciers and sea ice melt rapidly, greenhouse accelerates
- holthouse earth develops massive carbonate deposits
- carbonate formation reduces CO2, starts cycle again
Archean eon
- 4.0-2.5 billion years ago
- formation of protocontinents and greenstone belts
- no free oxygen
- life begins: stromatolites and other bacteria/archeabacteria
How can we determine when plate tectonics began?
1. Blueschists
2. Parallel strips of metamorphic rocks
Blueschists
- Metamorphic rocks formed under high pressure, low temperature
Greenstone- old oceanic crust
- greenstone belts formed- elongate area in a shield with metamorphic and deformed volcanic and sed-rich rocks
- chlorite-rich greenstone- green rocks unique to the precambrian & more mafic than modern rocks
- old oceanic crust
Early continental crust
- formed during the mobile crust phase when plates were moving quickly
- many subduction zones adjacent to protocontinents
Typical archean rocks
- no siliciclastic rocks
- chert
- BIFs
- stromatolites
Archean cherts
- marine
- plankton death
- no clastic rocks due to no land exposed above sea level
- continents are dense
Banded Iron Formations (BIF)
- interlayered chert and iron rich materials (hematite, magnetite)
- unique to precambrian
- times when there was no oxygen in the atmosphere
- main ore for human use- steel (Fe)
Conglomerates
- later archean
- mountain building
- environment- fast moving stream
Detrital pyrite
- sedimentary pyrite- clastic
- today would be oxidized- proves that oxygen levels were too low
Pillow basalt
- lava spill on ocean floor
- oceanic crust
Greenstones
- greenschist
- medium temperature and medium to low pressure
Autotrophs
- organisms that produce their own food
- earliest organisms
- chemosynthesis
- photosynthesis
- all feeding strategies are gained prior to end of precambrian
Heterotrophs
- Organisms that depend on other organisms for their food
- no heterotrophs before the precambrian
Chemosynthesis
- process in which chemical energy is used to produce carbohydrates
Photosynthesis
- Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy
Fossils in early Proterozoic
- early proterozoic life is still fossil poor until the Ediacaran (late proterozoic)
First Fossils
- simple burrows
- horizontal, near surface
Early Paleozoic
- cambrian and ordovician
- (542-444 Ma)
Middle Paleozoic
- Silurian and Devonian
- (444-359Ma)
Late Paleozoic
- Carboniferous and Permian
- (359-251 Ma)
Cambrian Explosion
1. appearance of numerous taxonomic groups (all marine)
2. Diversity
3. First good fossil record
- most phyla appear at this time: most animals can be traced back to this time
- about 40 Ma: which is not that much time for the amount of diversity
Cambrian Explosion Organisms
- vertebrates: jawless fish (Cambrian)
- phylum chordata: has a spinal cord- armored fish that appear later in early paleozoic are dominant vertebrates
Trilobites
- strong swimmers
- active burrowers for food
- opportunistic- eat anything they can find
- make it all the way through paleozoic
Cambrian Fossils
- first set of organisms with hard parts
- shells with keratin are better fossilized
1. biomineralized animals
2. non mineralized animals
3. trace fossils
Biomineralized Fossils
- original material replaced with phosphite
- most shells made of calcite: plankton, teeth
Nonbiomineralized Fossils
- skeletons of large animals
Trace Fossils
- increase in diversity of trace fossils and increase of amount of trace fossils
- new hunting strategies, new homes, new niches
- burrowing deeper
- complex branching from burrows
Burgess Shale
- famous outcrop with first fossilized soft parts and numerous shelly fossils
Cambrian Paleogeography
- rifting of supercontinent
- platea are pulling apart and creating new oceans
Ordovician Paleogeography
- closure of the Iapetus ocean
- future Atlantic ocean
- huge volcanic eruptions
Taconic Orogeny
- in early paleozoic
- Taconic orogeny: first of three mountain building events in Paleozoic
- creation of Appalachian mountains
- subduction of current East coast
- creating of Taconic Arc- volcanic islands
- arc eventually collides with North America
- a lot of sediment and end of volcanism
- taconic mountains
- wide range of metamorphic grade
Orogeny
- mountain building event
- look for:
1. eroded roots of mountains
2. sedimentary basins
Sedimentary Basins
- sequence of turbidites
- underwater basins
- grades beds of shales
Terrestrial Sediments
- shed off the mountains
- red beds
- this sedimentary sequence is common
Early Paleozoic Marine Reorganization
- sea level rise > more living space
- changes in ocean chemistry: increase in oxygen > more organisms can survive there
- nutrients from weathering
Predator-prey Relations
- arms race
- increase radiation
- example: anomalocaris and trilobites
- organisms become more efficient at escape: become faster at swimming, swimming backwards, hiding more efficiently
- development of spines and thicker skeletons
Ordovician (Or) Sea Level
- sea level is high at the beginning of Ordovician
- sea level drops and then rises- pretty high for most of period: caves > filled with petroleum
- major sea level drop at the end
Life on the Land
- plants are beginning to take root
Ordovician Glaciation and Extinction
- sea level drop
- glaciation on Gondwana
- 2nd most significant extinction event (Permian was the largest event)
- numerous tropical animals die out: brachiopods, corals, trilobites
- 2 stage event
First stage of Ordovician Glaciation and Extinction
- cooling stage
- drop exposes continental shelves
Second stage of Ordovician Glaciation and Extinction
- any species that ***
Paleomagnetism and Latitude of glaciers
- the latitude indicates that glaciers were present at the equator
- if glaciers are present at the equator (should be warmest) than the whole Earth is covered in snow
Limestone CaCO3
- reduces carbon dioxide in atmosphere
- colder climate
Modern Plate Boundary Rocks
- blueschists
- high pressure low temp rock related to subduction
Greenstone
- determine if there were plate tectonics in the Archean specifically
- super mafic rock that has been metamorphosed
Middle Paleozoic
- Silurian and Devonian
- 444 Ma-359 Ma
1. Evolution of land plants
2. Acadian Orogeny
3. Age of Fishes
Approximate Paleogeography of middle Paleozoic
- warm and wet
- Laurentia is south of equator
- shallow sea in Laurentia
- mountain range similar to Andes
Land Plants in middle Paleozoic
- plants are small
- no roots, no leaves, no seeds (spores), no woody tissue
- late Devonian- huge forests with huge trees
- 30 cm > 30 m
- root systems, seeds, woody tissue, leaf canopy present
- seeds can travel long distances: protected in colder weather
Old vs Modern Forests
- finger-like roots and not able to support super tall trees
- hollow inside
Late Devonian Plants
- development of larger leaf canopy
Significance of Leaf Canopy
- provides shade and shelter
- protects organisms (insects)
- creates leaf litter: habitat for bacteria and fungi
Affect on Streams
- roots stabilize the ground surface
- braided streams: wide stream channels
- many small channels in a wide area
- streams get localized and deeper
Black Marine Shales
- black shales in Appalachian basin
- forrests linked to black marine shale
- black in color due to organic materials
- due to amount of soil created, Nitrogen and Phosphorous get dumped in ocean
- encourages algae growth
- sea water becomes anoxic and toxic to marine life which eventually is killed off > organic material in shales
Forest and Coal Deposits
- plant material
- quiet environment > swamp
Changes in Climate and Atmosphere
- CO2 drops dramatically
- cooling event
Number of Predators vs Prey
- predators are 3 times more prevalent than prey
- arthropods: initially not much food available for herbivores
Acadian Orogeny
- second event leading to formation of the Appalachians and Pangea
- nearly identical to Taconic
- thrust faulting, metamorphism
Extension
- extension when pulling apart
- no extension in mountain building events
Age of Fishes
- Devonian: middle paleozoic
- must numerous vertebrates on Earth today
- huge diversity of fish at this time
Jawless Fish
- during Cambrian explosion
- lampreys and hagfishes: modern jawless fish
- ostracoderms: extinct due to slow swimming, ate plankton off sea floor
Jawed fish
- jawed fish
1. bony fish
- most fish we see today
2. cartilaginous
- have bones
- sharks
3. placoderms
- went extinct
Bony Fish
- difference in location of bones
- lobe-finned fish- evolve into amphibians
- lobe- bones are throughout the fin
- ray-finned- bones are just adjacent to fin
- most fish today are ray-finned
Cartilaginous Fish
- went extinct quickly
- rays, sharks, sawfish, skates: modern cartilaginous fish
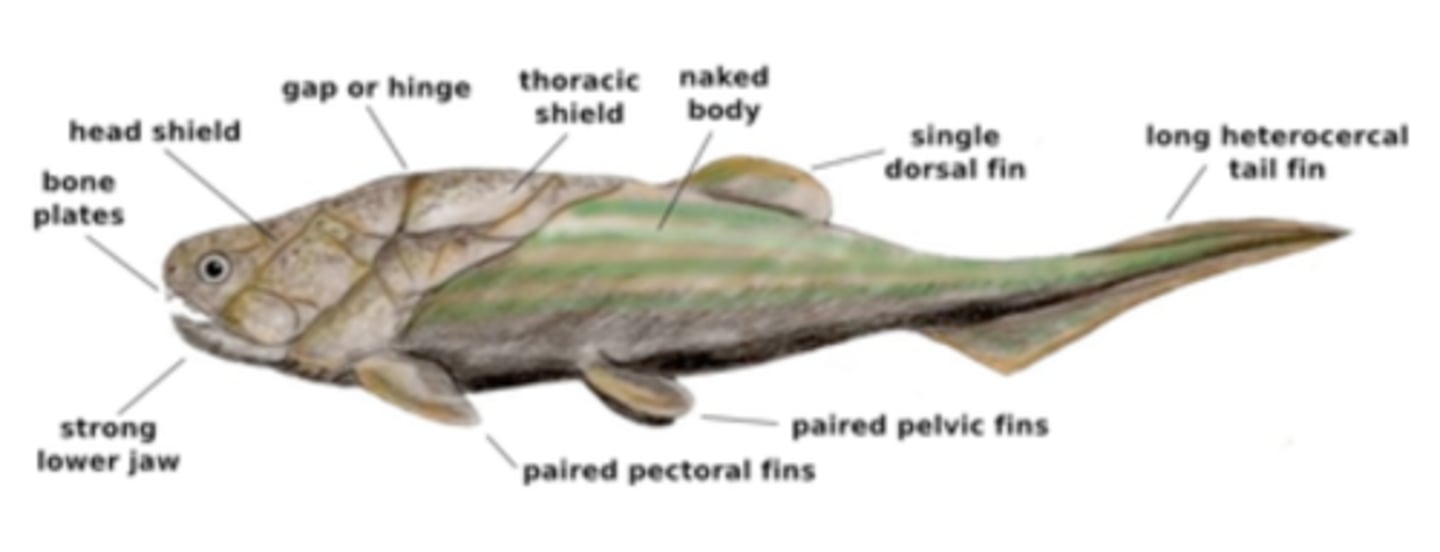
Placoderms
- top predators in middle Paleozoic seas
- first armored head
- biggest predators for awhile
- go extinct by the end of middle paleozoic
Late Devonian Mass Extinction
- protracted event: lasts a long amount of time for an extinction event
- 25 million years: 8-10 pulses of extinction
- mostly hits marine life
- lots of marine invertebrates: clams, nonfish (no spinal chord)
- reefs almost completely disappear
- some explanations relate to plants including ocean anoxia (low oxygen), global cooling
- other explanations include volcanism
Practice Question: What are the 3 main types of fossils that made their debut in the Cambrian period?
- three main types of fossils
1. biomineralized fossils: small shelly fossils replaced by phosphorus
2. non biomineralized fossils: have not been replaced by another mineral e.g. skeleton of an organism
3. trace fossils- complex burrowing patterns
Practice Question: How does carbon in rocks versus the atmosphere effect the climate and rock record?
- calcium carbonate in rocks: low CO2 in the atmosphere
- effect on climate: atmosphere gets colder
- calcium carbonate in atmosphere: higher CO2 in atmosphere
- effect on climate: atmosphere gets warmer
- more limestone
Practice Question: Difficulties when studying Archean life
- not many organisms
- do not fossilize well due to the presence of only hard parts which are rare
- fossils would be destroyed by metamorphism
Practice Question: 2 Stages of Ordovician Extinction Event
- first: global cooling which kills of tropical marine life
- second: warming quickly after the cooling > kills off organisms that adapted to the cold
Practice Question: First Vertebrates to Move to Land
- tetrapods (amphibians)- Tiktaalik
- live in the water as juveniles and move to land as adults
- evolved from lobe-finned fish