European Economic Integration
1/103
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Integration
removing frontiers in region
Integration Objectives
promote peace, economic stability, and cooperation among member states, values of EU
negative vs positive integration
negartive: liberation positive: supranational
Integration vs Cooperation
Integration: transfer sovereinty cooperation: common agreed policies
Intergovernmentalism vs Supragovernalism
Inter: volentary cooperation Supra: supranational insititutions
Stages integration low to high
Free Trade Area (no tariffs), Customs Union(equalization of outside tariffs), Customs Market(free movement of production factors), Economic Union (slected economic policies), Total integration (centralization)
Copenhagen Critearia
Politics: stable inistitutions, democarcy, rule of law, respect for human rights and minorities.
Economy: functioning market economy and the ability to cope with market forces.
Institutional: possiable to apply law and policies
Structure EU governance
EU council (poli leadership)
European Commission (general EU interest)
Council EU (general interest states)
European Court (legislative)
European parliament (judicative)
Single european Act
Qualified majority voting on issues (fiscal policy and harmonization, social cohesion)
liberation of government procurements and services in industries
Maastrict Treaty
A treaty signed in 1992 that established the European Union
led to the creation of the Euro,
setting out the framework for economic and political integration among member states
Monetary Union: ECB, ban excessive deficits, economic coordination
Three pillars EU:
European communities
common foreign and security policy
justice and home affairs
Subsidiarity
A principle in the EU that dictates decisions should be made at the closest possible level to the citizens affected, ensuring that higher levels of authority only intervene when necessary.
This is aimed at promoting local governance and efficiency in public affairs.
Arguments for Free Trade
Ricadian Theory: compertaive advantage argues that countries should specialize in the production of goods where they have a lower opportunity cost, promoting overall economic efficiency and increasing wealth for all trading nations.
Heckscher Olin Theodrem: suggests that countries will export goods that utilize their abundant factors of production and import goods that require scarce factors, thus enhancing global trade benefits.
Intra Industry Trade: trades within the same industry between countries, leading to specialization and increased competition, driving innovation and consumer choice.
Arguments for protection
Infant Industry: small young firms have it harder
Second Best: Some violate perfect competition
Optimal Tariff: maximize benefit for domestic firms and thus national welfare
Strategic Trade Theory: be used to max compertive and domestic economic power
Tariffs
Quotas
Volunteer export restrainers
dumping
export subsidies
technical barriers of trade
tax, levies imposed on imports
restrictive number on imports or the origin country
restrictions imposed by the exporting country
extreme quantities because of surplus dropped by the exporter compared to the domestic price
assistance to exportes
specific modifications which make trade harder ( health restrictions, substance restrictions, regulations, transport)
Import Demand with Export Supply
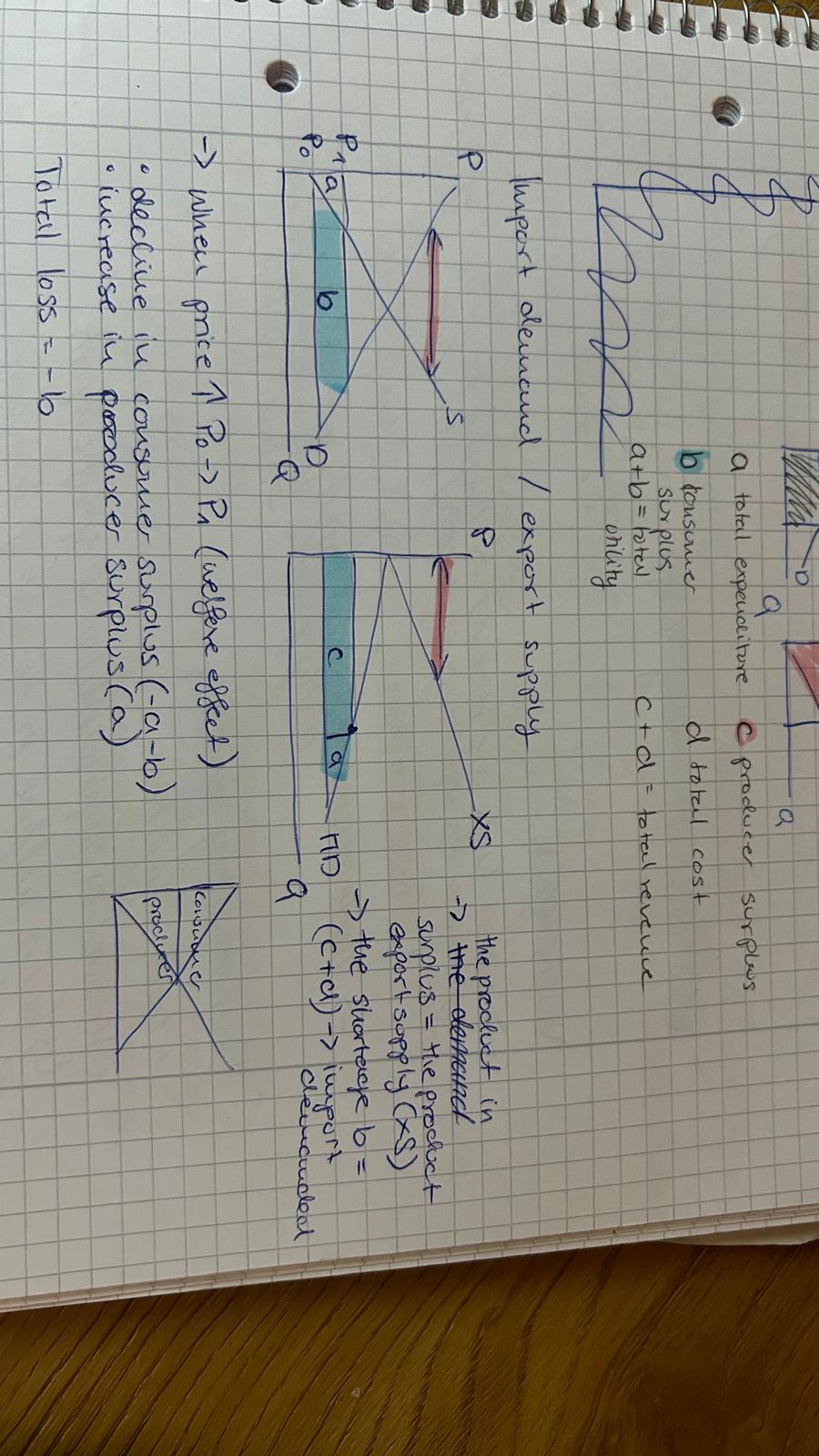
Free Trade Equilibrium
is a market condition where the quantity of goods demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers without trade barriers, leading to optimal resource allocation.
The P set by Home economy = demand foreogn economy
This equilibrium occurs when the international prices align with domestic demand, ensuring an efficient market for imports and exports.
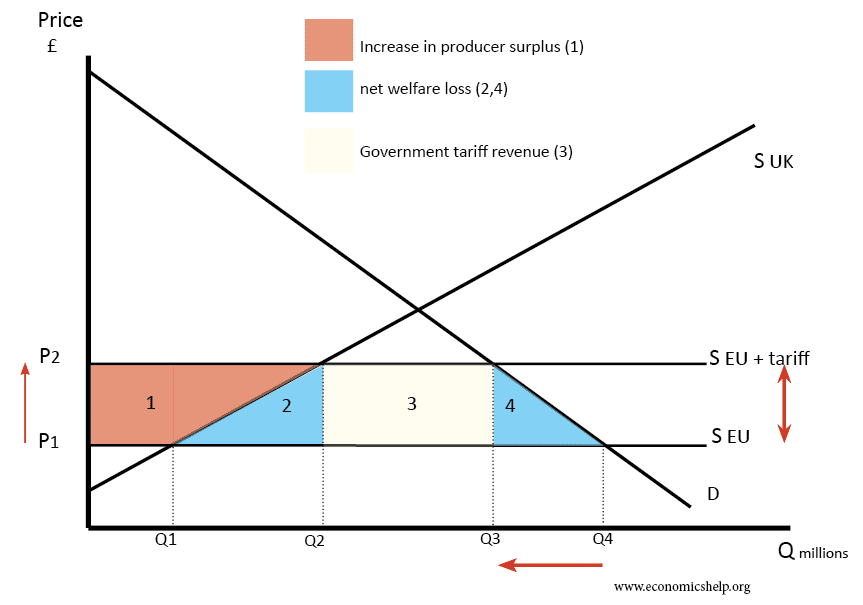
Impact of Tariffs
refers to the economic effects resulting from the imposition of tariffs, which typically leads to higher prices for consumers, reduced import volumes, and potential retaliation from trading partners, ultimately affecting overall trade dynamics and domestic industries.
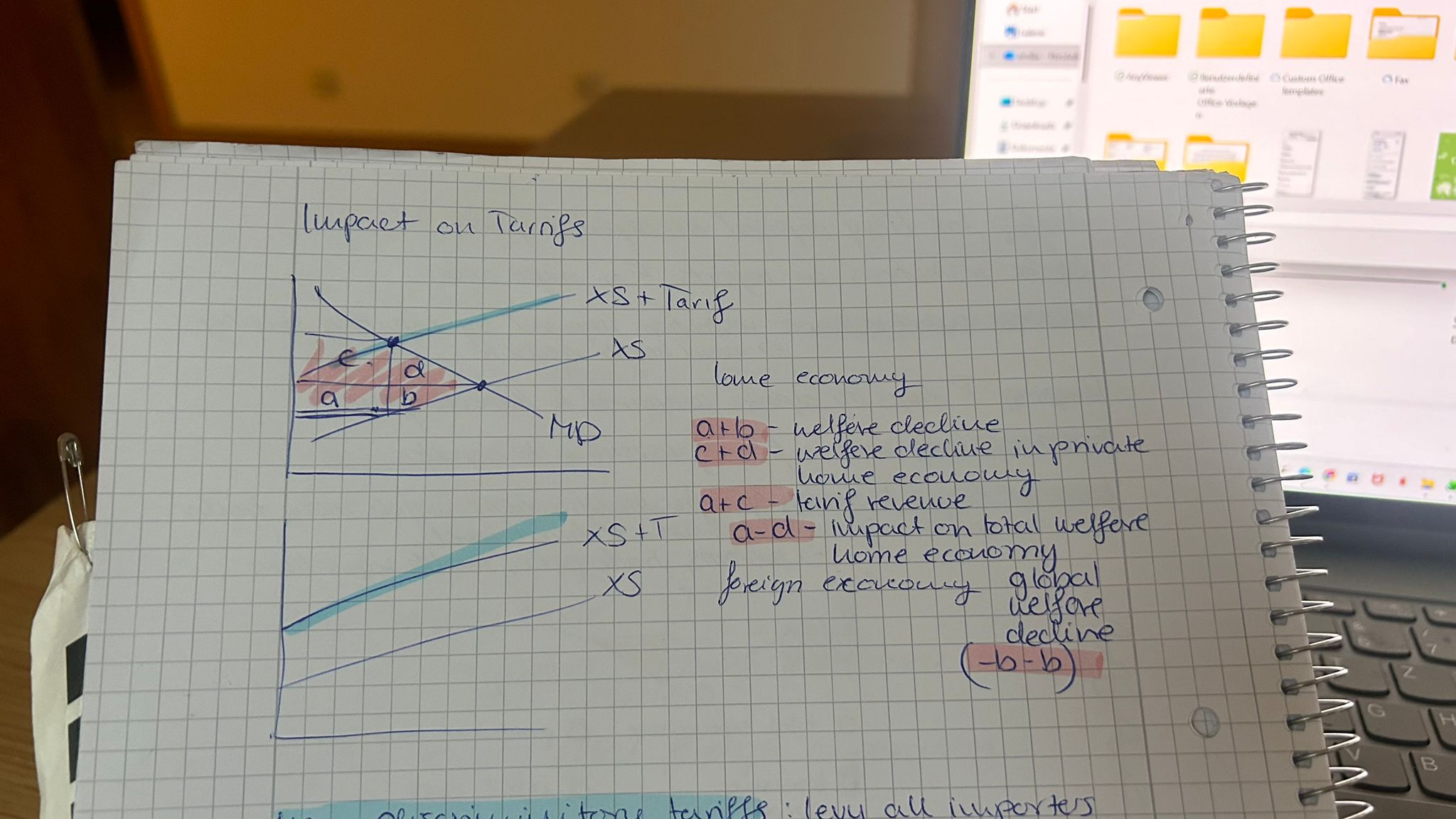
Non discriminitory Tariffs
are tariffs applied equally to all imports without favoring any particular trading partner, promoting fairness in international trade.
Viners effect
impact on welfare of customs unions and FTA
Trade Creation: occurs when high-cost domestic producers are replaced by lower-cost imports, leading to increased overall welfare.
Trade diversion: occurs when lower-cost imports from a member country replace previously imported goods from a non-member country, potentially resulting in a loss of overall welfare.
Dicriminatory tariffs
are tariffs that are applied differently to different trading partners, often favoring certain countries over others, and can lead to trade imbalances and disputes.
Custom Unions
A codefied form of trade liberation, eliminates tariffs while maintaining common external tariff
Services
are economic activities that provide value without the production of physical goods, often including sectors such as finance, healthcare, and education.
Freedom of services: the unrestricted movement of services across borders, facilitating trade and investment among member countries.
70% of EU activities
tradeables (cyclical)
non-tradeables (less cyclical)
Why regulate services:
Info asymmetry: difficult to assess the market, high quality might be pushed out
Imperfect competition: low contestability - can lead to monopoly
Systemisk risk: contagious effect
Social Considerations: discrimination in employment
Treaty Of Rome
right to provide services, right to set up establishments
Capital
factors of production, not for itself but for the ability of producing goods
Life Cycle foreign domestic investment
controlling a business in a foreign country through ownership or controlling interest.
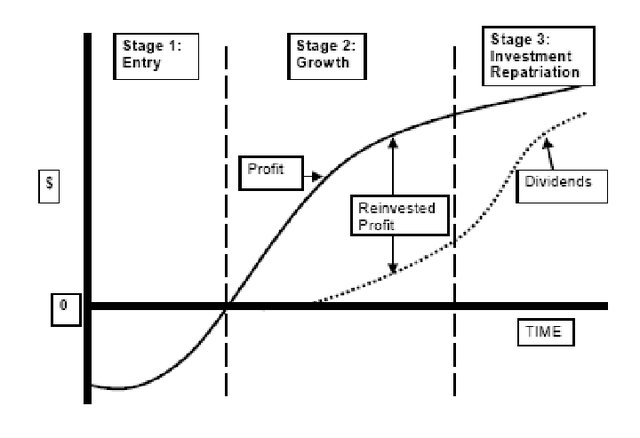
The effect of capital market integration
Through market integration, capital will move to where it yields the highest rates of return, thereby enhancing overall economic efficiency by allocating resources effectively.
Capital Controls
administrative (direct)
market-based (indirect)
direct. porhobitions
indirect: costly
Capital Flow
Long short term
Inlfow outflow
resident non resident
safe money, hot money (investments)
treatemnt of capital inflow and outflow (dutch disiease: too much inflow stops outflow)
control over domestic assets
Finantial Integration
full integrated market(same price everywhere)
the more integrated the better monetray policies
Benefits of Financial integration
Consumption smoothing (risk sharing), domestic investment growth, macroeconomic discipline, and financial and bank stability
Costs of Finantial Integration
Potential loss of monetary control, increased vulnerability to global shocks, herding, lack of access by other countries, misallocation
Monetary Policy
Successful: countercyclical
and stabilizes inflation; involves regulation of money supply and interest rates to influence economic activity.
expensitory: stimulates spending, boostst demand and promotes econ growth (higher GDP) - more money supply (lower interst rates) problem: raises inflation
contractionary: reduces spending - stops economic overheating , lowers demand, and curbs inflation - less money supply (higher interest rates) which can slow economic growth (lower GDP)
Conventional Monetary Policy
Increase/decrease Interest Rates, control the money supply, and influence inflation and economic activity.
Unconventional Monetary Policy
when cant decrease interst rates: #
Quantitive easing (balance sheets expands, liquidity unchanged)
Qualitative easing (balance sheet the same, changes composition )
Credit easing (expands sheet, liquidity decreases)
Forward Guiding:
Assymetric shocks in monetary Union
A situation where different regions within a monetary union experience economic shocks differently, leading to unequal effects on their economies. This can complicate the implementation of a unified monetary policy.
Solution: wage flexibility , price flexibility, fiscal transfer, coordination of fiscal policy, labor mobility
ECB will only rect when whole eu is effected
european Centran Bank
Governing council - main decsions every 6 weeks
General Council: advisors - info allocation
Impossiable trinity
The economic theory stating that it is impossible for a country to have all three of the following: a stable foreign exchange rate, free capital movement, and an independent monetary policy at the same time.
Tosovsky monetary dilemma
A situation in which a country faces a trade-off between maintaining currency stability, controlling inflation, and fostering economic growth, particularly in the context of economic integration.
optimun currecy areas
Regions that benefit from sharing a common currency due to economic similarities, which can enhance trade and stability.
Sysmetric shocks in OCA
Economic disturbances that affect all regions within an optimal currency area similarly, necessitating synchronized responses and policies.
decline in symetric shocks raises cost compared to benefit in monetary union
Logic OCA
where marginal benefit crosses marginal cost - optimal size
endogenity principle: a country does not need perfect condotions, if it joins the OCA will be established faster
Maastricht Criteria
price stability, long term interst rate convergence, ex r stability, sustainable public finance, independent national bank
Monetary Criteria:
Inflation: § lowest eu plus 1.5 % points
Interest rates must converge with the lowest three EU countries plus 2 percentage points.
Exchange rate stability must be maintained against EU currencies for at least two years.
Cost of Euro
loss independent monetary policy, limited reaction asymetric shocks, loww ex r adjustment, cost with change over
benefit of Euro
reduction of transaction cost, no exchange rate risk, greater transparency, fiscal stability, more effective CB
Prudential policy
Measures to ensure financial stability and mitigate systemic risks in the banking and financial system. - eliminate fragile equalibrium
Micro Prudential Policies
Banking Union: transfer of responsibilities, supervision, and regulation of banks to a centralized authority, aiming to enhance financial stability and mitigate systemic risks.
Fiscal Trilemma: fiscal stability, fiscal integration, national fiscal policy
Pillars of Banking Unions
single rulebook
single supervision
single resolutions
unified systems of deposit transfers
Micro Level prudential Policy Spervision
European security Market Authority (risk assesing)
European Banking Authority
european insurance and occupational pensions authority.
European Supervision Authority
Macro prudential Policy
Policies aimed at mitigating systemic risk and ensuring the stability of the financial system as a whole, differing from microprudential approaches that focus on individual institutions.
Based on indicators
Macro prduential Supervision
European Risk Board: gudiance, risk assessing framework for systemic risks, recommendations
neutral in normal times
counter cyclical in not normal times
Monetary vs Financial stability
normal times: Finantial report
Not normal: Inflation report
Instruments: Buffers, limits
Buffers and limits
Buffers: financial reserves used to absorb losses, while limits refer to constraints placed on exposure or risk-taking activities in the financial system to maintain stability.
Limits: constraints on risk exposure, ensuring that institutions do not exceed predetermined thresholds that could jeopardize financial stability.
Fiscal Policy
expansionary: increase gov spending, lowers tax, AD up, GDP growth
contractionary: lowers gov spending, higher taxes, AD down, GDP down
promotes balance of government budgets
Structual and cyclical defict
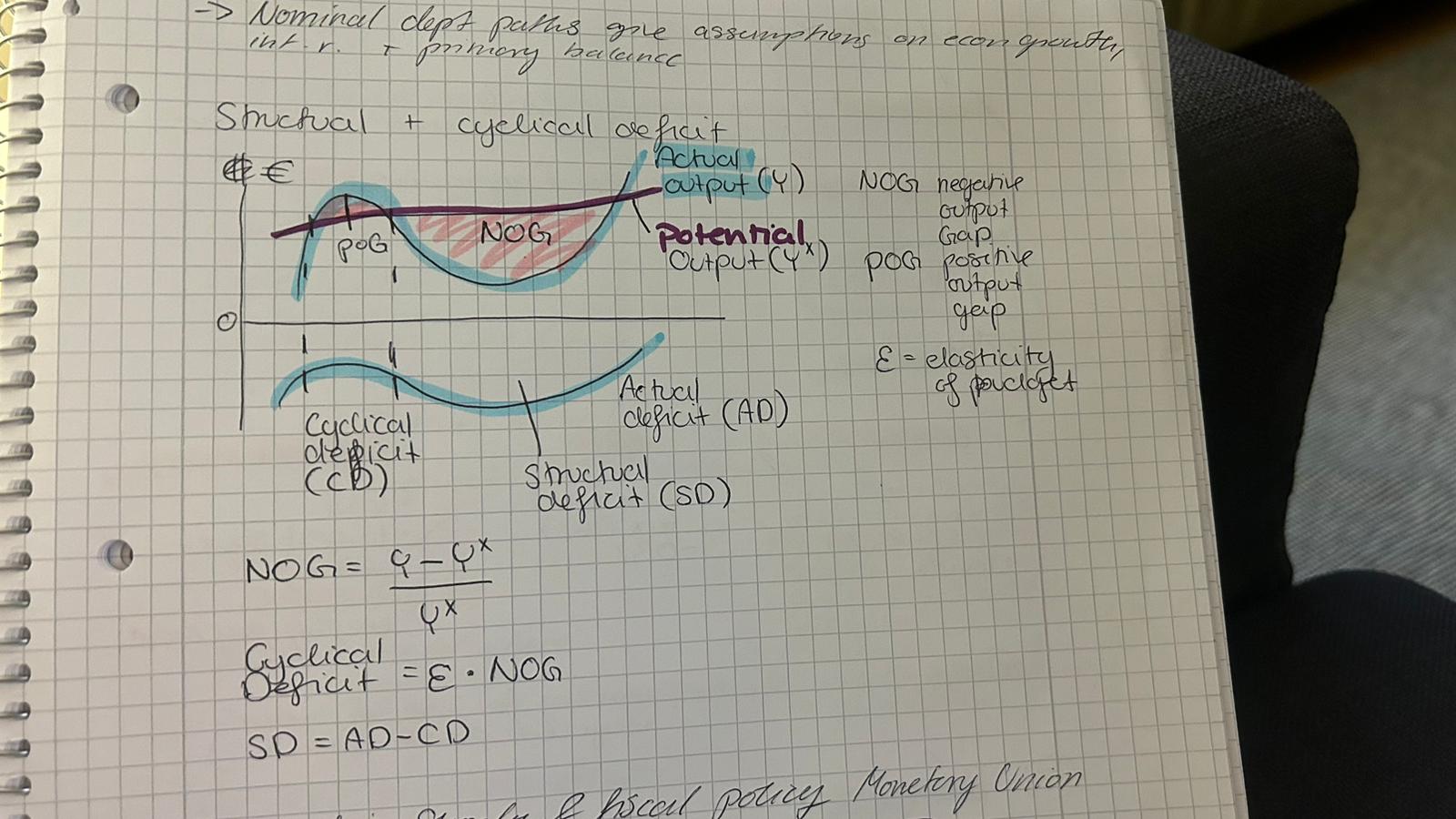
Asymmetric shocks in a monetary Union
occurrences that affect member countries differently, requiring varied responses from national policymakers.
solution:
fiscal policy - redistribution among members, shock absorption
tax contributions and benefits adjustments
EU Budget
reserves: Customs duty, value added tax, contribution, Plastic
spending: relatively small, 7-year spending plan (mutual financial market, Next Generation EU)
Taxes EU - Tax harmonization
Pro: fair competition, race to bottom taxes, costly maintance of fiscal frontires
con: loose sovergnty, potential diffirent outcomes, loss of discipline of government
Tax direct vs Indirect
direct: income tax indirect: VTA, customs, consumption tax
destination tax vs origin principle
destination tax is imposed based on where goods or services are consumed, while origin principle taxes are based on where the goods or services are produced.
Regional Policies region def
Subnational: government policies tailored to specific geographic areas within a country, aimed at addressing regional disparities.
supranational: region among countries
region NUTS
Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics, a classification system used by the European Union to collect, develop, and analyze regional statistics.
NUTS 1 - major socio economic policies
NUTS 2 - basic regional policies
NUTS 3 - specific disgonstics
Aggimeration vs Dispersion
The term "agglomeration" refers to the concentration of populations and economic activities in specific geographical areas, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. This phenomenon often occurs in urban areas where businesses and services cluster together.
could be a negative effect of intergration as it can lead to overcrowding, increased competition, and disparity between urban and rural areas.
Disperasion refers to the distribution of populations and economic activities across wider geographical areas, encouraging growth in rural regions and reducing urban congestion. This can be a positive outcome of integration, promoting balanced development.
Modern Growth Theory
More wealthy countries can enjoy prosperity longer. Disparities prevail though knowledge increases.
Priciples of Region Policy:
Consentration of regional objectives
Allocation of funds through multi year programs
cooperation among regional partners
suppport for underdevelpoed regions and promotion of sustainable development.
Structural funds regional policies
European Social Funds (75% below GDP)
Argiculturaö Guidance Funds
European regional development funds
financial instrument fishery guidance
cohesion funds (those 90% below EU average GDP)
EE-KK-Model
Aggomeration and Dispersion in diagram:
two region N and S
2 factors - mobile and immobile
2 sectors
Common Agricultural Policies Problems
Uncertainly, Unavoidability, externalies, social cohesion
Agricultural Intervention why?
income vunrability
long-term declining problem
social cohesion: highly competitive, income disparities
externalities: pollution, enviromental disparities
Cohweb Theorem
Small shocks are amplified due to the producer’s behaviour
Pricaples of CAP
market Unity, community preference, financial solidarity
CAP instruments:
Levys and tariffs
Interventions (intevention price - dumping)
Producer subsidies: pay farmers guaranteed price and direct payments to support income stability.
CAP Direct payments
pro: less contriversial, no market interverenvce, greater exposure to market sygnals
con: leakage, high red tape, dependency
Problems of CAP
down pressure on world P
ham less developed countries
dumping
potential trade conflicts
budget lower than actual cost
dependence
Paradox of CAP
often not felt by farmers, farms dissapearing, more support to the north
CAP trands 2010-2020
development
anti discrimination
cost efficiency
decoupling direct payments from production
Thoeries of trade
apsolute andcomparative advantage
Hecksher Olin Theodrem
new trade theory
Gravity Model
Leontif Paradox
Absolute Advantage
the ability of a country to produce a good more efficiently than another country.
Comperative advantage
the ability of a country to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country, which allows for beneficial trade between nations.
Hecksher Olin Theodrem
a theory in international trade that emphasizes the differences in factor endowments of countries to explain trade patterns. It suggests that countries export goods that utilize their abundant factors of production and import goods that utilize their scarce factors.
Leontif Paradox
the observation that countries with a higher capital-labor ratio tend to export labor-intensive goods, contrary to the Heckscher-Ohlin theory's predictions. (US should export less capital intensive goods - but dont)
New Trade Theory
a theory that explains international trade patterns based on increasing returns to scale and network effects rather than just comparative advantage, suggesting that countries can gain from trade even with similar factor endowments.
Home market effect: market will move where tarnsport cost is low
Gravity Model
a model in international trade that predicts trade flows between two countries based on their economic sizes and distance, suggesting that larger economies have more trade with each other and that greater distances reduce trade volume.
World Trade Set Up
Multilateralism - multiple countries
Regionalism - regional trade
Unilateralism - a single country's trade policies and actions, often leading to preferential treatment in trade agreements.
Pricaples of the WTO
non- discriminatory
Recreational: consessions extendend to all members, trade liberalization, and transparency in trade policies.
Relationship Budget and Account
Twin deficit
account deficit
feedback linkage
no linkage
Keysian Absorbtion theory
An economic theory that explains how a country can absorb its trade deficits through domestic consumption, investment, and savings adjustments.
Trade Integration
EU comission, Kurgman
Oragnisation of Trad ein EU
Commission: main head and decisions
Council: Approves negotiations
Complications - EC only for goods
Prefrence pyramid of EU trade
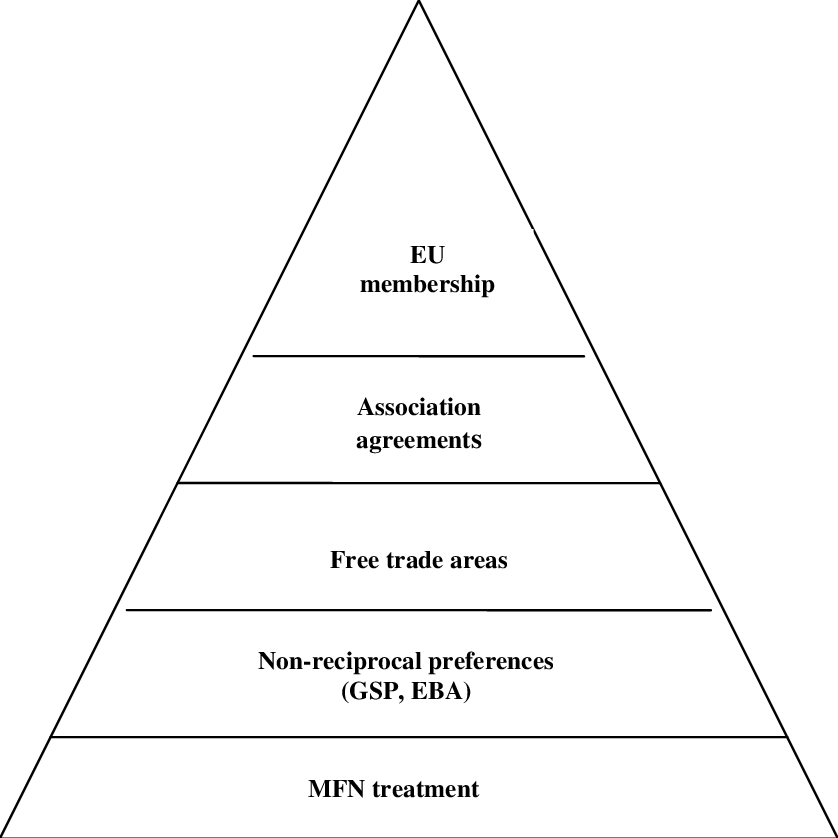
EEA
The European Economic Area, which extends the EU's internal market to non-EU countries.
Competition and Industrial Market Policy
A policy framework aimed at promoting competition and regulating industries within the EU to enhance market efficiency and consumer welfare.
fosters Innovation, wider choice, healthy competition
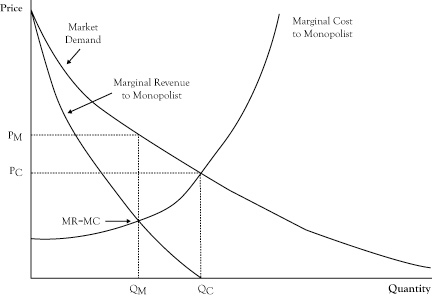
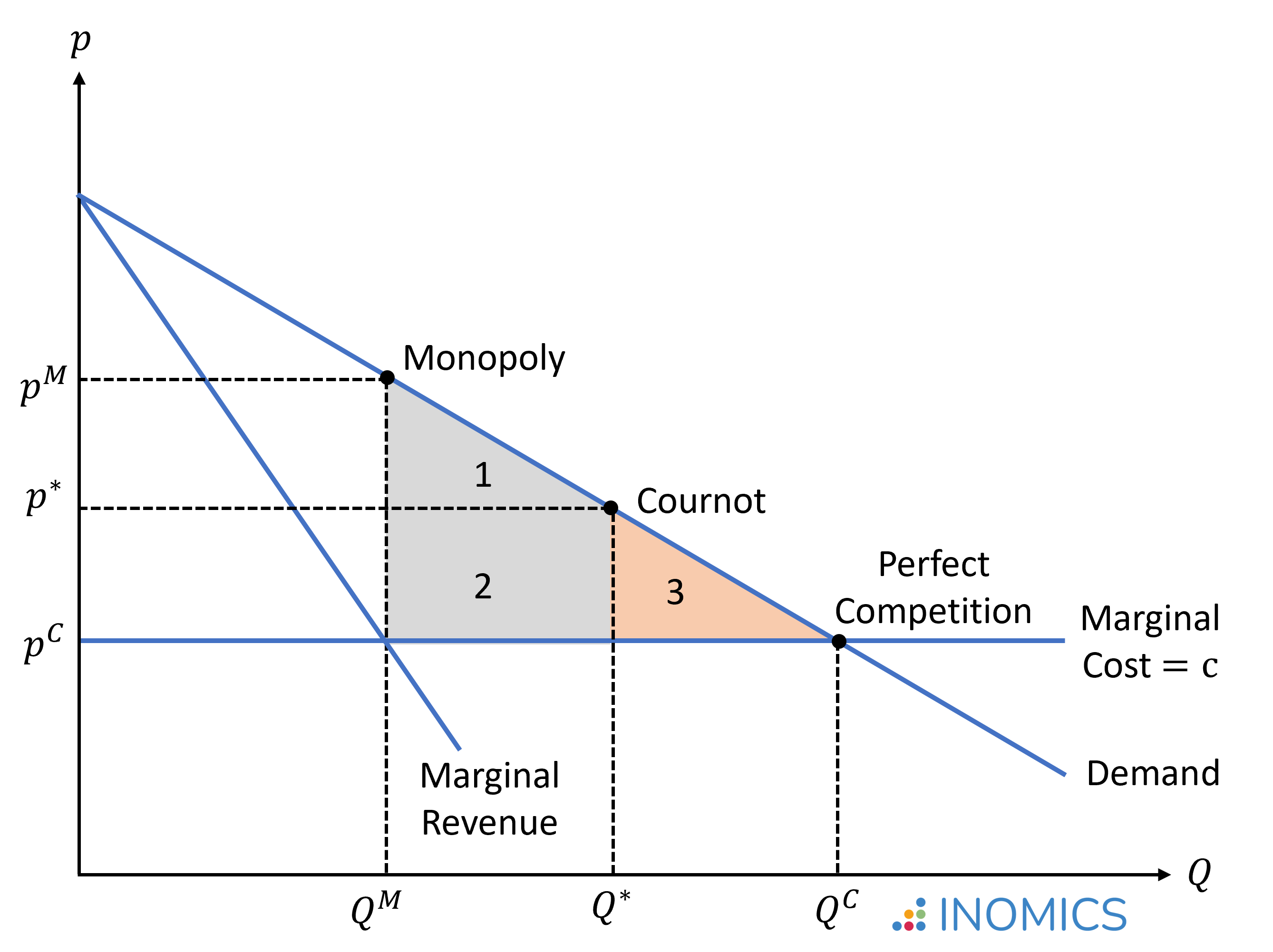
Monopolist Equalibrium
the profit-maximizing output and price for a single-seller market, found where Marginal Revenue (MR) equals Marginal Cost (MC), with the monopolist then setting the highest price the market will bear for that quantity, typically leading to higher prices and lower output than competitive markets, with significant profits possibl
Quantity competition
A market structure where firms compete on the quantity of output produced rather than prices, leading to strategic interactions in deciding production levels. Firms choose output levels to maximize profits while considering competitors' output decisions, typical in oligopolistic markets.
Wh Policy on Competition
proper function of internal market
avoid jurostiction
source discrimination: withstand global competition, national champions
Competition Policy among firms
Component 1
Component 2
Component 3
Component 4
Component 5
anti competitive agreemnt (horizontal and vertical)
Abuse dominant position (large firm advantage, sanctions)
merger control (focus on large companies, tries to avoid too many market shares)
control of state intervenence (no interstate lobbyism)#
liberation market which is usually state-owned (transport, oil, electricity)
Organisation Competition
national Competition Authorities
Court of first instance
european court of justice
National Courts
Alignemnt Euro area Convergence vs alignment
Convergence poorer countries will grow faster than wealthier once
Alignment refers to the economic policies and conditions in the euro area that aim to synchronize member states' economic performance and regulatory practices to ensure stability and coherence.
Real Convergence: even though grow faster still lack behind
PPP
Purchasing Power Parity, a theoretical exchange rate which would allow all goods to be bought by the same price (compare big macs)