cell division
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
dat bio ch. 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
what is the cell cycle in 2 steps
interphase
M phase
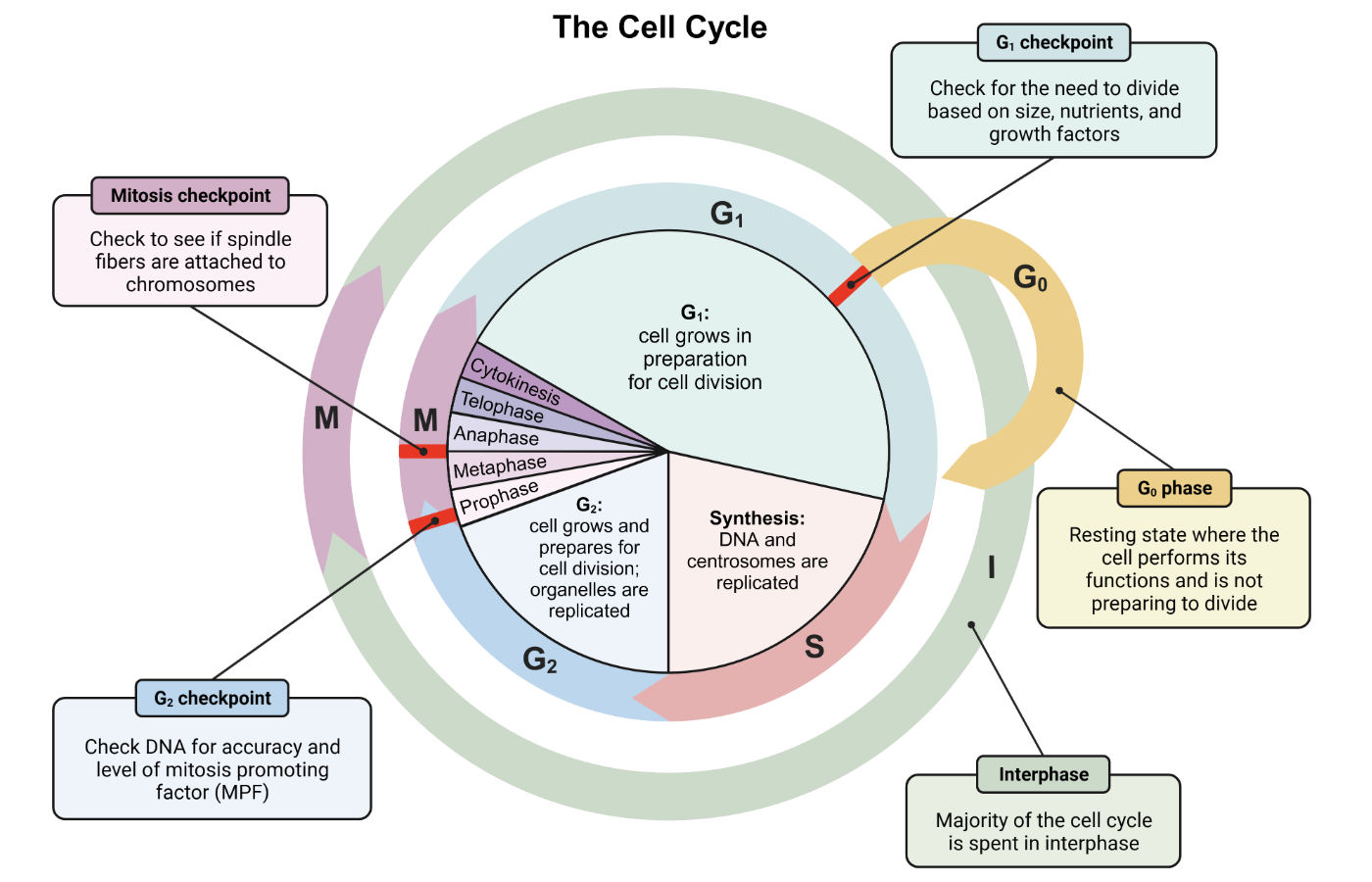
what are the 4 parts of interphase (in order)
G1, G0 , S, G2
Go Sam Go Make Cake
G - gap phase 1 (G1) of interphase
S - synthesis phase of interphase
G - gap phase 2 (G2) of interphase
M - mitosis of M phase
C - cytokinesis of M phase
G1 phase
cell grows in prep for cell division and checks for fav conditions; if favorable, then cell proceeds ot S phase
what happens during G0 (part of G1)
cell still carries out functions but not preparing for division
Cells that will not divide (e.g., neurons) are permanently in G0.
To divide, cells must exit the G0 stage and enter G1
S phase
cell replicates its genome and centrosome
genome
all DNA in cell
centrosome
organelle that aids in cell division
G2 phase
organelles replicated and DNA assessed for errors
checks mitosis promoting factor aka maturation promoting factor levels → sufficient amount needed to proceed to M phase
M phase
stage in cell cycle for karyokinesis and cytokinesis occur
types of karyokinesis in eukaryotes
mitosis + meiosis
utilize microtubule organizing centers
prokaryotes perform………
binary fission
genome replicates while cell division occurs (no S phase)
no microtubule organizing center
microtubule organizing centers
centrosome → MTOC in animal cells; replicate during S phase so each daughter cell gets one
form spindle apparatus, which guides chromosomes during karyokinesis
centrosomes made of pair of centrioles
pericentriolar material surrounds centrioles, responsible for microtubule nucleation
microtubules are made of …
tubulin
what are centrioles
hollow cylinders oriented at 90 degrees
attached by interconnecting fibers
made of 9 microtubule triplets (9×3 array)
cilia and flagella
made up of 9 microtubule doublets with two singlets in the center (9+2 array)
types of microtubule types
polar
astral
kinetochore
polar microtubule type
connect centrosomes and push them to opposite sides of the cell
astral microtubule type
attach to cell membrane to orient centrosome
kinetochore microtubule type
attach kinetochore
during which phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur
S phase
cell cycle has functional limitations and cell-specific regulations to …
help prevent uncontrolled growth (cancer)
ex of functional limitations
surface to volume ratio (S/V)
genome to volume ratio (G/V)
surface to volume ratio
cell volume becomes too large for surface area of plasma membrane to support → decrease in S/V leads to cell division
genome to volume ratio
cell volume becomes too large for genome to support → decrease in G/V leads to cell division
ex of cell-specific regulations
cell cycle checkpoints
cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs)
growth factors
anchorage dependence
density dependence
density dependent inhibition
cell cycle checkpoints
G1 restriction - conditions are favorable to grow and eventually divide
end of G2 - accurately replicated genome & sufficient MPF levels
M checkpoint - microtubules properly attached to chromosomes
cyclin-dependent kinases
phosphorylate certain molecules in order to signal cell cycle progression
activated by cyclin, a protein that cycles through stages of synthesis and degradation
growth factors
bind plasma membrane receptors to signal growth and cell division
anchorage dependence
cells divide only when attached to an external surface
density dependent inhibition
halting of cell division when cell density is too high
an increase in cyclin will ___ cell division
increase
genome
all DNA in the cell
chromatin
loosely winded DNA + protein complex
chromosome
separate DNA molecules that make up the genome
sister chromatids
identical copies of the same chromosome
dyad
identical sister chromatids joined to form an X shape
centromere
region connecting sister chromatids
kinetochore
proteins that associate with microtubules in cell division
stages of mitosis
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
cytokinesis
prophase
chromatin condenses into chromosomes
nucleolus and nuclear envelope disappear
spindle apparatus forms
metaphase
spindle apparatus guides chromosomes to metaphase plate (midpoint of cell) in single file
prometaphase
prior to metaphase, nuclear envelope fragments and spindle apparatus attaches to kinetochores
anaphase
kinetochore microtubules shorten to pull sister chromatids apart
sister chromatids are now considered individual chromosomes - chromosome count doubles
cleavage furrow
in animals, cytokinesis begins in late anaphase with the formation of __. contractile ring of actin microfilaments and myosin motors that pinches cell into two
telophase
chromosomes have separated, nuclear membrane and nucleolus reforms
chromosomes decondense into chromatin
spindle apparatus disappears
cytokinesis
→ completes once cells complete split
in plant cells, __ only begins in telophase with the formation of a cell plate, ends up producing middle lamella
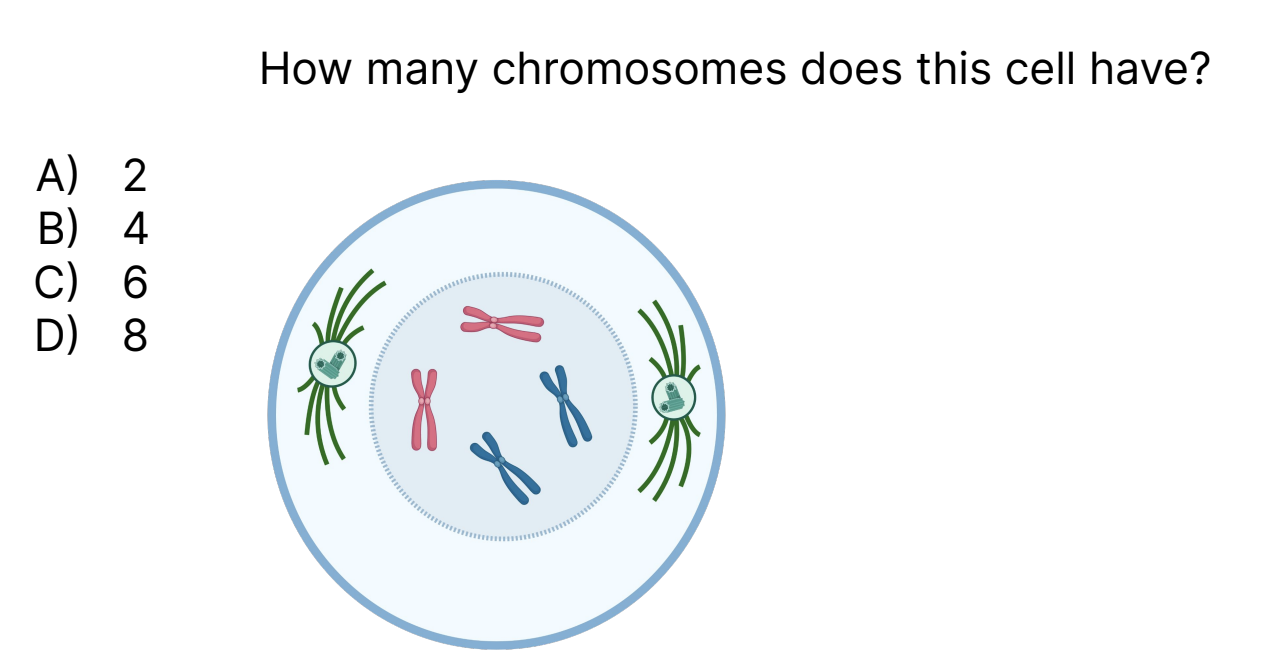
4
haploid
containng one set of chromosomes
diploid
containing tow sets of chromosomes, one from each parent
→ homologous chromosomes
homologous chromosomes
two different copies of the same chromosome in a diploid organism
mitosis vs meiosis
mitosis: division of a diploid cell into two genetically identical diploid cells
meiosis: two divisions of a diploid cell to produce four genetically distinct haploid daughter cells
meiosis is divided into
meiosis I: homologous chromosomes separate
reductional division
meiosis II: sister chromatids separate
somatic cells are…
diploid → 2n = 46
germ cells can…
divide via mitosis to form more diploid germ cells, or via meiosis to form haploid gametes
gametocytes are…
eukaryotic germ cells
gametes are…
haploid → n = 23
M1 - prophase I
DNA condenses into chromosomes
homologous chromosomes pair up/cross over & recombination occurs
nucleolus and nuclear envelope disappear & spindle apparatus forms
synapsis (M1 - prophase I)
homol chromosomes pair up to form tetrads (aka bivalents)
synaptonemal complex
protein structure that forms between homologous chromosome during synapsis
chiasmata
site of crossing over leads to genetic recombination
increases genetic diversity
M1 - metaphase I
homologous chromosomes line up (double file) at the metaphase plate
independent assortment increase genetic diversity
M1 - anaphase
homologous chromosomes are separated by shortening kinetochore microtubules
M1 - telophase I and cytokinesis
the cytoplasm divides and two haploid cells form
each chromosome is composed of two sister chromatids
nuclear membrane and nucleolus reforms
M2 - prophase II
DNA condenses into chromosomes; spindle apparatus forms & nucleolus and nuclear envelope disappear
NO CROSSING OVER
M2 - metaphase II
chromosomes line up (single file) at the metaphase plate
M2 - anaphase II
sister chromatids are separated by shortening kinetochore microtubules
sister chromatids = individual chromosomes - chromosome count doubles
M2 - telophase II and cytokinesis
cytoplasm divides and four haploid daughter cells form
chromosomes decondense → chromatin
spindle apparatus disappears, nuclear membrane and nucleolus forms
during what step of meiosis do homologous chromosomes separate from one another
anaphase I
During which stage of meiosis does the ploidy decrease from 2n to 1n?
a. meiosis I
b. meiosis II
meiosis I
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in mitosis prophase
46; 92
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in mitosis metaphase
46 ; 92
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in mitosis anaphase
92 both
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in mitosis telophase
92 both
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in mitosis cytokinesis
46 both
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in meiosis I prophase I
46 ; 92
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in meiosis I metaphase I
46 ; 92
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in meiosis I anaphase I
46 ; 92
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in meiosis I telophase I
46 ; 92
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in meiosis I cytokinesis I
23 ; 46
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in meiosis II prophase II
23 ; 46
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in meiosis II metaphase II
23 ; 46
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in meiosis II anaphase II
46 both
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in meiosis II telophase II
46 both
how many chromosomes & chromatids are there in meiosis II cytokinesis II
23 both
if a human cell undergoes mitosis, how many chromatids will be present in each daughter cell at the end of cytokinesis
46
karyokinesis
is the division of the nucleus, where one parent nucleus divides to form two daughter nuclei
cytokinesis
describes the division of the cytoplasm and cell membrane
During what phase of mitosis does cytokinesis begin in animal cells and plant cells, respectively?
Cytokinesis begins at the end of anaphase in animal cells. In contrast, cytokinesis starts in telophase in plant cells.
what structure cements neighboring plant cells together?
middle lamella