CH 11- Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue Pt 1.
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Nervous Tissue- Cells of nervous tissue
Neurons
Glial Cells
Neurons
Electrically excitable cells of the nervous system
Glial Cells
Supportive cells
Functions of Nervous System
Maintaining homeostasis
Receiving sensory input
Integrating information
Controlling muscles and glands
Establishing and maintain mental activity
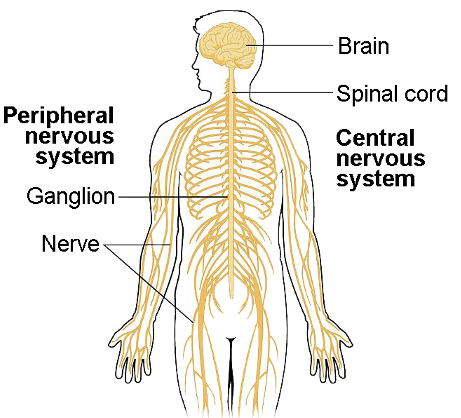
Divisions of the Nervous System
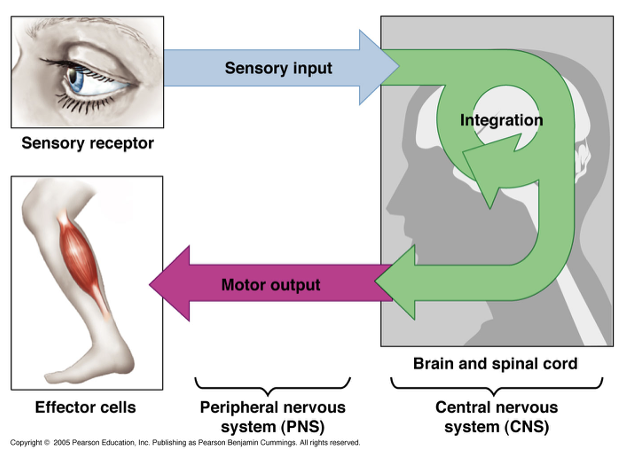
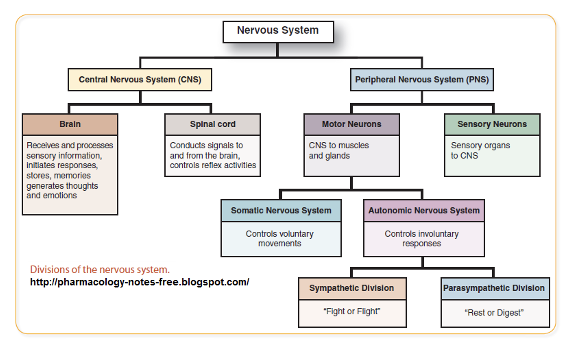
Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
receives information from and sends information to the body
decision maker
consists of the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Detects stimuli in and around the body
Carries information to the CNS and from the CNS to the body
Consists of nerves, ganglia, and sensory receptors
Structure of the CNS
Brain
housed in the skull
Spinal Cord
housed in the vertebral columns
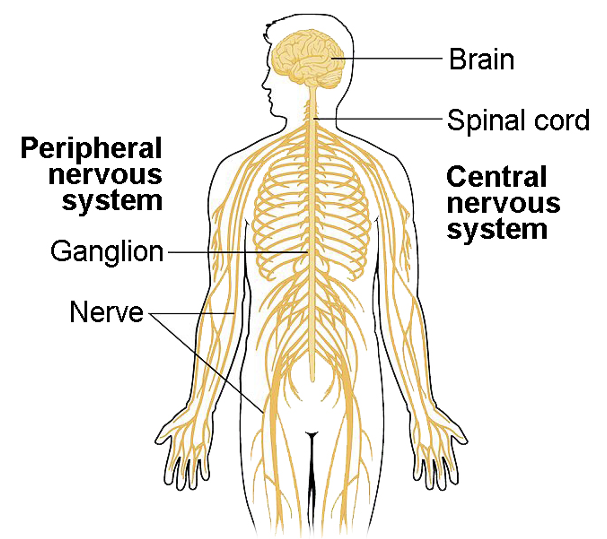
Structure of the PNS
Nerves
collection of axons outside the brain and spinal cord
can carry electrical signals away from or towards the CNS
Cranial nerves- 12 pairs or nerves originating from the brain
Spinal nerves- 31 pairs of nerves originating from the spinal cord
Plexus- bundle of nerves outside the brain and spinal cord
Ganglia
group of neuron cell bodies outside the brain and spinal cord
Sensory receptors
cells that respond to a specific stimuli
can be neurons or specialized cells
distributed throughout the body
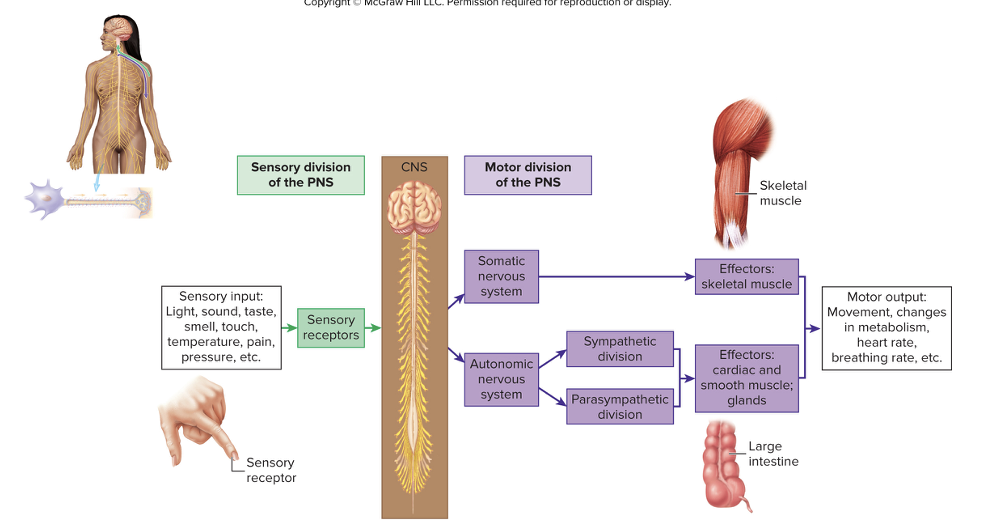
Divisions of the PNS
Sensory (afferent) division
Motor (efferent) division
Sensory (afferent) division
transmits electrical signals from receptors tot he CNS
Motor (efferent) division
Transmits electrical signals from the CNS to effector organs
Effector organs include muscle (skeletal, cardiac, smooth) and glands
Divisions of Motor Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous Sytem
Somatic Nervous System
voluntary division
controls movement of skeletal muscles
Autonomic Nervous System
involuntary division
regulates contract of cardiac and smooth muscles and secretions of glands
Division of the Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Enteric nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
prepares the body for physical activity
“fight or flight”
Parasympathetic nervous system
regulates resting function (digesting food)
“rest and digest”
Enteric nervous system
neuronal networks in the wall of the digestive tract
Flow of the nervous system
Cells of Nervous Tissue
Neurons
Glial Cells
Neurons
electrically excitable cells of the nervous system
~100 billion neurons in the body
Glial cells
supportive cells
50% of the brain’s weight
10-50 times more glial cells than neurons in various brain regions
Neuron Struture
Cell body (soma)
nissl bodies
Dendrites
dendritic spines
Axons
axoplasm
axolemma
axon hillock
initial segment
trigger zone
presynaptic terminal
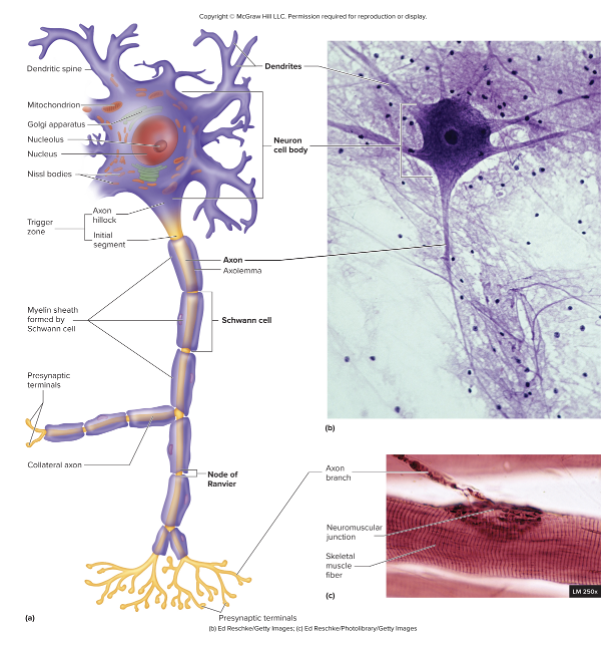
Cell body (Soma)
Single, centrally located nucleus with nucleolus
Nissl bodies- extensive rough endoplasmic reticulum
Abundant intermediate filaments (neurofilaments) and microtubules forming bundles int he cytoplasm
Dendrites
Processes off the cell body
Short, often highly branched
Tapered from base to tip
Receive input from other neurons and other sensory receptors
Dendritic spines
small extension on the surface where synapses are formed
Axons
Single process off the cell body
Constant diameter, varied length
Axoplasm
Axolemma
Axon hillock
Initial segment
Trigger zone
Presynaptic terminal
Axoplasm
cytoplasm of the axon
Axolemma
plasma membrane of the axon
Axon hillock
cone shaped area coming off cell body
Initial segment
formed by the narrowing of the axon hillock
Trigger zone
axon hillock and initial segment, where action potentials are generated
Presynaptic terminal
region at the end of the axon that house synaptic vesicles storing neurotransmitters
synapse
Synapse
point of contact between the axon ending and its effector
Fucntional classes of neurons are based on:
the direction of action potential conduction
Types of functional classes of neurons
Sensory (afferent) neurons
Motor (efferent) neurons
Interneurons
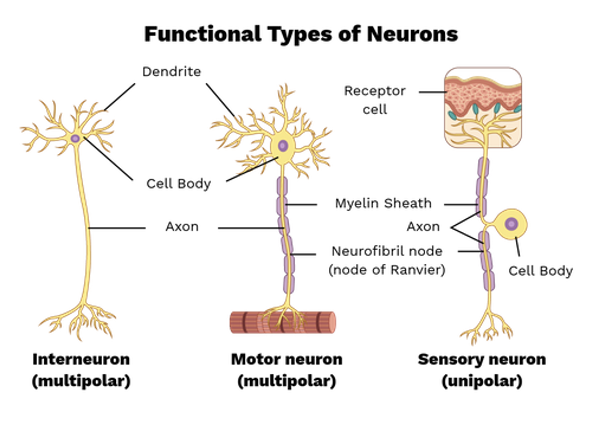
Sensory (afferent) neurons
conduct action potential toward CNS
Motor (efferent) neurons
conduct action potentials away from the CNS toward muscles or glands
Interneurons
conduct action potentials within the CNS
Structural classes of neurons
based on the number of dendrites
Types of structural classes of neurons:
Multipolar neurons
Bipolar neurons
Pseudo-unipolar neurons
Anaxonic neurons
Multipolar neurons
many dendrites and a single axon
dendrite number vary with varying branching
motor neurons of the PNS and most neurons within the CNS
Bipolar neurons
one dendrite and one axon
dendrites are often specialized to receive stimulus
axons conduct action potentials
located in sensory organs (retina of the eye, nasal cavity)
Pseudo-unipolar neurons
single process exits teh cell body and divides into two branches that work as a single axon
peripheral process
extends to the periphery and has dendrites that act as sensory receptors or communicate with sensory receptors
central process
extend to the CNS
most sensory neurons
Anaxonic neurons
do not have axons, only dendrites
found within the brain and retina
communicate using only graded potentials
Glial Cells of the CNS
Astrocytes
Ependymal cells
Microglia
Oligodendrocytes
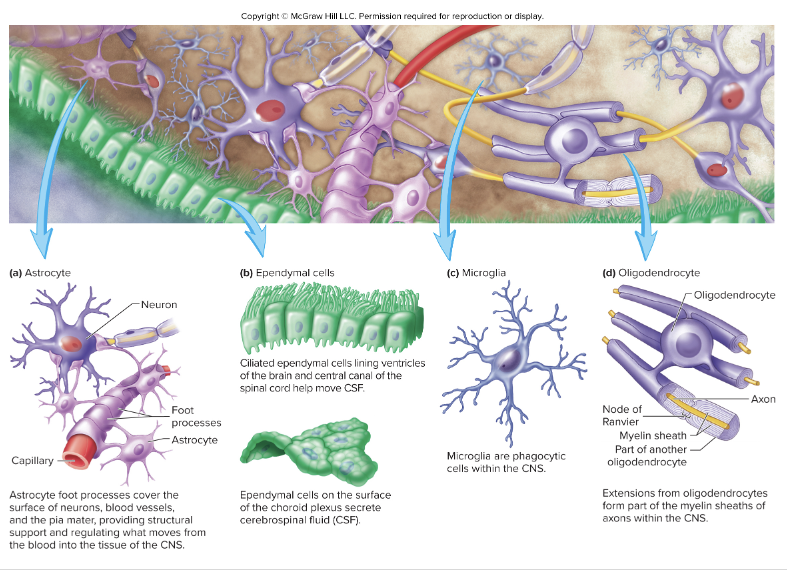
Glial Cells of the CNS: Astrocytes
Cytoplasmic processes extending from cell body
Foot processes cover blood vessels, neurons, and pia mater
Regulate the composition of extracellular brain fluid
produce chemicals that promote formation of tight junction between endothelial cells of capillaries to form the blood-brain barrier
Blood-brain barrier
Play a role in response to tissue damage in CNS
Reactive astrocytosis
Promote development of synapses and help regulate synaptic activity by synthesizing, absorbing, and recycling neurotransmitters
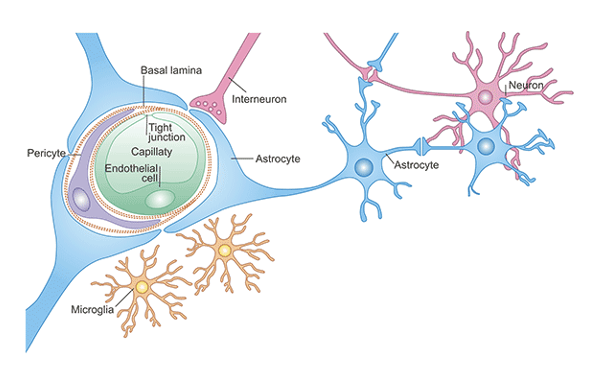
Blood brain barrier
controls substances that pass from blood into the brain and spinal cord
protects neurons from toxins
lets nutrients and waste products to be exchanged
prevents fluctuations in blood composition
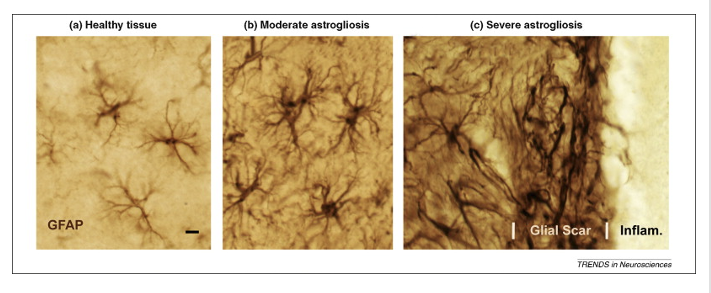
Reactive astrocytosis
caused by injuries in the CNS
astrocytes wall off injury site
limit spread of inflammation
limit regeneration of axons on injured neurons
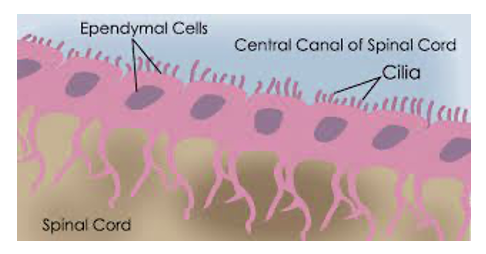
Glial Cells of the CNS: Ependymal Cells
Line ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord
Choroid plexuses
specialized ependymal cells and blood vessels located in regions of the ventricles
secretes cerebrospinal fluid
May of cilia to move CSF
Extension of the basal surface extedn deep into brain and spinal cord
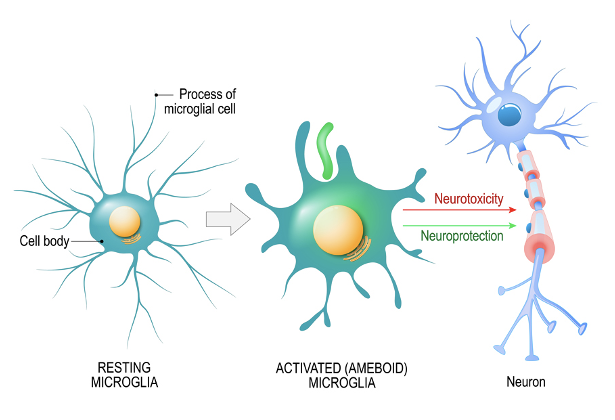
Glial Cells of the CNS: Microglia
CNS specific immune cells
Become mobile and phagocytic in response to inflammation
phagocytize necrotic tissue, microorganisms, and other foreign substances
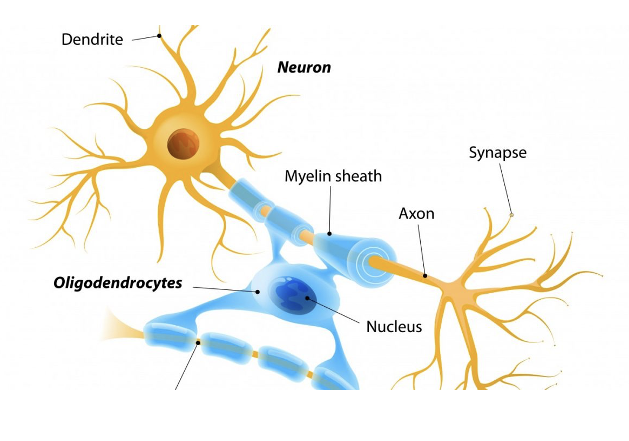
Glial Cells of the CNS: Oligodendrocytes
Form the myelin sheath
Cytoplasmic extension wrap around multiple axons
Insulate axons
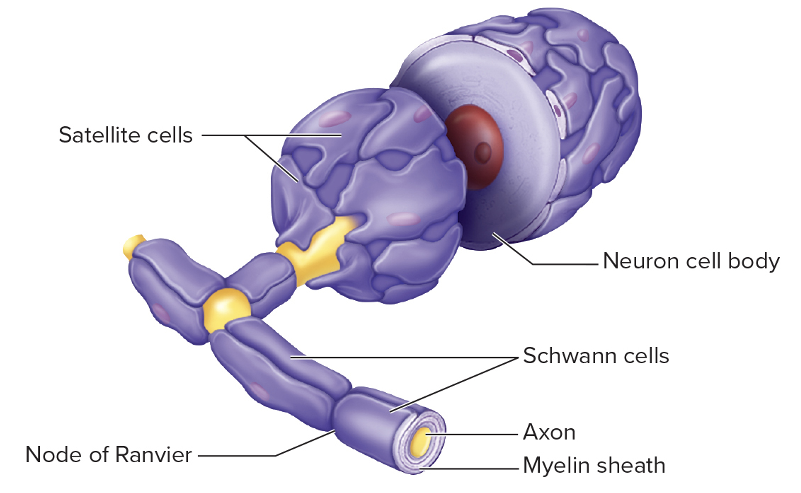
Glial Cells of the PNS
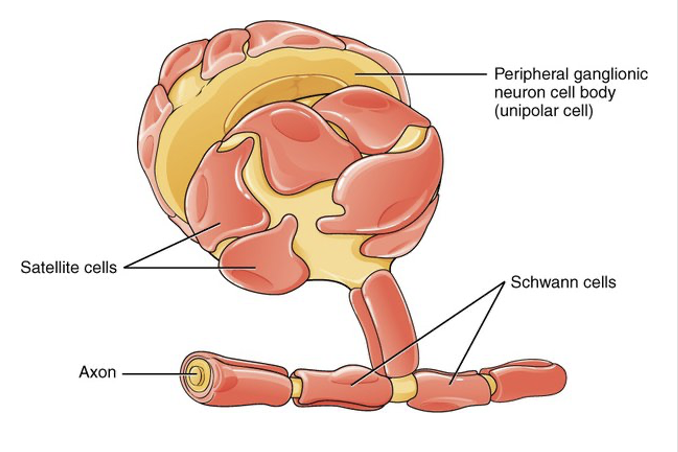
Schwann cells
Satellite cells
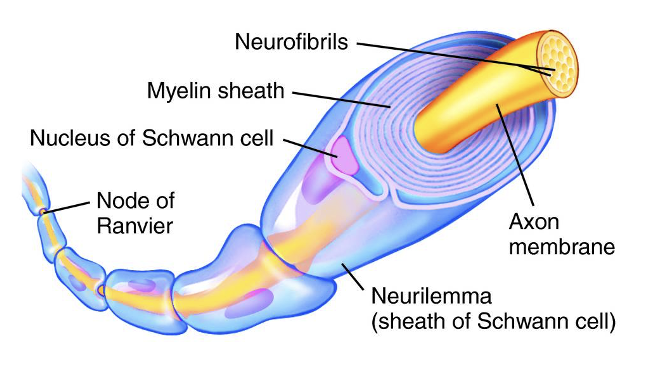
Schwann cells
Form the myelin sheath
Schwann cell wraps around only one axon
Neurilemma
outermost layer of each Schwann cell
contains majority of Schwann cell cytoplasm, nucleus, and organelles
Satellite cells
Surround neuron cell bodies in sensory and autonomic ganglia
Give support and nutrition
Protects neurons from heavy metal poisons
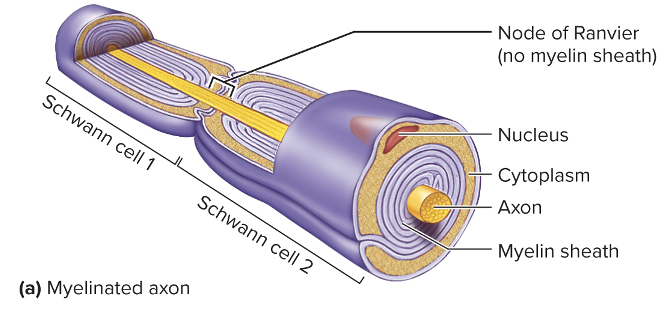
Myelinated Axons
Schwann cells (PNS) or oligodendrocytes (CNS) wrap around axons
Forms layers of phospholipids with small amounts of cytoplasm
Give myelinated axons a white appearance
Nodes of Ranvier- gaps in the myelin sheath
Schwann cells or oligodendrocytes extend across and connect
Protect and electrically insulate the axons
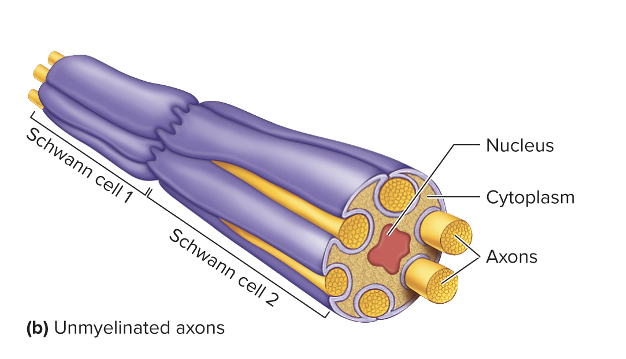
Unmyelinated Axons
Not devoid of myelin
Axons rest in invaginations of Schwann cells or oligodendrocytes
Protects axons
Development of Myelin Sheath
begins in late fetal development
continues rapidly until end of first year after birth
slows and continues after
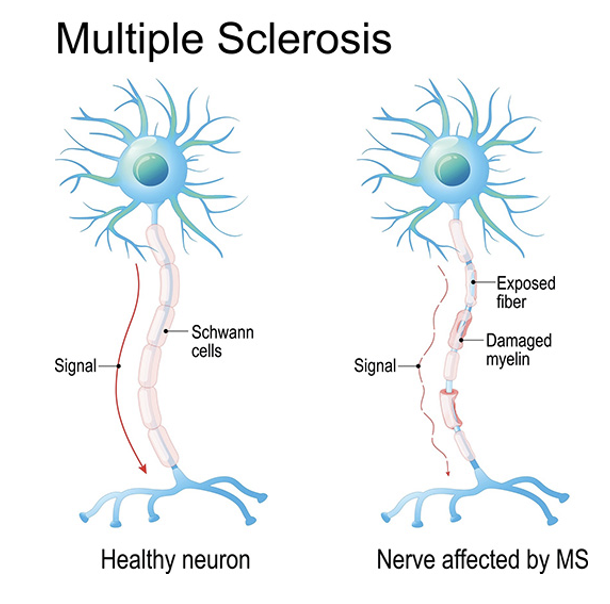
Multiple sclerosis
chronic disease of the CNS
gradual loss of myelin sheath
slows action potential transmission
impairs control of skeletal and smooth muscle