Modern Western Civilizations Final Terms Prep
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
short answer terms
Berlin Blockade
what: a 1948 Soviet attempt to cut off access to West Berlin, forcing the Allies to abandon the city.
importance: highlighted the competing economic and ideological visions for post-war Europe. The blockade helped to align West Berlin with the United States and Britain as the major protecting powers. It also contributed to the growth of the Cold War and the increased division between East and West Germany.
quantum theory
What: a scientific framework that explains the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic level, proposing that energy exists in discrete packets called "quanta," fundamentally changing our understanding of the universe by introducing concepts like wave-particle duality and the probabilistic nature of quantum events
importance: this concept really impacted science and technology at the time. it change the way scientist thought and created a new framework for new research.
Voltaire
What: His ideas and criticism of the social order were a key inspiration for the French Revolution beginning in 1789. he was a writer throughout the enlightenment and he greatly impacted those ideas
importance: his ideas impacted the French and American revolutionary ideas. and obviously the enlightenment
Enabling Acts
What: allowed the Reich government to issue laws without the consent of Germany's parliament, laying the foundation for the complete Nazification of German society.
importance: the importance of this was that it lead to complete nazi-ism in Germany and it took away democratic power in Germany to put into he hands of one man which lead to hitlers dictatorship.
Sigmund Freud
What: "the grandfather of modern psychology" he introduced psychoanalysis.
importance: he revolutionized how we think and treat mental disorders. also created psychoanalysis.
cottage industry
What: refers to a small-scale manufacturing system where individuals produce goods at home, often using basic tools, primarily before the Industrial Revolution. (women making textiles at home)
importance: was a way for rural households to earn more economic freedom. after industrialization in the US women were forced to move out of these home industries to work in factories due to the spinning Jenny. kids also had to being work early on due to industrialization and the home life of Americans (especially rural) change dramatically.
Self-determination
What: the right of a people to govern themselves and determine their own political status, particularly in the case of nations seeking independence from colonial powers.
importance: this concept was most prominently used to justify decolonization movements after World War I, significantly shaping the modern political map by enabling colonized nations to gain independence and form their own countries.
Congress of Vienna
What: a major diplomatic conference where European powers gathered to redraw the political map of Europe after the Napoleonic Wars
importance: restore stability and prevent future conflicts by re-establishing monarchies and balancing power between nations, essentially marking a significant turning point in European history by laying the foundation for a period of relative peace across the continent
Mohandas Gandhi
What: His non-violent resistance helped end British rule in India and has influenced modern civil disobedience movements across the globe.
importance: influenced non-violent protests around the world, brought attention to Indian and British conflicts
Otto Von Bismarck
What: Prussian statesman who is most recognized for unifying the various German states into the German Empire through a series of strategic wars,
importance: first Chancellor of Germany and earning the title "Iron Chancellor"; his policies, while initially maintaining peace in Europe, are also criticized for contributing to the rise of German nationalism which later played a role in the World Wars.
Suleiman the Magnificent
What: Sultan of the Ottoman Empire who reigned from 1520 to 1566, considered a pivotal figure in Ottoman history.
importance: significant military conquests, vast territorial expansion, and patronage of the arts, leading to a period often called the "Golden Age" of the Ottoman Empire.
D-Day
What: when Allied forces launched the largest amphibious invasion in history, landing on the beaches of Normandy, France, marking the beginning of the liberation of Western Europe from Nazi Germany during World War 2.
importance: provided a crucial foothold for the Allies on the European continent, ultimately contributing to the defeat of the Axis powers and the end of the war in Europe.
Glasnost
What: taken to mean increased openness and transparency in government institutions and activities in the Soviet Union
importance: allowing Soviet citizens to discuss publicly the problems of their system and potential solutions. big because no the gov. could be criticized and it gave the people more power.
Deism
What: a form of christianity that believed god created the universe, but hasn't intervened in human affairs since biblical times.
importance: prominent force in the enlightenment and influenced some ideals of it like rationality. it lead to ideas of religious freedom and a rejection to orthodox Christianity.
Bretton Woods
What: an international financial conference that established a world bank to offer loans to industrializing nations and loans for other needs
importance: significantly impacted global economics by creating a system of fixed exchange rates between major currencies, anchored to the US dollar which was pegged to gold, and by founding the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank
Scramble for Africa
What: a period in the late 19th century where European powers rapidly colonized and divided most of the African continent amongst themselves
importance: leading to the arbitrary drawing of borders that often ignored existing ethnic and tribal boundaries, with lasting impacts like ongoing conflicts and instability in many African nations today; this process was largely facilitated by the Berlin Conference of 1884 where European countries negotiated their territorial claims without any African representation
Thirty years war
What: a devastating conflict fought primarily in Central Europe from 1618 to 1648, initially sparked by religious tensions between Catholics and Protestants within the Holy Roman Empire, but eventually evolving into a wider power struggle between European nations
importance: impact on the political landscape by significantly weakening the Habsburg dynasty and establishing the principle of state sovereignty through the Peace of Westphalia
Dawes Plan
What: a financial agreement designed to ease the burden of war reparations on Germany following World War I, allowing them to make staggered payments and receive foreign loans to stabilize their economy, effectively ending the crisis caused by the French occupation of the Ruhr region
importance: temporarily removed the reparations that Germany owed to the allied forces for ww1. and improved global economics until the US went into the depression.

Auschwitz
What: a concentration camp in ww2 in Germany. this concentration camp housed thousands and thousands of jewish prisoners. here the prisoners were killed if they were no good for work, or killed once they could no longer work. they performed experiments on prisoners and gas chambers were used to mechanized mass murders.
importance: the gates of Auschwitz read "work will set you free" this was used to trick prisoners into working for germanys economy while being tortured, underfed, experimented on, and eventually executed. this camp was the biggest example of concentration camps in Germany and they were kept secret from eh rest of the world which is why it took so long for the rest of world to come in and retaliate. it was a ver horrific place that impacted jews the most throughout the war.
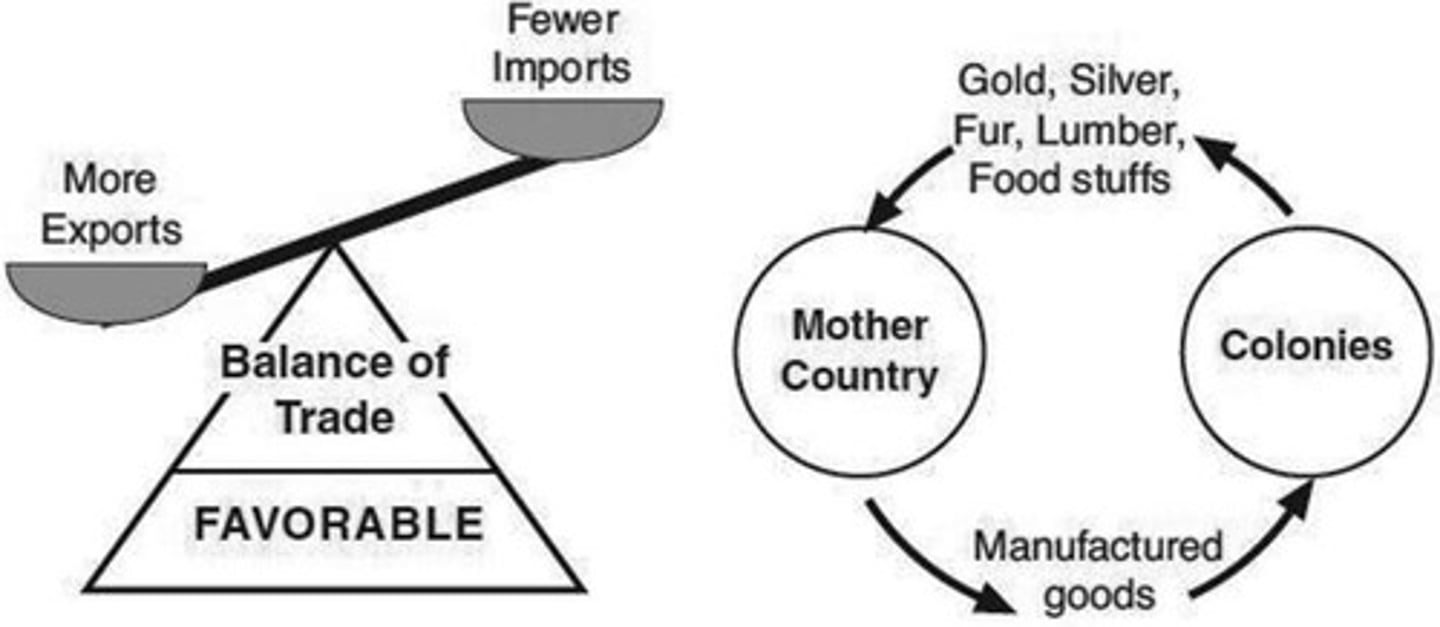
Mercantilism
What: a form of economic nationalism that sought to increase the prosperity and power of a nation through restrictive trade practices.
importance: fueling European colonization, contributing to tensions between colonial powers and their colonies (like the American Revolution), and promoting the development of the transatlantic slave trade to acquire raw materials from colonies
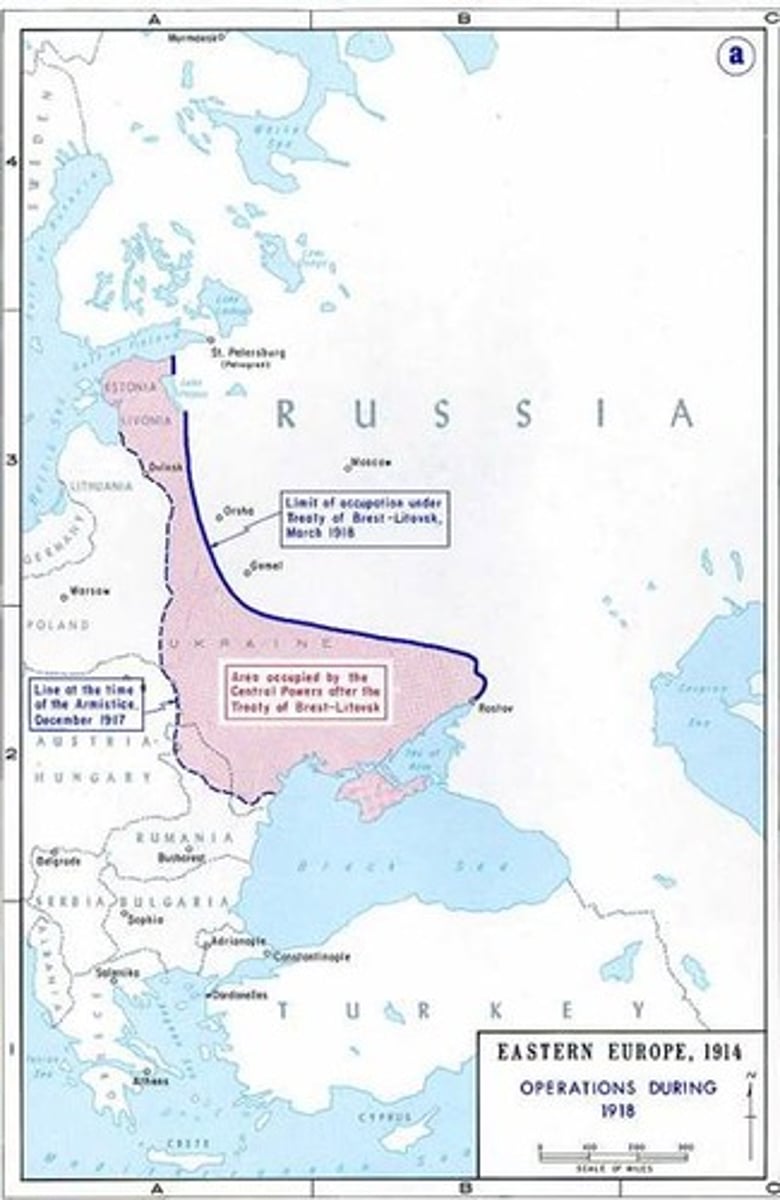
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
What: marked Russia's final withdrawal from World War I and resulted in Russia losing major territorial holdings
importance: political landscape of Eastern Europe following the war.
Isabella Beaton
What: a writer who is known for her book Mrs. Beeton's Book of Household Management. Her book was a guide for middle-class women on how to run a household, and it was a powerful force in the shaping of Victorian domesticity.
importance: considered a strong influence in the building or shaping of a middle-class identity of the Victorian era.
Karl Marx
What: best known for his theories that led to the development of Marxism. His ideas also served as the basis for communism
importance: Marx's ideas have had a profound impact on social and political thought, influencing labor movements, socialist and communist parties, and inspiring revolutions in many parts of the world.

Keynesian Economics
What: advocates for active government intervention in the economy, primarily through fiscal policy like increased government spending, to manage aggregate demand and stabilize the economy during recessions by stimulating employment and economic activity, particularly when private sector spending is low
importance: economic policy, particularly after the Great Depression, by legitimizing deficit spending to combat unemployment and economic downturns
Estates General
What: a political assembly in pre-revolutionary France that brought together representatives from the three social classes (clergy, nobility, and commoners) to advise the king on matters of taxation and policy
importance: due to the structure where each estate had only one vote, the Third estate (commoners) was often outvoted, leading to its pivotal role in sparking the French Revolution when they formed the National Assembly in 1789, marking the beginning of major political change in France
Maxim Gun
What: the first practical, fully automatic machine gun, utilizing the recoil energy from each shot to reload and fire the next, allowing for sustained rapid fire
importance: changed the nature of warfare by enabling a single weapon to inflict massive casualties on enemy forces, particularly during World War I where it was widely used and contributed to the development of trench warfare tactics
Edmund Burke
What: Renowned for his seminal work, Reflections on the Revolution in France (1790), his critique of the radical shifts brought about by the French Revolution and his advocacy for tradition, gradual reform, and the preservation of established institutions have shaped the foundation of modern conservatism.
importance: conservatism
Pablo Picasso
What: a dominant and influential artist in the first half of the 20th century. He is known for pioneering Cubism, inventing collage, and making contributions to Symbolism and Surrealism.
importance: modern art and modernism ideas. Picasso devoted himself to an artistic production that contributed significantly to the whole development of modern art in the 20th century
Jean-Paul Sartre
What: A leading figure in 20th-century French philosophy, was one of the leading voices of existentialism, a philosophical movement emphasizing individual freedom, responsibility, and the inherent meaninglessness of life. His famous line “existence precedes essence” means that humans are not born with a predetermined purpose—we must create our own meaning through choices and actions.
importance: Existentialism emerged strongly after World Wars I and II, during a time when people questioned traditional values, religion, and the meaning of life.
It addressed the deep sense of disillusionment and alienation people felt in a world marked by mass violence, technology, and instability.
Napolieonic Code
What: a comprehensive legal system implemented by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1804 that codified various branches of law including property, family, and commercial matters, effectively abolishing feudal privileges and establishing the principle of equality before the law across France
importance:influencing legal systems worldwide by spreading the ideals of the French Revolution through the territories Napoleon conquered; it is considered a landmark in the development of modern civil law systems.
essay prompt points
Hitler VS. Napoleon key points to consider:
- sim: both took over a large sum of Europe and implemented control. they were very authoritarian but charismatic leaders with extreme military expertise
-sim: both implemented control of speech. you could not criticize the gov.
-sim: nationalism. both leaders implemented strong nationalistic ideals and it aided in there support and is why there were able to reign control for so long.(the anti-criticism thing also helped there support)
- Dif: ideologies- Napoleon strived for individual glory and control while Hitler acted out not racism and and superiority
- Dif: brutality- while Napoleons wars ended w/ large death rates it Hitlers brutality and torture to jews was unparalleled
- Dif: legacy- Despite his military defeats, Napoleon is often viewed as a complex historical figure with some positive contributions to legal and administrative reforms, while Hitler is universally condemned for his horrific crimes.
scientific revolution key points to consider:
- Discoveries: astronomy, physics, and biology had extreme discoveries made during the time period.
- Figures: Nicolaus Copernicus, Galileo Galilei, Johannes Kepler
- Impact: The Scientific Revolution challenged traditional beliefs about the natural world, leading to a shift in thinking and paving the way for further scientific advancements and the Enlightenment era.
- Time Period: 16th and 17th centuries
- Inventions: telescope, microscope, barometer, thermometer, and pendulum clock were developed during this time.
Liberalism and conservatism how it has changed:(key points)
liberal ideals:
free market
personal freedoms
natural rights
Conservative ideals:
free market
hierarchy
natural rights (for some people)
socialist ideals:
controlled economy(market)
gov. control
natural rights
- all agree with rights, and free market. we doing have socialism anymore, so think of liberalism and how it has changed the world vs. conservatism.