Biology 🧬 Unit 7 - lesson 5 - the phloem
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/34
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
is the phloem a living tissue
Yes
2
New cards
The phloem has a relatively high rate of ……. ……. During transport
Aerobic respiration
3
New cards
What 2 main parts Does phloem tissue consist of
Sieve tubes and companion cells
4
New cards
Describe the features of sieve tubes
Has cellulose cell walls which do not become lignified
Made from living cells called sieve tube elements, allows long-distance transport of organic compounds such as sucrose, amino acids etc.
Made from living cells called sieve tube elements, allows long-distance transport of organic compounds such as sucrose, amino acids etc.
5
New cards
How are sieve elements arranged
Joined/arranged end to end vertically to form a long, narrow, continuous tube
Their end walls are known as ‘sieve plates’, these are large holes that perforate (pierce) the sieve tube
Their end walls are known as ‘sieve plates’, these are large holes that perforate (pierce) the sieve tube
6
New cards
Where the end walls of 2 sieve elements meet, a …… ….. is formed. This is made up of the walls of both elements perforated by large pores that remain open. The walls are thin thereby reducing ……., allowing the easy entry of water. This also stops ‘bulging’ of the vessels due to a build-up of pressure
These pores are easily visible with a good light microscope
These pores are easily visible with a good light microscope
Sieve plate
Resistance
Resistance
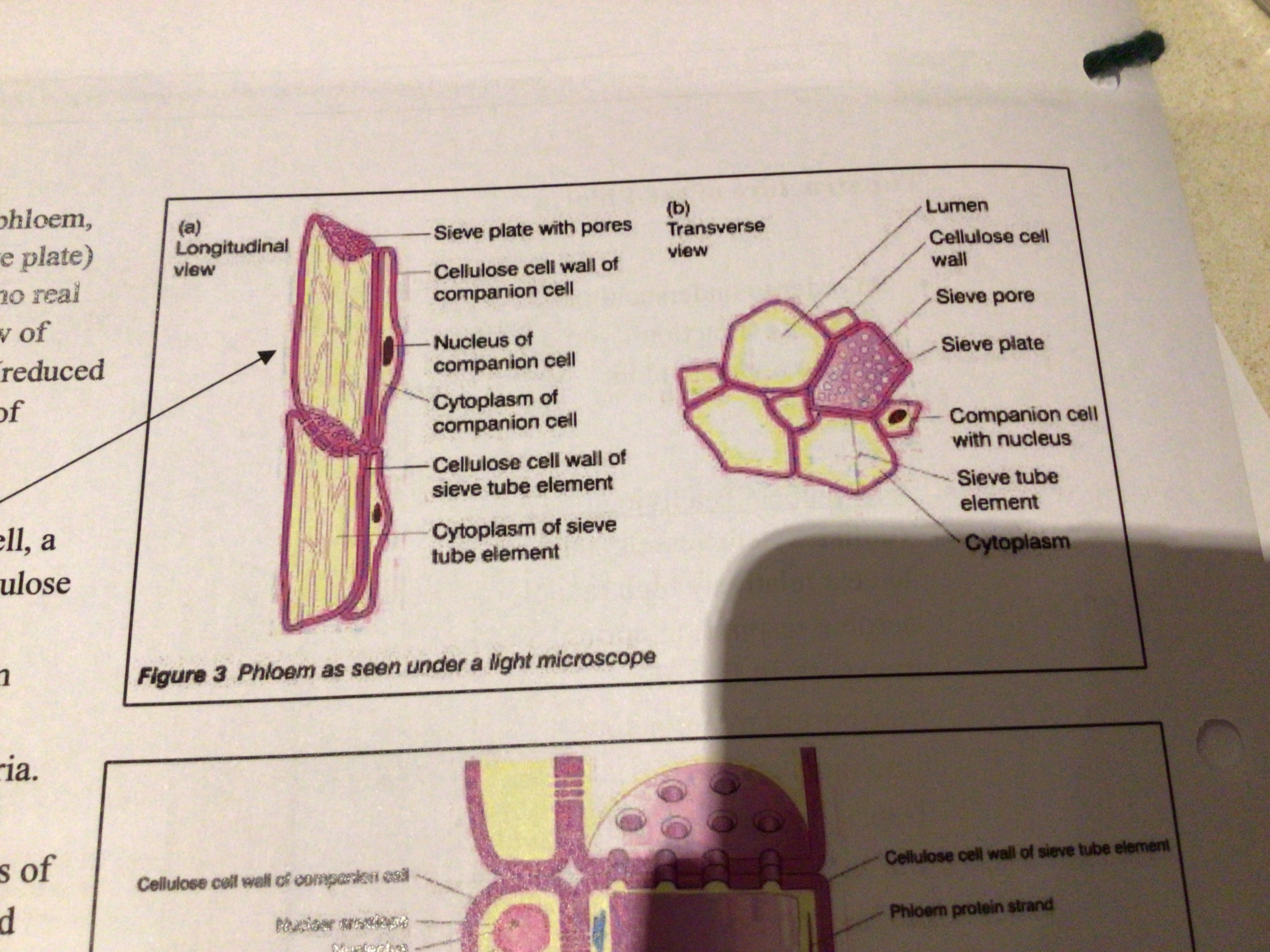
7
New cards
What organelles/elements of a ‘normal’ plant cell do sieve elements have
A cellulose cell wall, a cell surface membrane, cytoplasm containing endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria
No nucleus, or ribosomes
No nucleus, or ribosomes
8
New cards
What do sieve plates do to the walls of sieve elements
Sieve plates hold the walls of sieve elements together and prevent them from bursting due to bulging
9
New cards
How much cytoplasm do sieve elements contain
Very little, it only forms a thin layer lining the inside of the wall of the cell
10
New cards
What is each sieve tube connected to
At least one companion cell
11
New cards
How are sieve tubes connected to companion cells
By strands of cytoplasm called plasmodesmata that pass through narrow gaps (pits) in the cell walls
12
New cards
What does assimilation mean in biology
The process in which living organisms integrate the nutrients from various external resources to their body and utilises them to satisfy the energy demands and nutritional requirements to stay alive eg, sugars and amino acids are sometimes called assimilates
13
New cards
What organelles do companion cells have
Many mitochondria, a nucleus for gene coding, a nucleolus to synthesis ribosomes, and a lot of RER for protein synthesis
14
New cards
What is the special type of companion cell at the tips of veins in the leaf called and what features do they have
Transfer cells - they have very folded cell walls and membranes - their large SA increases rate of transfer of sucrose into the sieve tube elements
15
New cards
What is the liquid inside phloem sieve tubes called
Phloem sap
16
New cards
The contents of sieve tubes are under very high …..
pressure
17
New cards
If a sieve tube is cut, within minutes the sieve plate is properly sealed with what carbohydrate?
callose, a process sometimes called ‘clotting’
18
New cards
Is translocation active or passive
Has both components
19
New cards
What is translocation
how manufactured foods (assimilates) are moved from sources to sinks (where they are transported to, roots, flowers) to be used or stored for later use
20
New cards
Give an example of translocation using photosynthesis
Photosynthesis occurs in the leaves (source) and produces the sugar glucose which is converted into the disaccharide sucrose for transport
This sugar is needed in all parts of the plant (sinks) for respiration, thus translocation of molecules (here sucrose) in the phloem can be done in all directions around the plant (carried in sieve tube elements)
This sugar is needed in all parts of the plant (sinks) for respiration, thus translocation of molecules (here sucrose) in the phloem can be done in all directions around the plant (carried in sieve tube elements)
21
New cards
What is one way plants appear to load sucrose into the phloem sieve tubes
Process of apoplastic loading
22
New cards
What is apoplastic loading
The process of loading sucrose into the sieve tube elements
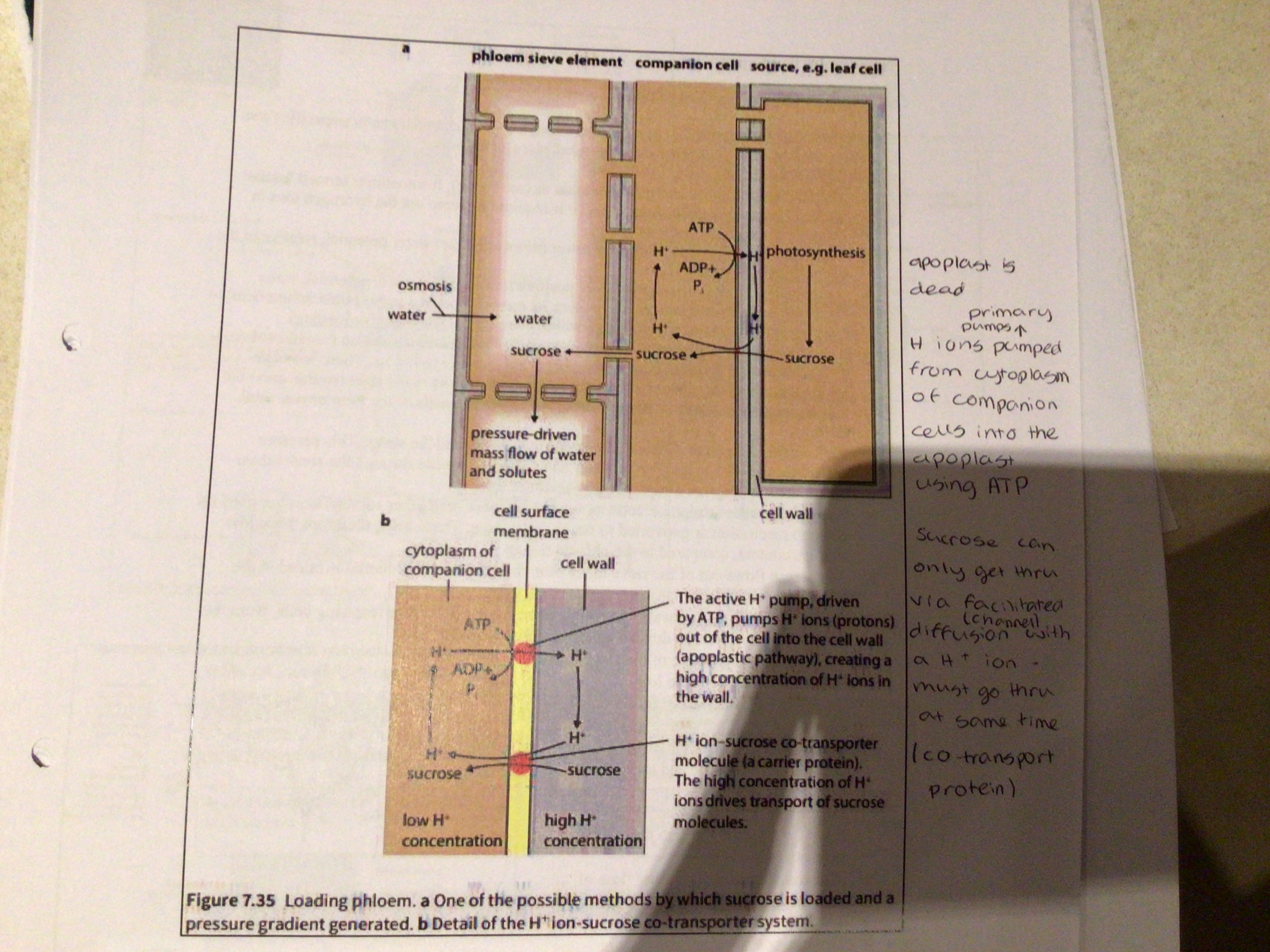
23
New cards
Where is sucrose manufactured
in cells with chloroplasts from the products of photosynthesis
24
New cards
Apoplastic loading 1:
H+ ions are actively pumped from the cytoplasm of …….. cells into the apoplast (cell walls of companion cells) using ATP
The pumps that do this are known as …….. ……..
This sets up a concentration gradient of hydrogen ions between the cell wall and interior of companion cell
H+ ions are actively pumped from the cytoplasm of …….. cells into the apoplast (cell walls of companion cells) using ATP
The pumps that do this are known as …….. ……..
This sets up a concentration gradient of hydrogen ions between the cell wall and interior of companion cell
Companion
Primary pumps
Primary pumps
25
New cards
Apoplastic loading 2:
As hydrogen ion concentration builds up in cell walls of companion cells, these hydrogen then flow down a concentration gradient, through ……….. proteins (………. Diffusion) back into companion cells
\
The sucrose molecules are co-transported along with the hydrogen ions in a process of …………
The carrier proteins are thus known as co-transport proteins or ……… …….
As hydrogen ion concentration builds up in cell walls of companion cells, these hydrogen then flow down a concentration gradient, through ……….. proteins (………. Diffusion) back into companion cells
\
The sucrose molecules are co-transported along with the hydrogen ions in a process of …………
The carrier proteins are thus known as co-transport proteins or ……… …….
co-carrier, facilitated
\
Co-transport, secondary pumps
\
Co-transport, secondary pumps
26
New cards
Both ……. And protons need to pass together to use the co-transport protein and travel through it
sucrose
27
New cards
Apoplastic loading 3:
This co-transport movement is ………….. the concentration gradient for sucrose and this movement is powered by the ‘passive’ flow of protons by …………. ………… back into the companion cell along a proton concentration gradient through the co-transport proteins
\
As sucrose solution accumulates in the companion cells, sucrose molecules then move via (passive) simple diffusion through the ……….. from the companion cell into the phloem sieve tube element
This co-transport movement is ………….. the concentration gradient for sucrose and this movement is powered by the ‘passive’ flow of protons by …………. ………… back into the companion cell along a proton concentration gradient through the co-transport proteins
\
As sucrose solution accumulates in the companion cells, sucrose molecules then move via (passive) simple diffusion through the ……….. from the companion cell into the phloem sieve tube element
against, facilitated diffusion
\
Plasmodesmata
\
Plasmodesmata
28
New cards
Apoplastic loading 4:
The accumulation (active loading) of sucrose in the phloem tissue …….. the water potential and water (from the xylem) follows towards the sucrose, diffusing down a water potential gradient into the Phloem. This creates a high ………… pressure in the sieve tubes of the source area
The accumulation (active loading) of sucrose in the phloem tissue …….. the water potential and water (from the xylem) follows towards the sucrose, diffusing down a water potential gradient into the Phloem. This creates a high ………… pressure in the sieve tubes of the source area
lowers
Hydrostatic
Hydrostatic
29
New cards
What is mass flow
The bulk movement of substance through a given channel/area in a specific time
30
New cards
Active loading/apoplastic loading causes the sieve tube elements to have a lower (more negative) water potential, relative to the accompanying xylem
As the xylem has a much higher water potential water moves from the xylem into the ………. ……. Via osmosis creating a high hydrostatic pressure within them at the site of active loading
As the xylem has a much higher water potential water moves from the xylem into the ………. ……. Via osmosis creating a high hydrostatic pressure within them at the site of active loading
sieve tubes
31
New cards
The principle of the pressure flow hypothesis is that the sugar solution flows down a hydrostatic pressure gradient. There is a …….. hydrostatic pressure in sieve elements near mesophyll cells in the light (source area) but low hydrostatic pressure in elements near starch storage cells of the stem or root (sink areas)
This creates a pressure difference between the source and sinks causing mass flow of water and dissolved solutes through sieve tubes from high to low pressure areas
This creates a pressure difference between the source and sinks causing mass flow of water and dissolved solutes through sieve tubes from high to low pressure areas
High
32
New cards
Why do respiring cells (sinks) have low sucrose content compared to the phloem tissue
Sucrose is used up through respiration or converted to starch for storage
33
New cards
As sucrose flows out of the sieve tubes near sinks, the water potential is ………. At the phloem tissue near sinks
Due to this increased water potential water moves into these respiring cells from the sieve tubes by osmosis
The hydrostatic pressure of the sieve tubes in this region in thus ……..
As a result of water entering the sieve tube elements at the source and leaving at the sink there is a high hydrostatic pressure at the …… and a low one at the ……
Thus there is a mass flow of sucrose solution down this hydrostatic pressure gradient
Due to this increased water potential water moves into these respiring cells from the sieve tubes by osmosis
The hydrostatic pressure of the sieve tubes in this region in thus ……..
As a result of water entering the sieve tube elements at the source and leaving at the sink there is a high hydrostatic pressure at the …… and a low one at the ……
Thus there is a mass flow of sucrose solution down this hydrostatic pressure gradient
Raised
Low
Source, sink
Low
Source, sink
34
New cards
The mass flow is caused by drops in ……… pressure at the sink as the sugar molecules are removed. This generates the next push of materials toward the sink
Turgor
35
New cards
What are the similarities and differences between xylem vessels and sieve tubes
Sieve tubes are made of living cells (cell membranes needed to not leak sucrose)
Xylem vessels have lignified walls whereas sieve tubes do not
In both liquid moves by mass flow down a pressure gradient through tubes formed by cells stacked end to end
Xylem vessels have lignified walls whereas sieve tubes do not
In both liquid moves by mass flow down a pressure gradient through tubes formed by cells stacked end to end