USC BISC 150
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Three components of cell theory
1. a cell is the smallest unit of life
2. cells make up all living things
3. new cells can arise only from preexisting cells
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
prokaryotes: structurally simpler, typically smaller, no organelles
eukaryotes: contain membrane-bound organelles (make up plants, animals)
How large are prokaryotes?
1-10 micrometers across
How large are eukaryotic cells?
10-100 micrometers across
What constrains the upper limit of cell size?
surface to volume ratio
describe the composition of the plasma membrane of a cell.
phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
What drives passive
transport across a cell membrane?
diffusion (high concentration to low concentration)
What drives active transport?
substance moves with the aid of a carrier protein and energy
What happens to red blood cells in an environment with a relatively higher salt concentration?
hypertonic solution: water rushes out of cell and leaves it shriveled
What happens to red blood cells in an environment with a relatively the same salt concentration?
Isotonic: stays in normal equilibrium
What happens to red blood cells in an environment with a a relatively lower salt concentration?
Hypotonic: water moves into the cell eventually causing it to burst (lysed)
What are the various roles played by proteins at the site of a synapse between two neurons?
sodium-potassium pump, potassium channel, sodium channel
How do proteins interact with opioids?
opioids bind to receptor proteins on neurons and inhibit the release of neurotransmitters that transmit signals for pain
What is the function of the nucleus?
contains cell's genetic information, controls cellular structure and function, contains a code for the production of proteins
What is the function of
mitochondria?
provide energy for the cell. cellular respiration occurs here
When did photosynthesis evolve?
by 2.7 bya, increase in atmospheric oxygen, chloroplasts were utilized in plants to convert light energy into sugar
What were the consequences for the environment and organisms living on Earth at the time?
evolution of cellular respiration (using O2 in the process of harvesting energy store in organic molecules) mitochondria is needed for this
How does the theory of endosymbiosis explain the origin of mitochondria? What evidence exists supporting this idea?
two independent bacterium, one engulfs the other and that one now lives inside the other. Beneficial for both and the internal bacteria is passed down generations.
Evidence:
-similarities in inner membrane structure and functions
-division is similar in these organelles and many prokaryotes
- DNA is short and circular
-transcribe and translate all their own DNA
-Ribosomes are more similar to prokaryotic than eukaryotic ribosomes
How is mitochondrial DNA inherited?
from the mother
What are some examples of macromolecules?
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
which monomers are macromolecules comprised of?
monosaccharides (carbs), fatty acids (lipids), nucleotides (nucleic acids), amino acids (proteins
Where in the body are nutrients absorbed into the bloodstream?
small intestine
What are the major chemical
elements found in the body?
oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen (almost always form covalent bonds)
What type of bonds do the chemical elements in the body almost always form with each other?
very strong covalent bonds
How is glucose processed
after absorption?
travels through liver before going to heart for circulation
What is the role of insulin?
-helps transport glucose from the blood into the cells
-stimulates the liver and muscles to take up glucose and convert it into glycogen (makes blood sugar lower)
-secreted by the pancreas before entering the blood stream
What is the role of glucagon?
-stimulates the breakdown of glycogen to make glucose available to cells in the body (makes blood sugar higher)
What is the relationship between ATP and ADP?
ATP, a high power molecule, converts to low-power ADP to continue the process of glycolysis (ATP has the extra phosphate group for extra energy)
Very generally speaking, how does cellular respiration generate ATP from the starting material
of glucose?
electrons from glucose are sent down the electron transport chain by NAD+ and FAD which turn into NADH and FADH2
What is the purpose of the proton (H+) concentration gradient created across the mitochondrial
membrane?
the flow of H+ back across the membrane powers ATP synthesis
How does ATP synthase function?
enzyme that transports a proton down the gradient and uses the energy to complete the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP
What process occurs in the absence of oxygen that still produces some ATP?
Fermentation
What causes
muscle pain after intense exercise?
Lactic Acid Fermentation
How do we define a tissue?
A group of cells that are similar in structure and perform a common function
What are the four types of tissues?
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
What are the various functions of each type of tissue?
Epithelial: covers body surfaces, lines body cavities and organs, and forms glands
Connective: serves as a storage site for fat, plays role in immunity, provides the body and its organs with protection and support
Muscle: responsible for body movement and for movement of substances through the body
Nervous: conducts nerve impulses from one part of the body to another
What is an example of where we might find each type of tissue?
Epithelial: kindney tubules, lining of mouth, esophagus, heart and blood vessels
Connective: tendons, ligaments, between muscles
Muscle: wall of heart, muscles attached to bones, muscles of digestive system
What are examples of connective tissue proper and specialized connective tissue?
Connective Proper:
-loose, areolar (between muscles, surrounding glands)
-loose adipose (fat) (underskin)
Dense (tendons ligaments)
Specialized Connective:
-cartilage (semisolid)
-bone (solid)
-blood (fluid)
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
How do the three types of muscle tissue differ in terms of location, structure, and control?
Skeletal: long cylindrical cells, muscles attached to bones, provides voluntary movement
Cardiac: Branching striated cells, wall of heart, contracts and propels blood through the circulatory system
Smooth: cells taper at each end, walls of digestive system, blood vessels, tubules of urinary system, propels substances or objects through internal passageways
integumentary system
Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail
Muscular System
powers and directs skeletal movement
endocrine system
regulates internal environment by secreting hormones that travel through the bloodstream to target areas
respiratory system
exchanges O2 and CO2 between the internal and external environmenr
digestive system
Breaks down nutrients from food into smaller molecules that can be used by cells
reproductive system
produces gametes (eggs and sperm) that form offspring ensuring survival of genes
skeletal system
support and protects, moves the body, stores minerals
nervous system
major regulatory system of the internal environment, senses changes, integrates and sends signals to effectors
cardiovascular system
transports nutrients, water, oxygen, hormones, wastes, and other materials within the internal environment
lymphatic system
drains excess fluid from tissues, cleans it, and returns it to the blood
urinary system
adjusts internal environment by excreting excess water, salt, and other substances
What are the demands of the body with respect to ultraviolet radiation? How does our skin
respond to these demands?
We require solar radiation for Vitamin D synthesis in the skin
How does skin pigmentation vary with latitude?
dark at equator for photoprotection
light at poles for vitamin D synthesis
In between: moderate levels of genetically determined pigmentation, with an enhanced ability to seasonally tan
Where is oxytocin produced?
posterior pituitary gland
What is the positive feedback loop in which it participates?
integrator (correction signals via oxytocin), effector stronger more frequent labor contractions), variable (fetus moves into birth canal) , sensor (feeds information via nerve fibers back to the brain)
Where is melanin produced? What controls its production?
melancytes, controlled by anterior pituitary
What is the importance of surface area for the respiratory system?
rate of oxygen diffusion is more efficient with more surface area
What is the importance of surface area for the digestive system?
ensure complete digestion and nutrient absorption.
How do we define homeostasis?
the relative constancy of the internal environment (sensor, control center, effector)
Generally speaking, how does our body maintain homeostasis?
sensor, control center, effector
positive and negative feedback loops
Where in the cell is DNA located?
nucleus and mitochondria
What is the form of a DNA molecule?
double helix
What are the four bases that comprise its interior?
adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine
Why do we refer to DNA replication as "semiconservative"?
each new helix contains one strand from the original helix from which it was copied
What is the relationship between DNA sequence and protein structure?
each gene tells the cell how to put together the building blocks for one particular protein, which in turn determines traits
What are the similarities between RNA and DNA?
DNA and RNA are both ribonucleic acids found in cells, and both are formed from nitrogenous bases
What are the differences between RNA and DNA?
different functions: DNA stores genetic material of an organism, and RNA conveys messages. Additionally, some of their nitrogenous bases are different. RNA contains uracil in place of DNA's thymine.
What are the three types of RNA discussed in lecture?
What are their specific functions?
mRNA: messenger RNA encodes amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
tRNA: Transfer RNA brings amino acids to ribosomes during translation
rRNA: Ribosomal RNA makes up the ribosomes along with ribosomal proteins (ribosomes translate mRNA)
What occurs during RNA processing?
putting a 5' guanine cap and a poly A tail on the 3' end prior to the mRNA leaving the nucleus
What is a point mutation?
a mutation affecting only one or very few nucleotides in a gene sequence.
What are "indels"?
insertion or deletion of a few base pairs
What is the effect of a missense mutation on the polypeptide being built?
switches one amino acid in the chain for another.
What is the effect of a nonsense mutation on the polypeptide being built?
a nonsense mutation results in a shorter chain because of an early stop codon.
What is the effect of a silent mutation on the polypeptide being built?
Silent mutations are base substitutions that result in no change of the amino acid or amino acid functionality
What is a frameshift mutation?
A frameshift mutation occurs when a protein is drastically altered because of an insertion or a deletion.
What is the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete?
somatic: all body cells except reproductive cells
gamete: a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization (conception) in organisms that sexually reproduce.
In humans, how many total chromosomes are present in each a somatic cell and a gamete?
somatic cell: 46 chromosomes (two chromosomes of each of 23 types)
Gamete: 23 chromosomes
Chomosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
Alleles
Different forms of a gene
Genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
What are the three different types of genotype for a simple Mendelian trait? To what phenotypes
do they correspond?
Homozygous dominant: two dominant alleles present.
Dominant phenotype present
Heterozygous: different alleles present
Dominant phenotype expressed
Homozygous recessive: two recessive alleles present
Recessive phenotype expressed
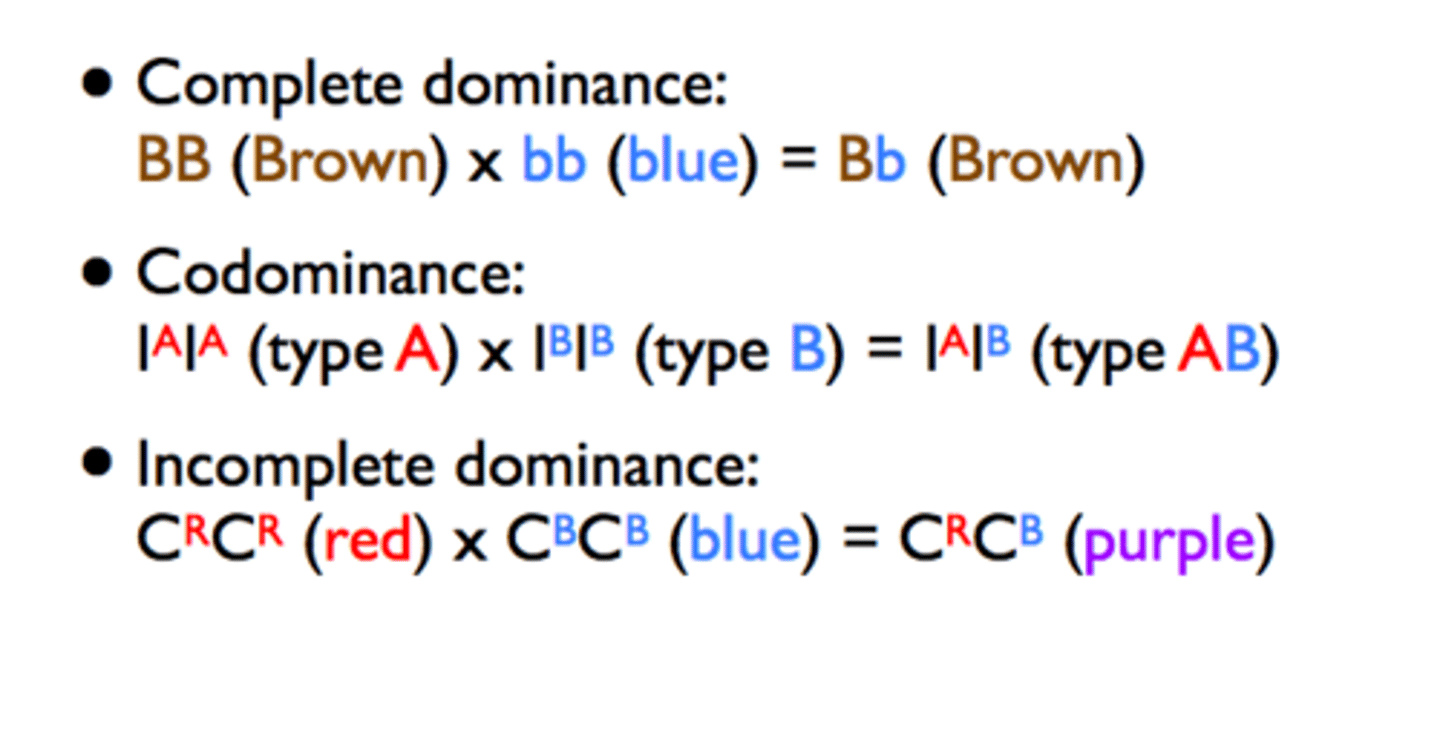
How does the phenotype of a heterozygote differ between complete dominance, codominance,
and incomplete dominance?
What are examples of each type of dominance?
What are the symptoms of Huntington's Disease?
-loss of mental faculties: irritability, depression, forgetfulness, impaired judgement, anxiety, aggressive outbursts
-loss of physical control: involuntary movements, difficulties with speech, swallowing, balance and walking
-Symptoms appear between ages 30-50
What is the genetic basis for HD?
Which chromosome?
Which form of inheritance?
What does the gene encode?
- autosomal dominant
-chromosome 4
-HD gene encodes for a protein huntingtin that directs delivery of vesicles to the outside of the cell
What is the form of the mutation for HD? Which cells are affected? What is the effect?
-Normally, the coding region contains the sequence CAG repeated again and again (~10-26 times)
-Individuals with HD have an abnormally high number of these CAG triplets (~40 or more)
-Disrupts protein function
-Accumulation of clumps of protein that become toxic
What treatments exist for HD?
there is no cure
treatments:
-antidepressants and antipsychotic drugs
-medication for movement disorders
-speech, physical, occupational, and psychotherapy
What are the symptoms of breast cancer?
Nipple retraction
Bleeding
Orange peel appearance
Dimpling (Paget's disease of the breast)
How does breast cancer begin?
initial tumor cell: one cell acquires mutations, causing loss of control of cell division.
cell divides more frequently than others
carcinoma in situ: tumor remains at its site of origin
cells of the tumor release growth factors to attract a blood supply
gain the ability to leave the other cells
spread to distant sites (metastasize)
Mutations in BRCA genes confer risks for what types of cancers?
high risk of:
-breast cancer
-ovarian cancer
-male breast cancer
-pancreatic cancer
-prostate cancer
What is the function of the BRCA genes?
tumor suppressor
What does it mean to say that a BRCA mutation is "dominant with incomplete penetrance"?
-one copy gives you a high risk of getting cancer, but doesn't guarantee that you will get it
-if the second copy becomes mutated and can't repair DNA breaks, this can lead to cancer
How does a mutation in BRCA predispose one to cancer?
a mutation in a tumor suppressor gene can promote cancer by taking the breaks off cell division
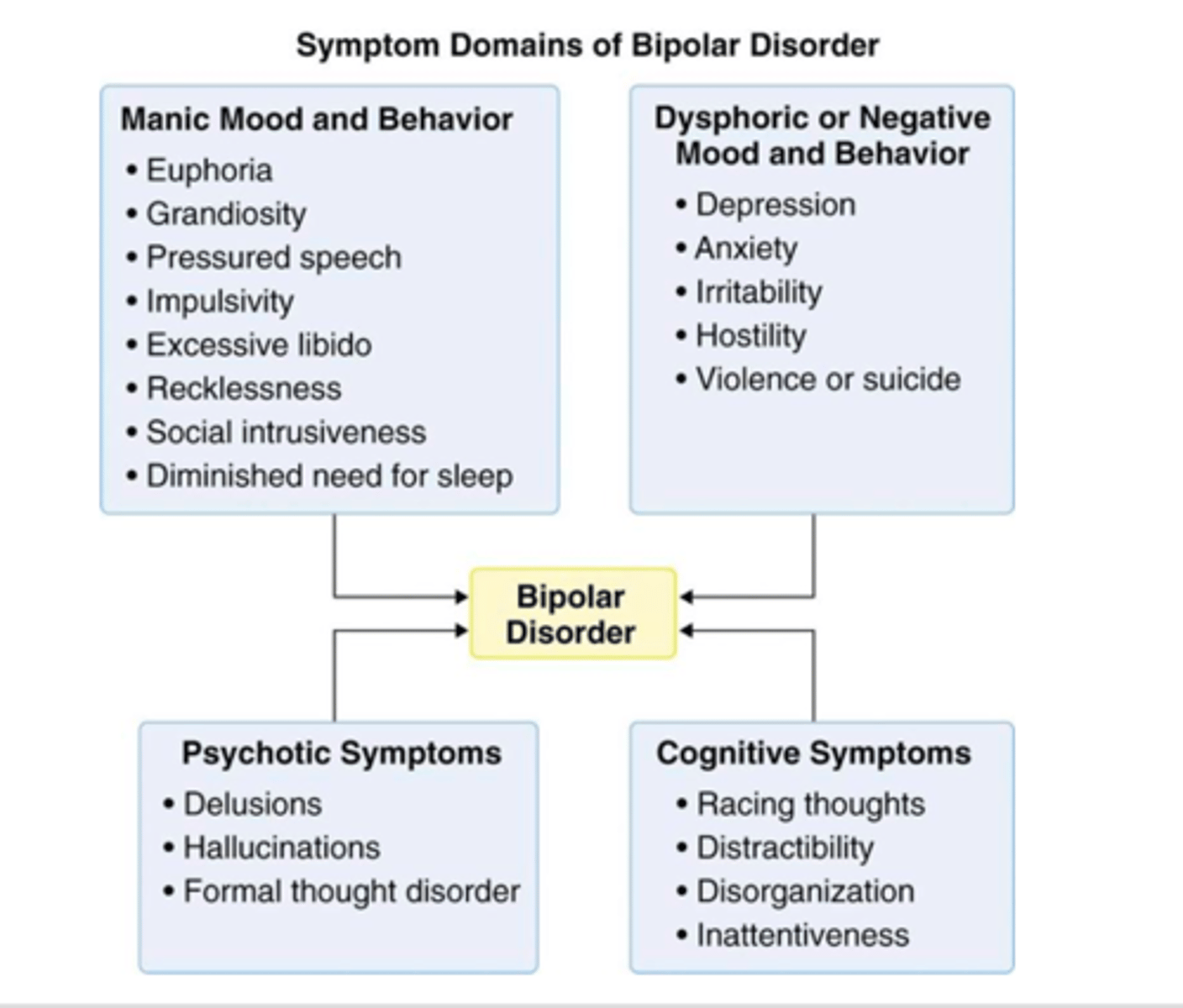
What are the symptoms of Bipolar Disorder? Why is it often misdiagnosed as depression?
often misdiagnosed as depression because the symptoms of BD are chronic and depressive
What suggests that there is a heritable genetic component to BD?
much higher risk of acquiring the disorder if you have a closer relative, who also has bipolar disorder
Candidate genes for BD are associated with which organ system?
expressed in brain tissue and are important for neuron growth, survival or signaling pathways
What is the difference between a benign and malignant tumor?
Benign: cells do not invade surrounding tissue or spread to distant locations. Can be removed completely by surgery
Malignant: do invade surrounding tissue and spread to distant locations. These cells are cancerous
What are the stages of cancer development?
Stage 0: carcinoma in situ- early form
Stage 1: localized
Stage 2: early locally advanced
Stage 3: late locally advanced
Stage 4: Metastasized (spreading throughout body)
What are the roles of proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes?
-proto-oncogenes, produces protein products that normally enhance cell division or inhibit normal cell death. The mutated forms of these genes are called oncogenes. -tumor suppressors, makes proteins that normally prevent cell division or cause cell death.