Physiology Exam 4 - Ch. 13-16
1/501
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
502 Terms
respiration (generally) requires the coordination of the __________ system and the __________ system
respiratory; circulatory
in respiration, the respiratory system’s purpose is…?
gas exchange with the environment
in respiration, the circulatory system’s purpose is…?
oxygen transport to tissues
__________ __________ conduct air between atmosphere and alveoli for gas exchange
respiratory airways
respiratory airways conduct air between _________ and __________ for gas exchange
atmosphere; alveoli
thoracic muscles (__________ and __________ muscles) regulate pumping and thoracic volume
diaphragm; intercostal
__________ __________ surrounds each lung, analogous to the pericardial sac in the cardiac system
pleural sac
__________ separates & lubricates lung & thorax movement during ventilation
pleura
what are the functions of the pleura during ventilation?
separate and lubricate lung and thorax movement
the pleura separates and lubricates _________ & __________ during ventilation
lung; thorax
pleural sac transfers __________ pressure gradient during inhalation
negative
what do goblet cells do?
produce mucus to trap particles
what do ciliated cells do?
mucociliary escalator - bring objects that don’t belong in the lungs up and out
what do club cells do?
secrete surfactants, detoxifying enzymes, & anti-inflammatory proteins - help to break surface tension of water (water wants it to collapse, these help to keep it open)
what do basal cells do?
progenitor cells, can turn into other types if the other cells get damaged
what do Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cells (PNECs) do?
release hormones and neurotransmitters, respond to O2 and CO2, regulate airway diameter - afferent sensors → vagus nerve
what do type I alveolar cells do? they are also called..?
form thin barrier between air and capillary (like endothelial cells in capillaries), pneumocytes
what do type II alveolar cells do?
generate/produce surfactant
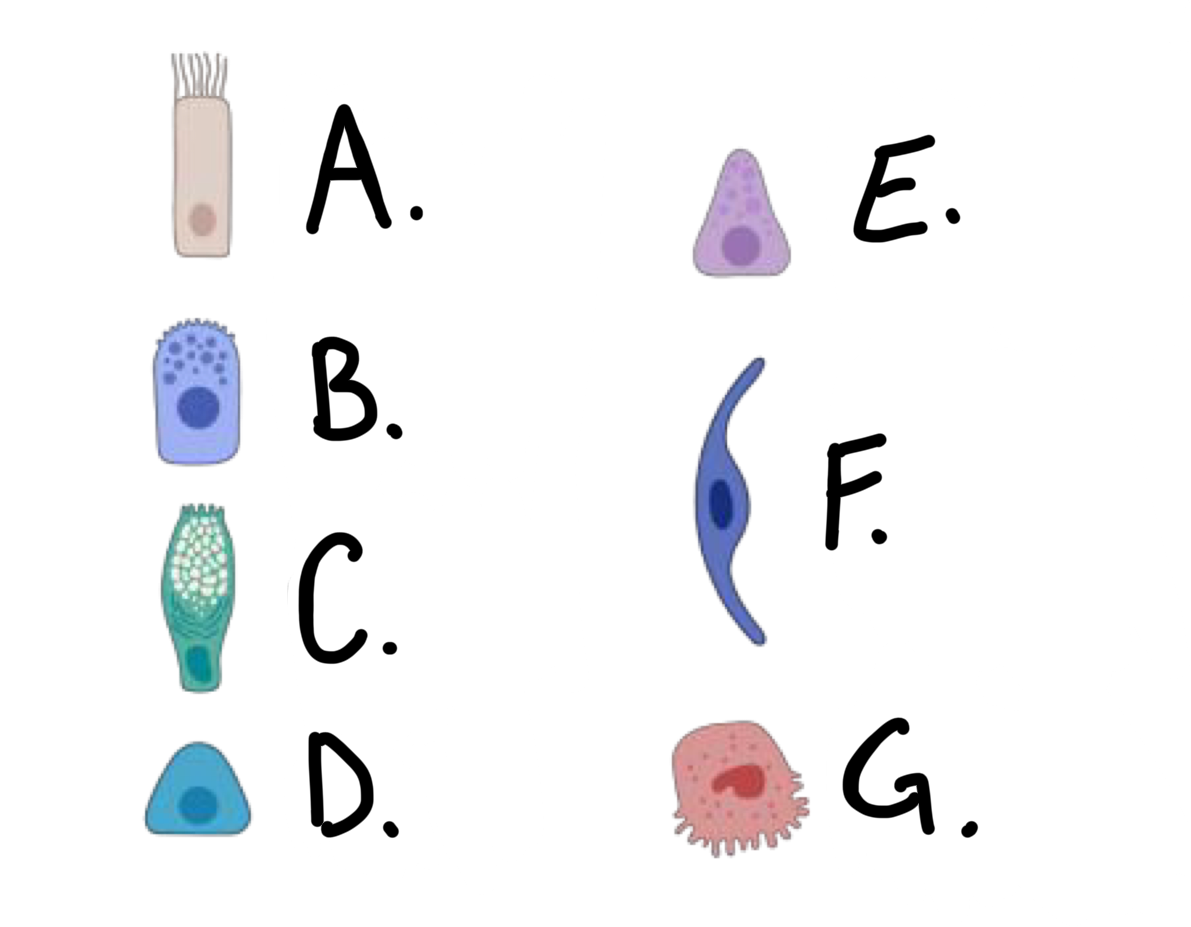
what kind of cell is cell A?
ciliated cell
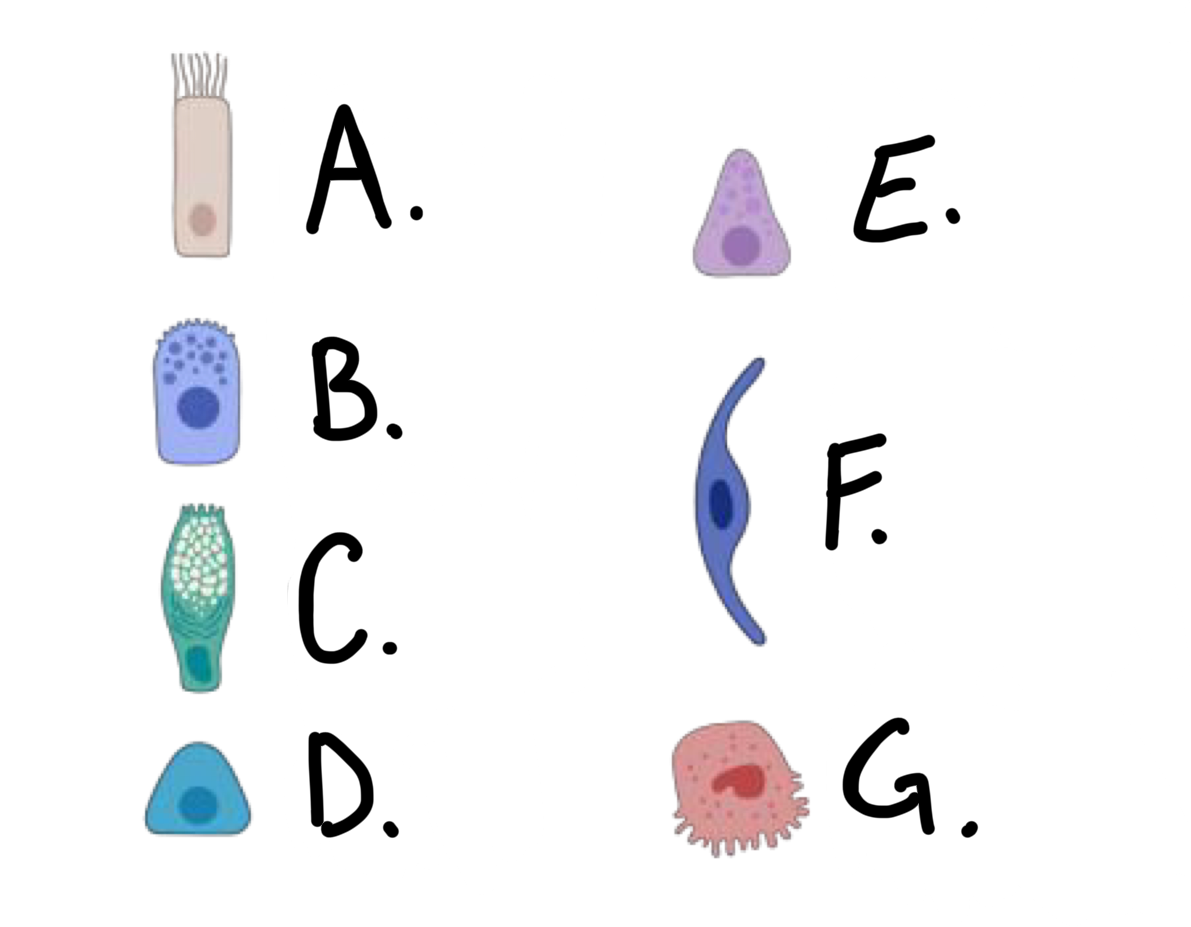
what kind of cell is cell B?
club cell
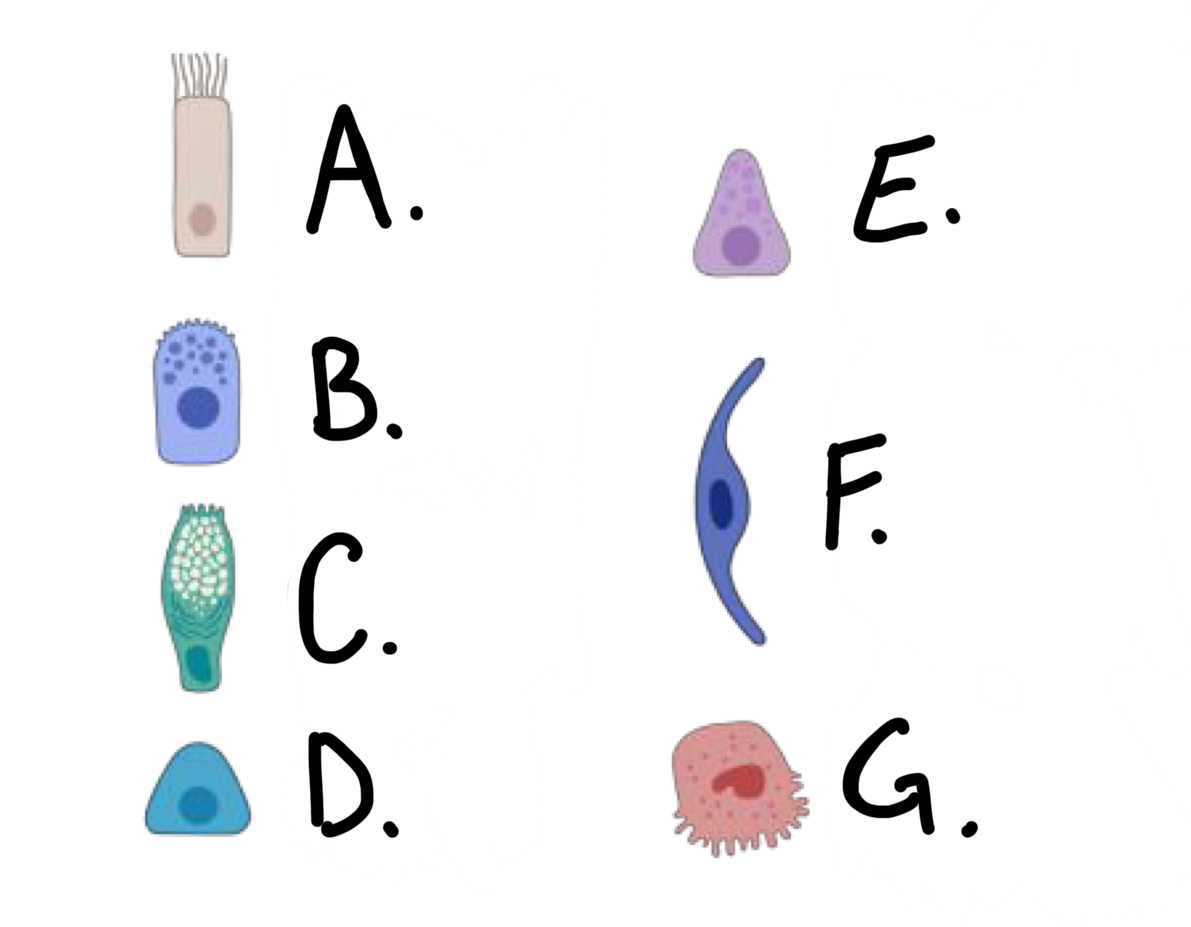
what kind of cell is cell C?
goblet cell
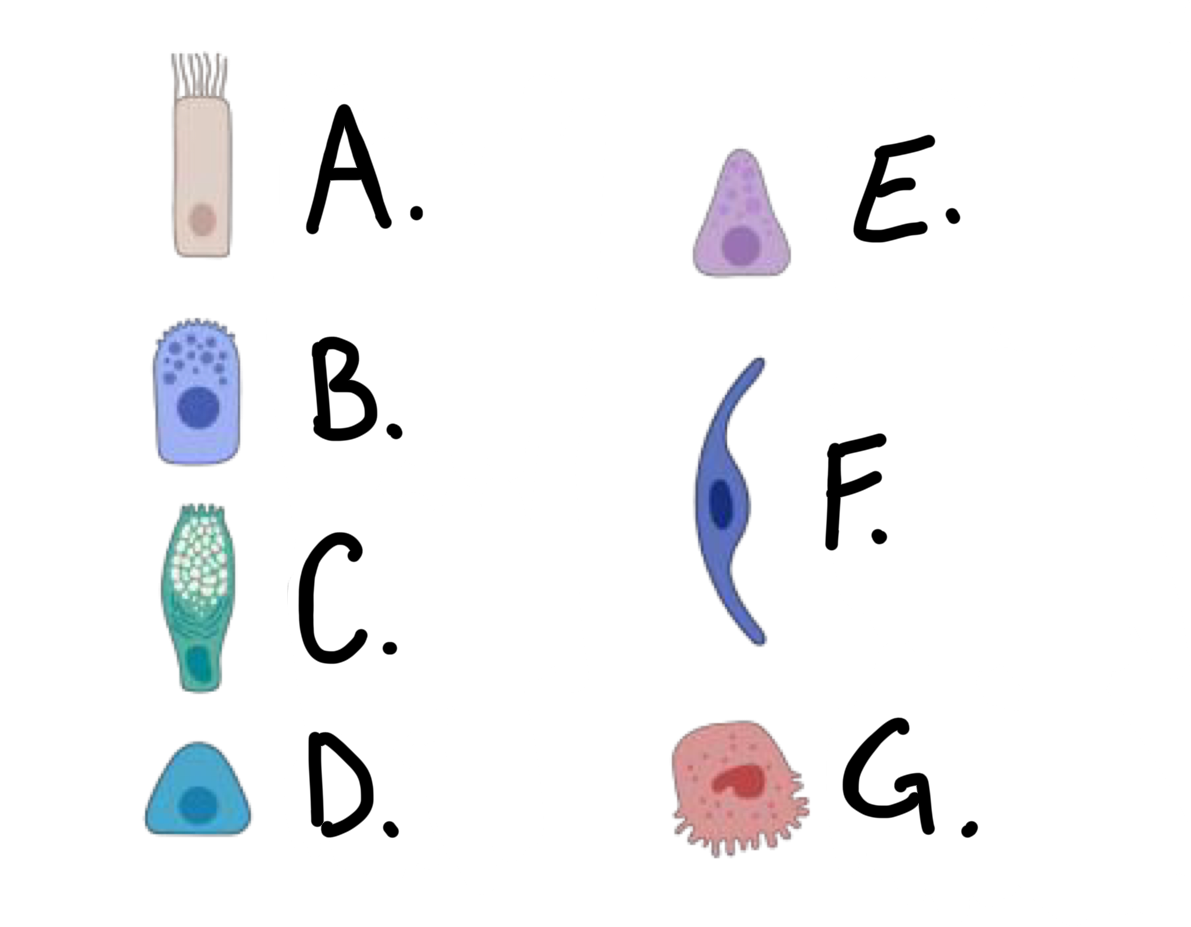
what kind of cell is cell D?
basal cell
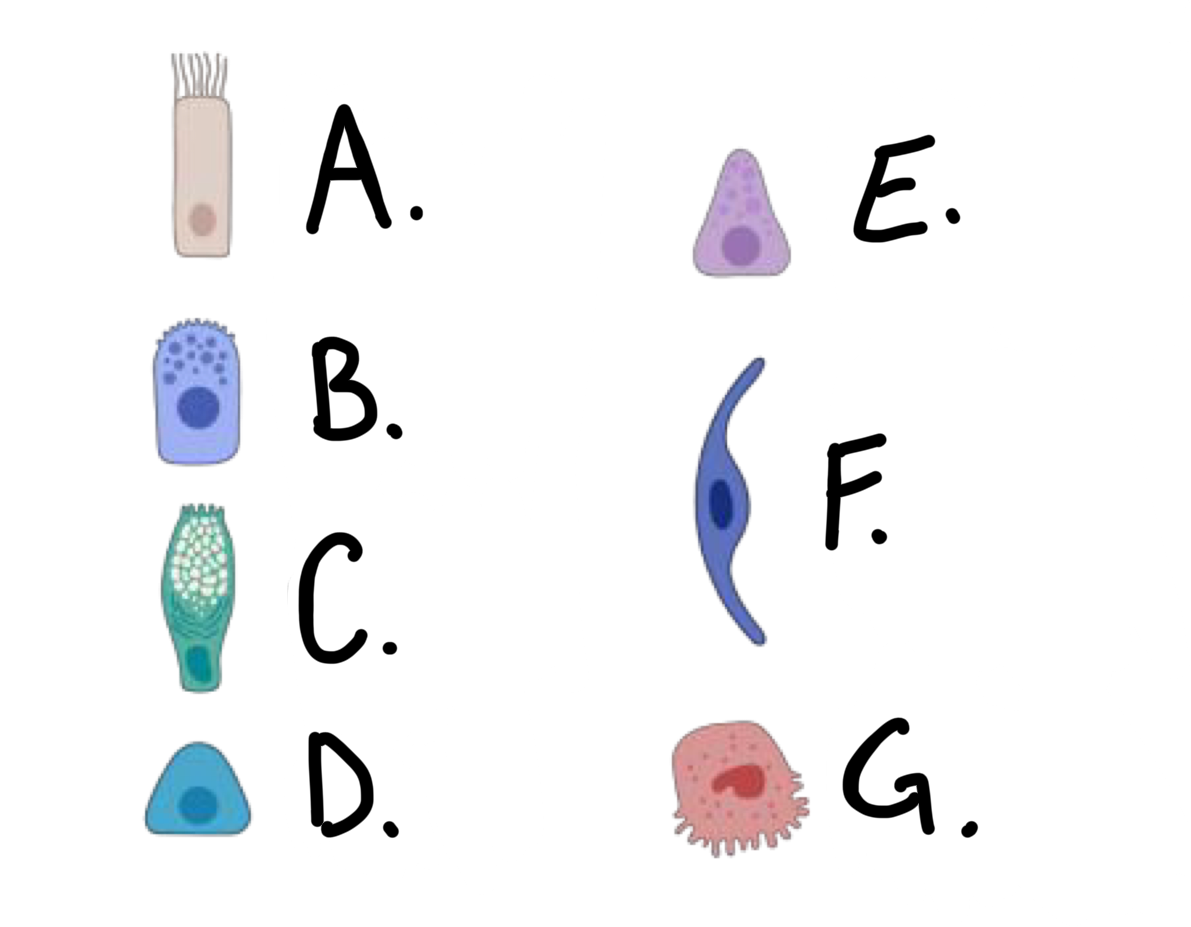
what kind of cell is cell E?
Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell (PNEC)
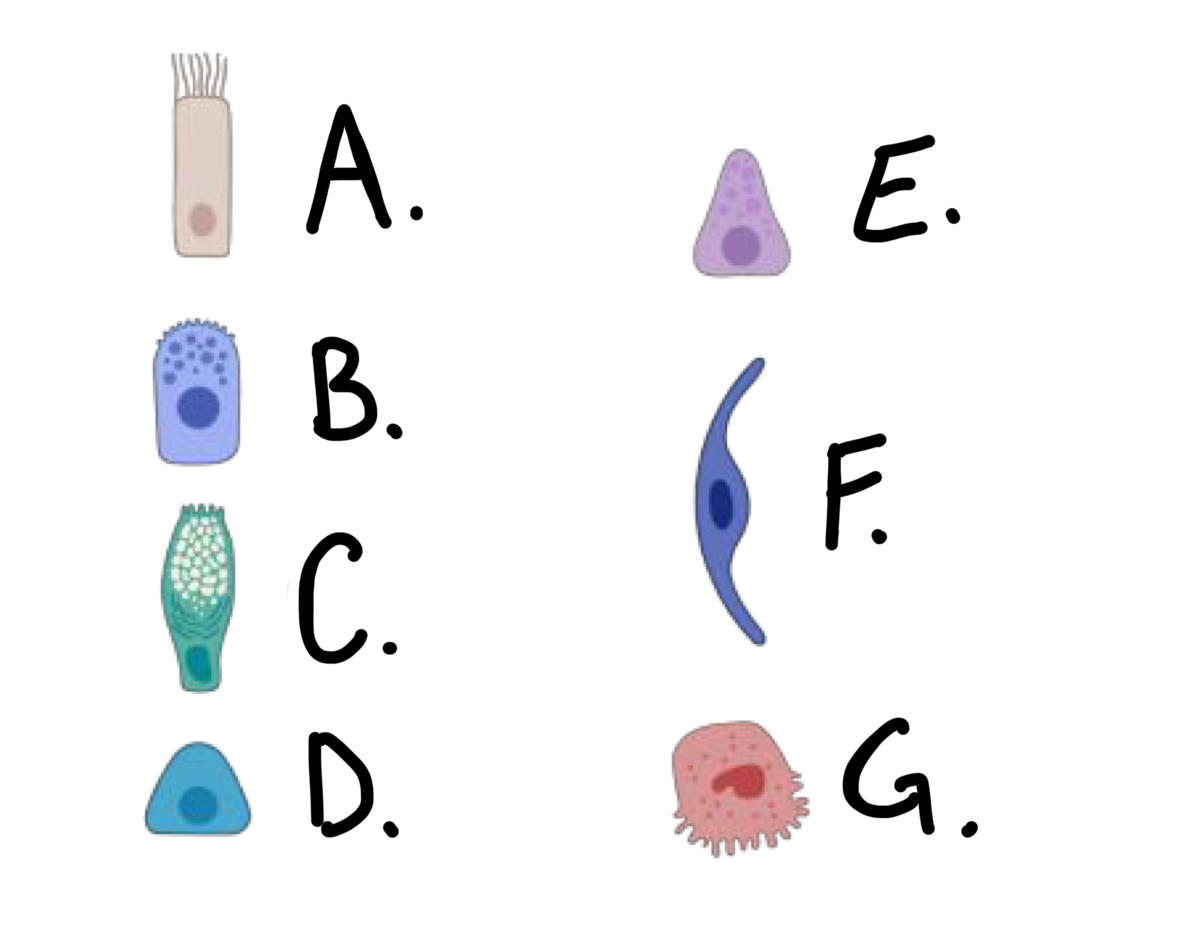
what kind of cell is cell F?
type I alveolar cell
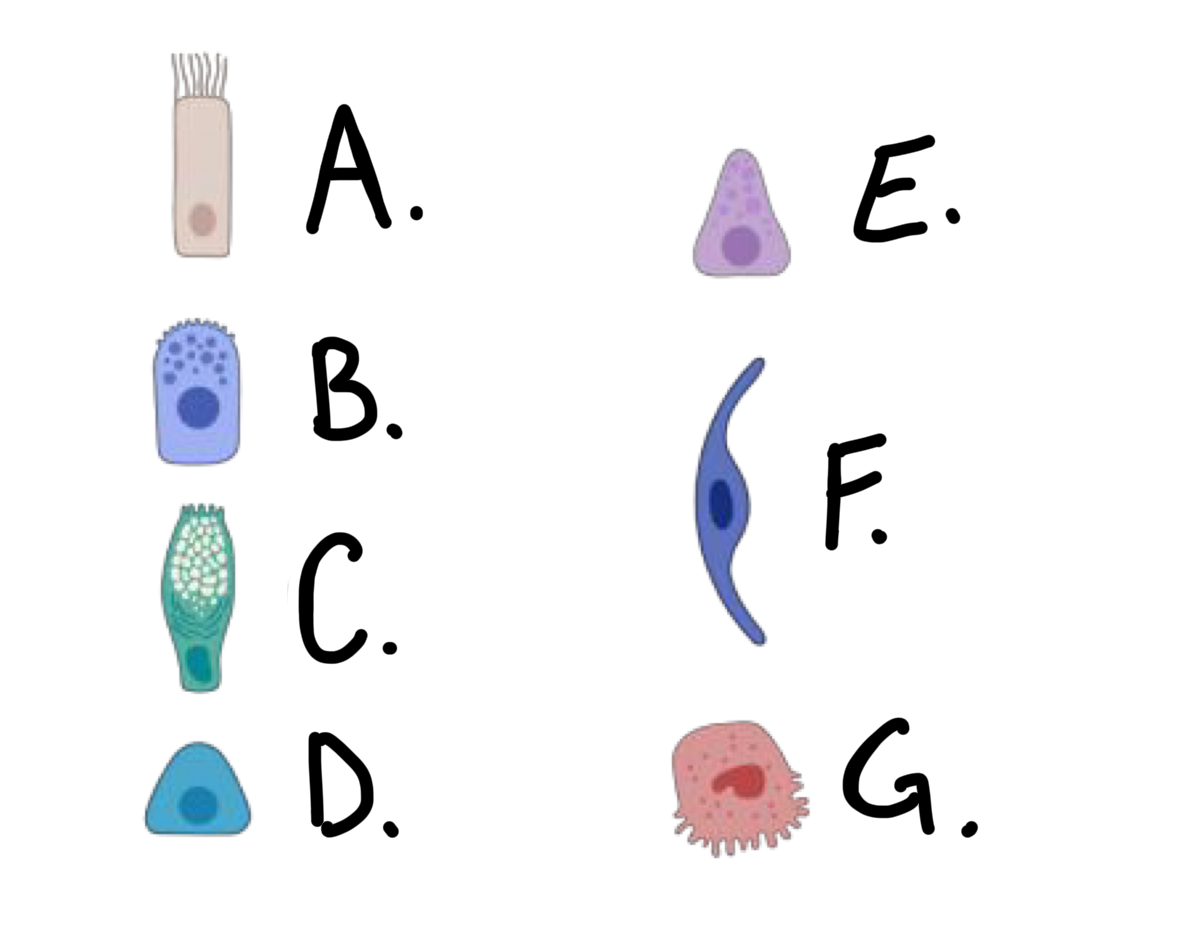
what kind of cell is cell G?
type II alveolar cell
ciliated cells are found in which of the following (all that apply)
a. trachea, bronchi
b. bronchioles to alveoli
c. alveoli
trachea, bronchi
bronchioles to alveoli (ci)
club cells are found in which of the following (all that apply)
a. trachea, bronchi
b. bronchioles to alveoli
c. alveoli
trachea, bronchi
bronchioles to alveoli (cl)
goblet cells are found in which of the following (all that apply)
a. trachea, bronchi
b. bronchioles to alveoli
c. alveoli
trachea, bronchi
bronchioles to alveoli (g)
basal cells are found in which of the following (all that apply)
a. trachea, bronchi
b. bronchioles to alveoli
c. alveoli
trachea, bronchi
bronchioles to alveoli (b)
Pulmonary Neuroendocrine cells (PNECs) are found in which of the following (all that apply)
a. trachea, bronchi
b. bronchioles to alveoli
c. alveoli
trachea, bronchi
bronchioles to alveoli
type I alveolar cells are found in which of the following (all that apply)
a. trachea, bronchi
b. bronchioles to alveoli
c. alveoli
alveoli
type II alveolar cells are found in which of the following (all that apply)
a. trachea, bronchi
b. bronchioles to alveoli
c. alveoli
alveoli
what kind of cells produce mucus to trap particles
goblet cells
what kind of cells are the mucociliary escalator, and bring objects that don’t belong in the lungs up and out
ciliated cells
what kind of cells secrete surfactants, detoxifying enzymes, and anti-inflammatory proteins
club cells
what type of cells are progenitor cells that can turn into other types if they are damaged
basal cells
what kind of cells release hormones and neurotransmitters, respond to O2 and CO2 and regulate airway diameter
Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cells (PNECs)
what kind of cells form a thin barrier between the air and the capillaries in the lung?
type I alveolar cells (pneumocytes)
what kind of cells generate/produce surfactant
type II alveolar cells
__________ __________ bring air to alveolar sacs
terminal bronchioles
terminal bronchioles bring air to __________ _________
alveolar sacs
adjacent alveoli car connected by…?
pores of Kohn
what surrounds the alveoli, and is necessary for gas exchange?
extensive capillary network
the small radius of alveoli combines with their large number results in…?
large surface area
thin _______________ provide thin barrier between air and blood
type I alveolar cells (pneymocytes)
total surface area of lungs is about __________m2, and if often compared to the surface area of a tennis court, but is close to …?
70-100m2; ½ of a singles court
is inhalation an active or passive process?
active
inhalation is the contraction of what muscles?
external intercostals and diaphragm
during inhalation, thorax expansion __________ pressure in lungs
decreases OR creates a negative
how does inhalation work?
the external intercostals and diaphragm contract, drawing the ribs up. this creates a negative pressure in the lungs, which draws air in so relieve the vacuum
is exhalation an active or passive process?
mostly passive in quiet breathing
exhalation is the relaxation and recoil of the…?
diaphragm and ribs
forced exhalation (heavy breathing) includes contraction of what muscles?
abdominal and internal intercostals
what is Boyle’s law?
P1V1=P2V2
compressing chamber volume __________ pressure
increasing
expanding chamber volume __________ pressure
decreases
resistance to airflow is inversely proportionate to…?
radius of conducting tube
what is the formula for airflow?
F=ΔP÷R
what is asthma
inflammation, mucus, bronchoconstriction
what condition is characterized by inflammation, mucus, and bronchoconstriction
asthma
what is bronchitis
inflammation, thickening of airways, and mucus
what condition is characterized by inflammation, thickening of airways, and mucus
bronchitis
parasympathetic stimulation results in broncho_______
constriction (smooth muscle constriction - R↑)
sympathetic stimulation and epinephrine results in broncho_______
dilation (smooth muscle relaxation - R↓)
healthy lung is __________ = needs little pressure difference to __________
compliant; expand
the healthy lung in compliant, unlike a lung with __________
fibrosis
in the process of ______________ elastin fibers and alveolar surface tension recoil lung tissue after expansion
elastic recoil
elastic recoil is made possible by elastin fibers and…?
alveolar surface tension
surface tension of __________ on alveolar surface constricts to collapse alveoli
water
_______ of water on alveolar surface constricts to collapse alceoli
surface tension
type II alveolar cells produce _________ - a mixture of proteins and phospholipids
pulmonary surfactant
what do surface tension and surfactant do?
increases pulmonary compliance to reduce work for inflation, and reduce recoil and collapse of alveoli
inspiration happens when ______ pressure < _______ pressure
intra-alveolar; atmospheric
expiration happens when ______ pressure > _______ pressure
intra-alveolar, atmospheric
intra-alveolar pressure equilibrates to _______ pressure
atmospheric
intrapleural pressure [< / >] intra-alveolar pressure
<
lungs are always being _____, even during expiration
stretched
what is a flail chest injury?
many ribs in one spot get broken - get pushed with air rather than the rest of the rib cage
what is tidal volume (TV)?
volume of air inhaled/exhaled during normal quiet breathing
what is inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)?
volume of air forcefully inhaled beyond tidal volume
what is expiratory reserve volume (ERV)?
volume of air forcefully exhaled beyond tidal volume
what is residual volume (RV)?
volume of air in lungs after maximum forced exhalation
what is vital capacity (VC)?
maximum volume exhaled after maximum inhalation
what is inspiratory capacity (IC)?
maximum volume inhaled after normal exhalation
what is functional residual capacity (FRC)
volume of air in lungs after normal exhalation
what is the term used for the volume of air inhaled/exhaled during normal quiet breathing
tidal volume
what is the term used for the volume of air forcefully inhaled beyond tidal volume
inspiratory reserve volume
what is the term for the volume of air forcefully exhaled beyond tidal volue
expiratory reserve volume
what is the term for volume of air in lungs after maximum forced exhalation
residual volume
what is the term for total volume of air in lungs after maximum inhalation
vital capacity
what is the term for the maximum volume inhaled after normal exhalation
inspiratory capacity
what is the volume of air in lungs after normal exhalation
functional residual capacity
efficient gas exchange requires matched __________ and __________
ventilation, perfusion
ventilation and perfusion are both greater at the ________ of the lungs, but this effect is greater on ________
bottom, perfusion
the “sweet spot” in the lungs where ventilation and perfusion overlap with V/Q is in what part of the lungs?
top-middle of the lungs
what happens to the arterioles and bronchioles in the presence of high O2 in the lungs?
arterioles - vasodilation
bronchioles - minimal direct effect
what happens to the arterioles and bronchioles in the presence of low O2 in the lungs?
arterioles - vasoconstriction
bronchioles - minimal direct effect
what happens to the arterioles and bronchioles in the presence of high CO2 in the lungs?
arterioles - minimal direct effect
bronchioles - bronchodilation
what happens to the arterioles and bronchioles in the presence of low CO2 in the lungs?
arterioles - minimal direct effect
bronchioles - bronchoconstriction
what is the formula for partial pressure of gas?
P=total pressure * fraction