EKG Final Review
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Going for an A
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Somatic Tremors
Shivering rhythm
Unifocal PVC
Similar Shape PVC
Coupling
2 PVCs together
Patient Feels ____ during SVT
Palpitations
What does stat mean?
Immediately
Electrical Current in heart
Pathway is the purkinje network
Each little box in a ECG is how many seconds
0.04 seconds
Inner most heart layer
Endocardium
Surrounding layer of heart
Pericardium, protects heart
Middle Muscular layer of heart
Myocardium, responsible for contraction
Outer layer of heart
Epicardium
Ability to receive and transmit electricity in heart
Conductivity
Mechanical response to electrical current
Contractility
Automaticity
Automatically
Excitability
Ability to respond to electrical activity
Leads 1/2/3 are called
Bipolar leads
What is the typical rate of Accelerated Idioventricular
40-100 bpm
What is the typical rate of Idioventricular rhythm
20-40 bpm,
What is an ECG
Electrical Acitivity of the heart
Classify SVT
Heart Rate of 150-250 bpm
What is the spike before QRS
Ventricular Pacemaker
What is the spike before Pwave
Atrial Pacemaker
What is the spike before both Pwave and QRS
Atrial Ventricular
Sinus Bradycardia typically has a rate of
<60bpm
Tachycardia
Palpitations
Chest Lead v4 goes
5th intercostal left midcavicular
Pacemaker has
Pacing spikesC
How to do an EKG on a crying infant
Wait for it to sleep
Electrical impulse comes from
AV Node depolarization retrograde
Inverted P Wave means
Junctional Rhythm
Agonal is
Ventricular Dysrhythmia <20bpm
ECG Tech does
View traces, alert physician for abnormalities
Basic Principal for Electronic Pacemaker
Fastest pacemaker inherits / takes over
Abnormal Heartbeat
Dysrhythmia
What to do when finished with ECG
Dispose electrodes
Normal Rate
60-100bpm
Ventricular fibrillation is
Chaotic
What is the rhythm when the Atria quivers like a bowl of jello
Atrial Fibrillation
Dextracardia
Heart on the right side
Normal QRS is
0.06 - 0.10s
What is the set paperspeed
25mm/s
Tachycardia has a rate of
100bpm or greater
Which heart block has a constant pr interval
1st Degree AV Block
What two forms of ID is needed before performing EKG
Name and ID #
What is the top 2 chambers of the heart called
Right and Left Atrium
What is the two lower chambers of the heart called
Right and Left Ventricle
Unwanted marks on ECG
Artifacts
What leads has specific anatomical landmarks
V1, V2, V4, V5, V6
Junctional Dysrhythmia QRS is
Measuring in normal limits
When analyzing the Pwave what do you look for
If each pwave has a QRS that follows
What method do you use for Irregular rhythms
6 second method
What is the typical rate of a Wandering Atrial Pacemaker
60 to 100 bpm
When doing an ECG on a 7 year old
Use no technical words
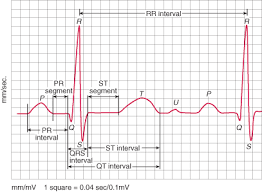
What method measures from
R-R Method
Heart block is when
Current has difficult time traveling down normal pathway
What to do before giving ECG to the Doctor
Determine Accuracy and check that everything is correct
Major health risk for Atrial Fibrillation
Thrombus formations and Embolisms
1st thing needed to perform an ECG is
Doctors order
Liable is
Written
Slander is
Deragatory RemarksS
Systolic
Heart pumps bloodD
Diastolic is
Heart filling with blood
Assault
Threaten harm
Battery
Actually harm
Venticular Rate Accelerated Junctional
60-100 beats per minute
Blood in the right ventricle is
Deoxygenated
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Rate
101-150 bpm
Sinus Arrest
SA nodes causes pause in electrical activity/ stops
SA Node sends electrical pulses down
Rate of 60-100bpm
Gain Control is normally set to
10mm/mv
Small child for ECG
v3 goes to other side of chest to avoid crowding
Blood returns to heart via
Vena Cava
Code Blue means
Unresponsive patient needs immediate assistance
Progressively longer PR Intervals
Mobitz Type 1
Inherent rate of Purkinje is
20-40 bpm
2 Semilunar valves are called
Aortic / Pulmonary
Before EKG on a patient, one must
Clarify and Answer any questions
Ethical means
Right or Wrong conduct
If a patient has a breast implant what modification is necessary
Place V1 and V2 Higher
Doctor that invented EKG
Willem Einthoven
P wave is primarily affected by
Atrial Dysrhythmia
Juntional Tachycardia rate is
100-180 bpm
2 Types of heart blocks with constant PRI is
1st Degree and 2nd Degree Type 2
Pattern in which every third complex is a premature beat is
Trigeminy
Cardiac Arrest
Heart is stopped
Myocardial Infarction
Heart Attack
v2 goes
4th intercostal, left of the sternum
Missing QRS with Constant PR interval
2nd Degree Type 2
Sinus Exit Block and Sinus Arrest results in similar ECG tracing
Pause duration is in multiple of PP and RR intervals
CAD is
Coronary Artery Disease
What Atrial Dysrhythmia has lower case F Waves
Atrial FibrillationPa
What are the Patients Vital Signs
Temp, BP, Pulse, Respiratory, Pain
is Level of Consciousness a vital sign
No
Where is the Mitral Valve located
Between Left Atrium and Left Ventricle
Where is the Triscupid located
Right atrium and Right Ventricle
Multifocal PVC
PVC has many varied shapes
Inherent rate of Junctional Escape
40-60 bpm
AV Node inherent rate is
40-60 bpm
HiPAA
Privacy, Health insurance, Accountability
What has Capital F Waves
Atrial Flutter