Fingerprints
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
patent prints
made after a finger comes in contact with a visible material
-blood, ink, grease, paint, etc
plastic prints
indented visible impressions left in soft material
-clay, wax, soap, vaseline, etc
latent prints
invisible prints that must be processed to be seen
-sweat
the core
approximate center of pattern
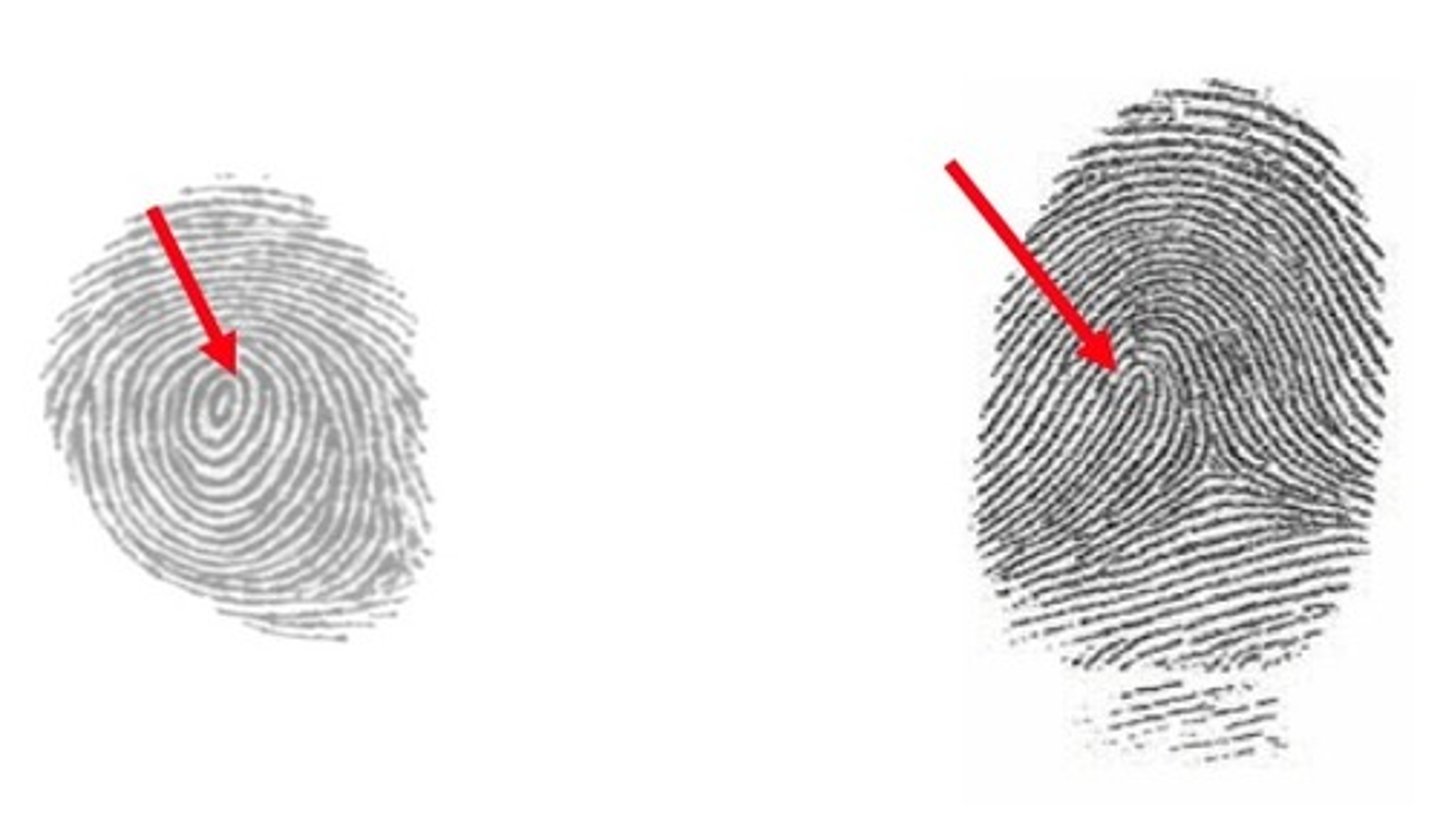

type lines
diverging ridges that surround the core
the delta(s)
triangular shape area where type lines meet
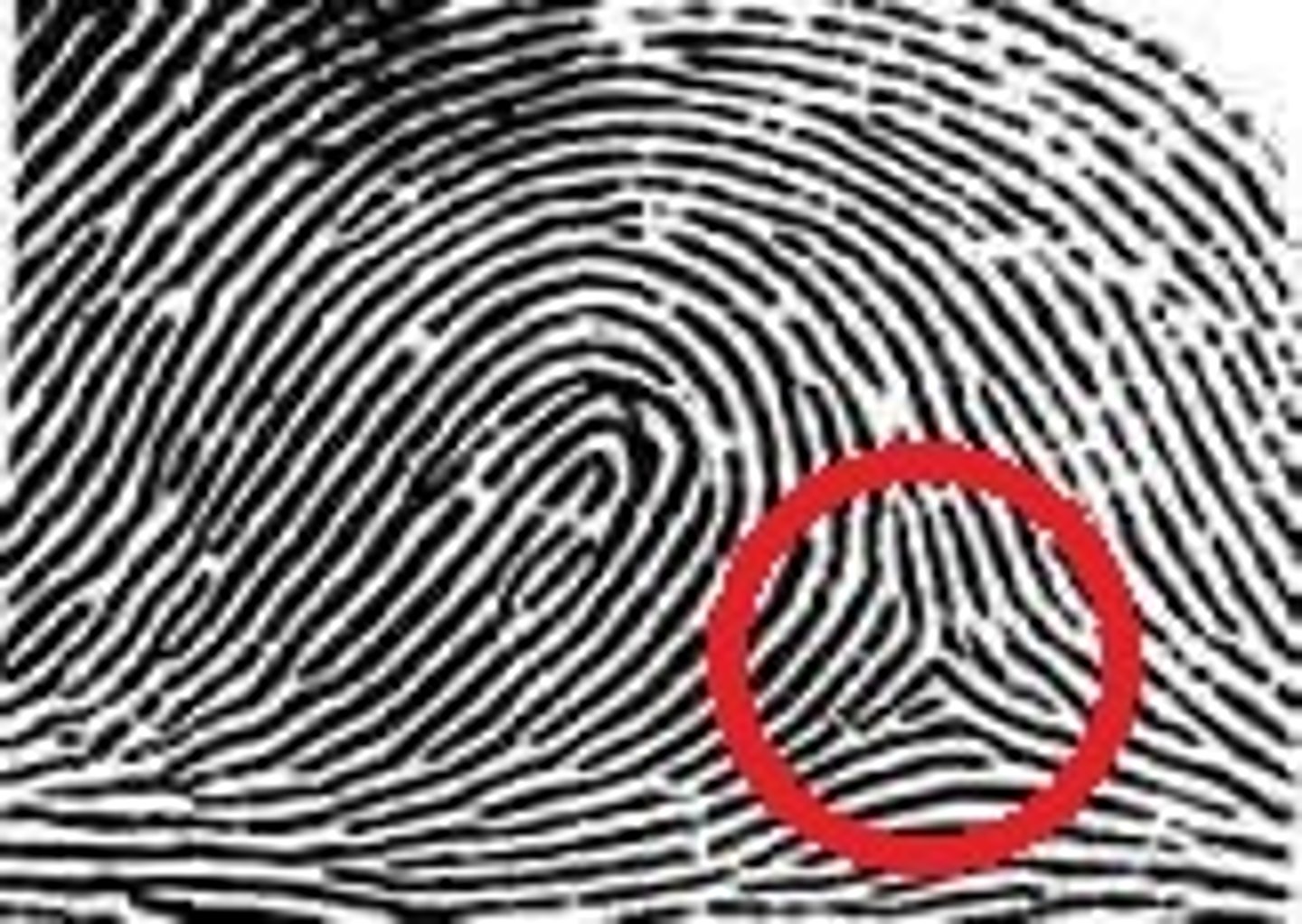

plain arch
-ridges start on one side, rise in the middle, and exit on the other side
-no core or deltas
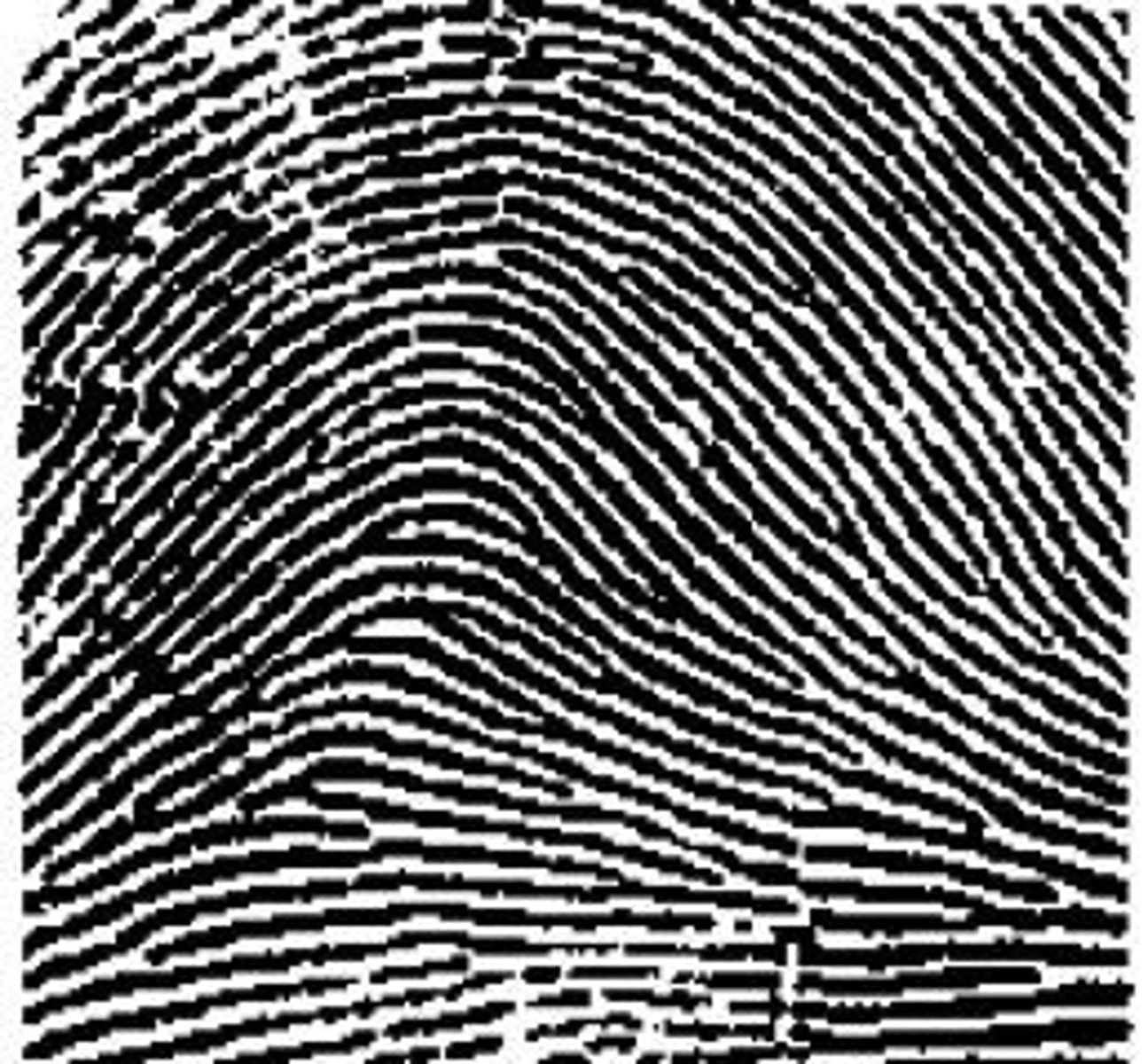

tented arch
ridges start on left, SHARP rise in middle and exit on right
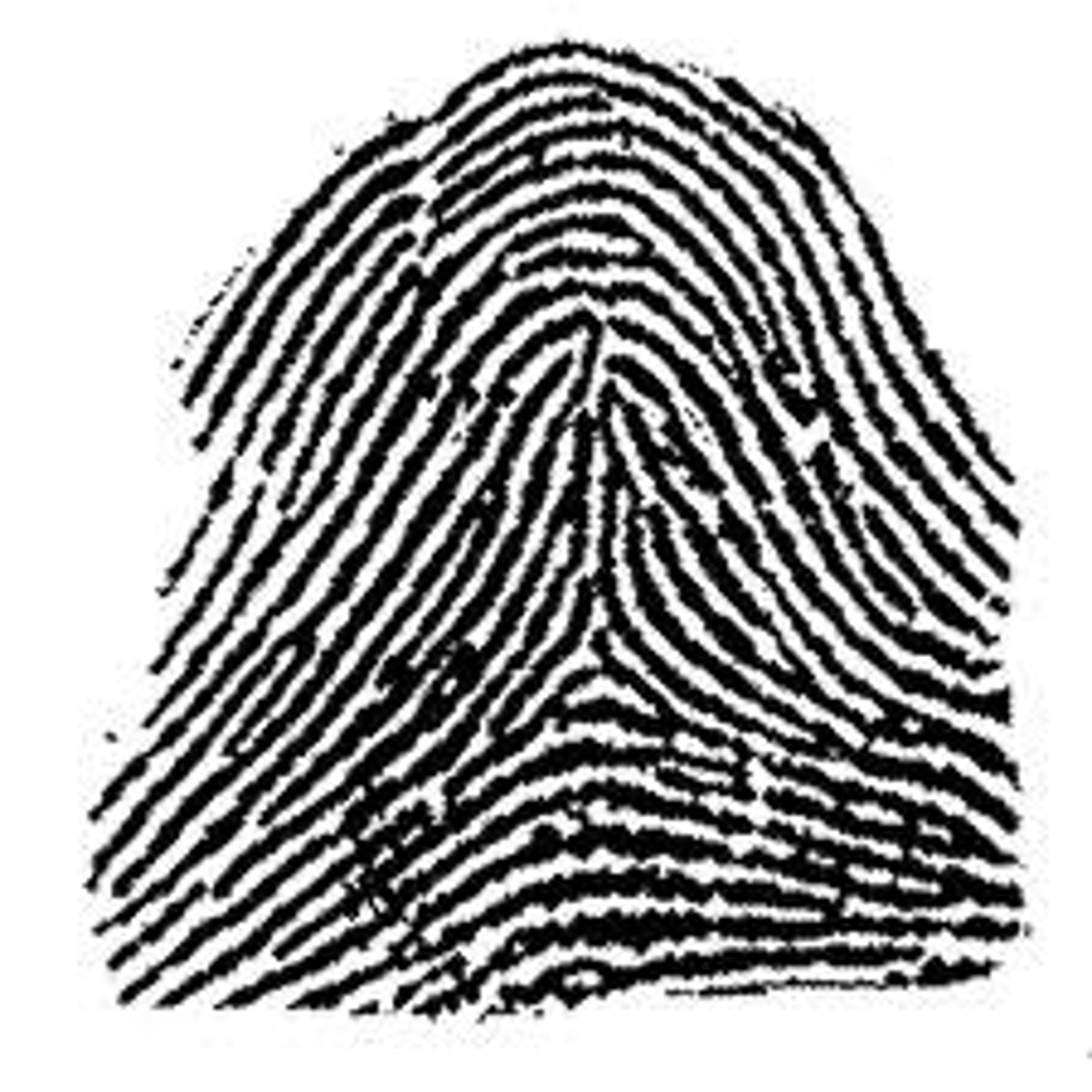

plain loop
ridges start on one side, loop around, and leave the same side

ulnar loop
-opens towards the pinkie
-right/left
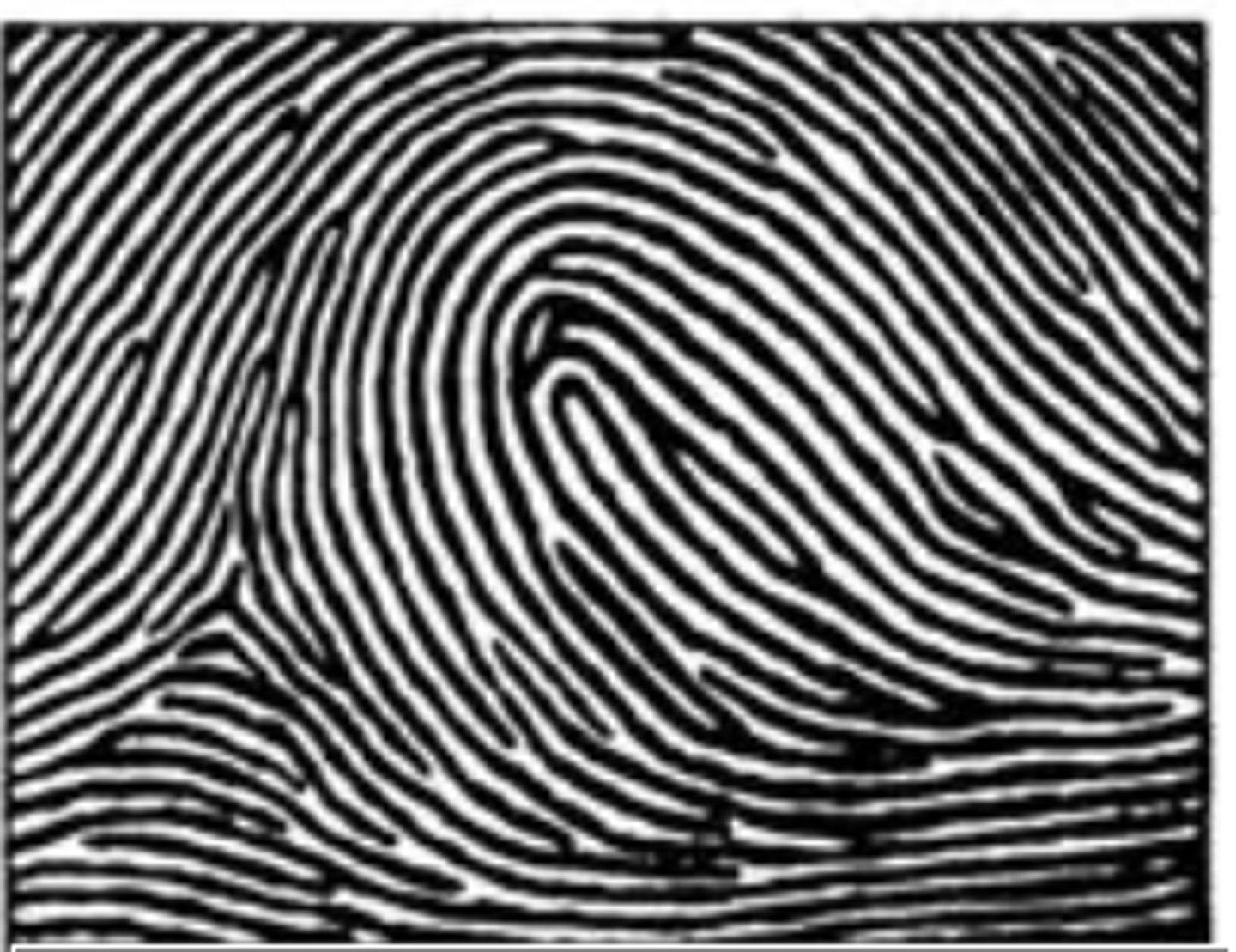

radial loop
-opens towards the thumb
-most often index finger
-right/left
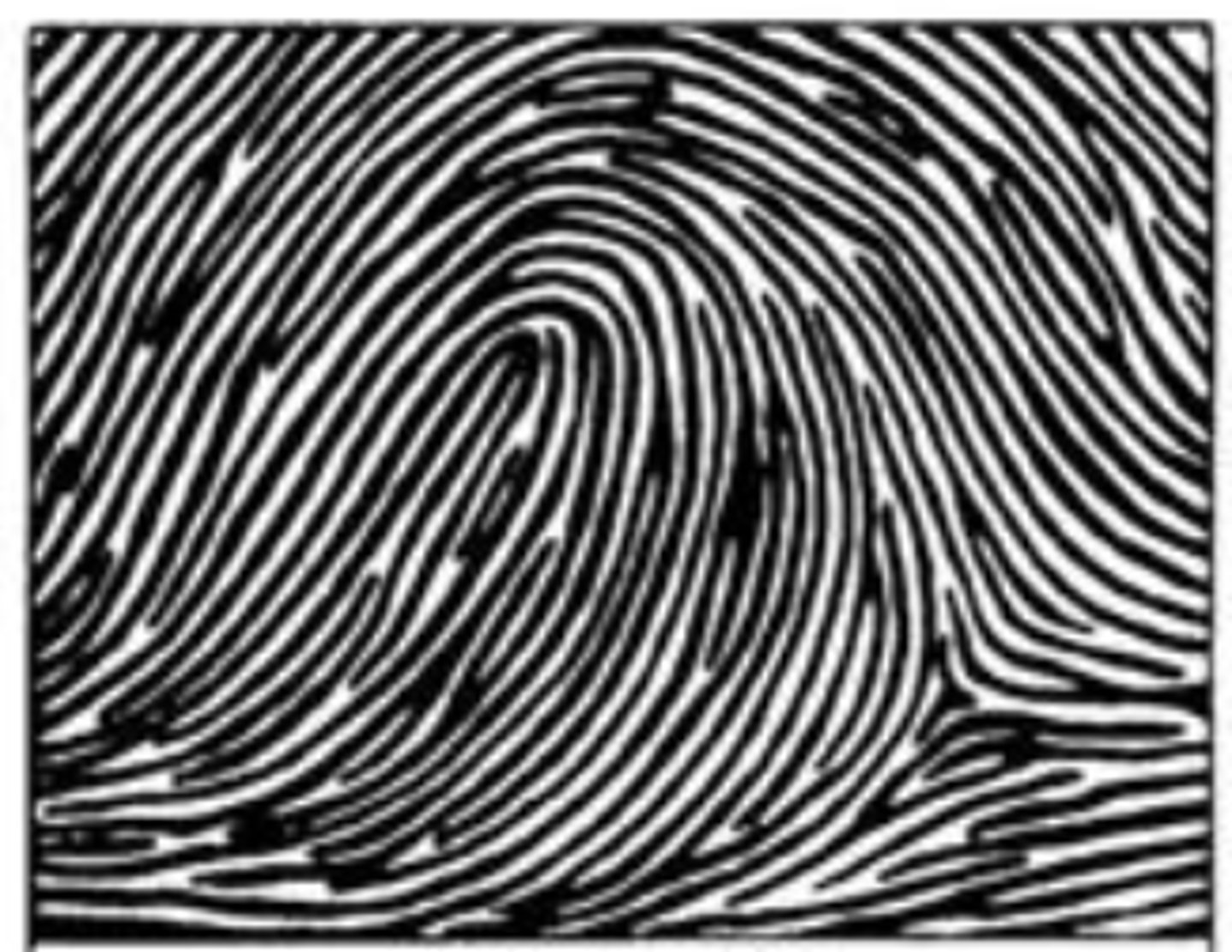

(plain) whorl
-circular pattern radiating around center of finger
-2 or more deltas
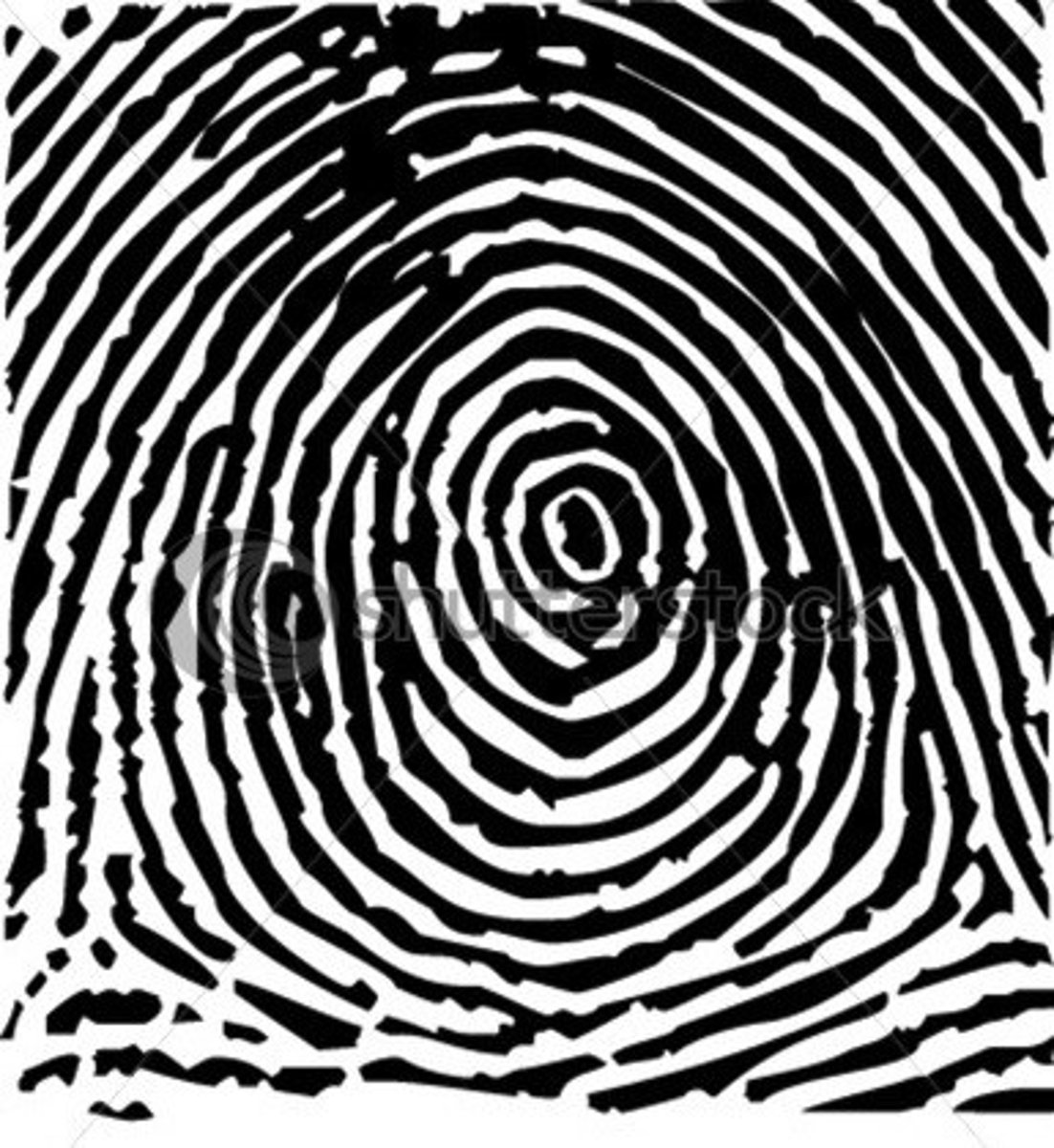

central pocket loop whorl
Line between deltas does not cross circular part of ridge pattern
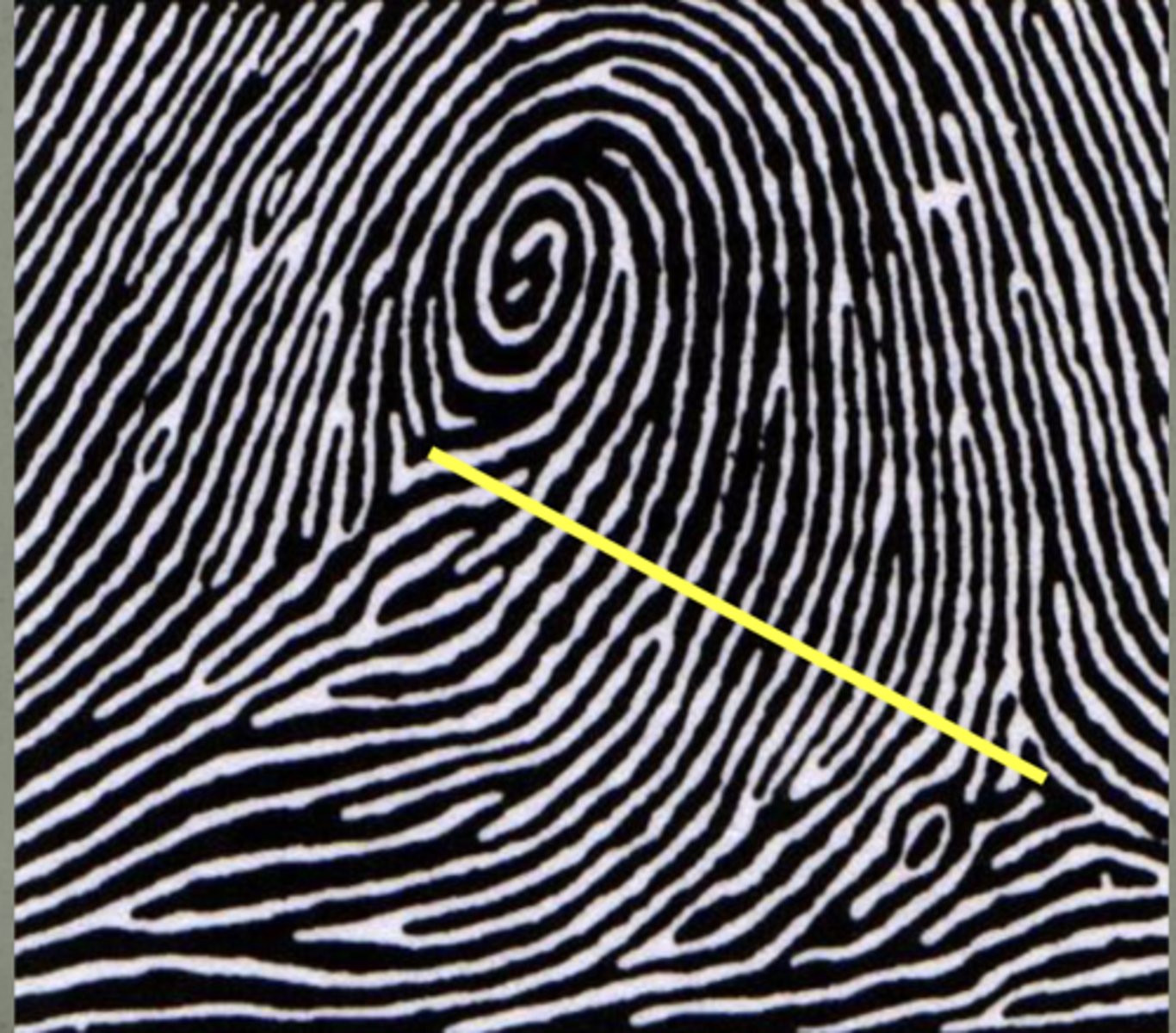
double loop whorl
two opposing loops side by side
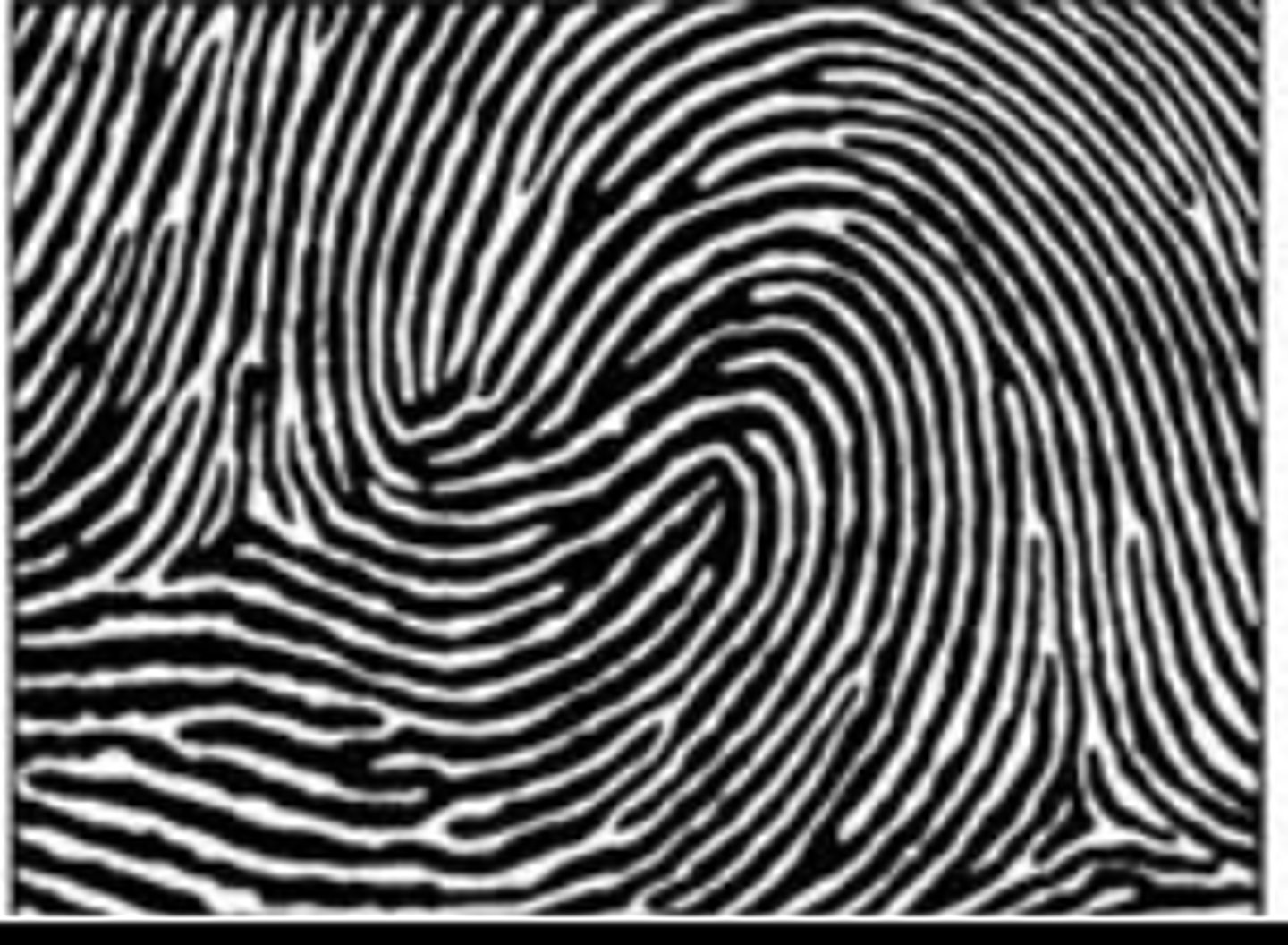

accidental whorl
combo of any two patterns except plain arch

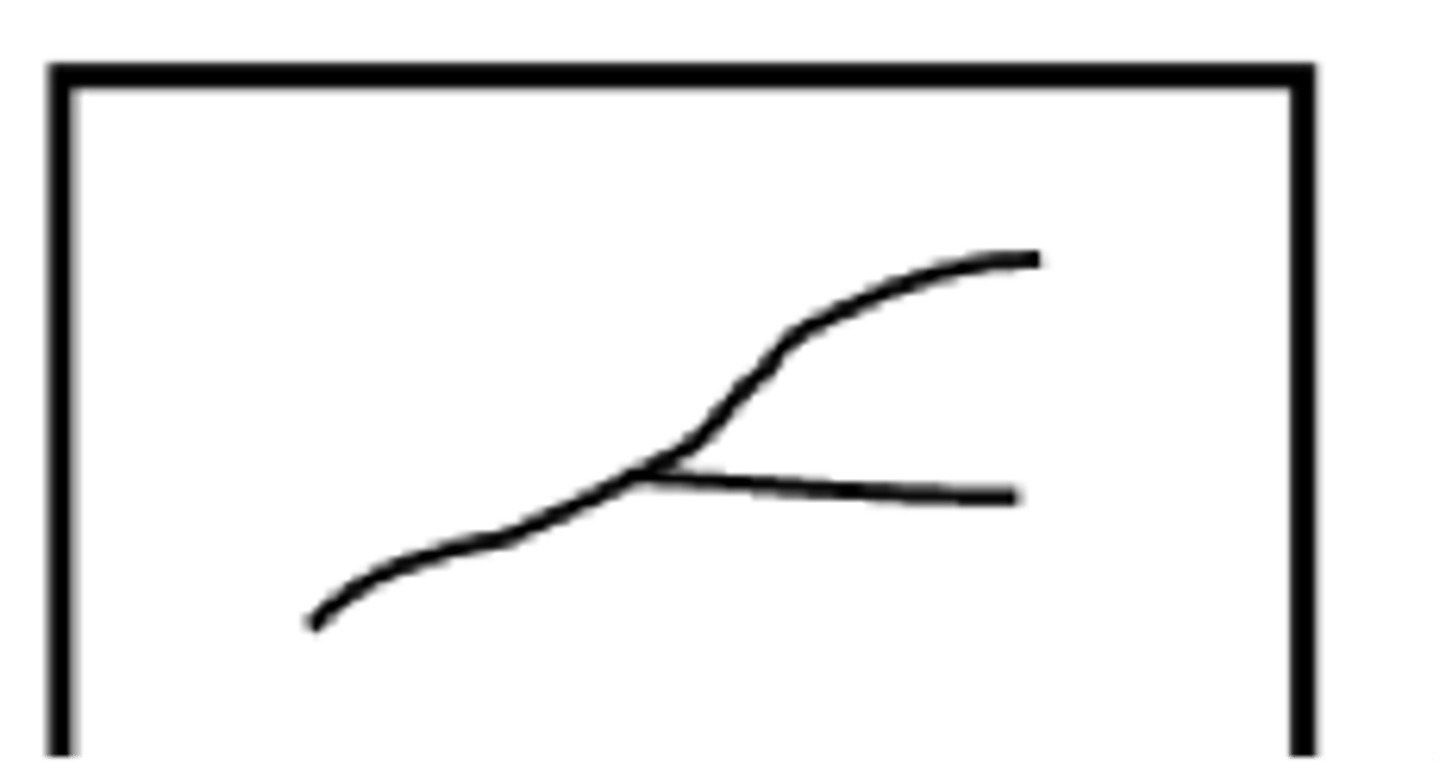
ridge ending
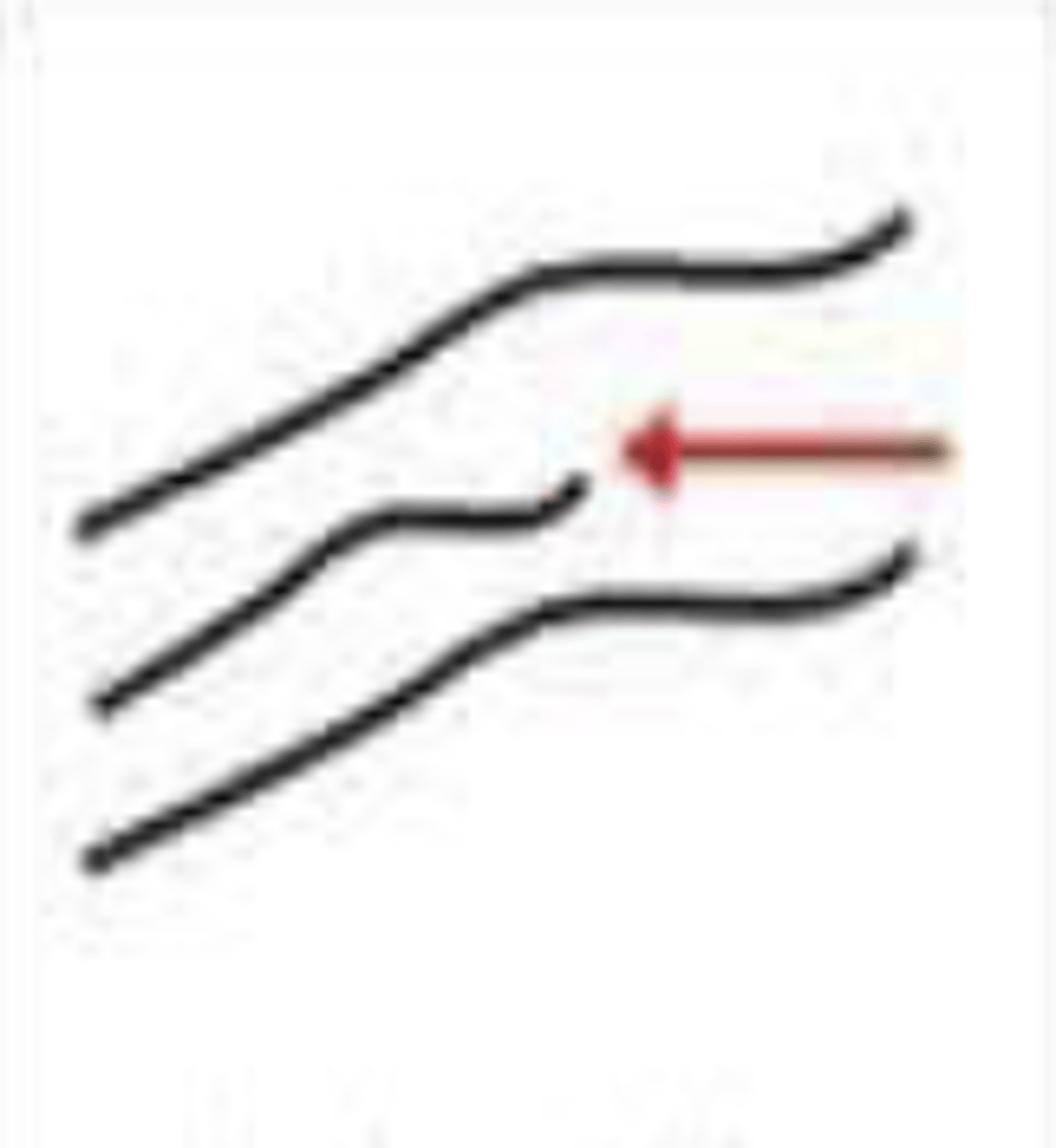
short ridge
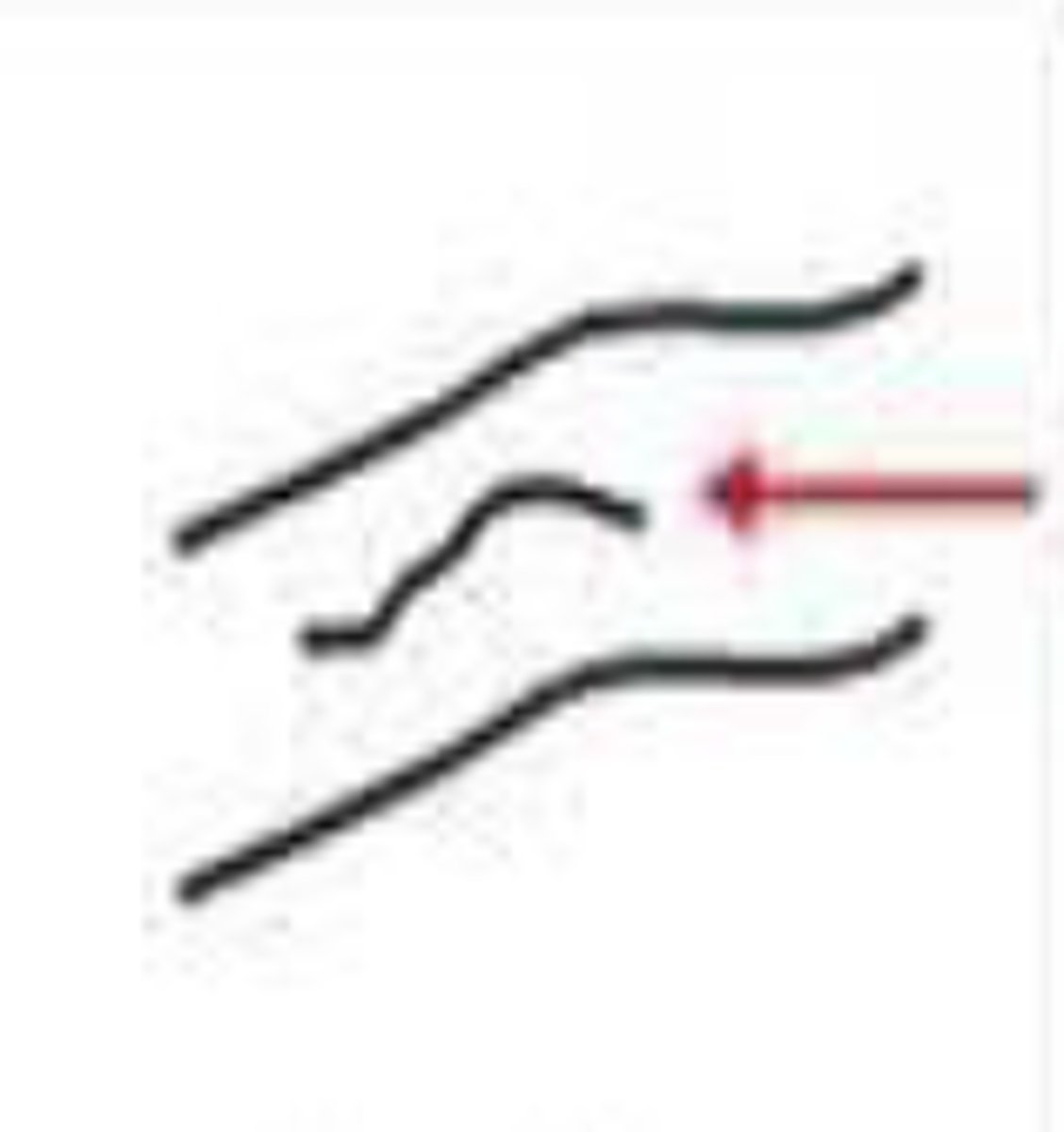
fork or bifurcation

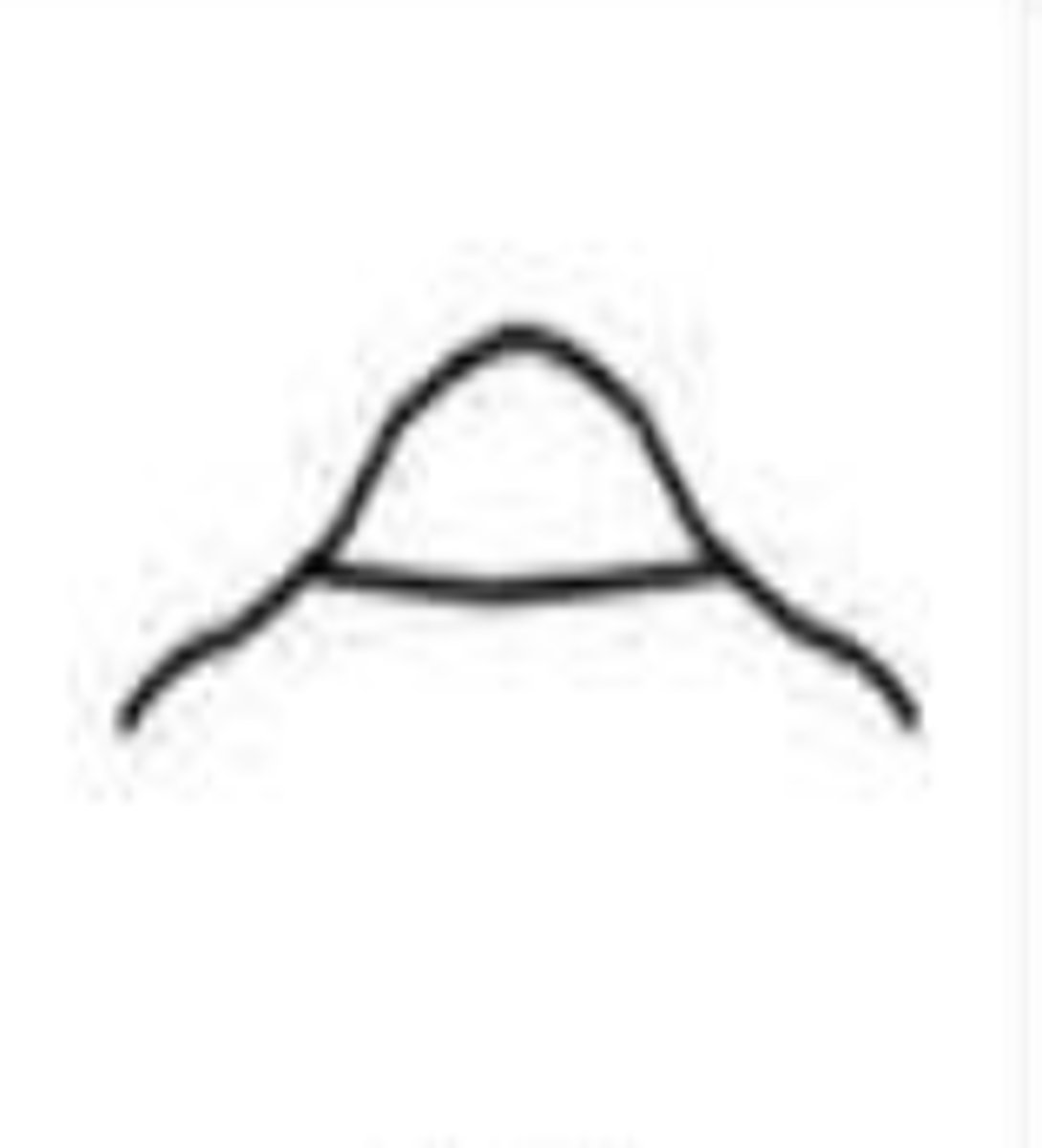
hook
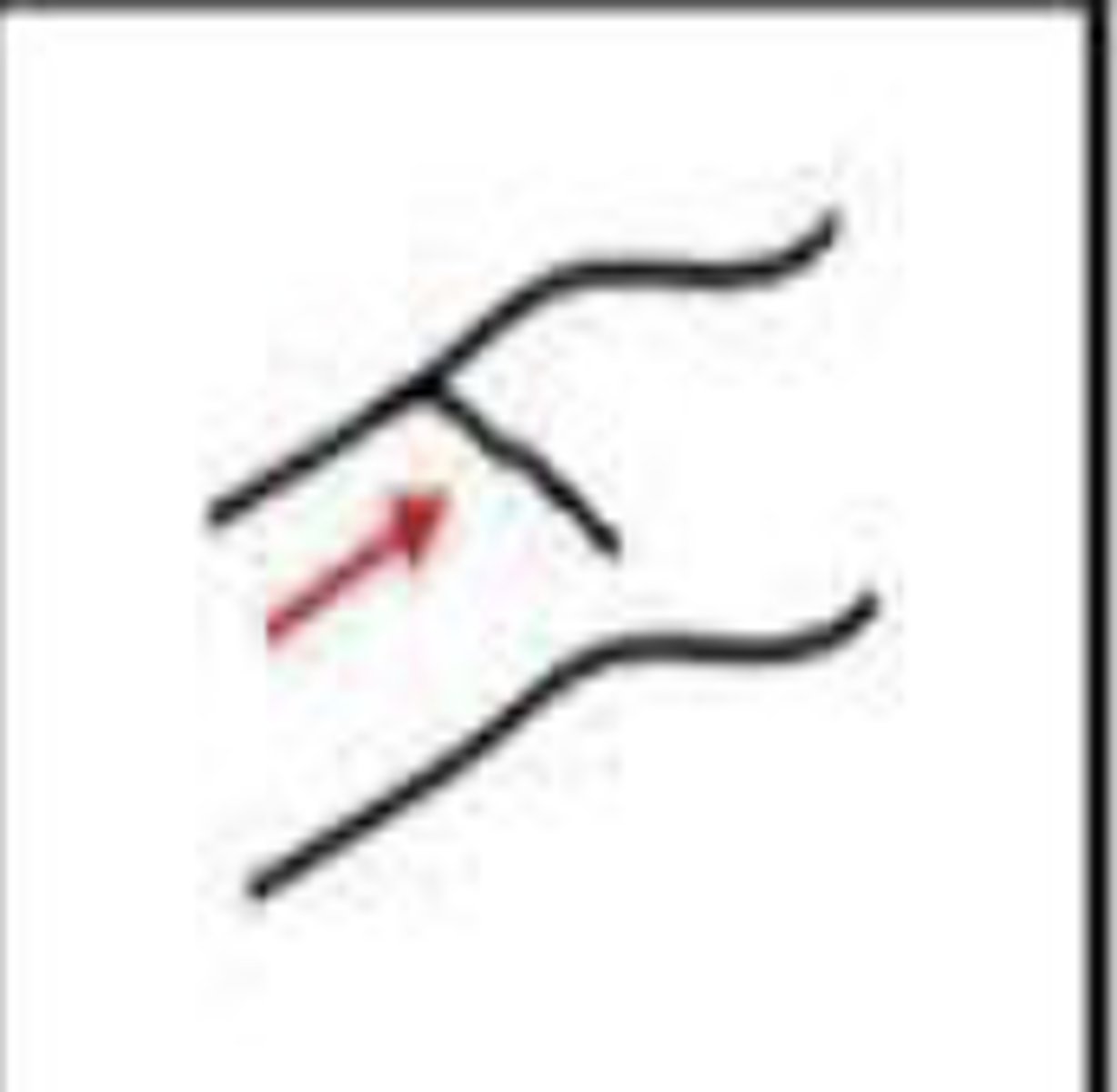
eye

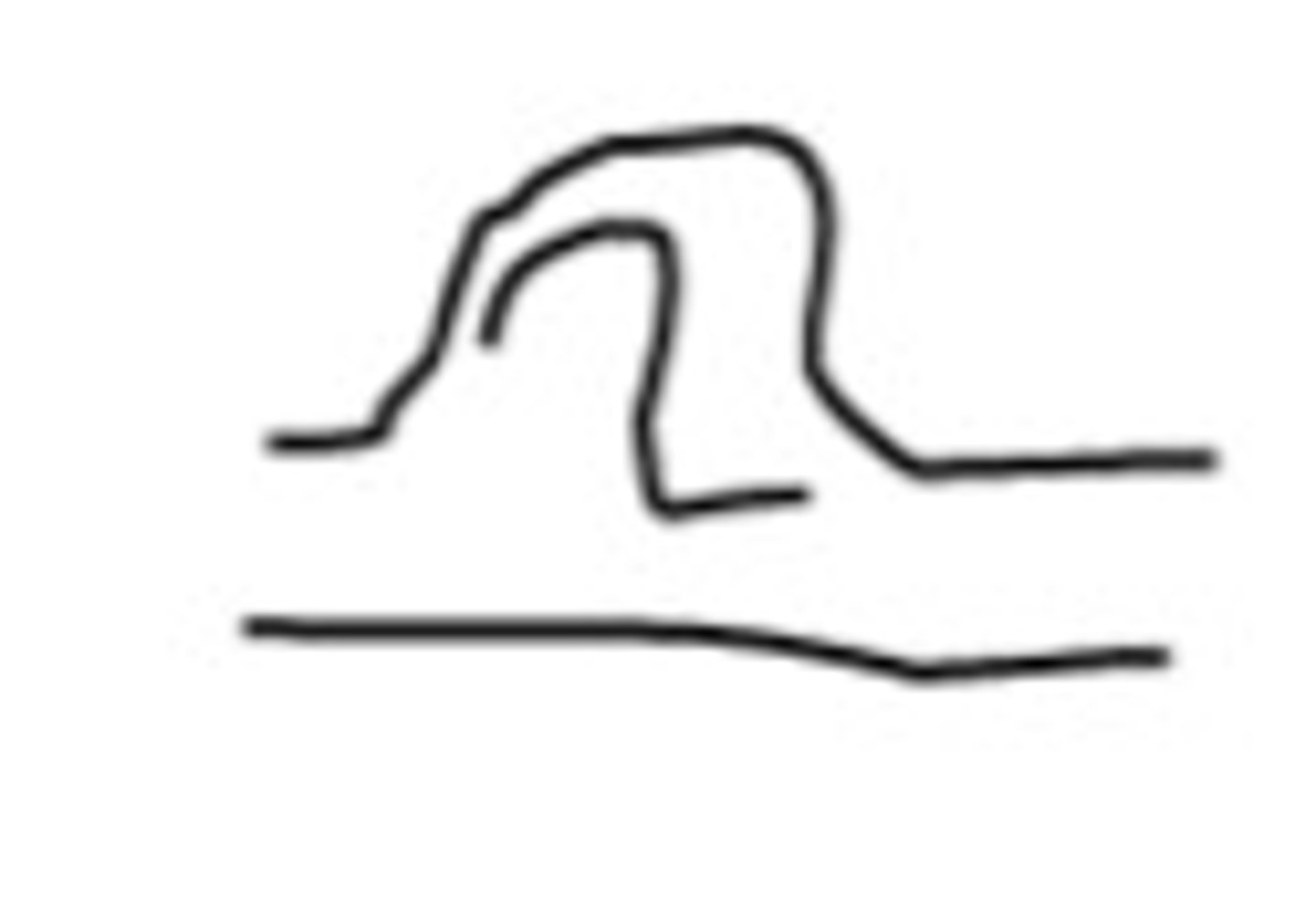
dot or island
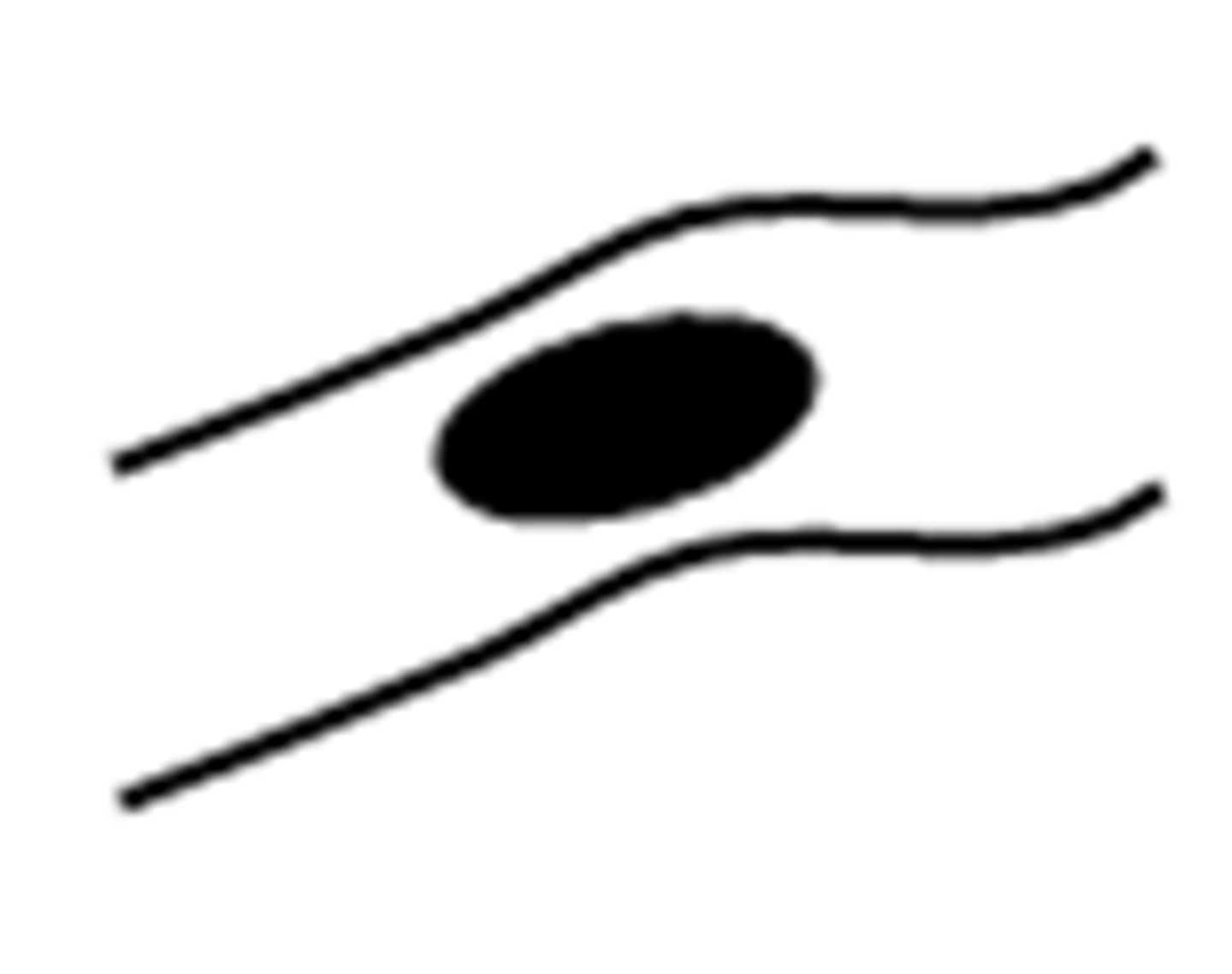
crossover
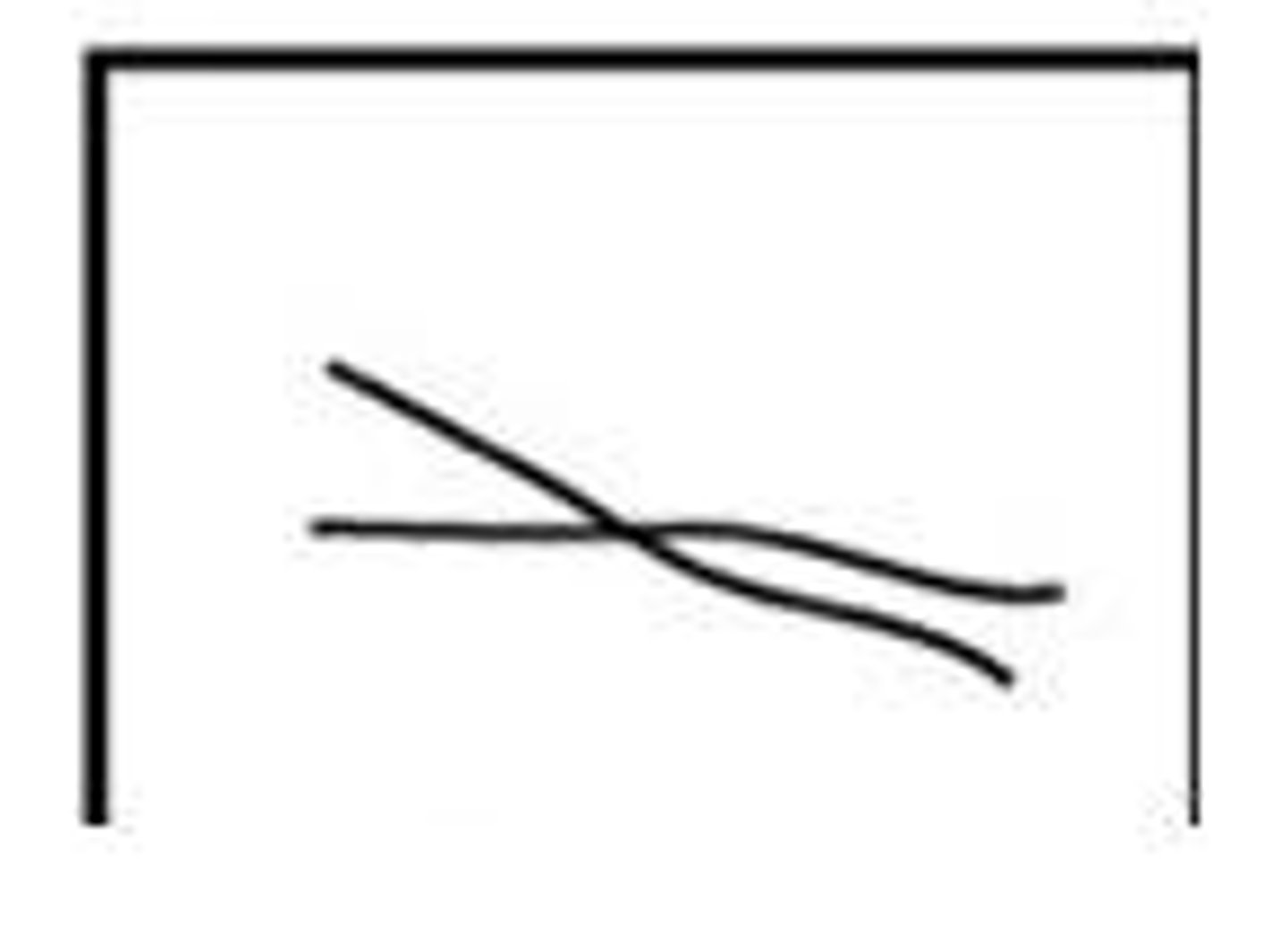
bridge

enclosures
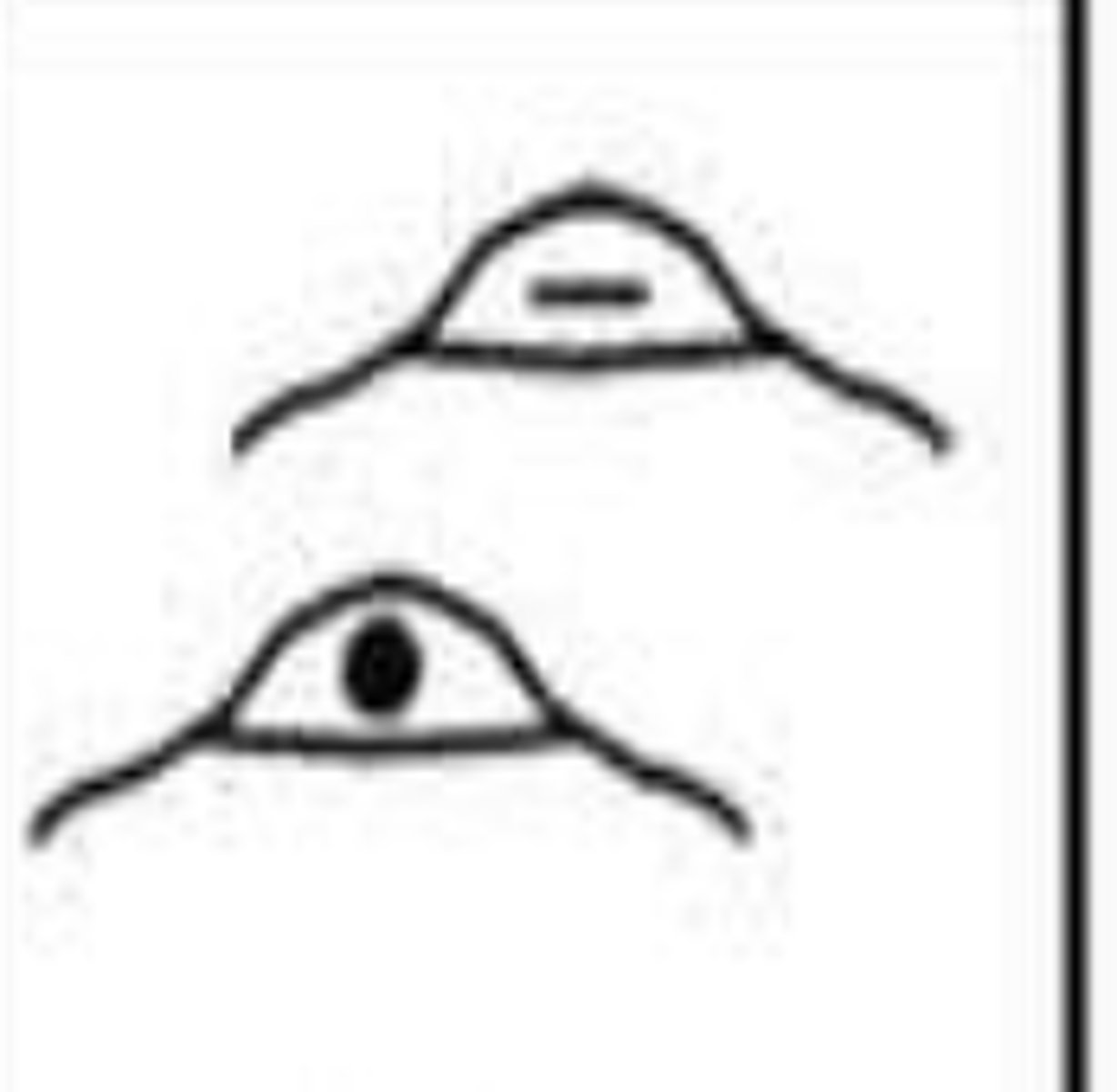
specialty

ACE-V
-Analysis
-Comparison
-Evaluation
-Verification
physical developments
-powder dusting w/ colored, fluorescent, and/or magnetic powders for dry, smooth, non-porous surfaces
-small particle reagent for hard surfaces that are or have been wet, sticks to fats/oils of prints
chemical developments
-cyanoacrylate (superglue)
-iodine fuming
-ninhydrin
ninhydrin development
reacts with amino acids in fingerprint residue and yield blueish purple color, useful on porous surfaces
sequential developments
multiple steps in order to get most information while maintaining as much evidence as possible
AFIS
automated fingerprint identification system
-scanning devices convert fingerprints into digital images and a search algorithm determines possible matches
-final decisions made by a trained examiner ALWAYS
fingerprint conclusions
-source identification
-inconclusive
-source exclusion
iodine fuming
interacts w/ oily residues to give deep brown print, do not las long (must be photographed)
cyanoacrylate
Superglue that is used to capture fingerprints on nonporous surfaces like glass and plastic.