Plasma Membrane
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
plasma membrane
phospholipid bilayer + embedded proteins → separate intracellular environment from extracellular environment
intracellular
inside a cell
extracellular
outside a cell
selective permeability / semipermeable
property that ensures only specific substances pass across it.
phospholipid bilayer
an amphipathic molecule that makes the membrane stable
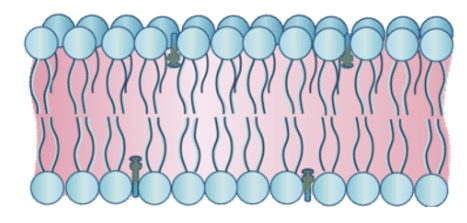
phospholipid bilayer structure
hydrophilic phosphate head
hydrophobic fatty acid tails

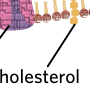
cholesterol
a steroid-alcohol that regulates fluidity in the P.M
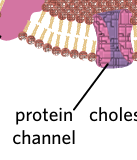
protein channels
pores or holes in the membrane that let a specific substance through.
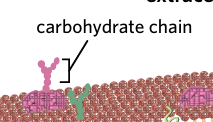
carbohydrate chains
aid with cell-cell communication
signalling
recognition of self or non-self (foreign) molecules
adhesion
glycolipid
a phospholipid bound to a carbohydrate.
stabilises membrane
acts as recognition site

glycoprotein
protein bound to a carbohydrate
cell signaling
cell-cell recognition
cell adhesion

passive transport
movement of molecules through semipermeable membrane, down the concentration gradient without energy
active transport
movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane that requires energy
diffusion
passive movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration
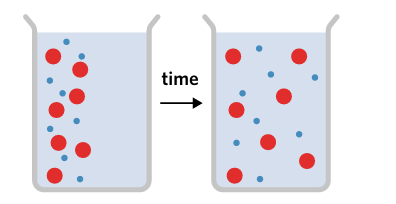
concentration gradient
the difference in solute concentration between two adjacent areas
solute
a substance dissolved in the solvent
solvent
a liquid in which a solute is dissolved, forming a solution
nonpolar
a molecule without a clearly positive or negative end, generally hydrophobic
hydrophobic
water hating
hydrophilic
water loving
polar
a molecule with both a positive end and a negative end, tend to be hydrophilic
facilitated diffusion
the passive movement of molecules down their concentration gradient through a membrane-bound protein
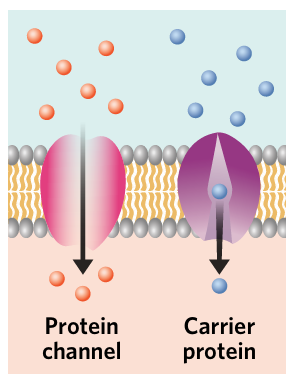
carrier protein
membrane protein that undergoes conformational change to transport molecules across a membrane
osmosis
the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration
tonicity
measure of the relative concentration of solutes on either side of a semipermeable membrane
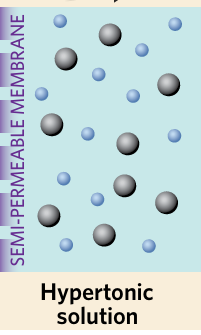
hypertonic
a solution with a higher solute concentration when compared to another solution
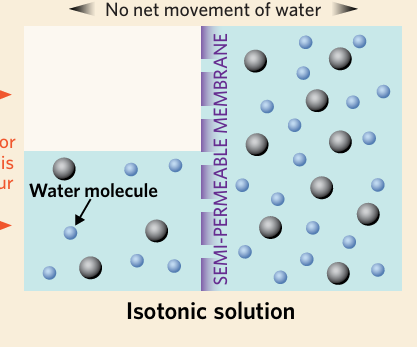
isotonic
describes a solution with the same solute concentration as another solution
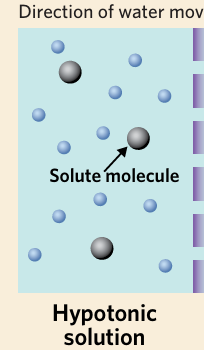
hypotonic
describes a solution with a lower solute concentration when compared to another solution
protein-mediated active transport
involves using membrane proteins to move molecules across a membrane against their concentration gradient
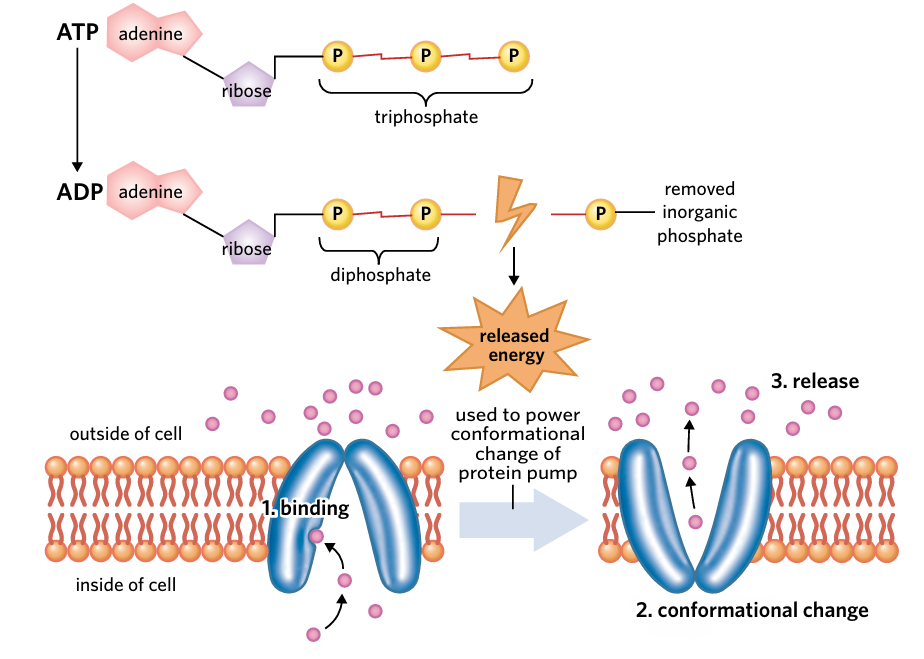
ATP
Molecule that can be used for energy
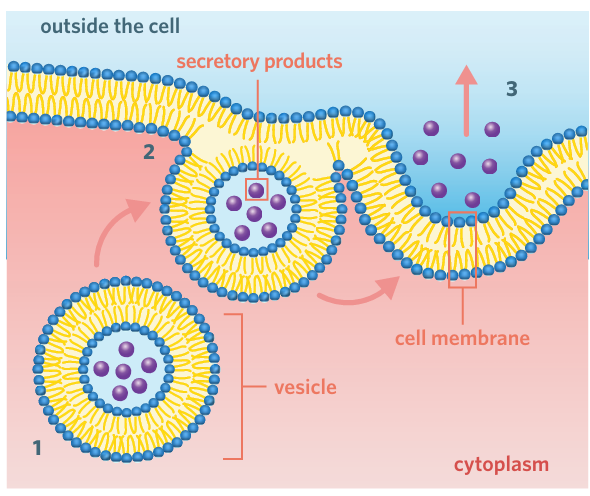
Exocytosis
exocytosis is the process by which the contents of a vesicle are released from a cell.
exocytosis steps
1 Vesicular transport – a vesicle containing secretory products is transported to the plasma membrane
2 Fusion – the membranes of the vesicle and cell fuse
3 Release – the secretory products are released from the vesicle and out of the cell.
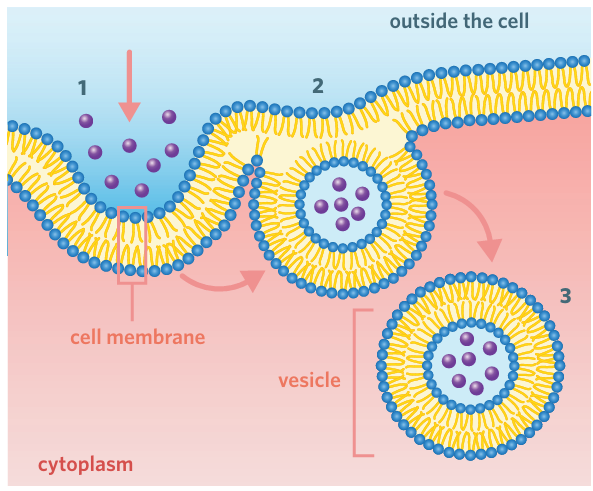
endocytosis
endocytosis involves transporting large molecules or groups of molecules into the cell.
endocytosis steps
1 Fold – the plasma membrane folds inwards to form a cavity that fills with extracellular fluid and the target molecules.
2 Trap – the plasma membrane continues folding back on itself until the two ends of the membrane meet and fuse. This traps the target molecules inside the vesicle.
3 Bud – the vesicle (or endosome) pinches off from the membrane. It can then be transported to the appropriate cellular location or fused with a lysosome for digestion.
cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton gives shape and support to the cell and transports molecules around the cell.