Adrenal Glands
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
adrenal gland location
sit on top of kidneys.
Blood supply to the adrenals
Superior adrenal arterty
middle adrenal artery
inferior adrenal artery
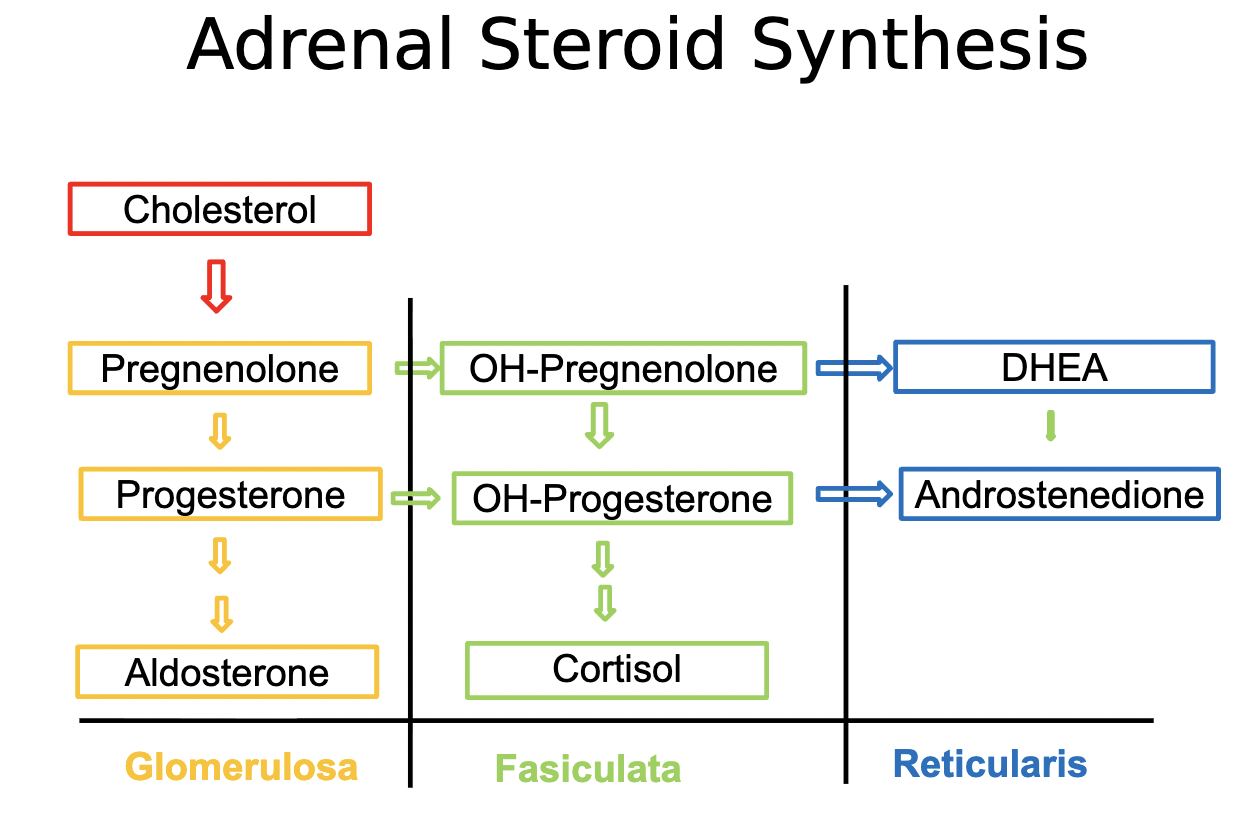
Layers of the adrenal gland
capsule on the outside
Adrenal cortex ‘looks like thick skin’
Adrenal Medulla in the centre.
Layers of the adrenal cortex
zona glomerulosa
zona faschiculata
zona reticularis
Zona glomerulosa function
secretes aldosterone
Mineral corticoid → causes uptake of sodium in the kidney
water follows the minerals → when there is more sodium in the blood stream, there will also be more water, meaning higher blood pressure.
Angiotensin II, aldosterone and filtration
Stimulus: low blood pessure or low blood volume. When blood pressure drops, kidneys respond.
renin release: kidneys release renin into the bloodstream → renin converts angiotensinogen (from the liver) into angiotensin I.
Angintensin I to angiotensin II: Angiotensin I travels to the lungs, where ACE( angiotensin converging enzyme) converts it into angiotensin II → the active form.
Effects of angiotensin II: vasoconstriction → narrowing of blood vessels → increase in blood pressure. Stimulates aldosterone release.
Aldosterone action: Acts on the kidneys to increase reabsorbtion of sodium and chloride since water follows sodium by osmosis.
result → increase in blood volume, therefore, increase in blood pressure.
overall → feedback loop that maintains blood pressure and fluid balance by constricting blood vessels and retaining salt and water in the kidneys.
Zona fasiculata
secretes cortisol → glucocorticoid (changes glucose concentration and is a cortical steroid).
Causes glucogemesis from lipolysis and protein catabolism so blood glucose increase and the immume system is inhibited.
90% of the hormones produced by the adrenal cortex is cortisol.
Control of corticosterioids
corticotropin releasing hormone causes adrenal corticotropic hormone (ACTH or corticotropin, a tropic hormone) to be secreted which then causes cortisol production in the adrenal cortex.
This causes:
Glucogenesis from protein and fat catabolism, heatic glucose secretion and immuno suppression.
These act as a negative feedback loop to downregulate cortocotripin releasing hormone.
Zona reticularis
secretes androgens → main products are the androgen androstenedione and the androgen precursos (DHEA)
Androstendione promotes growth and development
DHEA is converted into other androgens (male sex steroids).
Disease of the adrenal cortex
all due to over / underproduction of adrenal hormones
Good to know image →
Hypercortisolemia (cushings syndrome)
cortisol and its synthetic analogs have a wide range of effects that lead to a cushoing syndrome.
Cortical steroids increase the rate of
glucogenesis
glucose secretion by the liver
breakdown of fat and protain
this is to supply material for glucogenesis.
decreased glucose uptake and use by peripheral tissues:
With extremely high amounts of cortisol, or a synthetic cortical steroid, lack of tissue repair can lead to striae.
Large doses of cortical steroids cause hyperglycemia and the breakdown of muscle.
Fat gets redistributed
Abdomen, posterior nck
Cushings disease
due to an adenoma that produces ACTH, leading to an ectremely high cortisol.
Congenital adrenal hypoplasia (CAH)
inability to produce cortisol / aldosterone, leading to an overproduction of androgens in the fetus.
Lack of negative feedback from cortisol means precursoes are made in huge amounts and make more andrpgens.
overproduction of androgens causes virilxation of the XY fetus, causing them to be intersex.
Addison disease
addison disease (primary adrenal insufficiency) occurs due to an autoimmune attack on the adrenal cortex, so that cortisol cannot be made.
aldosterone and androgen production would also be decreased.
with the destruction of so many cortical steroids, you get the following symptomr:
weight loss, dehydration, hypotensionl, hyponateamia, hyperkalemia, hypoglycemia as a result.
Adrenal medulla
secretes chatecholamines
epinepherine and norepinepherine → made by chromaffin cells.
epinepherine and norepinepherine stimulate the sympathetic nervous system (fight, flight, fight).
innervation of the adrenal medulla
stictly from sympsathetic branch
when SNS nerves synapse on the chromaffin cells which release E and NE.
The adrenal medulla is a modified sympathetic ganglion.
Stress and the adrenal
sympathetic neural stimulus → epinepherine and norepinepherine are released by the adrenal medulla.
Stimulation by ACTH causes cortisol and other cortical hormones to be released from the adrenal cortex.