HL Biology Unit 6.2 The Blood System
1/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is blood comprised of?
55% Plasma, 45% Erythrocytes, <1% Leukocytes and Platelets
What is the blood’s Buffy Coat comprised of?
Leukocytes (white blood cells) and Platelets
Which two systems does circulation occur in?
Pulmonary (heart to/from lungs), and Systemic (heart to body)
Function of Arteries
Carries blood away from the heart an regulates blood flow by vasoconstriction/vasodilation
Artery Structure
Muscle + elastic fibers to maintain blood pressure between pumps (elastic membrane)
Thicker walls and narrower lumens
Function of Veins
Moves blood back to heart to be oxygenated by squeezing skeletal muscles and using pocket valves to prevent backflow
Layers of both veins and arteries
Tunica adventitia/externa: Tough outer layer of connective tissue
Tunica Media: thick layer of smooth muscle + protein elastic fibers
Tunica Intima: Smooth endothelium/inner lining
Name all parts of the heart
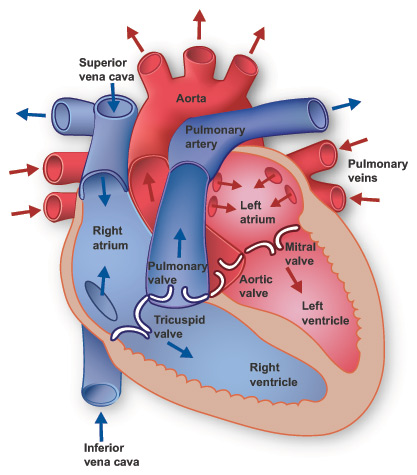
Why is the right side of the heart smaller/weaker?
The left side has more muscles to pump oxygenated blood everywhere, while deoxygenated blood only goes between heart and lungs
Function of capillaries
Tiny vessels that connect arteries and veins, used for material exchange between
Structure of Capillaries
High pressure in arterioles forces fluid out of capillaries, low pressure in venules allows reuptake of fluid
All of the following are adaptations for material exchange:
Branching = larger surface area
Thin Walls = only one cell wide
Fenestrations: small holes to increase permeability
What is Tissue Fluid?
Fluid that bathes cells, allowing diffusion through capillaries: glucose/O2 diffuses INTO cells while CO2/waste diffuses OUT
Differences between Tissue Fluid and Plasma
Large molecules (ex. proteins) remain in plasma but not tissue fluid (vital nutrients are contained in tissue fluid, like amino acids).
Function of Lymph Ducts
Collects excess tissue fluid (lymph) and all converge, emptying into the subclavian (under collarbone) vein to return fluid to blood supply
Structure of Lymph Ducts
Thins walls and gaps increase fluid absorption
Valves allow one-way movement of lymph fluid
What is the cardiac cycle?
Human heart activity from the beginning of 1 heartbeat to the beginning of the next
What is heart rate?
Pace of the cardiac cycle
What is the Sinoatrial Node?
A bundle of nerves controlling heartrate by initiating contraction in the right atrium, setting the pace of beats
What is the Cardiovascular Center?
Receives impulses from pH, blood pressure, and oxygen receptors to increase/decrease heart rate using the sympathetic or vagus nerves, respectively.
What does it mean that the heart is myogenic?
It can beat on its own without other nerve impulses to control it
What is Atherosclerosis?
The development of excessive fatty tissue (atheroma) in cell walls after a tear in the artery
What causes Atheroslerosis?
Cause unknown, but associated with:
High LDL Levels
High blood glucose
High BP
Consuming Trans Fats
What are the 5 steps in the process of getting Atherosclerosis?
LDL enters through endothelium
Intimal LDL is oxidized into proinflammatory lipids
Oxidized LDL (OxLDL) causes adhesion/entry of monocytes and T lymphocytes into artery
Monocytes differentiate into macrophages and consume LDL, becoming foam cells
Foam cells release growth factors (cytokines), promoting plaque growth
What are the health risks associated with atherosclerosis?
Occlusion of arteries = ↑ heart disease risk
↑ BP, Heart Rate, Blood Clot risk = ↑ Stroke/Heart Attack Risk
What is double circulation?
Circulation occurring in all mammals that divides oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
What is an example of a single circulation system?
Bony fish have a single circulation system where, since Gill capillaries have a high enough pressure to circulate it to all tissue, all blood in the heart is deoxygenated.
What is a normal Blood Pressure, and how can you read it?
Normal BP is 120/80, top number is the Systolic BP measuring the pressure in arteries when the heart beats, the bottom number is the Diastolic BP measuring pressure in arteries when the heart is resting between beats