BIO 212 Q5
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
Phylogeny
the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species
2
New cards
systematics
classifies organisms and determines their evolutionary relationships
3
New cards
Systematists use ___ to infer evolutionary relationships
fossil, morphological, and molecular data
4
New cards
Taxonomy
the ordered division and naming of organisms
5
New cards
Carolus Linnaeus published a system of taxonomy based on
resemblances
6
New cards
binomial
The two-part scientific name of a species
7
New cards
genus
the first part of the name
8
New cards
specific epithet \[i.e., species\]
the second part of the name, unique for each kind within the genus
9
New cards
the taxonomic groups from broad to narrow
domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species
10
New cards
taxon
A taxonomic unit at any level of hierarchy
11
New cards
Systematists depict evolutionary relationships in branching
phylogenetic trees
12
New cards
A phylogenetic tree represents a
hypothesis about evolutionary relationships
13
New cards
each branch point represents
the divergence of two species
14
New cards
Sister taxa
groups that share an immediate common ancestor
15
New cards
a rooted tree includes
a branch to represent the last common ancestor of all taxa in the tree
16
New cards
basal taxon \[outgroup\]
diverges early in the history of a group and originates near the common ancestor of the group
17
New cards
polytomy
a branch from which more than two groups emerge
18
New cards
Phylogenetic trees show ____ not ____
patterns of descent, phenotypic similarity
19
New cards
Phylogenetic trees typically do not indicate
when species evolved or how much change occurred in a lineage
20
New cards
To infer phylogenies, systematists gather information about
morphologies, genes, and biochemistry of living organisms
21
New cards
homologies
Phenotypic and genetic similarities due to shared ancestry
22
New cards
When constructing a phylogeny, systematists need to distinguish whether a similarity is the result of
homology or analogy
23
New cards
Homology
similarity due to shared ancestry
24
New cards
analogy
similarity due to convergent evolution
25
New cards
bat and bird wings are homologous as
forelimbs
26
New cards
bat and bird wings are analogous as
functional wings
27
New cards
Convergent evolution occurs when
similar environmental pressures and natural selection produce similar \[analogous\] adaptations in organisms from different evolutionary lineages
28
New cards
Molecular systematics
uses DNA and other molecular data to determine evolutionary relationships
29
New cards
Cladistics
groups organisms by common descent
30
New cards
clade
includes an ancestral species and all its descendants
31
New cards
monophyletic grouping
a valid clade, consists of the ancestor species and all its descendants
32
New cards
paraphyletic grouping
consists of an ancestral species and some, but not all, of the descendants
33
New cards
polyphyletic grouping
consists of various species with different ancestors
34
New cards
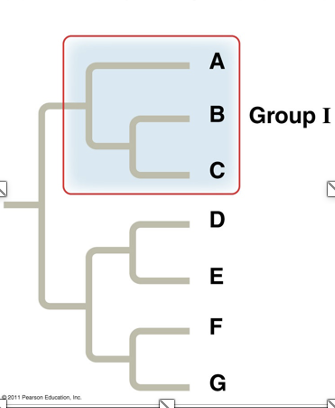
What type of grouping is this?
monophyletic
35
New cards
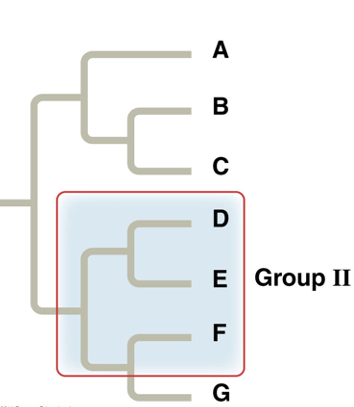
What type of grouping is this?
Paraphyletic
36
New cards
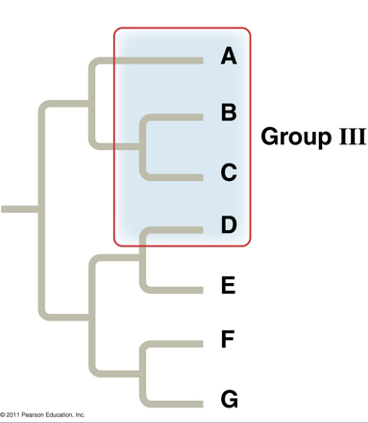
What type of grouping is this?
Polyphyletic
37
New cards
shared ancestral character
a character that originated in an ancestor of the taxon
ex. vertebratal column
ex. vertebratal column
38
New cards
shared derived character
an evolutionary novelty unique to a particular clade
ex. hair
ex. hair
39
New cards
outgroup
species or group of species that is closely related to the ingroup
40
New cards
ingroup
the various species being studied
41
New cards
Systematists compare each ingroup species with the outgroup to differentiate between
shared ancestral and shared derived characteristics
42
New cards
In some trees, the length of a branch can reflect the
number of genetic changes that have taken place
43
New cards
Methods of narrowing the possibilities of the best phylogenetic tree
maximum parsimony and maximum likelihood
44
New cards
Maximum parsimony assumes that
the tree that requires the fewest evolutionary events \[appearances of shared derived characters\] is the most likely
45
New cards
maximum likelihood states that
given certain rules about how DNA changes over time, a tree can be found that reflects the most likely sequence of evolutionary events
46
New cards
Phylogenetic bracketing
allows us to predict features of an ancestor from features of its descendents
47
New cards
What are some shared features of birds and crocodiles?
four-chambered hearts, vocalization, nest building, and brooding
48
New cards
The shared features of birds and crocodiles likely evolved in a
common ancestor
49
New cards
The shared features of birds and crocodiles were
shared by all of its descendants, including dinosaurs
50
New cards
What is a valuable approach for tracing organisms’ evolutionary history?
Comparing nucleic acids or other molecules to infer relatedness
51
New cards
Ribosomal RNA changes
relatively slowly
52
New cards
Ribosomal RNA is useful for investigating
branching points hundreds of millions of years ago
53
New cards
mtDNA evolves
rapidly
54
New cards
mtDNA can be used to
explore recent evolutionary events
55
New cards
\-nae
sub family
56
New cards
\-dae
family
57
New cards
What are the three domains?
the Archaea, the Bacteria, and the Eukarya