Chapter 24: Electromagnetic Waves
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Amplitude
the height, or magnitude, of an electromagnetic wave
Amplitude Modulation (AM)
a method for placing information on electromagnetic waves by modulating the amplitude of a carrier wave with an audio signal, resulting in a wave with constant frequency but varying amplitude
Carrier wave
an electromagnetic wave that carries a signal by modulation of its amplitude or frequency
Electric Field
a vector quantity (E); the lines of electric force per unit charge, moving radially outward from a positive charge and in toward a negative charge
Electric Field Lines
a pattern of imaginary lines that extend between an electric source and charged objects in the surrounding area, with arrows pointed away from positively charged objects and toward negatively charged objects. The more lines in the pattern, the stronger the electric field in that region
Electric Field Strength
the magnitude of the electric field, denoted E-field
Electromagnetic Spectrum
the full range of wavelengths or frequencies of electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic waves
radiation in the form of waves of electric and magnetic energy
Electromotive force (emf)
energy produced per unit charge, drawn from a source that produces an electrical current
extremely low frequency (ELF)
electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths usually in the range of 0 to 300 Hz, but also about 1kHz
frequency
the number of complete wave cycles (up-down-up) passing a given point within one second (cycles/second)
frequency modulation (FM)
a method of placing information on electromagnetic waves by modulating the frequency of a carrier wave with an audio signal, producing a wave of constant amplitude but varying frequency
gamma ray
(𝛾 ray); extremely high frequency electromagnetic radiation emitted by the nucleus of an atom, either from natural nuclear decay or induced nuclear processes in nuclear reactors and weapons. The lower end of the 𝛾-ray frequency range overlaps the upper end of the X-ray range, but 𝛾 rays can have the highest frequency of any electromagnetic radiation
hertz
an SI unit denoting the frequency of an electromagnetic wave, in cycles per second
infrared radiation (IR)
a region of the electromagnetic spectrum with a frequency range that extends from just below the red region of the visible light spectrum up to the microwave region, or from 0.74𝜇𝑚 to 300𝜇𝑚
intensity
the power of an electric or magnetic field per unit area, for example, Watts per square meter
magnetic field
a vector quantity (B); can be used to determine the magnetic force on a moving charged particle
magnetic field lines
a pattern of continuous, imaginary lines that emerge from and enter into opposite magnetic poles. The density of the lines indicates the magnitude of the magnetic field
magnetic field strength
the magnitude of the magnetic field, denoted B-field
maximum field strength
the maximum amplitude an electromagnetic wave can reach, representing the maximum amount of electric force and/or magnetic flux that the wave can exert
Maxwell’s Equations
a set of four equations that comprise a complete, overarching theory of electromagnetism
Microwaves
electromagnetic waves with wavelengths in the range from 1 mm to 1 m; they can be produced by currents in macroscopic circuits and devices
oscillate
to fluctuate back and forth in a steady beat
radar
a common application of microwaves. Radar can determine the distance to objects as diverse as clouds and aircraft, as well as determine the speed of a car or the intensity of a rainstorm
radio waves
electromagnetic waves with wavelengths in the range from 1 mm to 100 km; they are produced by currents in wires and circuits and by astronomical phenomena
resonant
a system that displays enhanced oscillation when subjected to a periodic disturbance of the same frequency as its natural frequency
RLC circuit
an electric circuit that includes a resistor, capacitor and inductor
speed of light
in a vacuum, such as space, the speed of light is a constant 3 x 108 m/s
standing wave
a wave that oscillates in place, with nodes where no motion happens
thermal agitation
the thermal motion of atoms and molecules in any object at a temperature above absolute zero, which causes them to emit and absorb radiation
transverse wave
a wave, such as an electromagnetic wave, which oscillates perpendicular to the axis along the line of travel
TV
video and audio signals broadcast on electromagnetic waves
ultra-high frequency (UHF)
TV channels in an even higher frequency range than VHF, of 470 to 1000 MHz
ultraviolet radiation (UV)
electromagnetic radiation in the range extending upward in frequency from violet light and overlapping with the lowest X-ray frequencies, with wavelengths from 400 nm down to about 10 nm
very high frequency (VHF)
TV channels utilizing frequencies in the two ranges of 54 to 88 MHz and 174 to 222 MHz
visible light
the narrow segment of the electromagnetic spectrum to which the normal human eye responds
wavelength
the distance from one peak to the next in a wave
X-ray
invisible, penetrating form of very high frequency electromagnetic radiation, overlapping both the ultraviolet range and the 𝛾-ray range
Electromagnetic waves consist of
oscillating electric and magnetic fields and propagate at the speed of light 𝑐.
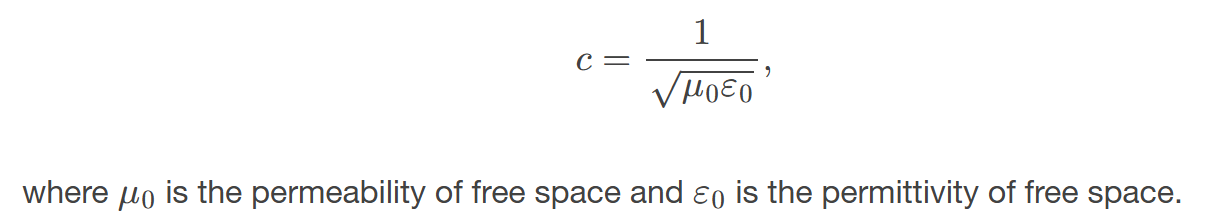
The strengths of the electric and magnetic parts of the wave are related
to the energy and intensity of the electromagnetic wave.
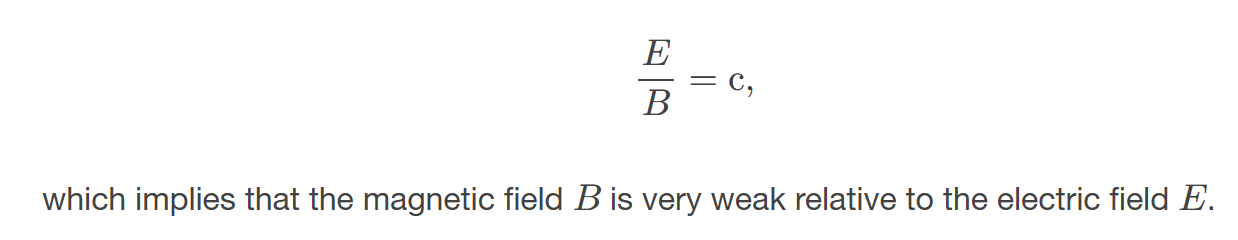
speed of propagation, wavelength, and frequency for electromagnetic waves
are inversely related, with the speed of light being constant.

Intensity of Electromagnetic waves
is the power per unit area carried by the wave, proportional to the square of the electric field amplitude.
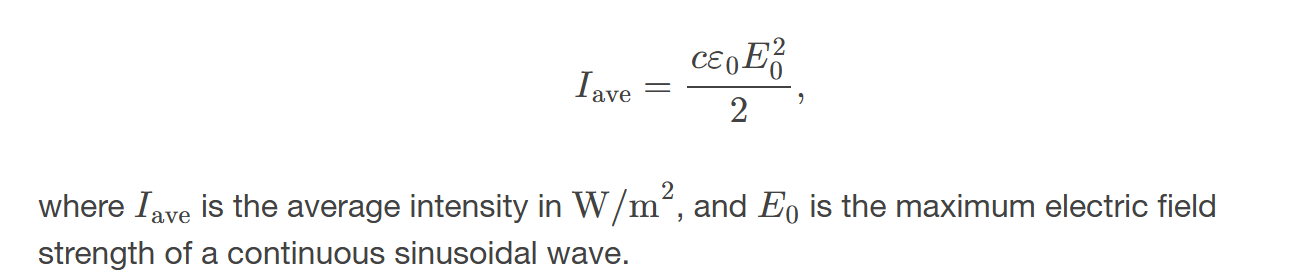
Intensity of Electromagnetic waves (with max magnetic field strength)
is the maximum power per unit area of the wave, determined by the square of the peak magnetic field amplitude.
