Bio Vocab
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Psychology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Nature
Definition: The biological/genetic predispositions that impact one’s human traits
Characteristics/facts:
physical
emotional
intellectual
Examples: eye color, hair color, and skin color
Non-examples: outlook on life
Nurture
Definition: The influence of learning and other environmental factors on these traits
Characteristics/facts:
physical
emotional
intellectual
Examples: confidence, behavior, and life outlook
Non-examples: eye color, hair color, and skin color
Eugenics
Definition: The practice or advocacy of controlled selective breeding of human populations
Characteristics/facts:
started in the late 1800s
still exists in the US
mostly affects people of color, LGBTQ+ individuals, and those with disabilities
Examples: The nazis’ justification for their treatment of the jews
Non-examples: A mixed couple having children
Twin studies
Definition: Research designs used in psychology to measure the influence of genetic factors on human behavior by comparing identical twins with fraternal twins
Characteristics/facts:
all studied traits are partly influenced by genetic differences
height = stronger influence
personality = intermediate level
Examples:
Non-examples:
Serotonin
Definition: A substance that is found mostly in the digestive tract, central nervous system, and platelets. Acts as a neurotransmitter substance that nerves use to send messages
Characteristics/facts: Plays a key role in -
mood
sleep
digestion
bone health
too low or too high can cause physical and psychological health problems
Examples: Aerobic exercise can significantly increase serotonin production in the body
Non-examples: Dopamine
Dopamine
Definition: A neurotransmitter and hormone that acts on areas of the brain to give you feelings of pleasure, satisfaction, and motivation
Characteristics/facts:
“feel-good” hormone
involved in movement
involved in memory
Examples: Anything that makes you happy releases dopamine like eating good food.
Non-examples: Seratonin
Sympathetic nervous system
Definition: A network of nerves that helps your body activate its “fight-or-flight” response
Characteristics/facts:
Adrenaline
increased heart rate
increased breathing rate
increased pupil size
increased blood pressure
decreased digestion
Examples: When you feel threatened your sympathetic nervous system is activated and you either run or fight
Non-examples: Ability to relax (parasympathetic)
Parasympathetic nervous system
Definition: Part of the body’s autonomic nervous system. Controls the body’s ability to relax. Sometimes called the “rest and digest” state
Characteristics/facts:
decreased respiration
decreased heart rate
increased digestion
Examples: Undoes all of the work of the sympathetic nervous system, causing the body to relax and return to resting state
Non-examples: “Fight or Flight” (sympathetic)
Acetylcholine
Definition: A compound that occurs throughout the nervous system, in which it functions as a neurotransmitter
Characteristics/facts: Plays a role in-
memory
learning
attention
muscle movement
Examples: Attaches to ACH receptors and signals for the release of calcium. The calcium then binds with troponin, pulling the tropomyosin and exposing the actin-binding site. The myosin filament head is now able to bind with the actin filament, forming the crossbridge. When returning to the rested position the myosin pulls the actin till it snaps back (like a rubber band). This is a muscle contraction
Non-examples: Anticholinergics (blacks the action of ACH)
Leptin
Definition: A protein produced by fat cells that is a hormone acting mainly in the regulation of appetite and fat storage
Characteristics/facts:
inhibit hunger
regulate energy balance
Examples: When the fat cells increase leptin levels increase
Non-examples: When fat cells increase leptin levels decrease
Ghrelin
Definition: A hormone produced by your stomach
Characteristics/facts:
other parts of your body like your brain, small intestine, and pancreas also release small amounts of ghrelin
also known as the “hunger hormone”
Examples: Ghrelin increases food intake and helps your body store fat
Non-examples: Amylin- a hormone that decreases food intake
GABA
Definition: A neurotransmitter that slows down your brain by blocking specific signals in your central nervous system
Characteristics/facts:
creates or sends chemical messages to other nerve cells
lessens the ability of a nerve cell to receive
Examples: Like brakes on a car
Non-examples: Like the gas in a car
agonists
Definition: A substance that initiates a physiological response when combined with a receptor. (a drug that produces a response)
Characteristics/facts:
selectivity
affinity
intrinsic activity
Examples: Full agonists like heroin and oxycodone
Non-examples: Antagonist, drugs that block or oppose the natural action or response of a receptor
antagonists
Definition: A substance that blocks or inhibits the function of a neurotransmitter in the brain by blocking the receptor
Characteristics/facts:
bind to the receptor
shift the dose-response curve
do not alter the magnitude of the maximum response
Examples: naltrexone and naloxone
Non-examples: methotrexate (inhibitor)
Re-uptake inhibitors
Definition: A substance that interferes with the reabsorption of neurotransmitters.
Characteristics/facts:
increase in extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter
increase in neurotransmission
Examples: SSRIs- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, a type of antidepressants
Non-examples: naltrexone and naloxone (antagonists)
Reward center
Definition: A complex network of neural circuits that help regulate motivation, reinforcement, and pleasure response
Characteristics/facts:
reward-related cognition
associative learning
incentive salience
Examples: reward-related activities like eating, substance use, and social interactions
Non-examples:
Amygdala
Definition: Region of the brain primarilly associated with emotional processes
Characteristics/facts:
regulating anxiety
aggression
fear
emotional memory
Examples:
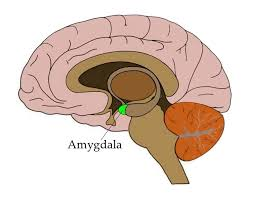
Non-examples: pons and medulla
Hypothalamus
Definition: Region of the forebrain below the thalamus that coordinates both the autonomic nervous system and the activity of the pituitary
Characteristics/facts: Controls
body temp
thirst
hunger
Examples:
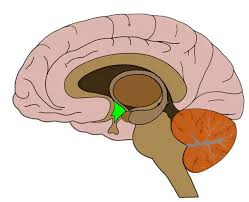
Non-examples: amygdala and pons
Hippocampus
Definition: The part of your brain that’s responsible for your memory and learning
Characteristics/facts:
a layer of densely packed neurons
curls into an S-shaped structure
Examples:
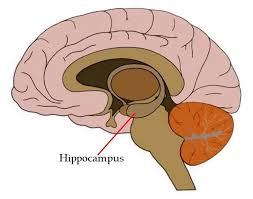
Non-examples: hypothalamus and amygdala
Higher-order thinking
Definition: Thinking on a level that is higher than memorizing facts or telling something back to someone exactly the way it was told to you
Characteristics/facts:
prepares students to be original thinkers and learners for life
self-directed
Examples: application and critical thinking
Non-examples: skills at the bottom of blooms taxonomy hierarchy
Executive functioning
Definition: A set of cognitive processes and mental skills that help an individual plan, monitor, and successfully execute their goals
Characteristics/facts: can improve execution functioning by
using a planner
establish routines
managing time
Examples: planning, organization, and attention
Non-examples: difficulty planning, organizing, and managing time and space
Re-uptake (mechanism)
Definition: The process in which the presynaptic neuron reabsorbs its released neurotransmitter after the neurotransmitter has done its job by binding to the postsynaptic neuron-reabsorbs
Characteristics/facts:
guards against neuronal overstimulation
enables energy conservation
Examples: the re-absorption of serotonin
Non-examples: inhibitors and antagonists
Plasticity
Definition: The brain’s malleability or ability to change
Characteristics/facts:
neuroplasticity allows nerve cells to change or adjust
Can reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life
Examples: Learning a new language or practicing music
Non-examples: requireing brain surgery
Reflex arc
Definition: An involuntary sequence or aaction (nearly instantaneous) response to a stimulus
Characteristics/facts: Five main components-
receptors
sensory neurons
interneurons
motor neurons
muscles
Examples: When we touch something hot
Non-examples: grabing a box off a shelf
Pituitary gland
Definition: A small, pea-sized gland located at the base of your brain below your hypothalamus
Characteristics/facts:
below your hypothalamus
endocrine gland
located at the base of your brain
Examples:
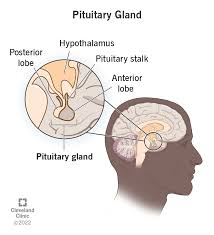
Non-examples: amygdala and pons
Lesion
Definition: An area of damage, injury, or abnormal change to a part of the brain
Characteristics/facts: Symptoms-
Weakness
disruption of senses
confusion
Examples: Phineas Gage, a man who had a steel rod penetrate his frontal lobe
Non-examples: Someone who has never expericenced an injury