BIOL 111 - Exam 2
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
210 Terms
Prokaryote
A microscopic, single-celled organism (bacteria, archaea etc.)
Nucleoid
Where DNA is located in prokaryotes
Peptidoglycan cell wall
A rigid layer surrounding bacterial cells, providing support and protection. Composed of alternating sugar chains linked by peptides
Pili
Help prokaryotes exchange genetic information during conjugation using plasmids; also help bacteria move
Flagella
Long, whip-like structures found in some cells that aid in movement. They are made up of microtubules and can be found in organisms like bacteria and sperm cells
Fimbriae
Short, hair-like structures found on the surface of some bacteria that help them attach to surfaces or other cells.
Bacterial resistance
Occurs because bacteria can exchange genetic information
Transduction
used to insert the genes of choices in animals & plant cells to modify their DNA & achieve desired characteristics. It can be used for gene therapy
Endosymbiosis
The hypothesis that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as independent prokaryotic organisms.
Evidence for endosymbiosis
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes
Mitochondria have a bacterial structure in their inner membrane and a eukaryotic structure in their outer membrane
Mitochondria divide by a binary fission like mechanism like bacteria
Extracellular matrix
A large network of proteins and other molecules that surround, support, and give structure to cells and tissues in the body
Allows cells in tissue to communicate with each other
Secretory vesicles
Move molecules (signaling and functional) outside of the cell through exocytosis
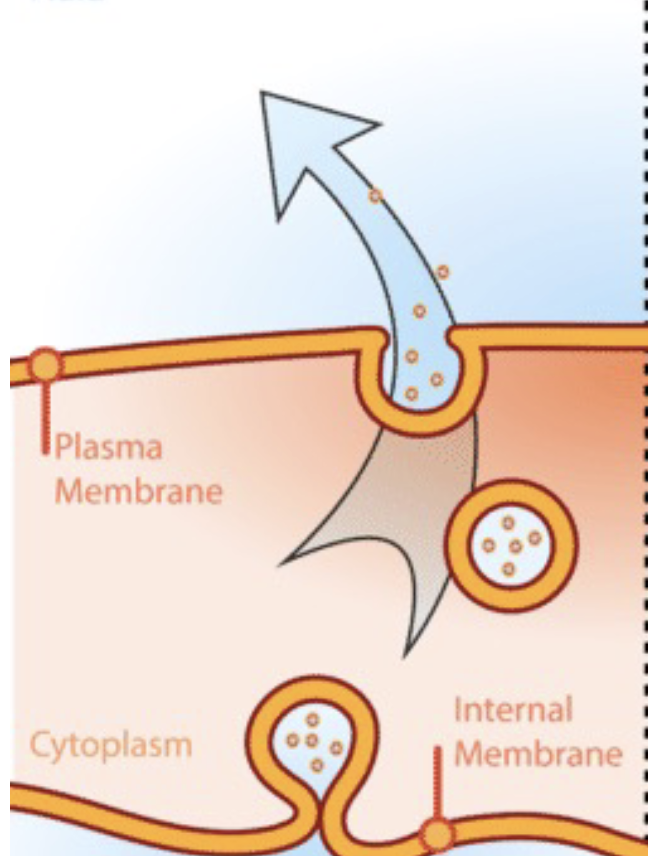
Exocytosis
Vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane & releasing contents to the outside of the cell
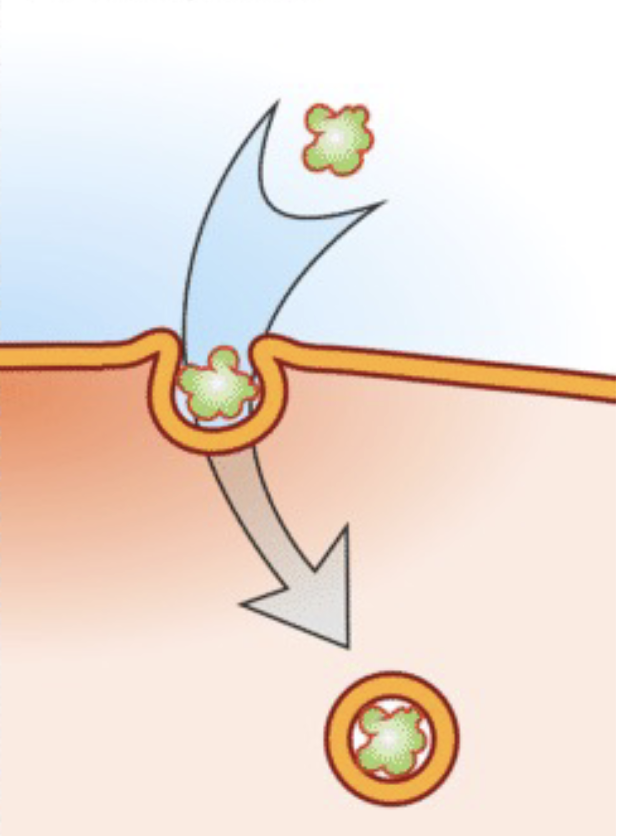
Endocytosis
Capturing a substance or particle from outside the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane
Intracellular junctions
Direct channels of communication between cells
Connect plasma membranes of adjacent cells
Tight junctions
Watertight seals between 2 adjacent cells
Proteins claudins and occludins hold the cells against each other
Found in epithelial cells that line internal organs and cavities
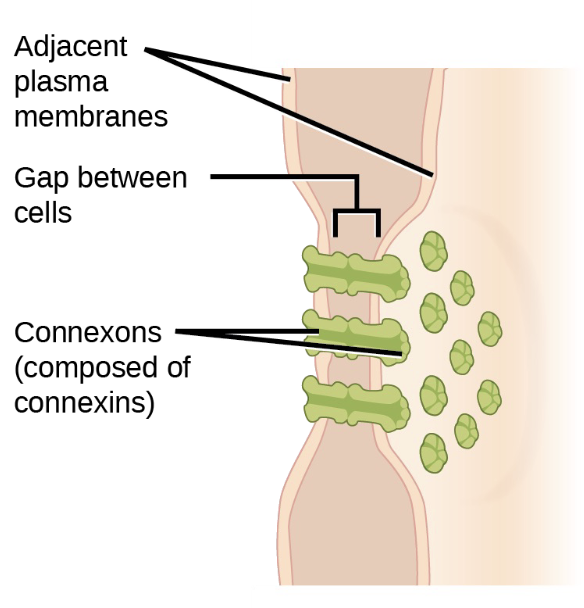
Gap junctions
Channels allow ions, nutrients and other small molecules to move between cells
Develop when 6 proteins (connexins) form an elongated doughnut-like structure (connexon) in the plasma membrane
Coordinates the activity of adjacent cells
Important in cardiac muscles
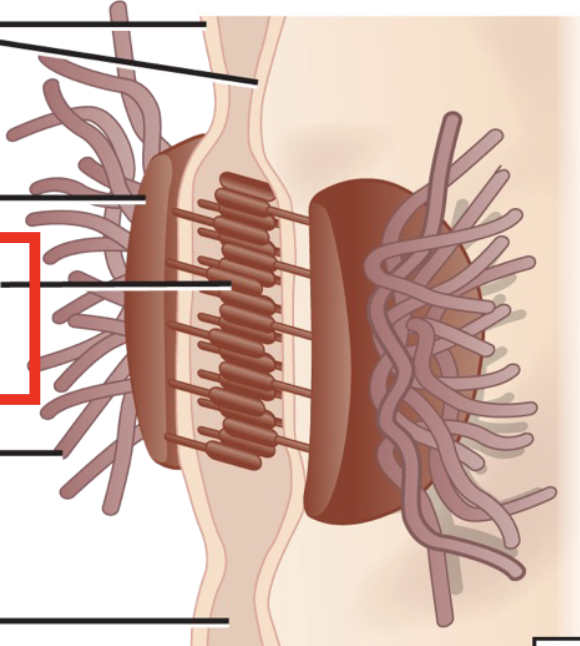
Desmosomes
Strong adhesions between cells in tissues that are under a lot of mechanical stress
Maintains a sheet-like formation
Includes cadherins, plaques and intermediate filaments
Known as spot welds because they are tethered to the intermediate filament network
Where are tight junctions found?
Blood brain-barrier, bladder
Where are gap junctions found?
Cardiac muscles, nerves and smooth muscles in intenstines
Where are desmosomes found?
Cardiac cells, bladder, gastrointestinal tract, and epithelia
Plasmodesmata
How plant cells communicate
Transports water, nutrients and proteins
Apoplastic pathway
Inside cell wall, outside plasma membrane
Transports water
Symplastic pathway
Cytoplasm to cytoplasm
Transports metabolites and proteins
Cell membrane functions
Defines cell borders
Selectively permeable
Must serve cell’s functions
Carries surface markers
Contains complex integral proteins
Components of the cell membrane
Phospholipids
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Fluid mosaic model
A collections of cellular membrane components give the membrane a complete and fluid character
Membrane fluidity factors
Temperature
Cholesterol
Unsaturated/saturated fats
Increases in membrane viscosity (thickness) →
disease states ( onset of atherosclerosis, malignancy, diabetes and hypercholesterolemia)
Increase in membrane fluidity (liquidity) →
effects on normal cell function via lipids in the membrane
Phospholipid head components
glycerol molecule
polar phosphate group
Phospholipid tail components
2 fatty acid chains (saturated and unsaturated)
Protein function in cell membranes
Transporters
Receptors
Enzymes
Binding and adhesion
Integral proteins
Combined completely into the bilayer
One or more hydrophobic regions
Peripheral proteins
Occur only on the surfaces
Carbohydrates
Found on the exterior of the plasma membrane bound to proteins or lipids
Function as labels and points of attachment for other cells
Passive transport
Cellular transport that does not require energy
Types of passive transport
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Active transport
Cellular transport that requires energy
Types of active transport
Protein pumps
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a membrane
Direction of osmosis
High water concentration → low water concentration
Aquaporins
Quickly transport water across a cell membrane (ex: liver, kidneys, lungs, eyes, etc.)
Tonicity
The ability of a solution to modify the volume of cells by altering their water content
Osmolarity
Total solute concentration of a solution
Hypotonic osmolarity
Outside water concentration > inside water concentration
Water moves inside
Lysed cell
Isotonic osmolarity
Outside water concentration = inside water concentration
Equilibrium
Normal cell
Hypertonic osmolarity
Outside water concentration < inside water concentration
Water moves outside
Shriveled cell
Osmoregulation
The process by which organisms regulate the balance of water and solutes in their bodies to maintain internal stability
Osmoregulation in organisms with cell walls
Prefer hypotonic extracellular solutions
Turgor pressure
Plasmolysis
Process in which a plant cell loses water due to a hypertonic environment, causing the cell membrane to shrink away from the cell walld
Freshwater protist osmoregulation
Contractile vacuoles pump water out of the cell to prevent bursting
Molecules that can be passively transported
O₂
CO₂
lipid hormones
Factors that increase diffusion rates
Greater concentration gradient difference
Smaller molecules
Higher temperature
Lower solvent density
Nonpolar solutes
Increased surface area
Smaller distance traveled
Greater cell pressure
Facilitated passive transport
Moves substances (ions and small polar molecules) down their concentration gradients using integral membrane proteins; energetically spontaneous
Channel protein
Passively transports ions and polar molecules; has a hydrophilic amino acids
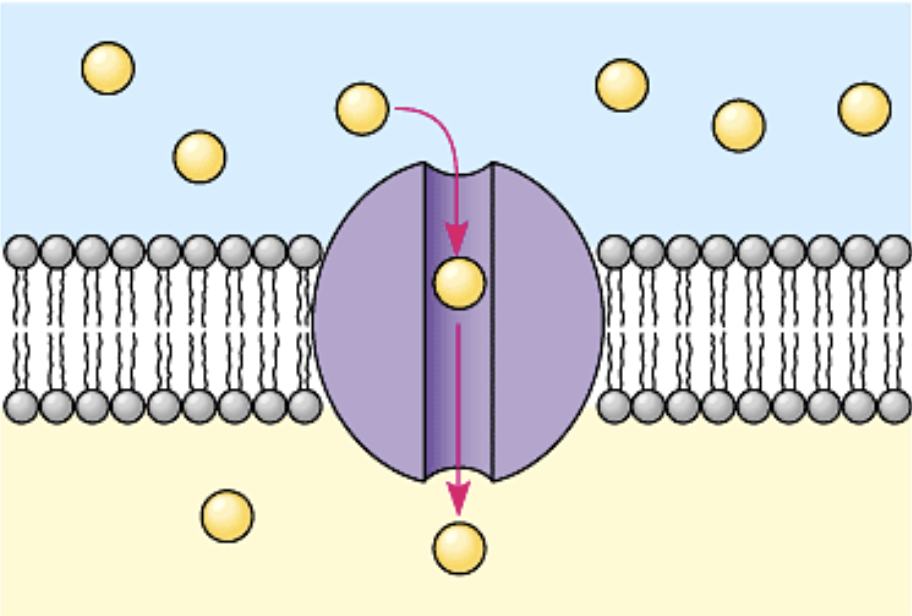
Carrier protein
Passively transports glucose; changes shape
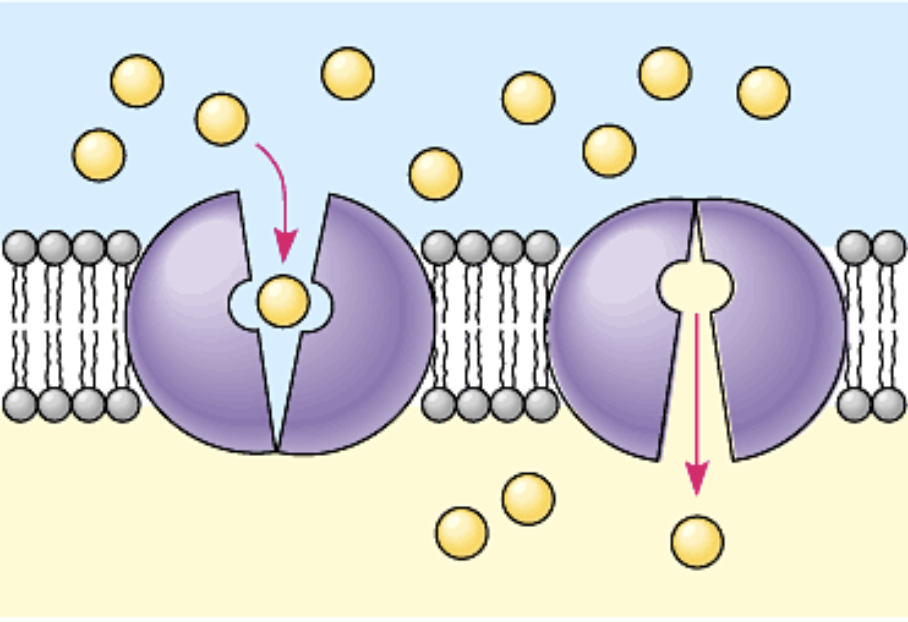
Function of active transport
Moves substances against the concentration gradient
Moves substances against its electrochemical gradient
Primary active transport
Active transport when ATP provides the energy to establish a gradient
Secondary active transport
Active transport when an electrochemical gradient provides the energy
Uniporter carrier protein
Carries one molecule or ion
Symporter carrier protein
Carries two different molecules or ions in the same direction
Antiporter carrier protein
Carries two different molecules or ions in different directions
Electrogenic pumps
Primary active transport
Generate voltage across the cell membrane
Sodium-potassium pump
Primary active transport
Pumps sodium out and potassium in; ratio of 3Na per 2K
Nerve transmission
Proton pump
Primary active transport
Pushes protons across the membrane
When does secondary active transport happen?
When glucose is more concentrated inside than outside but the cell needs more glucose to meet its metabolic needs.
How is ATP made from using active transport?
Potential energy accumulated in stored hydrogen ions gets translated into kinetic energy when the ions move through the channel protein which is used to convert ADP into ATP
Endocytosis
Importing particles in bulk
Exocytosis
Exporting particles in bulk
Types of endocytosis
Phagocytosis
Pinocytosis
Receptor mediated endocytosis
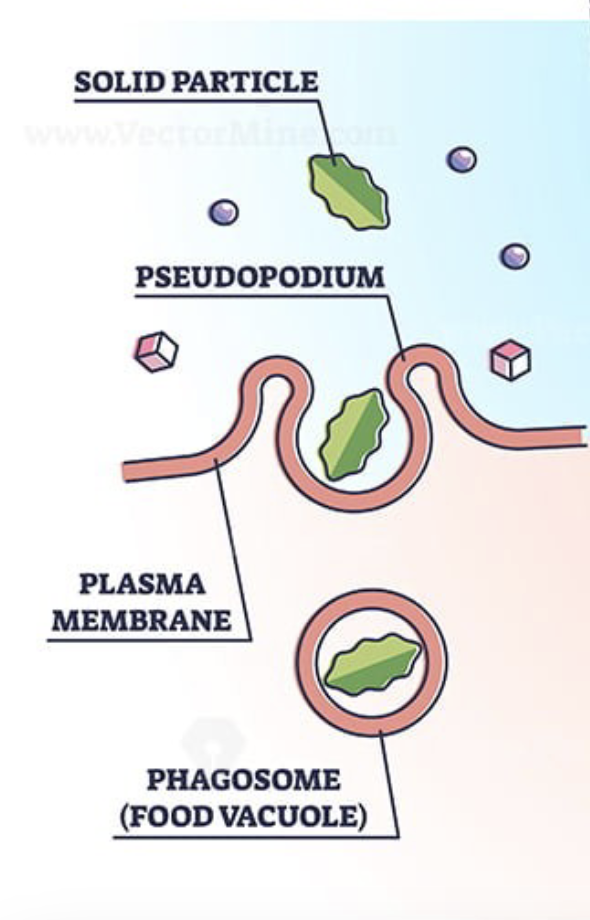
Phagocytosis
Cellular eating; a particle is surrounded and engulfed by the cell membrane
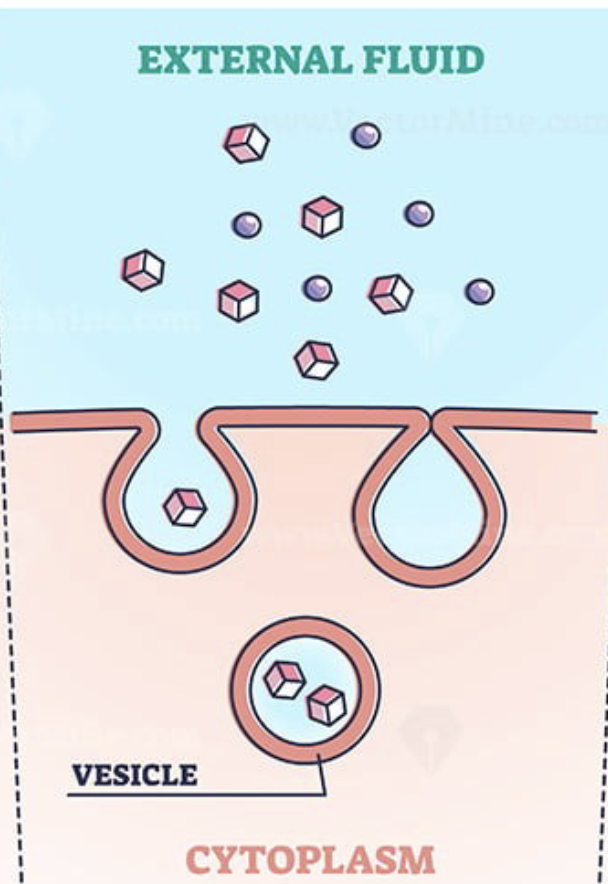
Pinocytosis
Cellular drinking; cell membrane forms a cavity, surrounds a fluid and pinches off
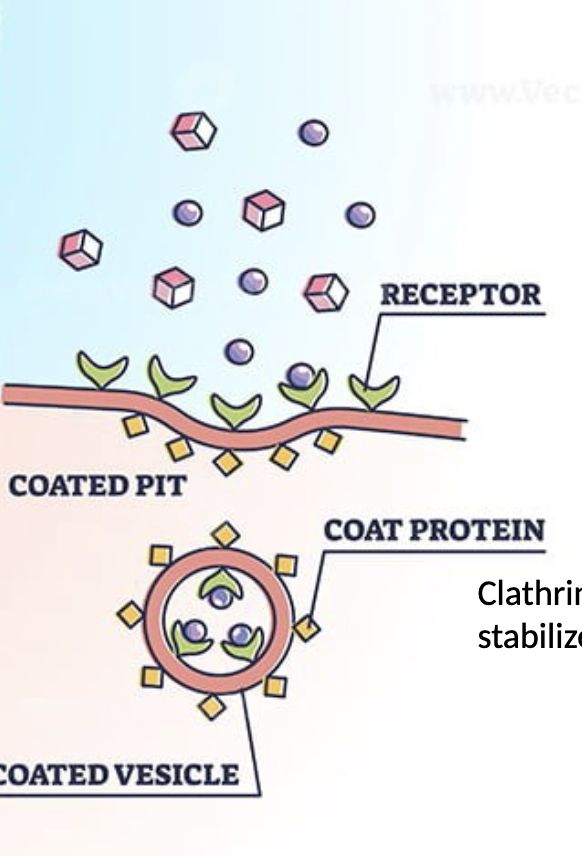
Receptor mediated endocytosis
Specific substances are targeted by binding receptors on the external surface of the membrane
Bioenergetics
The study of energy flow through living organisms
Metabolism
All chemical reactions taking place inside a cell that keep the body alive and healthy
1st Law of Thermodynamics
The total energy of an isolated system is constant; energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only transformed
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Entropy constantly increases in a closed system
Potential energy
Electrochemical gradients across the plasma membrane
Kinetic energy
Energy released when a bond breaks
Anabolic pathway
Small molecules are built into large ones
Uses energy
Endergonic
Catabolic pathway
Large molecules are broken down into large ones
Releases energy
Exergonic
Gibbs free energy
Amount of energy available to perform work
Exergonic reactions
∆G<0; energy released
Energy of products < energy of substrates
Cellular respiration
Endergonic reactions
∆G>0; energy required
Energy of products > energy of substrates
Photosynthesis, Na-K pump
ATP energy coupling via phosphorylation
ATP is hydrolyzed
ATP phosphate transfers to another molecule
Conformational change is induced
Endergonic and exergonic reaction relationship
Energy released by exergonic is used for the endergonic reaction
If not coupled, energy is lost as heat
Activation energy
Energy required for a reaction to proceed
Heat energy is the main source
Transition state
The state when reactants become unstable which allows bonds to be broken/made
Enzymes
Biological catalysts
Lower activation energy
Very specific but recyclable
Enzyme specificity
The ability of an enzyme to select a specific substate from a range of chemically similar compounds
Active site
The location where the enzymes interacts with substrates
Induced fit
Mild shift in shape that triggers catalysis
How enzymes lower activation energy
Positioning
Optimal environment (temperature, pH)
Contorting/stressing the substrate to make it less stable
Temporarily reacting with substrate
Factors that regulate enzymes
Changes in temperature or pH
Production of molecules that can inhibit/promote enzyme function
Availability of coenzymes or cofactors (enzyme helper molecules)
Competitive inhibitors
Slow enzyme function
Similar shape to the substrate
Competition for substrate
Noncompetitive inhibitors
Slow enzyme function
Bind to enzyme at allosteric location (different location)
Decreased affinity for the substrate
Positioning two substrates so they align perfectly for the reaction
Enzymes lowering activation energy
Providing an optimal environment (i.e. acidic or polar), within the active site for the reaction
Enzymes lowering activation energy
Contorting/stressing the substrate so it is less stable and more likely to react
Enzymes lowering activation energy