Myers Psychology for AP MEMORY
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
memory
The persistence of learning over time through the storage and retrieval of information.

encoding
The processing of information into the memory system.

storage
The retention of encoded information over time.

retrieval
The process of getting information out of memory storage.

sensory memory
The immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system.
short-term memory
Activated memory that holds a few items briefly before the information is stored or forgotten.

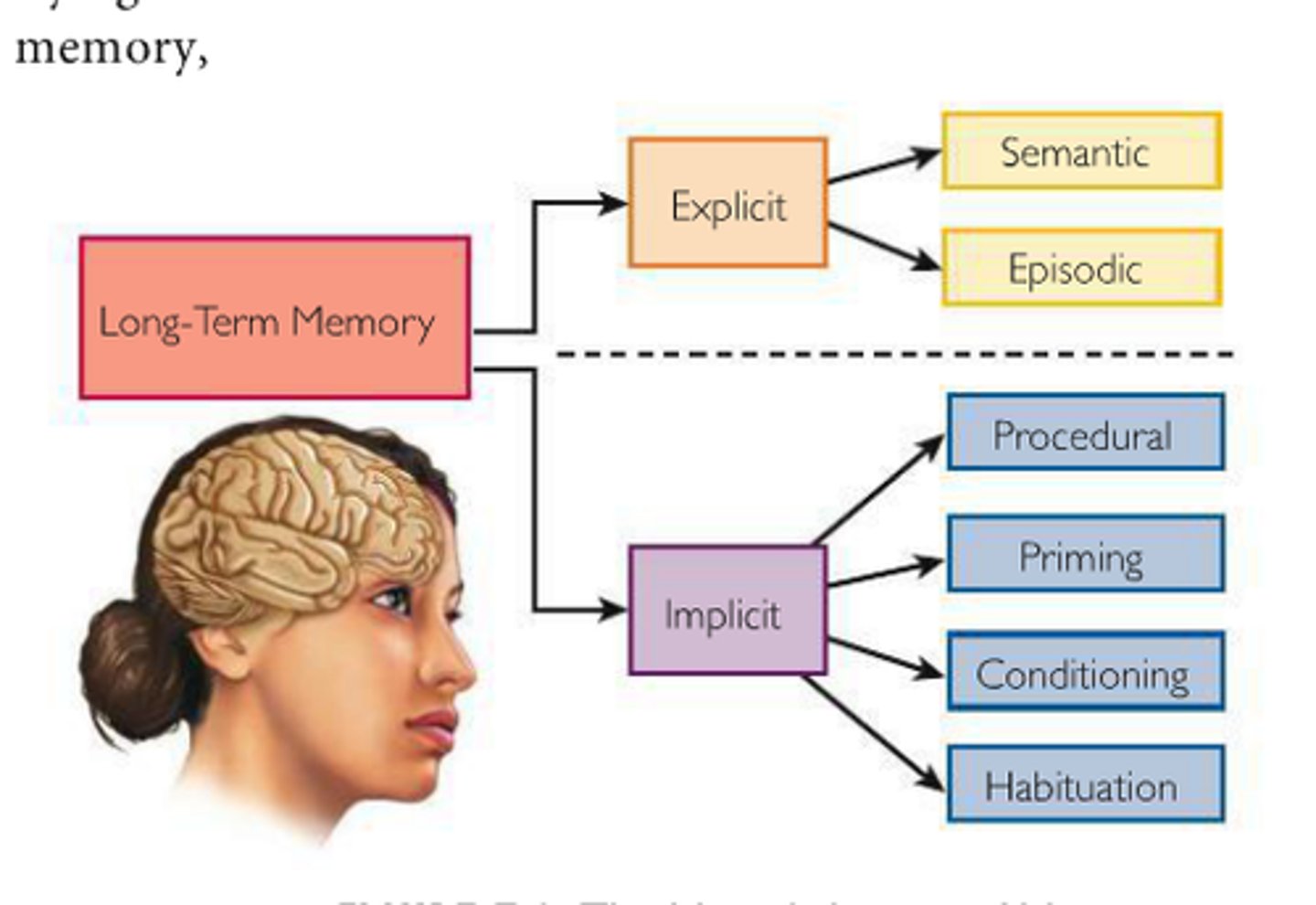
long-term memory
The relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system, including : knowledge, skills, and experiences.
working memory
A newer understanding of short-term memory that focuses on conscious, active processing of incoming auditory and visual-spatial information, and of information retrieved from long-term memory.
parallel processing
The processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain's natural mode of information processing for many functions.
automatic processing
Unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time, and frequency, and of well-learned information.
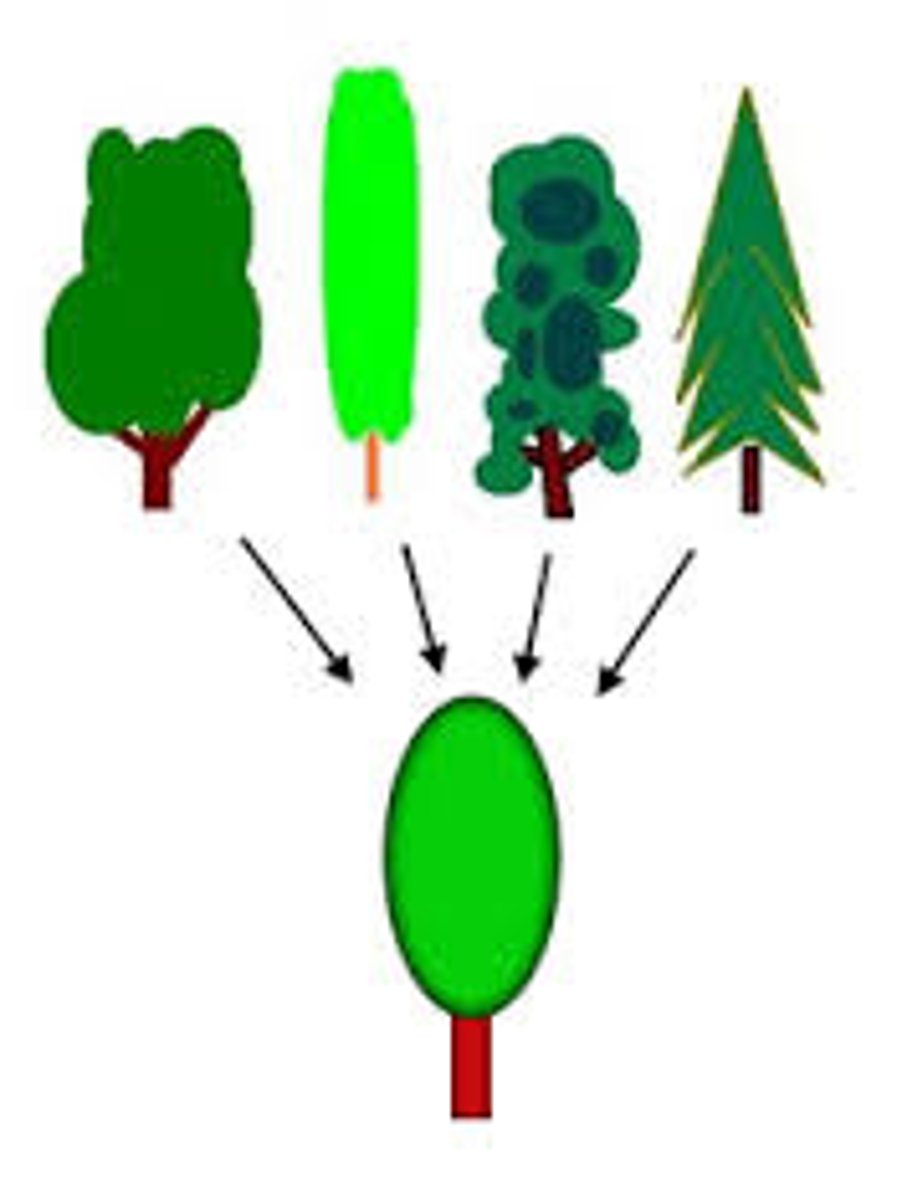
effortful processing
Encoding that requires attention and conscious effort.

rehearsal
The conscious repetition of information, either to maintain it in consciousness or to encode it for storage.

spacing effect
The tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice.

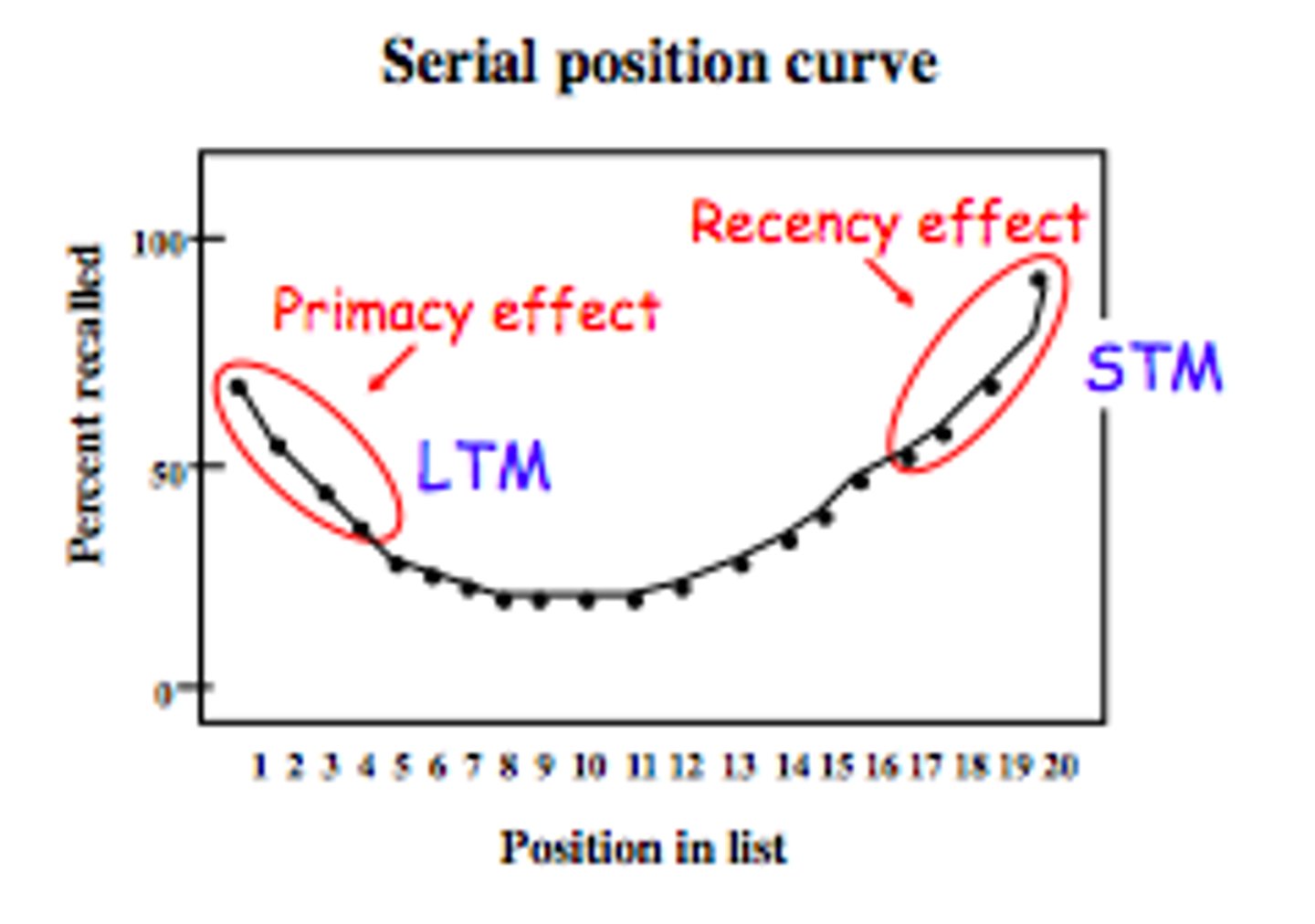
serial position effect
Our tendency to recall best the last and first items in a list.
visual encoding
The encoding of picture images.

acoustic encoding
The encoding of sound, especially the sound of words.

semantic encoding
The encoding of meaning, including the meaning of words.
imagery
Mental pictures; a powerful aid to effortful processing.

mnemonics
Memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices.

chunking
Organizing items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically.

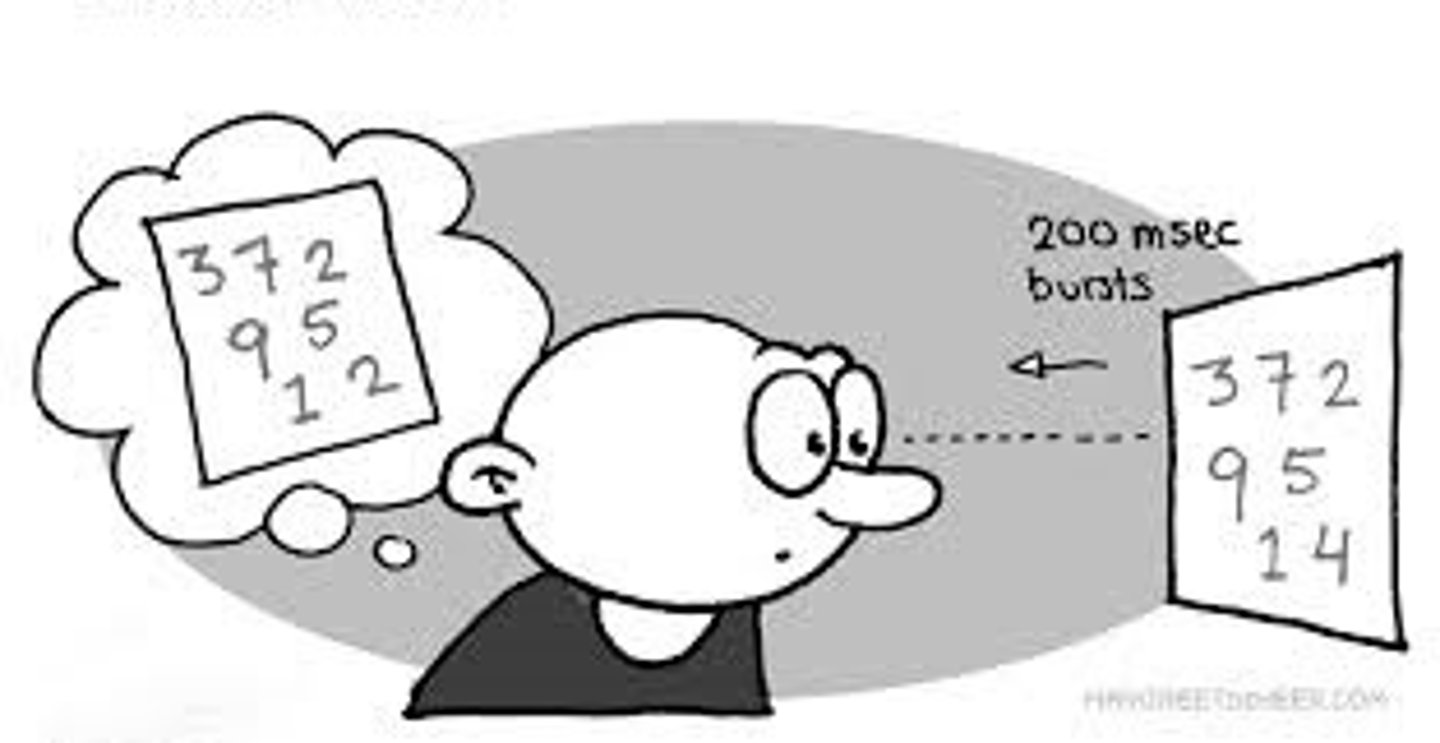
iconic memory
A momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a photographic or picture-image memory lasting no more than a few tenths of a second.
echoic memory
A momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli; if attention is elsewhere, sounds and words can still be recalled within 3 or 4 seconds.

long-term potentiation (LTP)
An increase in a synapse's firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation.
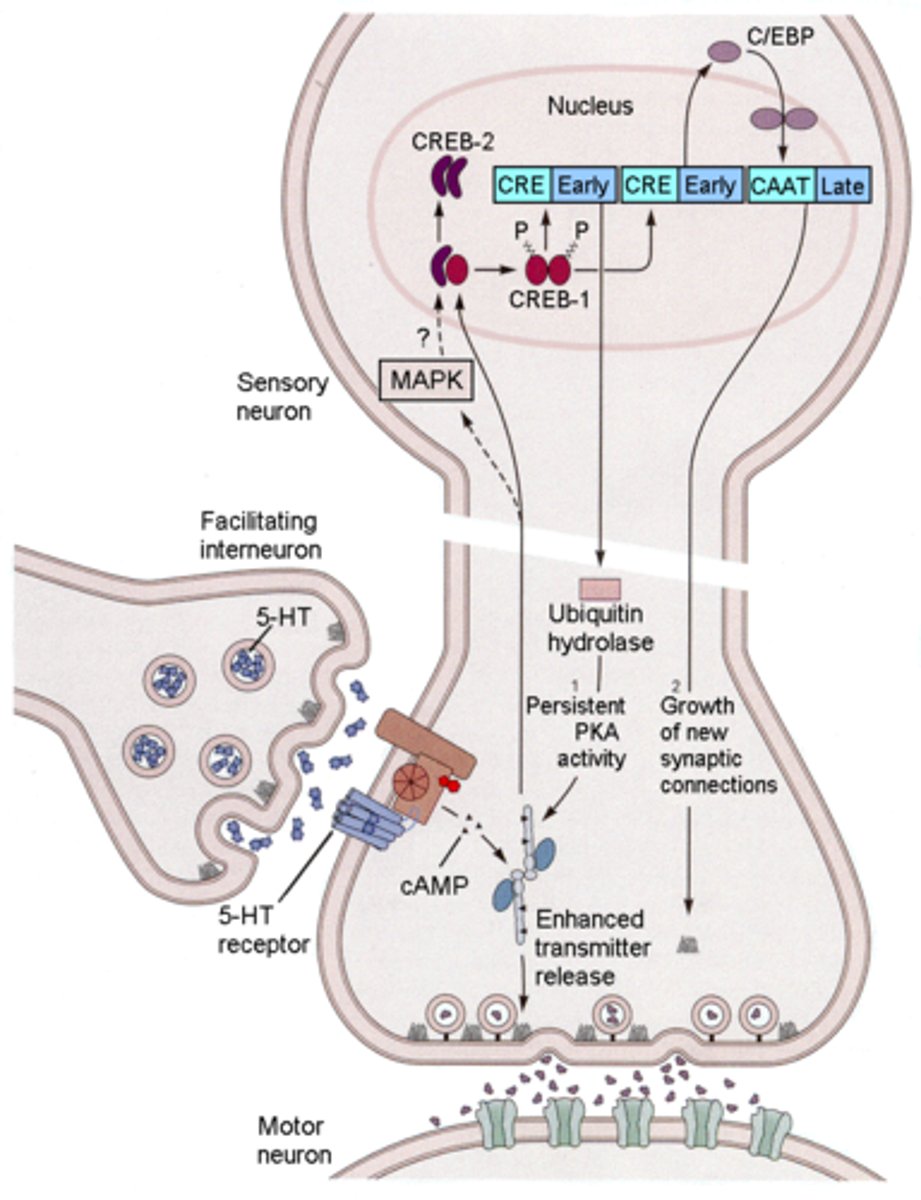
amnesia
The loss of memory.

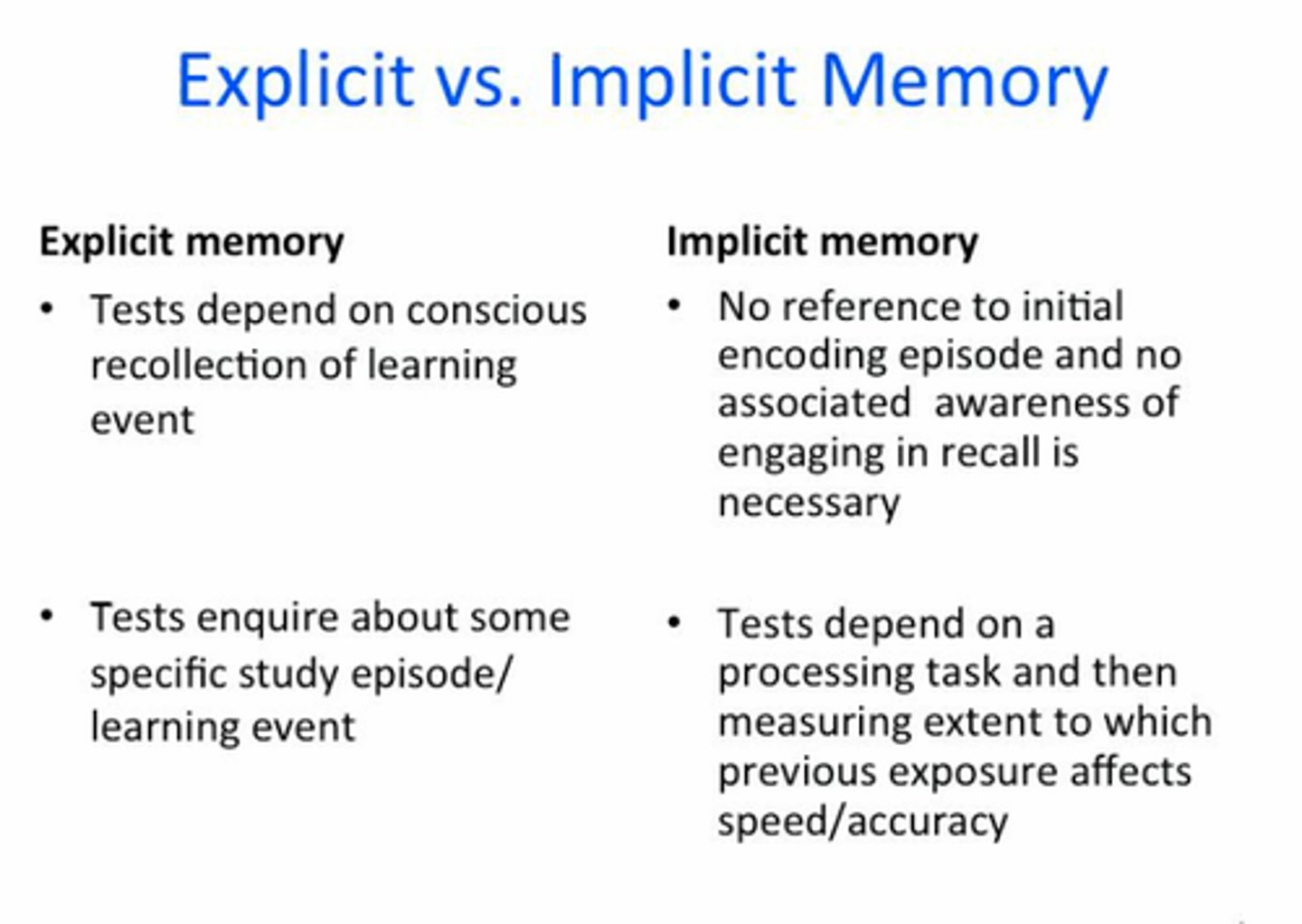
implicit memory
Retention independent of conscious recollection (nondeclarartive or procedural memory).
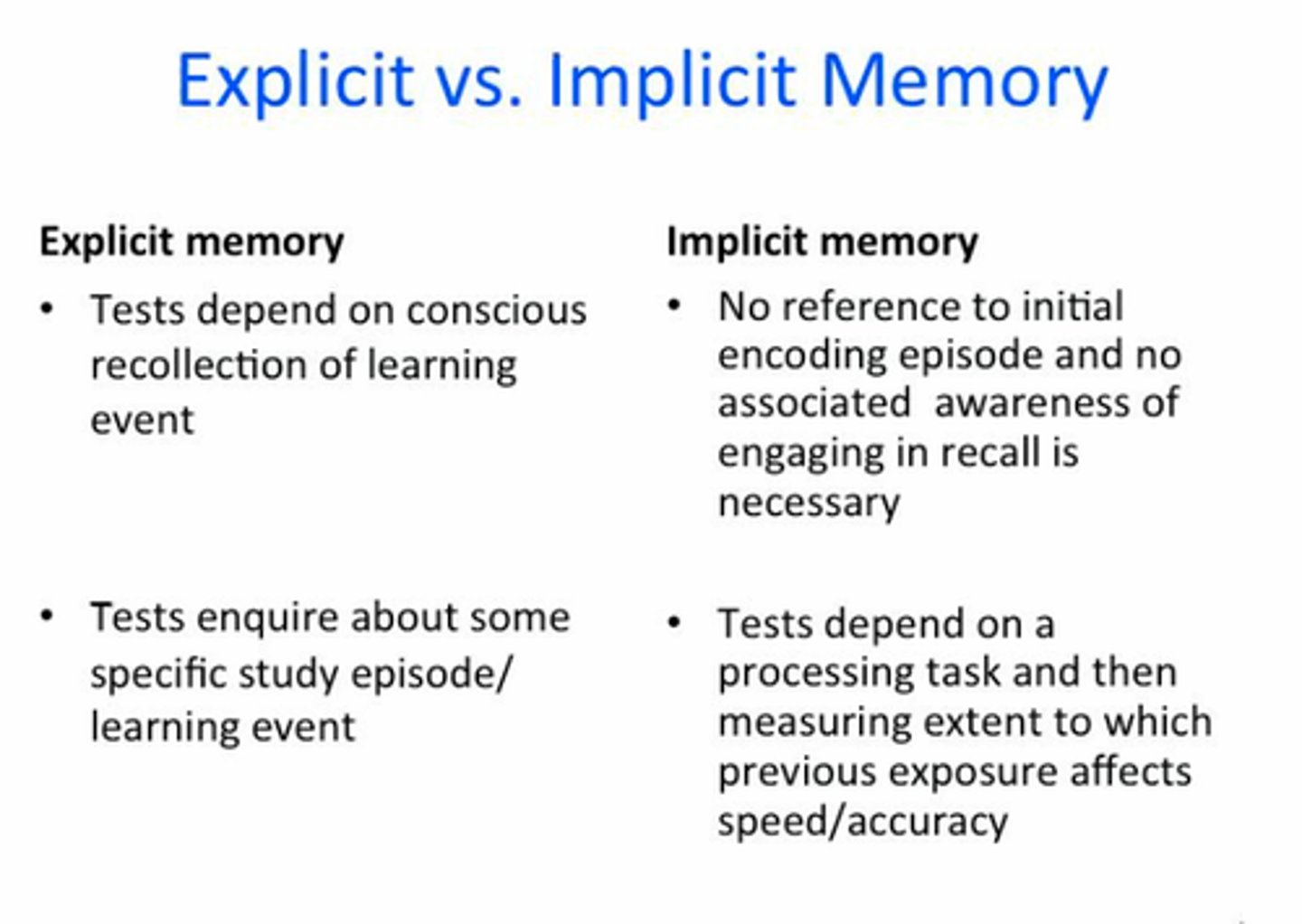
explicit memory
Memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare" (declarative memory).
hippocampus
A neural center that is located in the limbic system; helps process explicit memories for storage.

recall
A measure of memory in which the person must retrieve information learned earlier.

recognition
A measure of memory in which the person need only identify items previously learned.

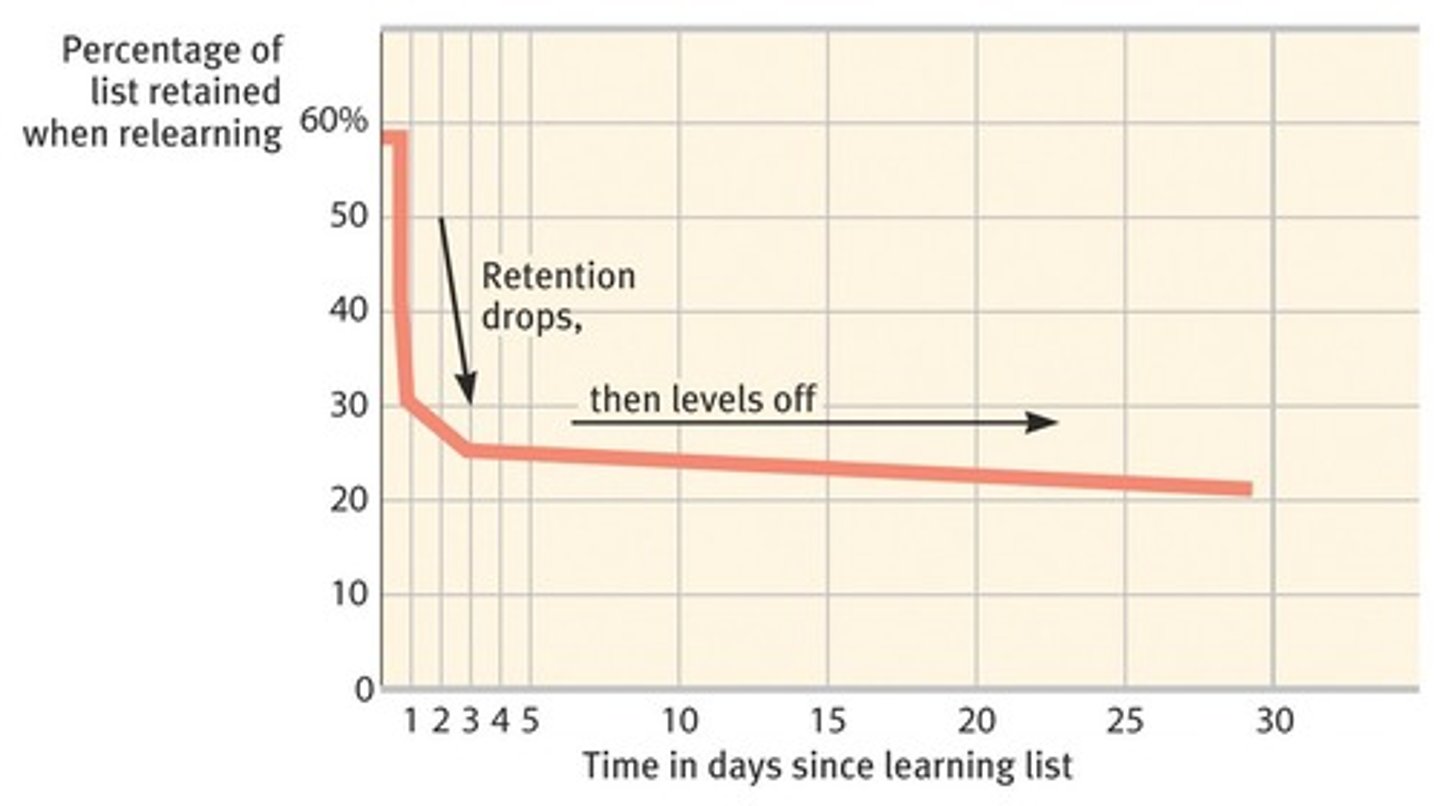
relearning
A measure of memory that assesses the amount of time saved when learning material for a second time.
priming
The activation, often unconsciously, of particular associations in memory.

déjà vu
That eerie sense that "I've experienced this before." Cues from the current situation may subconsciously trigger the retrieval of an earlier experience.

mood-congruent memory
The tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one's current good or bad mood.
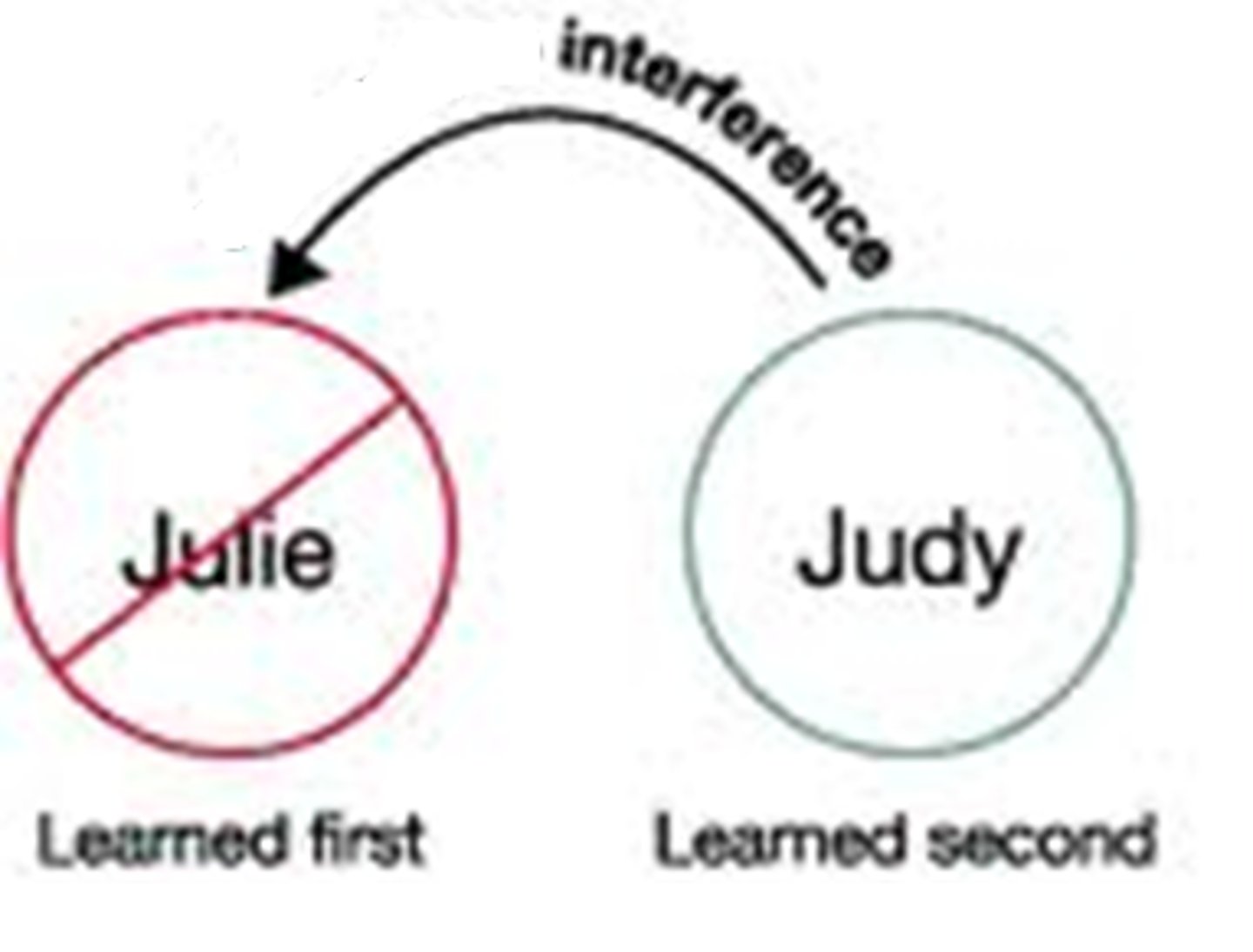
proactive interference
The disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new information.
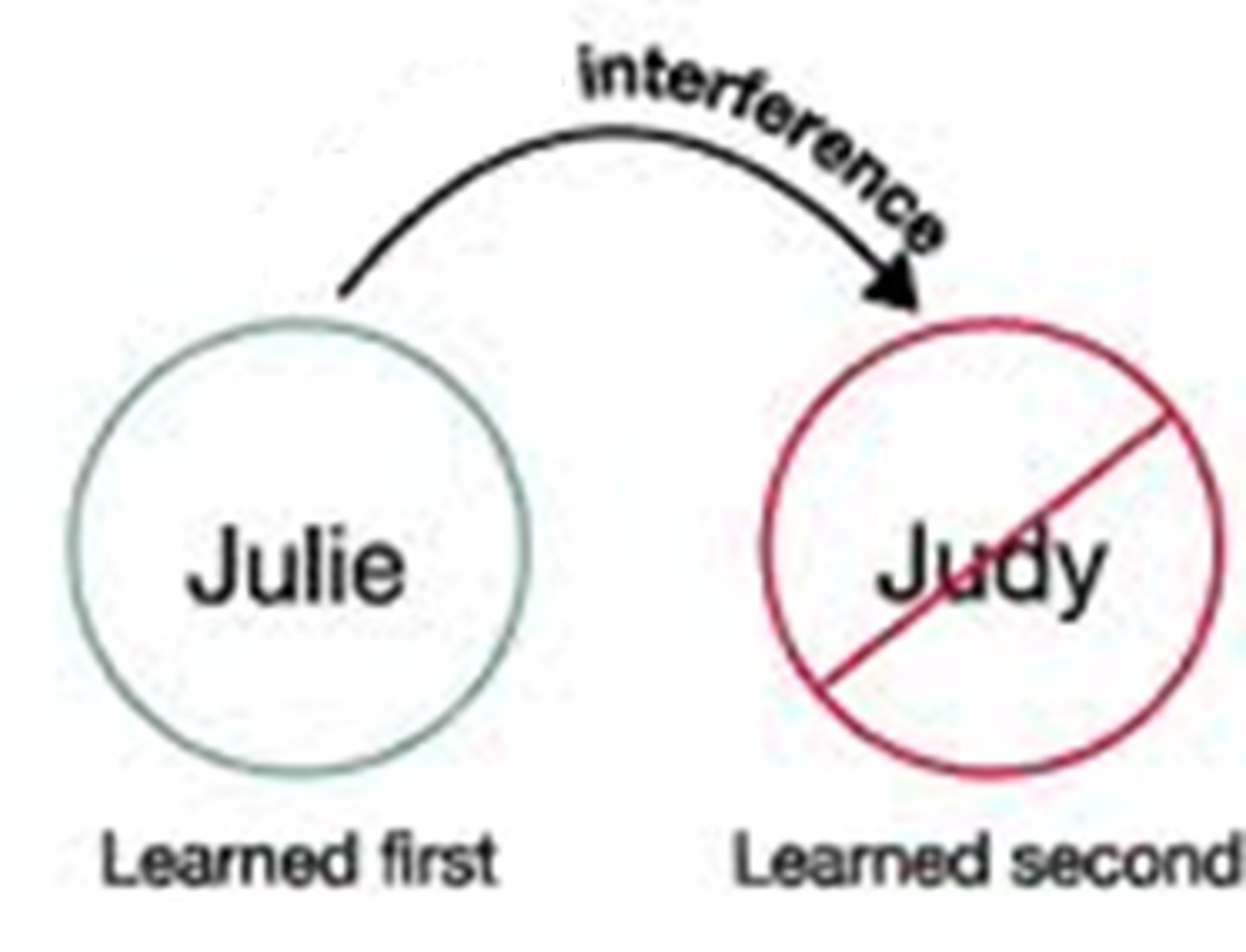
retroactive interference
The disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information.
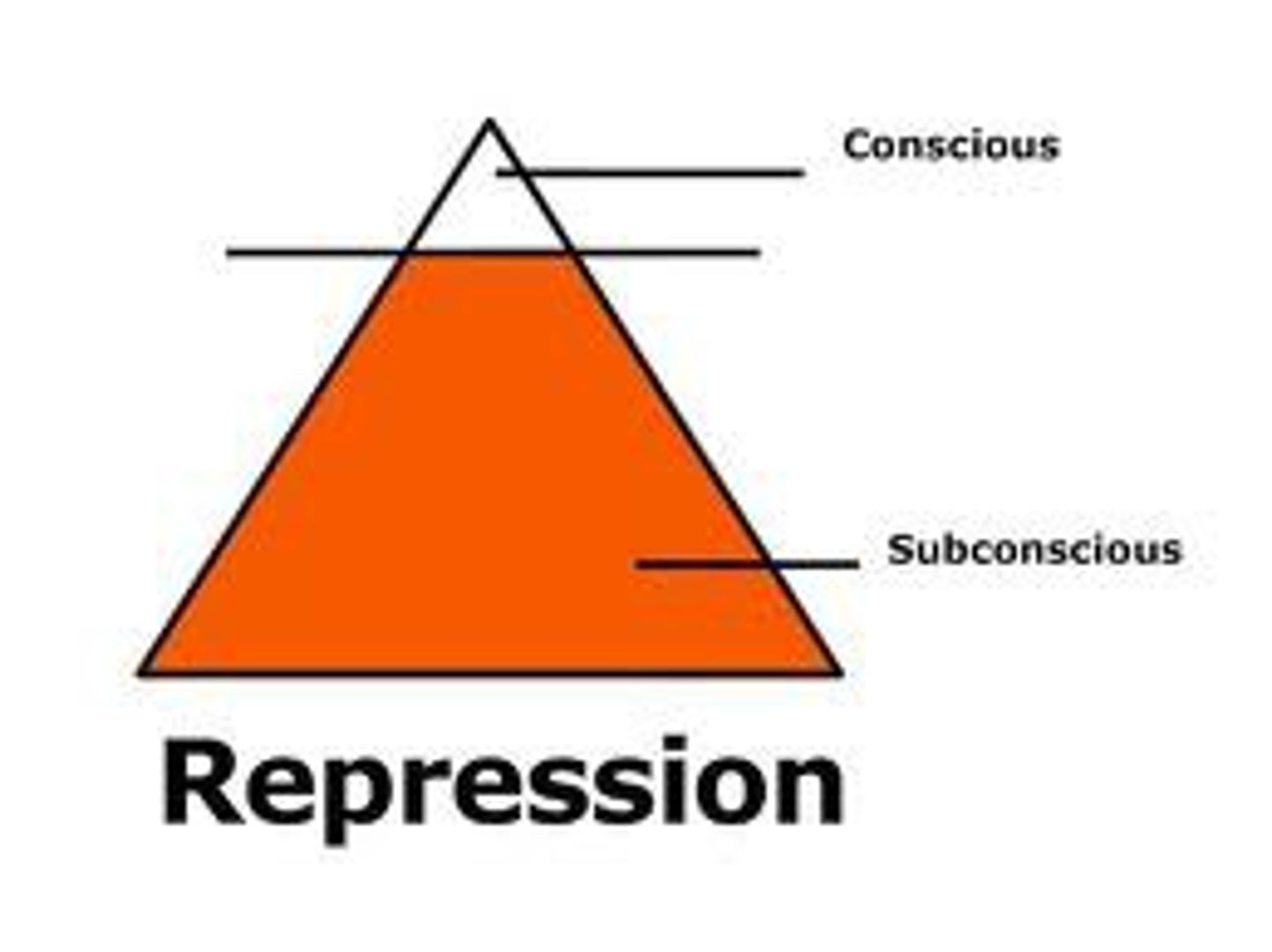
repression
In psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories.
misinformation effect
Incorporating misleading information into one's memory of an event.
source amnesia
Attributing to the wrong source an event we have experienced, heard about, read about, or imagined (source misattribution).

cognition
The mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating.

episodic memory
the memory of autobiographical events that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred at a particular time and place.

flashbulb memory
a highly detailed, exceptionally vivid 'snapshot' of the moment and circumstances in which a piece of surprising and consequential (or emotionally arousing) news was heard.
