Political Organizations
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
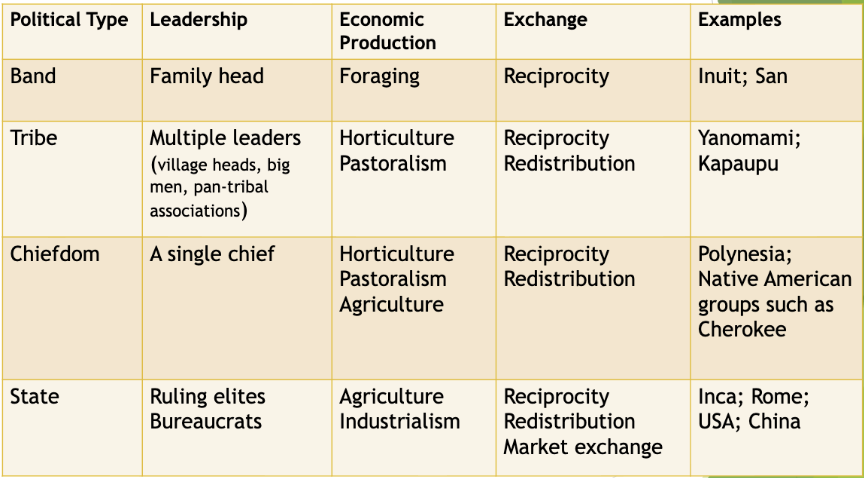
Elman Service’s Typology (1962)
Bands
tribe
Chiefdom
State
Bands, tribes, and chiefdoms also survived into modern times and exist in minder nation-states
Bands
Kin-based groups among foragers
the basic social unit of foragers
a band can consist of one to several extended families
Bands are egalitarian societies: equality, sharing, open
resourcesEgalitarian relations had characterized the human social
life for most of our history
Bands have two types of social distinctions:
A division of labor division based on gender
Social distinctions based on age.
The band is a very mobile unit
collecting food
gathering food from different places
the seasonal split of the band for gathering food
shift band membership
Band’s Leadership
Family head leadership; informal
Decision making through consensus
Tribes
A form of political organization encompassing a number of economically self-sufficient villages that are united and defined by common descent, language, or culture
Economy—Tribes
tribes typically have a horticultural or pastoral economy
it is the need to cope with external threats, instead of economic necessity, that leads to the unification of the villages
Different well-defined tribal leadership position
Village head
“Big man”
Pan-tribal associations
Tribes—“Big Man”
leadership is based on influence, not authority
not a hereditary position
the status doesn’t involve a formal office
having the support of multi-villages

Pan-tribal associations
Various formal groups that cut across villages within a tribe and bring people together through common concerns, age, skills, or interests
What was the Kayapo and the Belo Monte Dam Project?
People of the Kayapo tribe protested against the Belo Monte Dam, a massive hydroelectric dam complex on the Xingu River in Brazil, that would’ve affected the natural lands of the Kayapo people.
Leadership—Tribes
Although leadership positions (village heads, big men, and pan-tribal associations) exist, there is no central government to impose rules or punishment; leaders have no sure means of enforcing political decisions
Social relationships—Tribes
Primarily egalitarian with some tribes showing the traits of ranking
Chiefdoms
A form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families. These elites form a political aristocracy relative to the common people
a lot of chiefdoms still survive today, modern anthropologists actually were able to study them in real life by living with them
Leadership—Chiefdoms
Formalized and centralized leadership, with a single hereditary chief with full formal authority
A Big Man vs. a Chief:
Big man
informal
achieved status
first among equals
works with the people
Chief
formal
hereditary status
position of authority
exempt from ordinary work
Similarities: certain characters are emphasized (such as generosity,
kindness, and bravery)
Economy—Chiefdoms
horticulture, pastoralism, and agriculture
A chiefdom consists of several economically interdependent villages
A tribe consists of several economically self-sufficient
villages
Social relation—Chiefdoms
Unlike a band or tribe, a chiefdom is not an egalitarian society, but a ranked one
States
A politically organized unit with a large population, which occupies a definite territory and has a formal central government that maintains a monopoly of the legitimate use of force
Ex.) ancient Mesopotamia, contemporary USA, China, Germany…
Characteristics of State Systems— the presence of a Bureaucracy
Bureaucrat: a person to whom a political leader delegates certain authority and powers
Acts on behalf of and depends on the political leaders
Carries out the day to day governing of the polity
Facilitating the expansion of the size of a polity
Characteristics of State Systems—Multiethnic Population
The existence of different ethnic groups within a polity, with one group being the politically dominant group
Characteristics of Stats Systems—Specialized Subsystems
Population control
Judiciary
Law enforcement
Fiscal systems
Population Control
territories
census
administrative subdivision
citizens and non-citizens
Judiacary