Chapter 1: Scientific Foundations of Psychology
Roots of Psychology
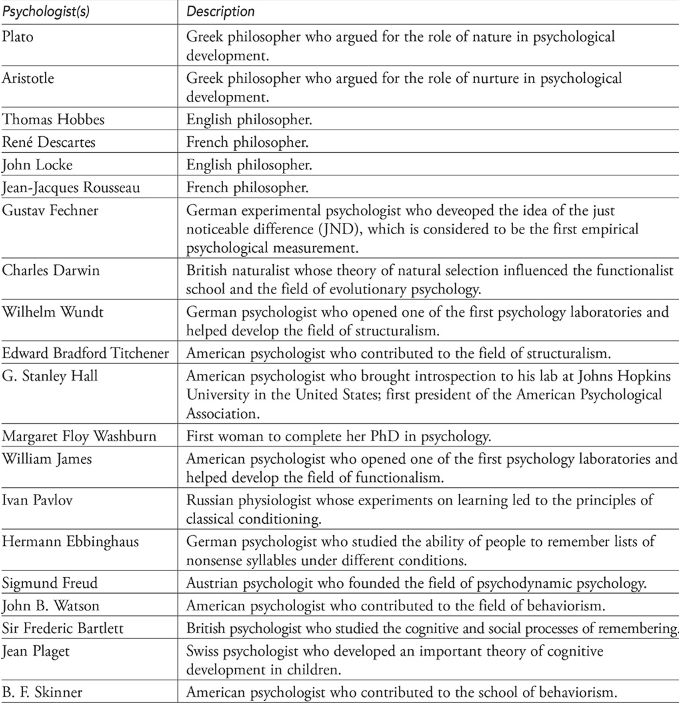
- Roots of psychology can be traced to philosophy and physiology/biology over 2,000 years ago in ancient Greece.
- As a result of examining organisms, physician/philosopher/physiologist Hippocrates thought the mind or soul resided in the brain but was not composed of physical substance (mind-body dualism).
- Philosopher Plato (circa 350 BC), who also believed in dualism, used self-examination of inner ideas and experiences to conclude that who we are and what we know are innate (inborn).
- Plato’s student, Aristotle, believed that the mind/soul results from our anatomy and physiological processes (monism), that reality is best studied by observation, and that who we are and what we know are acquired from experience.
- Descartes defended mind-body dualism (Cogito ergo sum—“I think, therefore I am”) and that what we know is innate.
- Empirical philosopher Locke believed that mind and body interact symmetrically (monism), knowledge comes from observation, and what we know comes from experience since we are born without knowledge, “a blank slate” (tabula rasa).
- Nature-nurture controversy: which our behavior is inborn or learned through experience.
Leading Psychologists
Structuralism
- In 1879, Wilhelm Wundt founded scientific psychology by founding a laboratory in Leipzig, Germany, to study immediate conscious sensation.
- He taught his associates and observers to introspectively analyze their sensory experiences (inward-looking).
- Replicating results under different conditions was his requirement.
- Wundt used trained introspection to study the mind's structure and identify consciousness's basic elements—sensations, feelings, and images.
- G. Stanley Hall founded the American Psychological Association, founded a psychology lab using introspection at Johns Hopkins University, and became its first president.
- Edward Titchener brought introspection to his Cornell University lab, analyzed consciousness into its basic elements, and investigated how they are related.
- Structuralism included Wundt, Hall, and Titchener.
- Titchener's first graduate student and first female psychology PhD was Margaret Floy Washburn.
Functionalism
- American psychologist William James thought structuralists were asking the wrong questions.
- James studied behavioral functions.
- He believed humans actively processed sensations and actions.
- James, James Cattell, and John Dewey were Functionalist psychologists who studied mental testing, child development, and education.
- Functionalists used various methods to apply psychological findings to practical situations and study how mental operations adapt to the environment (stream of consciousness).
- Behaviorism and applied psychology followed functionalism.
- First female American Psychological Association president Mary Whiton Calkins studied psychology under James at Harvard.
- Her self-psychology reconciled structural and functional psychology.
Principal Approaches to Psychology
Behavioral Approach
- The behavioral approach focuses on measuring and recording observable behavior in relation to the environment.
- Behaviorists think behavior results from learning.
- Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov trained dogs to salivate in response to the sound of a tone, demonstrating stimulus–response learning.
- Pavlov’s experiments at the beginning of the 20th century paved the way for behaviorism, which dominated psychology in America from the 1920s to the 1960s.
- Behaviorists examine the ABCs of behavior.
- They analyze Antecedent environmental conditions that precede a behavior, look at the Behavior (the action to understand, predict, and/or control), and examine the Consequences that follow the behavior (its effect on the environment).
Psychoanalytic/Psychodynamic Approach
- Sigmund Freud opposed behaviorists in Austria.
- He talked with mental patients for long periods to reveal unconscious conflicts, motives, and defenses to improve self-knowledge.
- Psychoanalytic theory explained mental disorders, personality, and motivation through unconscious internal conflicts.
- Freud believed that early life experiences shape personality and that the unconscious is the source of desires, thoughts, and memories.
- Psychodynamic psychoanalysis includes Carl Jung, Alfred Adler, Karen Horney, Heinz Kohut, and others.
Humanistic Approach
- In contrast to behaviorists and psychoanalysts, Abraham Maslow, Carl Rogers, and other psychologists believed that humans have unique behavior.
- Free will and personal growth shape behavior and thought.
- Humanists value feelings and believe people are naturally positive and growth-seeking. Humanists interview people to solve their own problems.
Evolutionary Approach
- An offshoot of the biological approach, evolutionary psychologists, returning to Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection, explain behavior patterns as adaptations naturally selected because they increase reproductive success.
Cognitive Approach
- Psychologists could study cognition—thinking and memory—again thanks to technology.
- Cognitive psychologists emphasize receiving, storing, and processing information, thinking and reasoning, and language to understand human behavior.
- Jean Piaget's cognitive development research influenced preschool and primary education.
Sociocultural Approach
- Travel and the economy globalized in the second half of the 20th century, increasing cross-cultural interactions.
- Psychologists found that different cultures interpret gestures, body language, and speech differently.
- Psychologists studied social and environmental factors affecting cultural differences in behavior.
- The sociocultural approach examines cultural differences to understand, predict, and control behavior.
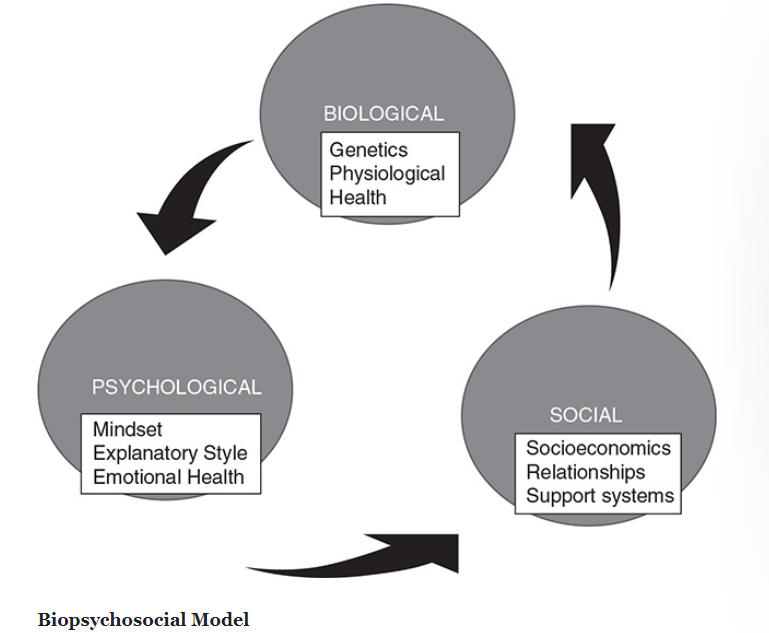
Biopsychosocial Model
Psychologists who use techniques and adopt ideas from a variety of approaches are considered eclectic.
The biopsychosocial model integrates biological processes, psychological factors, and social forces to provide a more complete picture of behavior and mental processes.
The model is a unifying theme in modern psychology drawing from and interacting with the seven approaches to explain behavior.
Domains of Psychology
- Research and applied psychologists deal with a huge number of topics.
- Topics can be grouped into broad categories known as domains.
- Psychologists specializing in different domains identify themselves with many labels.
- Clinical psychologists evaluate and treat mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
- Clinical psychologists treat people with temporary psychological crises like grief, addiction, or social issues and those with chronic psychiatric disorders.
- Clinical psychologists can specialize in children, the elderly, or specific disorders or work with a wide range of populations. Hospitals, community health centers, and private practice employ them.
- Counseling psychologists help people adapt to change or make changes in their lifestyle.
- Counseling psychologists are similar to clinical psychologists, but they focus more on lifestyle changes than psychological disorders.
- Schools, universities, community mental health centers, and private practice employ these psychologists.
- Developmental psychologists study psychological development throughout the life span.
- They study intellectual, social, emotional, and moral development.
- Some specialize in adolescence or geriatrics.
- Developmental psychologists work in schools, daycare centers, social service agencies, and senior and geriatric facilities.
- Educational psychologists focus on how effective teaching and learning take place.
- They study human learning and create materials and strategies to improve it.
- Universities, labs, and publishers employ educational psychologists.
- Forensic psychologists apply psychological principles to legal issues.
- They are concerned with the numerous facets of the law, such as determining a defendant’s competence to stand trial, or whether a victim has suffered psychological or neurological trauma.
- Health/positive psychologists concentrate on biological, psychological, and social factors involved in health and illness.
- They focus on psychology's role in health promotion and illness prevention and treatment.
- This may include creating and promoting programs to help people quit smoking, diet, manage stress, and exercise.
- Hospitals, rehabilitation centers, public health agencies, and private practice employ them.
- Industrial/organizational psychologists aim to improve productivity and the quality of work life by applying psychological principles and methods to the workplace.
- They manage organizational efficiency through human resources.
- Organizational psychology emphasizes employee well-being and development, while industrial psychology emphasizes performance appraisals, job design, and selection and training.
- Business, factories, and research facilities employ I/O psychologists.
- Neuropsychologists explore the relationships between brain/nervous systems and behavior.
- Biological psychologists, biopsychologists, behavioral geneticists, physiological psychologists, and behavioral neuroscientists are neuropsychologists.
- They study biochemical mechanisms, brain structure and function, and emotional chemical and physical changes.
- They can diagnose and treat brain and nervous system dysfunction-related behavior.
- Hospitals have most doctoral and postdoctoral positions.
- Psychometricians, sometimes called psychometric psychologists or measurement psychologists, focus on methods for acquiring and analyzing psychological data.
- Psychometrists can create and modify intelligence, personality, and aptitude tests.
- They may help psychology and other researchers design and interpret experiments.
- They work in universities, testing centers, research firms, and government agencies.
- Social psychologists focus on how a person’s mental life and behavior are shaped by interactions with other people.
- They study how others influence our thoughts, feelings, and actions.
- Hospitals, federal agencies, and businesses are hiring social psychologists for applied research.
Experimental Method
The Controlled Experiment
- The laboratory tests hypotheses, predictions of how two or more factors are likely to be related.
- Variables are factors with multiple values.
- In a scientific experiment, the researcher controls a variable and observes the response.
- The researcher manipulates the independent variable (IV).
- The dependent variable (DV) is the factor that may change as a result of manipulating the independent variable.
- The researcher can draw the conclusion that the change in the independent variable caused the change in the dependent variable if the dependent variable changes when only the independent variable is changed.
- The independent variable causes the dependent variable.
- Only a controlled experiment can prove cause-and-effect.
- The population includes all the individuals in the group to which the study applies
- Sample: a subgroup of the population.
- Random selection can be achieved by putting all the names in a hat and picking out a specified number of names, by alphabetizing the roster of enrollees and choosing every fifth name, or by using a table of random numbers to choose participants.
- Experimental group: receives the treatment
- Control group: does not receive the treatment.
- Between-subjects design: The participants in the experimental and control groups are different individuals.
- Random assignment of participants to the experimental and control groups minimizes the existence of preexisting differences between the two groups.
- Confounding variables: Differences between the experimental group and the control group other than those resulting from the independent variable.
- Subjects: attend the same two sessions upon which the quiz is based.
- Operational definition describes the specific procedure used to determine the presence of a variable.
Eliminating Confounding Variables
Experimenter bias (also called the experimenter expectancy effect) is a phenomenon that occurs when a researcher’s expectations or preferences about the outcome of a study influence the results obtained.
Demand characteristics: The clues participants discover about the purpose of the study, including rumors they hear about the study suggesting how they should respond.
Single-blind procedure, a research design in which the participants don’t know which treatment group—experimental or control—they are in.
Double-blind procedure, a research design in which neither the experimenter nor the participants know who is in the experimental group and who is in the control group.
Placebo: The imitation pill, injection, patch, or other treatment
Placebo effect is now used to describe any cases when experimental participants change their behavior in the absence of any kind of experimental manipulation.
Within-subjects design: A research design that uses each participant as his or her own control.
Counterbalancing, a procedure that assigns half the subjects to one of the treatments first and the other half of the subjects to the other treatment first.
Quasi-Experimental Research: Quasi-experimental research designs are similar to controlled experiments, but participants are not randomly assigned.
Correlational Research: Correlational methods look at the relationship between two variables without establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
- The goal is to determine to what extent one variable predicts the other.
Naturalistic Observation: Naturalistic observation is carried out in the field where naturally occurring behavior can be observed.
- Naturalistic observation studies gather descriptive information about typical behavior of people or animals without manipulating any variables.
Survey Method: researchers use questionnaires or interviews to ask a large number of people questions about their behaviors, thoughts, and attitudes.
Retrospective or ex post facto studies look at an effect and seek the cause.
Test Method: Tests are procedures used to measure attributes of individuals at a particular time and place.
- Like surveys, tests can be used to gather huge amounts of information relatively quickly and cheaply.
- Results of tests can be used for correlational analysis or for generating ideas for other research.
Reliability is consistency or repeatability.
Validity is the extent to which an instrument measures or predicts what it is supposed to.
Case Study: is an in-depth examination of a specific group or single person that typically includes interviews, observations, and test scores.
Elementary Statistics: Statistics is a field that involves the analysis of numerical data about representative samples of populations.
- A large amount of data can be collected in research studies.
Descriptive Statistics: Numbers that summarize a set of research data obtained from a sample.
Frequency distribution, an orderly arrangement of scores indicating the frequency of each score or group of scores.
Histogram—a bar graph from the frequency distribution
Frequency polygon—a line graph that replaces the bars with single points and connects the points with a line.
Measures of Central Tendency
- Measures of central tendency describe the average or most typical scores for a set of research data or distribution.
- The mode is the most frequently occurring score in a set of research data. If two scores appear most frequently, the distribution is bimodal; if three or more scores appear most frequently, the distribution is multimodal.
- The median is the middle score when the set of data is ordered by size.
- The mean is the arithmetic average of the set of scores.
- The normal distribution or normal curve is a symmetric, bell-shaped curve that represents data about how many human characteristics are dispersed in the population.
- Distributions where most of the scores are squeezed into one end are skewed.
Measures of Variability
- Variability describes the spread or dispersion of scores for a set of research data or distribution.
- The range is the largest score minus the smallest score.
- Variance and standard deviation (SD) indicate the degree to which scores differ from each other and vary around the mean value for the set.
Correlation
- Scores can be reported in different ways.
- One example is the standard score or z score.
- Standard scores enable psychologists to compare scores that are initially on different scales.
- Percentile score, indicates the percentage of scores at or below a particular score.
- A statistical measure of the degree of relatedness or association between two sets of data, X and Y, is called the correlation coefficient.
- The strength and direction of correlations can be illustrated graphically in scattergrams or scatterplots in which paired X and Y scores for each subject are plotted as single points on a graph.
Inferential Statistics
- Inferential statistics are used to interpret data and draw conclusions.
- They tell psychologists whether or not they can generalize from the chosen sample to the whole population, if the sample actually represents the population.
- Statistical significance (p) is a measure of the likelihood that the difference between groups results from a real difference between the two groups rather than from chance alone.
- Meta-analysis provides a way of statistically combining the results of individual research studies to reach an overall conclusion.
Ethical Guidelines
- The American Psychological Association (APA) lists ethical principles and code of conduct for the scientific, educational, or professional roles for all psychologists.
- They include psychology practice, research, teaching, and trainee supervision.
- They also include all aspects of their performance in public service, policy development, social intervention, and development and conduction of assessments, to name but a few.
- The code applies to all communications, including phone, social media, and in-person.
- Discuss intellectual property frankly: The “publish-or-perish” mindset can lead to trouble when it comes to determining credit for authorship.
- The best way to avoid disagreements, according to the APA, is to discuss these issues openly at the start of a working relationship, even though many people often feel uncomfortable about such topics.
- Be conscious of multiple roles: This includes avoiding relationships that could negatively affect professional performance or exploit or harm others.
- Participation in a study should be voluntary, and not coerced or influenced as part of a grade, raise, or promotion.
- Follow informed consent rules such as IRBs, which ensure that individuals are voluntarily participating in the research with full knowledge of relevant risks and benefits.
- The purpose, expected duration, and procedures of the research.
- Their rights to decline to participate and withdraw from the research once it has begun, as well as consequences, if any, of doing so.
- Factors that might influence their willingness to participate, such as possible risks, discomfort, or adverse effects.
- Any possible research benefits.
- Limits of confidentiality and when that confidentiality must be broken.
- Incentives for participation, if any.