Physics A-Level (AQA) : Particles
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Last updated 10:55 AM on 10/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
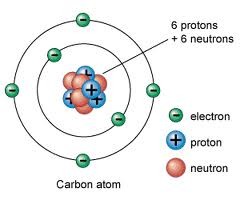
Simple model of the atom
Atom contains a positively charged nucleus composed of protons and neutrons and electrons that surrounds the nucleus.
2
New cards
Charge and mass of proton, neutron and electron in SI units
Proton: charge +1.60x10^-19 C, mass 1.67x10^-27 kg
Neutron: charge 0 C, mass 1.67x10^-27 kg
Electron: charge -1.60x10^19 C , mass 9.11x10^-31 kg
Neutron: charge 0 C, mass 1.67x10^-27 kg
Electron: charge -1.60x10^19 C , mass 9.11x10^-31 kg
3
New cards
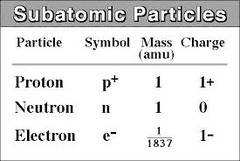
Charge and mass of proton, neutron and electron in relative units
Proton: charge +1, mass 1
Neutron: charge 0, mass 1
Electron: charge -1, mass 1/1840
Neutron: charge 0, mass 1
Electron: charge -1, mass 1/1840
4
New cards
What is specific charge?
Charge divided by mass, unit C kg-1
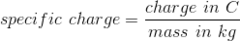
5
New cards
What is proton number (atomic number)?
Number of protons in the nucleus, symbol Z
6
New cards
What is nucleon number (mass number)?
Number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, symbol A
7
New cards
Example of nuclide notation
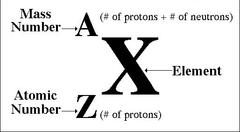
8
New cards
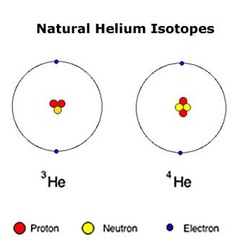
What are isotopes?
Atoms with the same number of protons and different number of neutrons
9
New cards
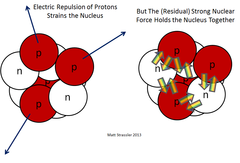
What is the role of the strong nuclear force?
Overcomes electrostatic repulsion between protons and keeps the nucleus stable
10
New cards
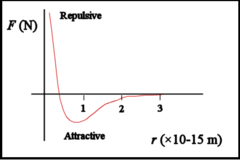
How does the strong nuclear force vary with separation?
Closer than 0.5fm - repulsive
Between 0.5-3.0fm - attractive
Further than 3.0fm - no effect / zero
Between 0.5-3.0fm - attractive
Further than 3.0fm - no effect / zero
11
New cards
What is alpha decay?
Unstable nucleus emits alpha particle (helium nucleus)
Equation: X(A,Z) -> Y(A-4,Z-2) + α(4,2)
Equation: X(A,Z) -> Y(A-4,Z-2) + α(4,2)
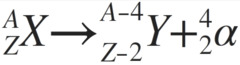
12
New cards
What is beta (minus) decay?
A neutron in the nucleus changes into a proton and emits fast-moving electron and electron antineutrino
Equation: X(A,Z) -> Y(A,Z+1) + e-(0,-1) + _νe(0,0)
Equation: X(A,Z) -> Y(A,Z+1) + e-(0,-1) + _νe(0,0)
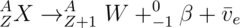
13
New cards
Why was the existence of the neutrino hypothesised?
To account for conservation of energy in beta decay. Observation showed energy of particles after beta decay was less than it was before. Some of the energy must had been carried away by undetected particles (neutrino).
14
New cards
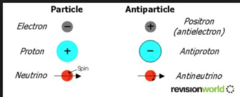
What is antiparticle?
For every type of particle, there is a corresponding antiparticle
15
New cards
Comparison of particle and antiparticle masses, charge and rest energy
Particle and its corresponding particle have equal masses and rest energy, but opposite charge.
16
New cards
Antiparticles of the electron, proton, neutron and neutrino
Positron, antiproton, antineutron, antineutrino
17
New cards
Photon model of electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic waves are emitted as discrete wavepackets and each wavepacket is referred to as a photon.
E = hf, E = hc/λ
E = photon energy, J
h = planck constant, 6.63x10^-34 J s
f = frequency, Hz
c = speed of light, 3.00x10^8 m s-1
λ = wavelength, m
E = hf, E = hc/λ
E = photon energy, J
h = planck constant, 6.63x10^-34 J s
f = frequency, Hz
c = speed of light, 3.00x10^8 m s-1
λ = wavelength, m
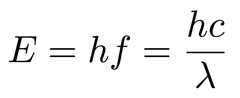
18
New cards
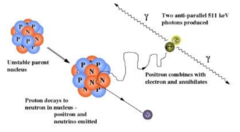
What is annihilation?
A particle and a corresponding antiparticle meet and their mass is converted into radiation energy as two photons. Two photons are produced in this process to conserve momentum.
19
New cards
What is pair production?
A photon interacts with a nucleus or an electron and creates a particle-antiparticle pair, its radiation energy is converted into mass.
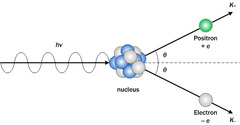
20
New cards
Energies involved in annihilation and pair production
Rest energy and kinetic energy of the particle-antiparticle pair is equal to the energy of the photon / two photons
21
New cards
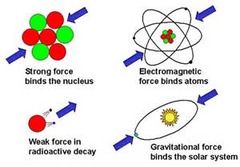
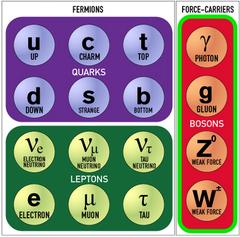
What are the four fundamental interactions?
Gravity, electromagnetic, weak nuclear, strong nuclear/interaction
22
New cards
What is the concept of exchange particles?
Exchange particles are transferred between particles when a force acts between them. Exchange particles transfer energy and momentum.
23
New cards
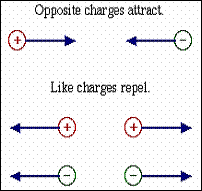
What is the electromagnetic force?
The force that acts between charged particles
24
New cards
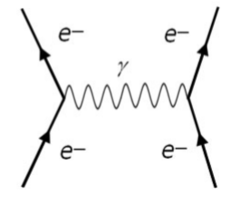
What is the exchange particle of the electromagnetic force?
Virtual photons - they have zero mass, infinite range and no charge.
25
New cards
What is the weak interaction?
The force that is responsible for β- decay, β+ decay, electron capture and electron-proton collisions.
26
New cards
What is exchange particle of the weak interaction?
W bosons - they have a non-zero rest mass, a short range of no more than 0.001fm, and are positively charged (W+ boson) or negatively charged (W- boson).
27
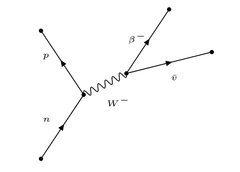
New cards
Feynman diagram: β- decay
28
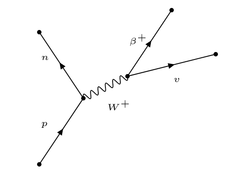
New cards
Feynman diagram: β+ decay
29
New cards
Feynman diagram: electron capture
30
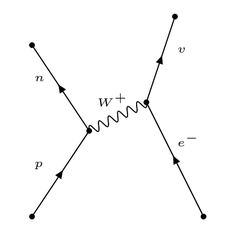
New cards
Feynman diagram: electron-proton collisions
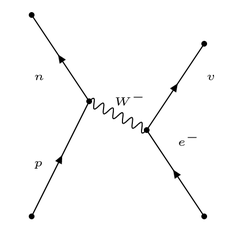
31
New cards
What are hadrons?
Particles that are subject to the strong interaction
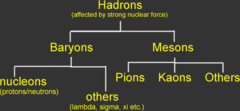
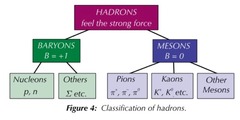
32
New cards
The two classes of hadrons
Baryons / antibaryons and mesons
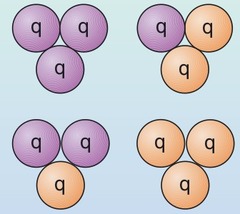
33
New cards
What are (anti)baryons?
Particles that consist of three (anti)quarks
34
New cards
Examples of baryons and antibaryons
Baryons: proton, neutron
Antibaryons: antiproton, antineutron
Antibaryons: antiproton, antineutron
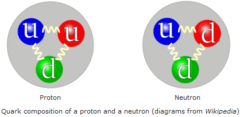
35
New cards
What are mesons?
Particles that consist of one quark and one antiquark
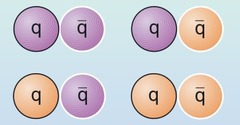
36
New cards
What is baryon number?
A quantum number that must be conserved in all interactions.
Baryon: 1
Antibaryon: -1
Non-baryon: 0
Baryon: 1
Antibaryon: -1
Non-baryon: 0
37
New cards
What is the only stable baryon?
The proton, into which other baryons eventually decay
38
New cards
What is the pion?
The exchange particle of the strong nuclear force
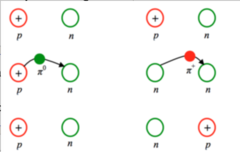
39
New cards
What is the kaon?
A strange particle that can decay into pions
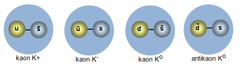
40
New cards
What are leptons?
Leptons are fundamental particles and are not subject to the strong interaction
41
New cards
Example of leptons and anti-leptons
Leptons: Electron (e-), muon (μ-), electron neutrino (νe), muon neutrino (νμ)
Their antiparticles: Positron (e+), anti-muon (μ+), electron antineutrino (_νe), muon antineutrino (_νμ)
Their antiparticles: Positron (e+), anti-muon (μ+), electron antineutrino (_νe), muon antineutrino (_νμ)
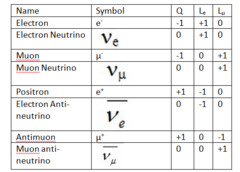
42
New cards
What is lepton number?
A quantum number that must be conserved in all interactions; lepton number for electron leptons and muon leptons must be conserved in all interactions.
Lepton: 1
Anti-lepton: -1
Non-lepton: 0
Lepton: 1
Anti-lepton: -1
Non-lepton: 0
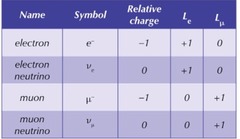
43
New cards
What is the muon?
A particle that decays into an electron

44
New cards
What are strange particles?
Strange particles contain strange quark. They are produced through the strong interaction and decay through the weak interaction.
45
New cards
What is strangeness?
A quantum number to reflect the fact that strange particles are always created in pairs. It is conserved in strong interaction but can change by 0, +1 or -1 in weak interaction.
Strange quark: -1
Anti-strange quark: 1
Strange quark: -1
Anti-strange quark: 1
46
New cards
Properties of quarks and antiquarks
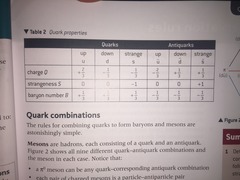
47
New cards
Quark combinations of hadrons
Proton: u u d
Neutron: u d d
Antiproton: _u _u _d
Antineutron: _u _d _d
π+: u _d
π-: _u d
π0: u _u, d _d, s _s
K+: u _s
K-: _u s
K0: d _s
_K0: _d s
Neutron: u d d
Antiproton: _u _u _d
Antineutron: _u _d _d
π+: u _d
π-: _u d
π0: u _u, d _d, s _s
K+: u _s
K-: _u s
K0: d _s
_K0: _d s
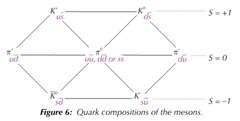
48
New cards
Decay of the neutron
n -> p + e- + _ve
49
New cards
Change of quark character in β- decay
d -> u + e- + _ve
50
New cards
Change of quark character in β+ decay
u -> d + e+ + ve
51
New cards
What are conserved in interactions?
Energy, charge, momentum, baryon number, lepton number are conserved in all interactions. Strangeness is not conserved in weak interaction.