QA
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
When calibrating ion chambers, which of the following correction factors are needed?
1. barometric pressure
2. volume of the chamber
3. temperature
What is the main disadvantage of using a film badge to monitor radiation exposure?
must be sent out for a reading
A pocket dosimeter is a:
low energy dosimeter used for personnel monitoring.

The basic types of interaction between X-radiation and matter include all of the following except:
A. Compton scattering
B. radiative bremsstralung production
C. photoelectric absorption
D. pair production
B. radiative bremmsstrahlung production
(Bremsstrahlung radiation is a product of electron interaction with matter.)
A stochastic effect is best defined as one in which:
A. severity is easily predicted
B. severity is dose dependent
C. probability is dose dependent
D. severity has a threshold
c. probability is dose dependent
Beam symmetry and flatness are defined over what percentage of the field?
80%
When radiation interacts with radiographic film contained in the film badge, after development:
The film darkens proportional to the exposure.
All naturally occurring radioactive series ultimately decay to a stable form of:
lead
In radiation therapy, which of the following interactions with matter are least important?
photoelectric effect
Which of the following is true of Beta+ decay?
proton is converted into a neutron
(Beta+ decay occurs in nuclides that are neutron deficient. Thus the neutron/proton ratio is increased by converting a proton to a neutron and emitting excess energy in the form of a positron.)
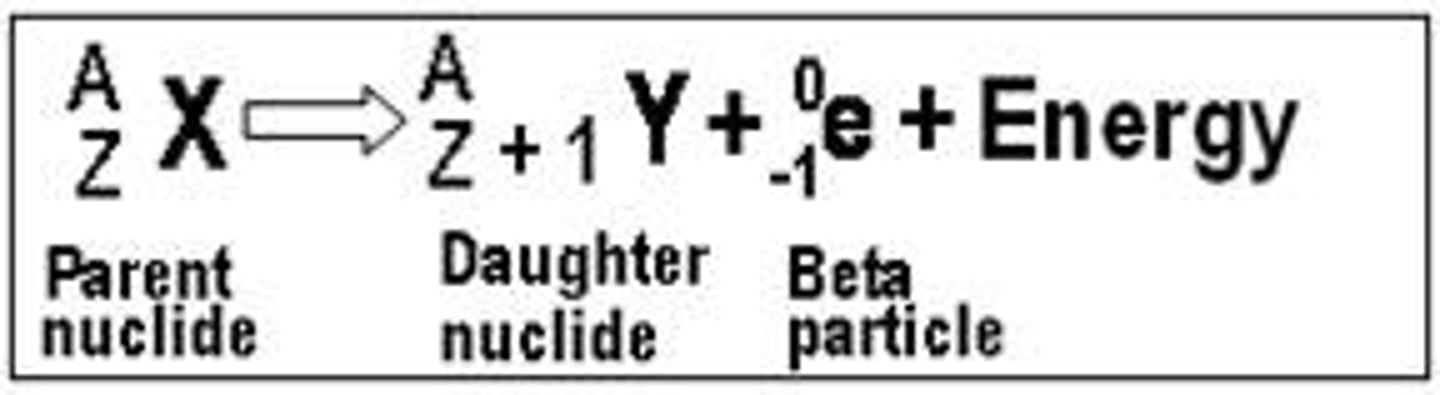
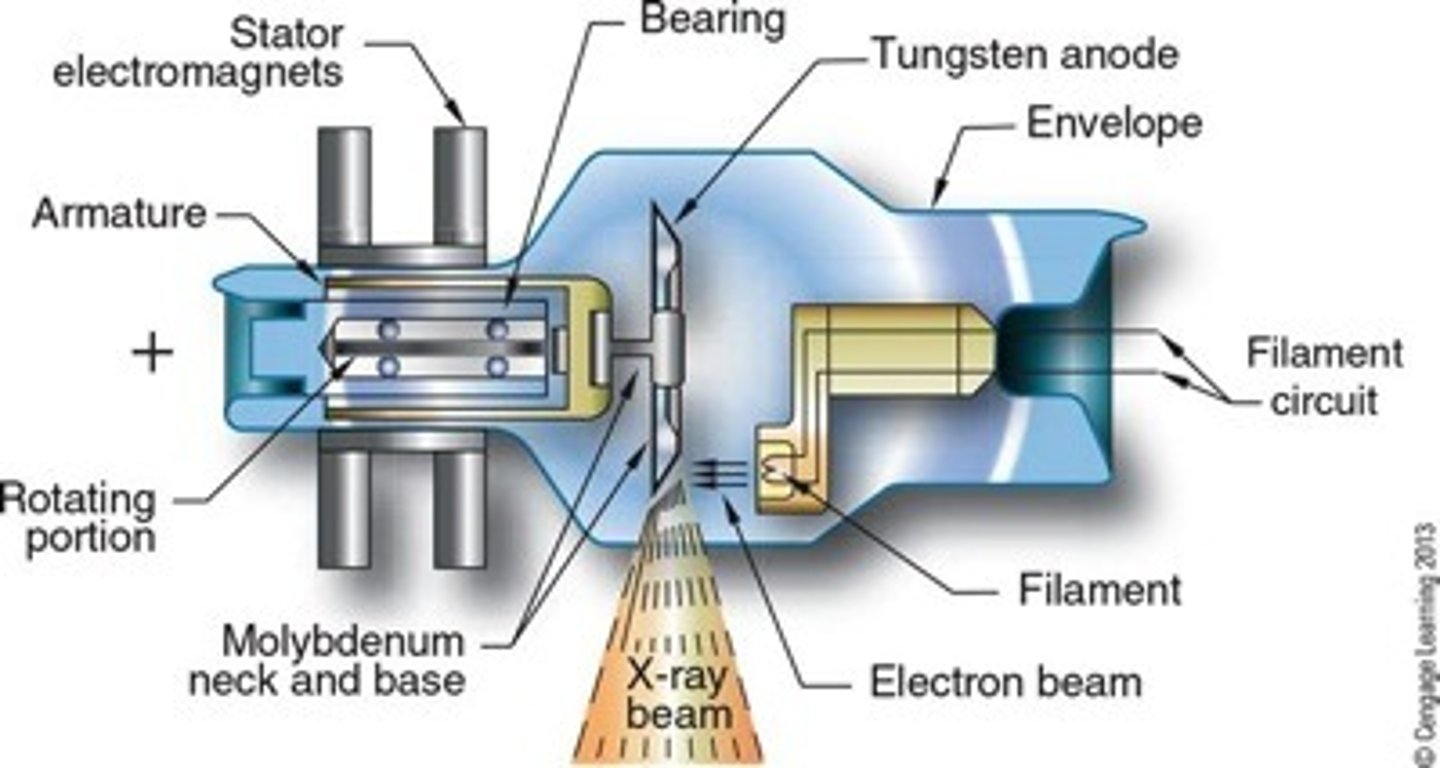
In a diagnostic X-ray tube, A/C is converted to D/C by means of:
rectification circuit
What are rectification circuits also known as?
Diodes
What do rectification circuits restrict?
The flow of current to one direction
What happens to current when the polarity reverses in a rectification circuit?
Current does not flow in the opposite direction
In a rectification circuit, in which direction do electrons move?
From the cathode to the anode
The rate of kinetic energy lost per unit path length is referred to as:
stopping power
The linear attenuation coefficient (μ) is expressed in:
1/cm
μ is a dimensionless unit expressed in 1/cm. It is defined as the fraction of photons attenuated per unit mass.
What are the components of the Fricke dosimeter?
Ferrous sulfate, sodium chloride, and sulfuric acid.
What does the monitoring process of the Fricke dosimeter rely on?
Chemical reaction following exposure.
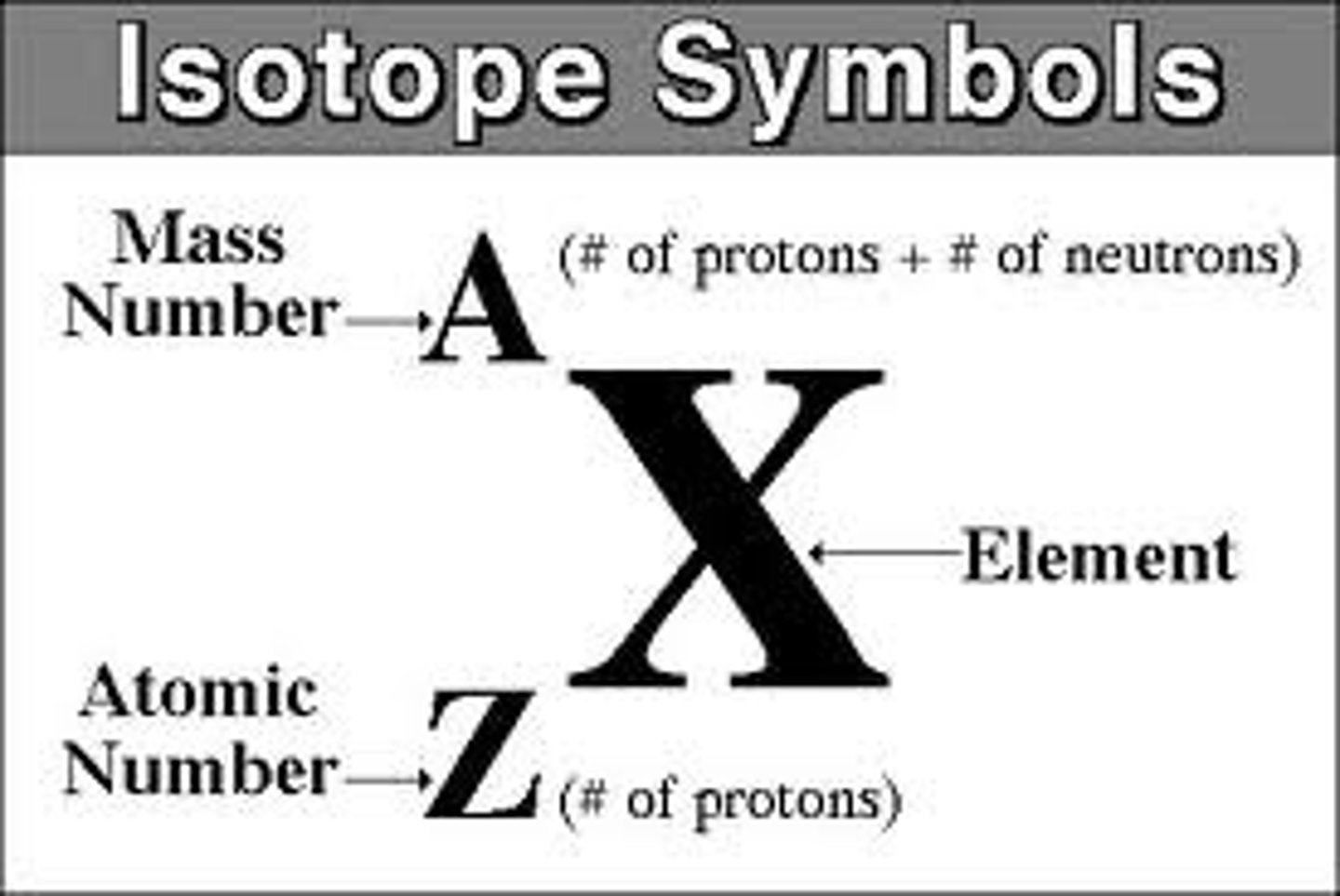
Co-60 and Co-57 are elements that have:
same number of protons but different number of neutrons
They are isotopes
What is the advantage of a rotating anode versus a stationary anode in an X-ray tube?
larger exposures are possible without overheating the tube
The most convenient and economical method for whole body personnel radiation monitoring is the:
film badge
Facts about Late Effects
- Late effects depend on total dose and dose per fraction.
- Late effects tend to be more severe then acute effects.
- Late effects can develop from severe acute effects.
Acute effects are more sensitive to:
increased overall treatment time.
Which of the following cells has the highest radiosensitivity?
A. neurons
B. chondrocytes
C. osteoblasts
D. lymphocytes
Osteoblasts are the most sensitive because these bone cells are young and immature. Therefore they are still dividing, making them the most sensitive.
Penumbra increases with source size and SSD, but it is independent of __________.
source size & SSD
independent of field size
When clinically setting up an electron field, the electron cone should not be pointed obliquely to the patient surface because:
A. The depth of Dmax in the patient can shift toward the surface.
B. Beam penetration can be reduced.
C. Side scatter to the patient increases.
What is the recommended distance for positioning the cone applicator?
100 cm SSD
What should be ensured about the cone applicator's position relative to the patient surface?
The end of the cone should be parallel to the patient surface.
Side scatter to the tissue at shallower depths increases as a result of:
beam obliquity
The probability of bremsstrahlung production:
A. decreases with atomic number
B. increases with atomic number
C. is independent of atomic number
D. decreases with the square of the atomic number
increases with atomic number
In a craniospinal treatment technique, the angle that the treatment couch is tilted toward the collimator is dependent on:
A. the length of the lateral brain field in the direction of the junction of the lateral brain field and the posterior spine field
B. the treatment distance where the lateral brain field size is defined
Light field and radiation field congruence should be checked:
monthly
Why is Ir-192 the commonly used source in High Dose Rate (HDR) afterloading brachytherapy?
It has a high specific activity and lower photon energy & requires less shielding.
The mass attenuation coefficient (μ/ρ) is independent of:
density
Which theory of radiation interaction is illustrated by the operating principles of an ionization chamber?
Bragg-gray cavity theory
(Bragg-Gray cavity theory states that ionization in an air cavity can be related to ionization in a medium.)

Increasing the mA when performing a CT scan increases:
the current to the tube, which results in more electrons hitting the target and more photons being created.
Photon production from a diagnostic X-ray tube requires:
a direct current
a voltage potential
What is required to attract electrons from the cathode to the anode in diagnostic x-ray tubes?
Electrostatic pressure from a voltage potential
What type of current is required to maintain consistent polarity in diagnostic x-ray tubes?
Direct Current (D/C)
Why is Direct Current (D/C) used in diagnostic x-ray tubes?
To ensure that electrons constantly flow in one direction
What is involved in correctly matching the beam divergence of the lateral brain fields?
Rotating the collimator of the lateral fields.
What adjustment is made to the treatment couch for matching the beam divergence?
Angling the treatment couch towards the collimator.
Which of the following best describes an isodose curve?
Points within the patient receiving the same dose are joined together forming a curve.
1 gGray = 1 joule/kg.
Therefore 1 rad = _____ gGray = ______ joule/kg.
01 gGray = .01 joule/kg.
Photoelectric effect
-The incident photon energy must be great enough to overcome the binding energy of the K-shell electron.
-The incident photon will give up all its energy to the electron. -The photoelectric effect decreases with increasing photon energy.
.Ion chambers depend on the ionization effect in air. _________ and _________ are required for readings.
Voltage and current are required for readings.
A high-energy photon strikes an orbital electron and scatters exactly 180 degrees. What is the maximum energy of the scattered photon?
255 kv
When electrons from a higher shell drop down to a lower shell, _______________ radiation is emitted.
characteristic
Which of the following photon interactions with matter involves energy being converted to mass?
pair production
What would be considered a typical α/β ratio for early responding tissue?
A. 1.5 Gy
B. 3 Gy
C. 5 Gy
D. 10 Gy
10 Gy
The linear quadratic relationship between radiation effect and dose indicates a larger α/β ratio for early responding tissue.
Which of the following radiation measuring devices is appropriate for verifying dose calculations in specific areas of a treated field?
TLD
Which of the following is true regarding a source-surface distance (SSD) treatment technique?
Dose is normalized to dmax
Radon half life
4 days
Tc 99 Half Life
6 hours
Planks constant
6.62 x 10^34 J-sec.
Which of the following does not belong in the group listed?
A. gamma rays
B. electrons
C. neutrons
D. protons
A. gamma rays
(Gamma rays are photons or bundles of energy emerging from the nucleus and emitted during nuclear transformation. All others are particles naturally at rest in the atom.)
What is the energy threshold for triplet production?
2.044 MV
Electromagnetic radiation
- The electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to one another.
- Electromagnetic radiation has a dual nature exhibiting a wave model and a quantum model.
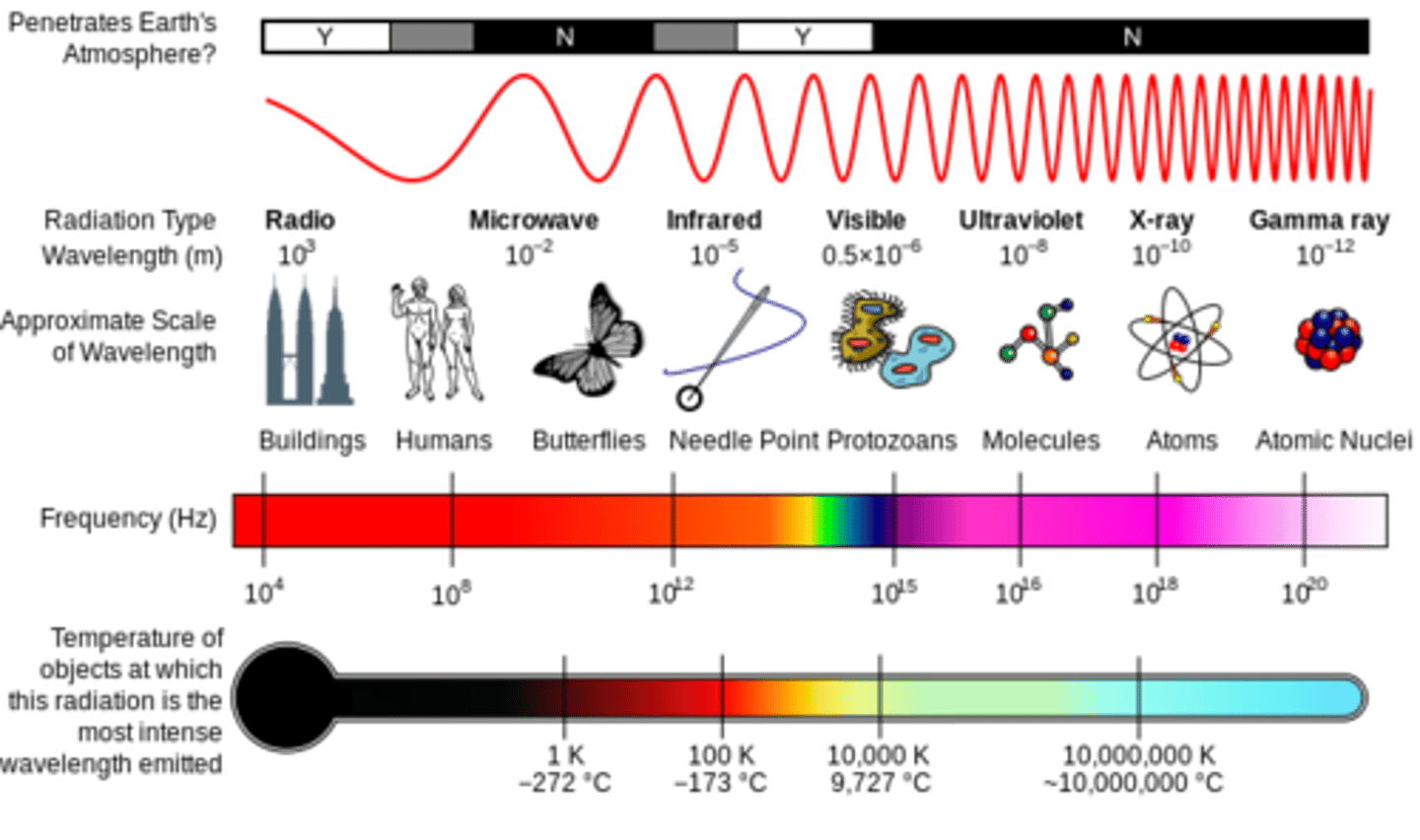
Which of the following radiation interactions with matter occur independently of atomic number?
A. pair production
B. photoelectric effect
C. coherent scattering
D. Compton effect
D. Compton effect
The incident photon has a high energy compared to the binding energy of an orbital electron. Thus the photons interact with essentially free electrons.
The use of iodine or barium contrast in CT scanning exploits the characteristics of:
photoelectric effect
Contrast material has K-shell edges that make it optimal for visualization on diagnostic images due to increased local photon absorption.
The photoelectric effect is a result of interaction between a
photon and bound electron.
Which of the following best defines a wedge factor?
ratio of dose at depth with the wedge inserted to the dose at depth with no wedge inserted
If the threshold energy of 1.022 MeV is not present for Beta+ decay to occur, then a nucleus with an excess number of protons will release energy by:
electron capture
Monthly Linac checks
A. light/radiation field coincidence
B. beam flatness and symmetry
C. field size indicators
Which of the following is the light-sensitive material contained in radiographic film emulsion?
silver halide
LET is measured in
keV/micrometer.
When protons interact with matter:
A. The rate of ionization increases as the proton is slowed down in matter.
B. Energy can be given off as bremstraahlung.
How much energy is in one atomic mass unit (amu)?
931 MeV
What happens to the biological effect if the protraction is shorter while keeping fraction size and total dose the same?
The biological effect would increase.
What happens to the biological effect if the protraction is longer while keeping fraction size and total dose the same?
The biological effect would decrease.
The alpha particle consists of two protons and two neutrons. Such decay occurs in radioactive nuclides with very high atomic numbers.