Bio 225 Exam 1 - Metabolism and Cell Signaling - Lloyd
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Metabolism and Cell Signaling
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Gluconeogenesis input, output, and location
starts with amino acid, pyruvate, or small lipids
output is glucose or glycogen
occurs in mitochondria and cytoplasm
(aerobic) Glycolysis input, output, and location
starts with glucose (or glycogen)(other hexoses are converted to glucose)
end product is 2 pyruvate; 2 ATP; and 2 NADH; H20
occurs in cytoplasm
anaerobic glycolysis outcomes are
3 possible outcomes: ethanol, propionate, or lactate
species and condition dependent
pyruvate oxidation anaerobic and aerobic product
lactic acid; acetyl CoA
Lipids are
composed of glycerol and up to 3 fatty acids
fatty acids are
long chains of hydrocarbons
highly non-polar
Hydrocarbon chains saturated v. monounsaturated v. polyunsaturated
no double bonds
one double bond
more than one double bond
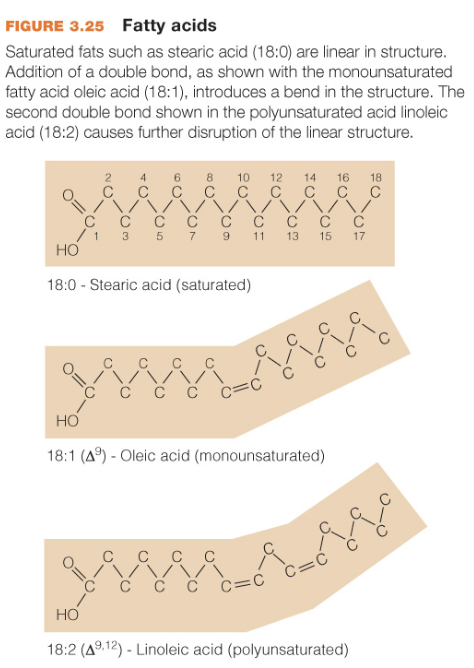
Steroid molecules and the blood…
steroid molecules require something to carry them so that they do not form lipid “rafts”
Fatty acid oxidation
fatty acids are broke down to produce acetyl-CoA; each pair of carbons in FA chain are used to produce 1 acetyl-CoA
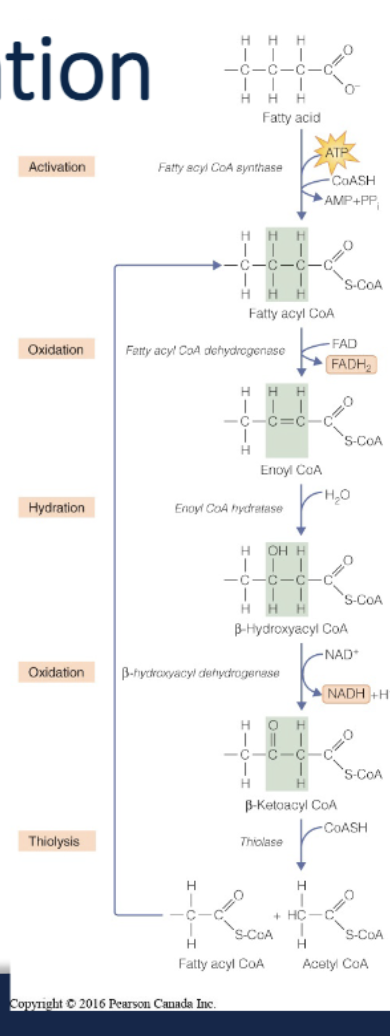
Acetyl-CoA can also be
used to make ketone bodies
Acetyl-CoA can be produced from diverse metabolites
amino acids, glucose (dietary starch, dietary sucrose), glycogen, lactate (lactic acid), pyruvate, fatty acids, ketone bodies
Citric Acid Cycle other names
Kreb’s cycle
tricarboxylic acid cycle
Citric acid cycle input, output, and location
Acetyl CoA
3NADH, FADH2, GTP, 2CO2
mitochondria
Oxidative phosphorylation / Electron Transport Chain
Complex I collects electrons from NADH produced by various mitochondrial dehydrogenases
Complex II, or succinate dehydrogenase, transfers electrons from succinate to FAD
Both complex I and II, as well as other FAD-linked dehydrogenases not shown, transfer electrons to ubiquinone (Q)
Electron transfer continues through complex III, cytochrome c, and finally complex IV, cytochrome oxidase
During electron transport, complexes I, III, and IV also pump protons out of the mitochondrial matrix, creating the proton motive force
The mitochondrial F1F0 ATPase (complex V) uses proton motive force to fuel ATP synthesis
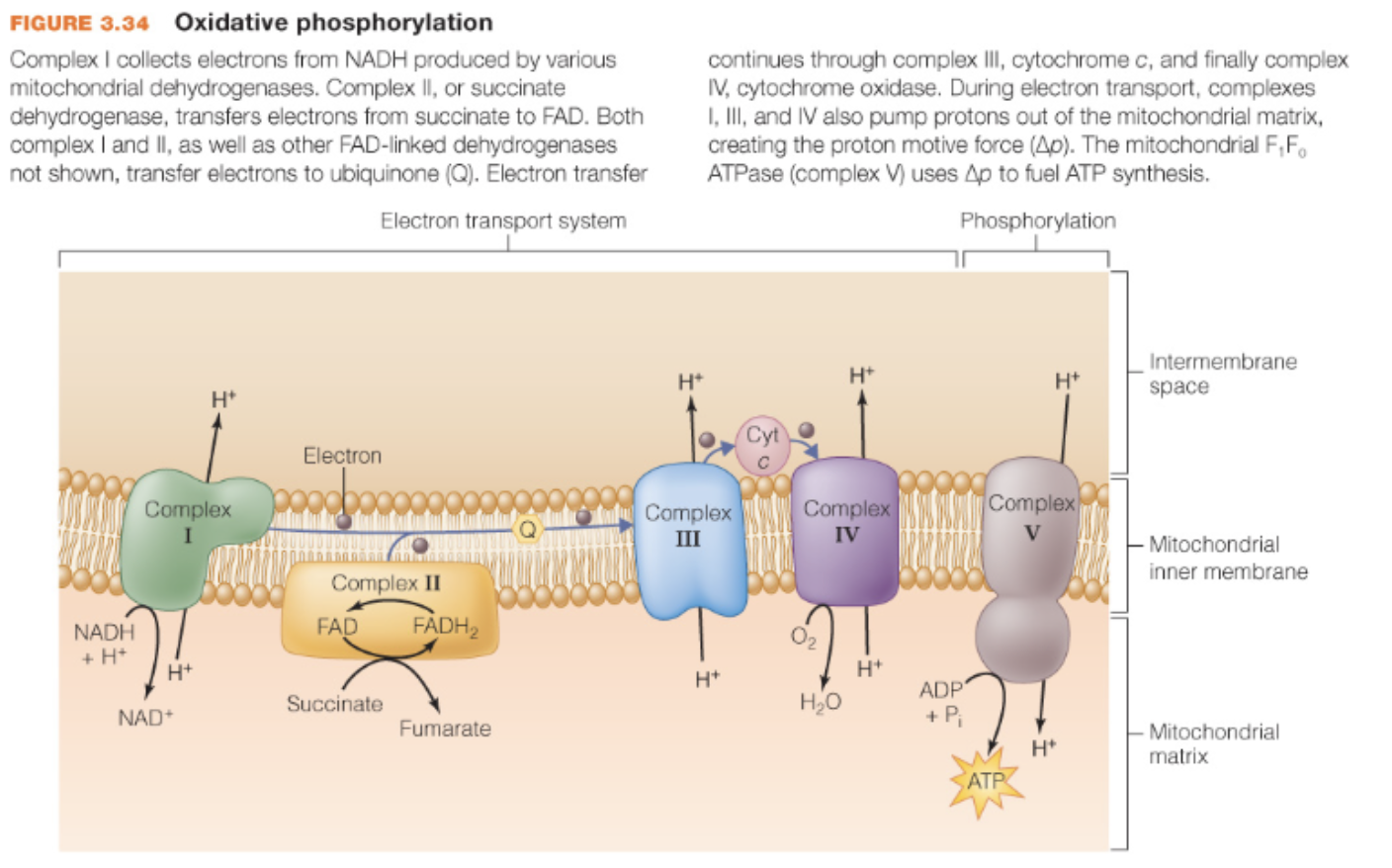
Oxidative phosphorylation occurs where
within the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotic cells
Why don’t cells always do TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation if it produces so much more ATP than glycolysis alone?
oxidative phosphorylation is obligated to be aerobic
Types of cell signaling
direct cell signaling, autocrine and paracrine signaling, endocrine signaling, neural signaling
a ligand is
a chemical message sent from one cell to another
a receptor is
a target for a ligand and binding elicits (causes signal transduction) or prevents a response (stops/prevents signal transduction)
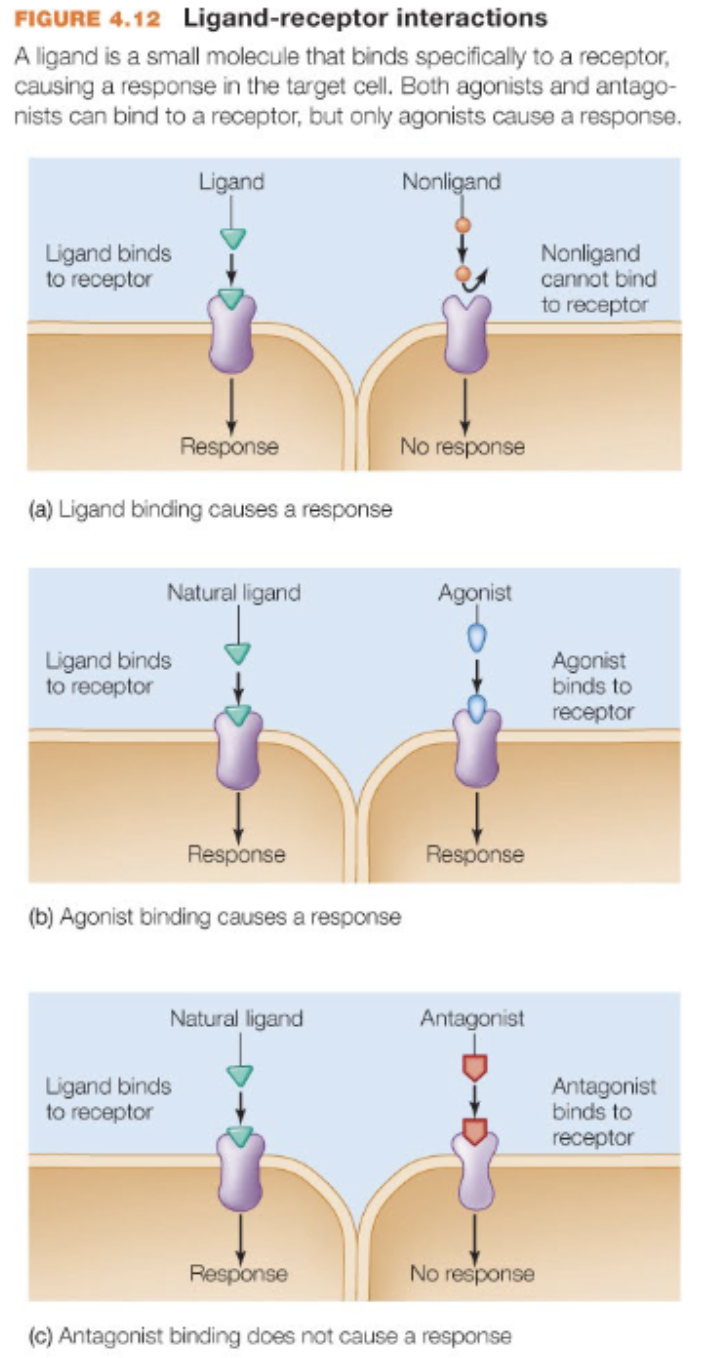
agonist
mimics the natural ligand
antagonist
binds to prevent ligand binding
natural ligand is
endogenously (internally) produced
signal transduction ia
a cascade of molecular events triggered by ligand/receptor binding
receptors have two different domain types
binding domains and functional domains
functional domains do what
determine the effect of the ligand/receptor binding
What determines the effect of ligand-receptor binding
the receptor type
receptors can be
external (transmembrane) or internal
Gap junctions
provide direct connections b/w cells that are in contact; traffic is generally controlled by diffusion and ligands are usually hydrophilic (not always); fast, and efficient
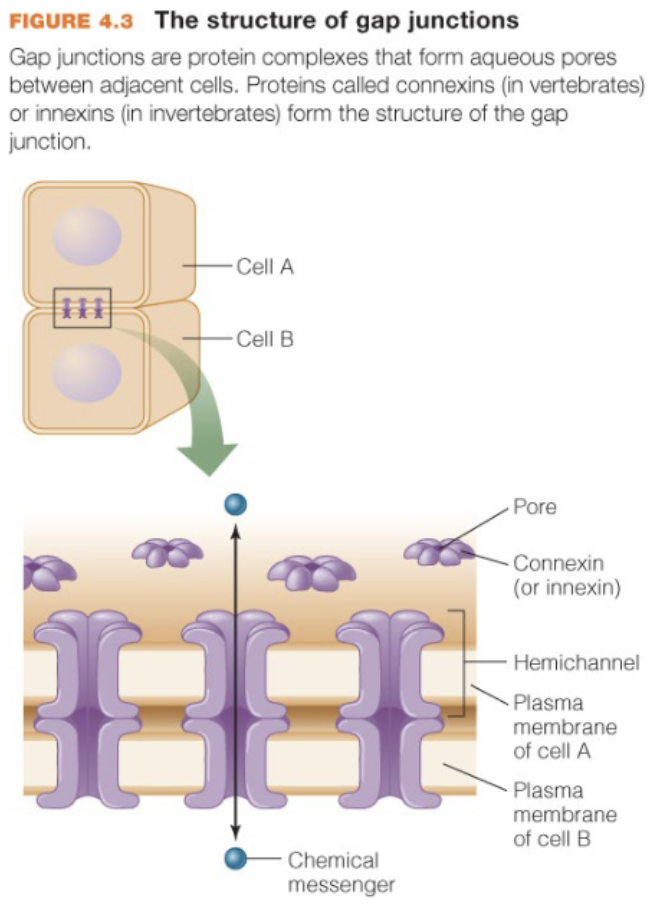
What molecules are transported via gap junctions
generally small molecules such as ions and cell messengers (ex: cAMP)
Desmosomes
non-communicating; generally for connection only; found in tissues which are exposed to high levels of stress
ex: cardiac tissue; skin
True gap junctions (function, types of transported molecules, example)
allow exchange of substances from one cell to another (small molecules, ions, metabolites); mostly functionally bilaterally; might be a chemical or an electrical synapse
ex: gap junctions in cardiac cells
autocrine/paracrine/endocrine signaling all involve and are differentiated by
the release of chemical messenger into the extracelullar matrix
target of the chemical messenger determines the type
autocrine signaling
the target receptor is on the releasing cell
ex: IGF, IL-1
paracrine signaling
the target is cells very near the releasing cell
ex: Wnt family of signals (carcinogenesis, embryonic development, etc)
Endocrine
the target is cells (relatively) distant to the releasing cell
ex: estrogens, thyroid hormones, cortisol, insulin
neural signaling (electrochemical) involves (what cells)
always involves connection b/w neural cells and other neural cells or tissues/sensors
neural signaling (electrochemical) how it works basic
involves the change in membrane potential due to changes in ion locations inside or outside neural cells
endocrine v. neural signaling
neural is faster than endocrine but it is targeted
endocrine is slower, longer lasting, and sent everywhere