2. Persuasion and Marketing
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is the definition for persuasion?
A change in attitude, beliefs or behaviour in response to direct messages
persuasion requires internalisation
What are the 3 attitude components that people may or may not include when defining what an attitude is?
Affect: evaluation (+/-)
Behaviour: readiness to act
Cognition: A collection of thoughts
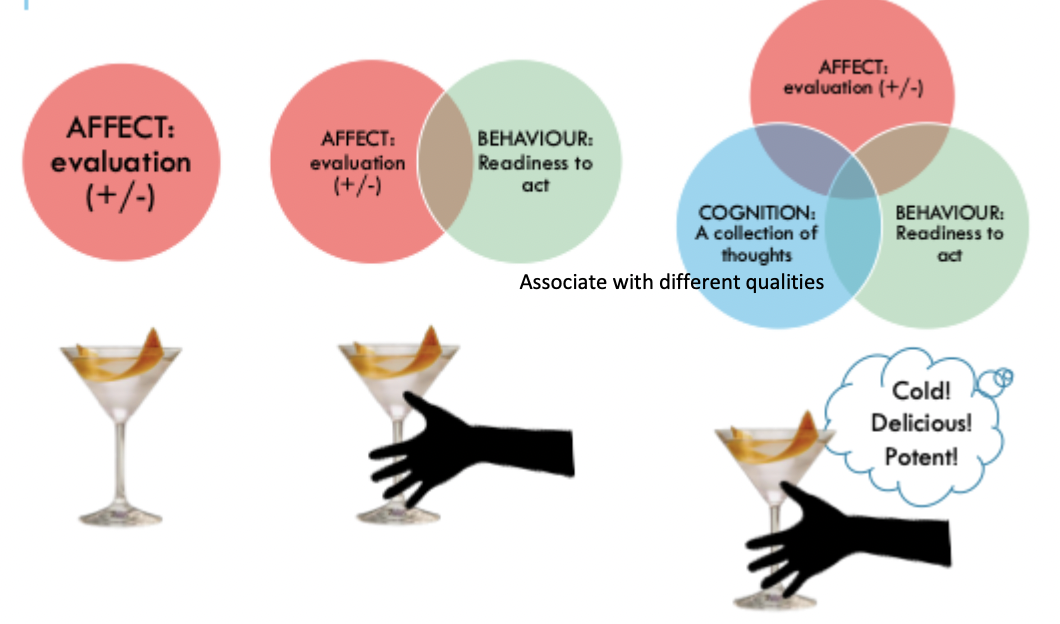
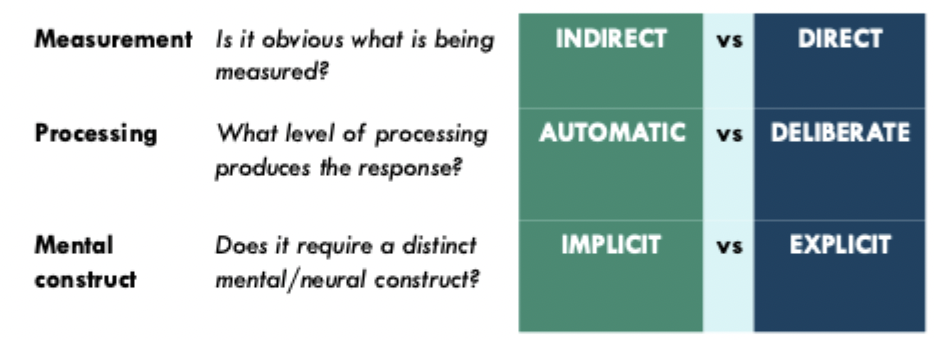
What question do we ask when deciding whether mental construct is implicit or explicit?
does it require a distinct mental/neural construct?
The attitude to behaviour gap: why is it difficult to show the attitude to behaviour link in the laboratory?
not clear which component of the three component model is important in a given situation
not clear which attitude is driving behaviour in a given situation - lots of different targets
behaviour toward one attitude object could be controlled by attitude toward another
What are the key features of heuristic processing?
argument quality is not so important
less cognitively demanding
relies upon simple rules: “majority rules”, “he looks trustworthy”, lecturers are always right”
What are they key features of systematic processing?
argument quality is important
involves the effortful scrutiny of all relevant information: “are the arguments logically coherent?”, “do they fit with my existing knowledge?”
attitude change is more enduring and more resistant to change
When is heuristic processing most likely to occur?
most likely to occur as the default
when is systematic processing most likely to occur?
when
one has the motivation to be accurate, defend an attitude, or create a positive impression
one has the cognitive capacity for effortful processing
one tends, by personality, to need clear explanation
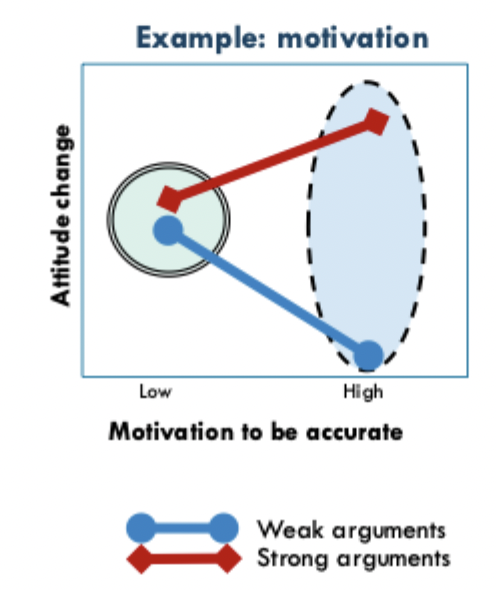
What kind of arguments are most effective in high and low motivation states and which kinds are employed as a result?
strong arguments lead to greater attitude change with high motivation to be accurate.
opposite with weak arguments, systematic processing occurs
heuristic processing occurs in low motivation state, different arguments have no difference
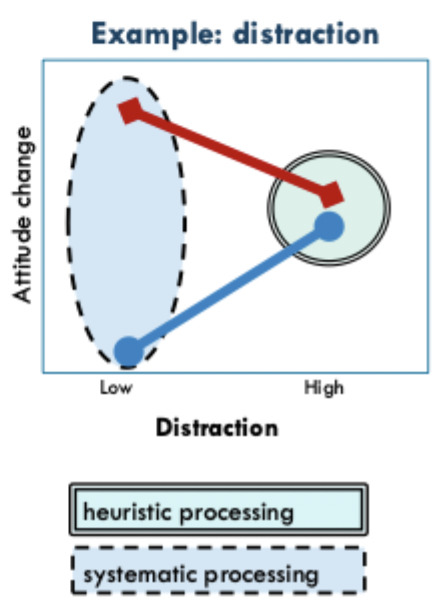
What kind of arguments are most effective in high and low distraction states and which kinds are employed as a result?
strong arguments most effective in low distraction, systematic processing occurs
no difference between kinds of arguments in high distraction, heuristic processing occurs

Which three factors affect persuasion?
source
message
audience
these factors interact to determine the efficacy of persuasion
Which factors affect the Source as a factor affecting persuasion?
expertise
trustworthiness
likeability
status
group membership
Which factors affect the Message as a factor affecting persuasion?
one vs two-sided arguments
emotional vs cognitive appeal
explicit vs implicit conclusion
Which factors affect the Audience as a factor affecting persuasion?
intelligence
self-esteem
need for cognition
cognitive load
What was the procedure of Dubois et al used to examine how sources are more persuasive when they share characteristics with the audience?
participants were put in groups where power was made salient through recalling events (baseline, low power or high power)
they were given the role of either communicator (e.g. write a persuasive speech), or audience
they measured audience attitudes toward the university, coding of argument competence, coding of argument warmth (more emotional)
What were the result of Dubois et al used to examine how sources are more persuasive when they share characteristics with the audience?
supports the matching hypothesis
with high audience power - high power communicator were more persuasive
with low power audience - low power communicator more persuasive
What might explain the high-power individuals behaviour in Dubois study
high power individuals
less dependent on others
more agentic
focused on competence

What might explain the low-power individuals behaviour in Dubois study
low-power individuals
more dependent on others
more “communal”
focused on warmth (affiliation)
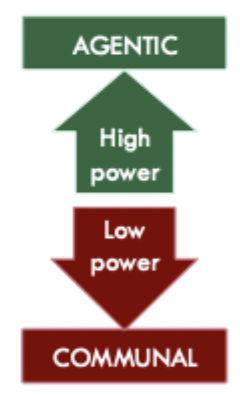
What was found by dubois in the high power communicators speeches
used more competence-related arguments
competence related arguments more persuasive among high power audiences
What was found by Dubois in the low power communicators speeches?
used more warmth-related arguments
warmth-related arguments more persuasive among low-power audiences
How has need for cognition/affect been operationalised to be able to test the effect of matching message and audience
need for affect: scale from -3 (strongly disagree) to +3 (strongly agree) to rate items such as: i like to dwell on my emotions
need for cognition: scale from 1 to 5 to rate items such as: i really enjoy a task that involves coming up with new solutions to problems
What was the procedure of Haddock’s Lemphur study which investigated the effect of matching the audience and message on persuasion
participant who had either need for cognition or need for affect
shown affects vs cognition oriented message about imaginary animal
measured their result attitude toward lemphurs


What were the results of Haddock’s Lemphur study
affect orientated messages did predict audience attitude for those who have need for affect
cognition orientated messages did predict audience attitude for thsoe who have need for cognition
there was a matching effect
Source expertise and audience motivation: do experts make us think and attend more carefully or do we readily accept their message?
findings are mixed
people process experts’ message heuristically when not very motivated
however, people are likely to attend more closely to expert’s arguments (and process them systematically) when they are interested
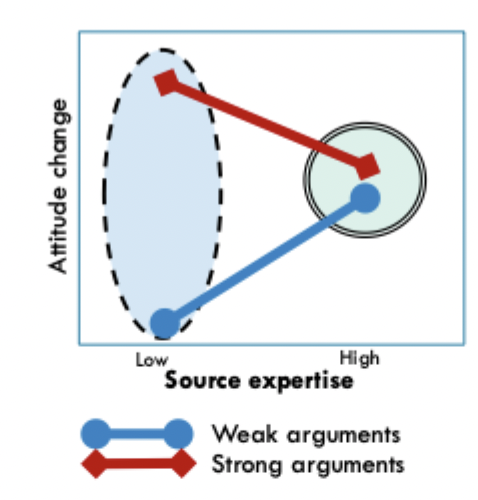
Why might we systematically process expert’s messages more than non-experts when motivated?
we seek to confirm our existing attitudes
What are our attitudes towards experts in proattitudinal situations?
when people agree with us, we trust experts and process their arguments heuristically
but we scrutinise non-experts in order to identify weaknesses in “our side”
What are our attitudes towards experts in counterattitudinal situations?
when people disagree with us, we ignore non-experts
but we scrutinise experts in order to better counter them
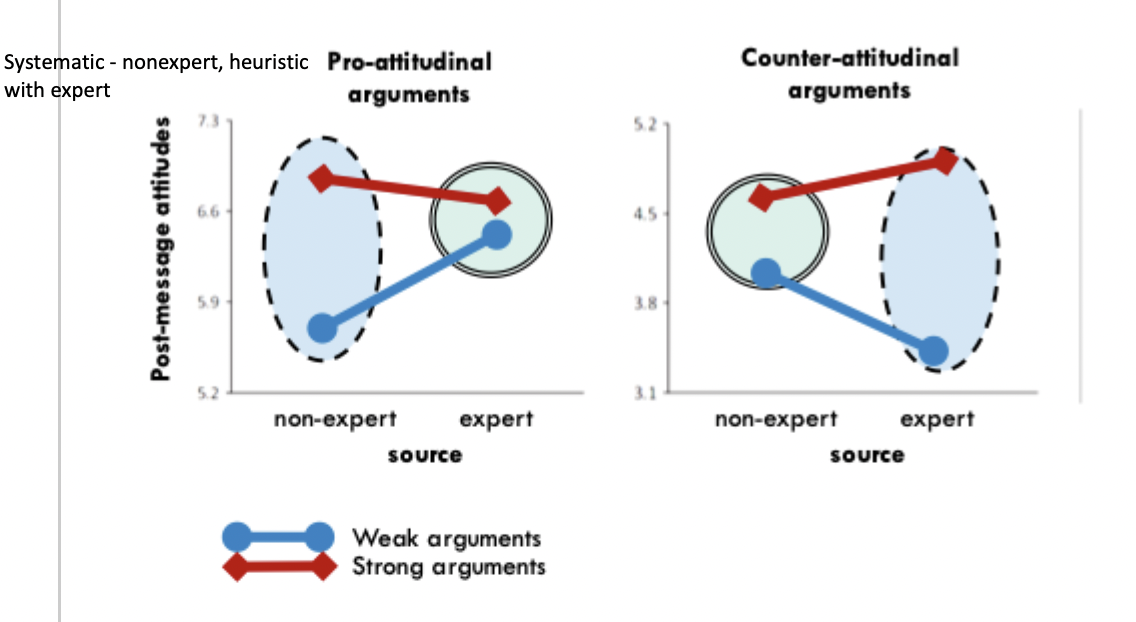
What procedure did Clark et al use to examine expertise, argument and audience?
attitude pre-assessment separated ppts into pro-attitudinal arguments and counter-attitudinal arguments
then put into expert/non-expert condition (leading scholar/ high school junior)
argument manipulation: strong condition had millions of dollars at stake, weak conditions: smaller amount of money
then an attitude post-assessment
What were the results of Clark et al examining expertise, argument and audience
How might we perceive brands as social objects
brands are social objects and, like humans, are perceived in terms of intentions and ability (analogous to warmth and competence) the combination of these dimensions elicits different emotional responses

What are some effects of strong brand relationships?
elicit loyalty that goes beyond habit
reflect or contribute to self concept
lead to resistance to negative information about the brand
lead to feelings of betrayal when the brand falls short of expectations
rely to some extent on anthropomorphism of the brand
vary with individual differences in personality
What is anthropomorphism in the context of branding
the attribution of human characteristics to inanimate objects, animals, etc
used in branding whereby brands themselves are anthropomorphised
used in product design whereby products have humanlike features
these features can have a positive effect on product impressions
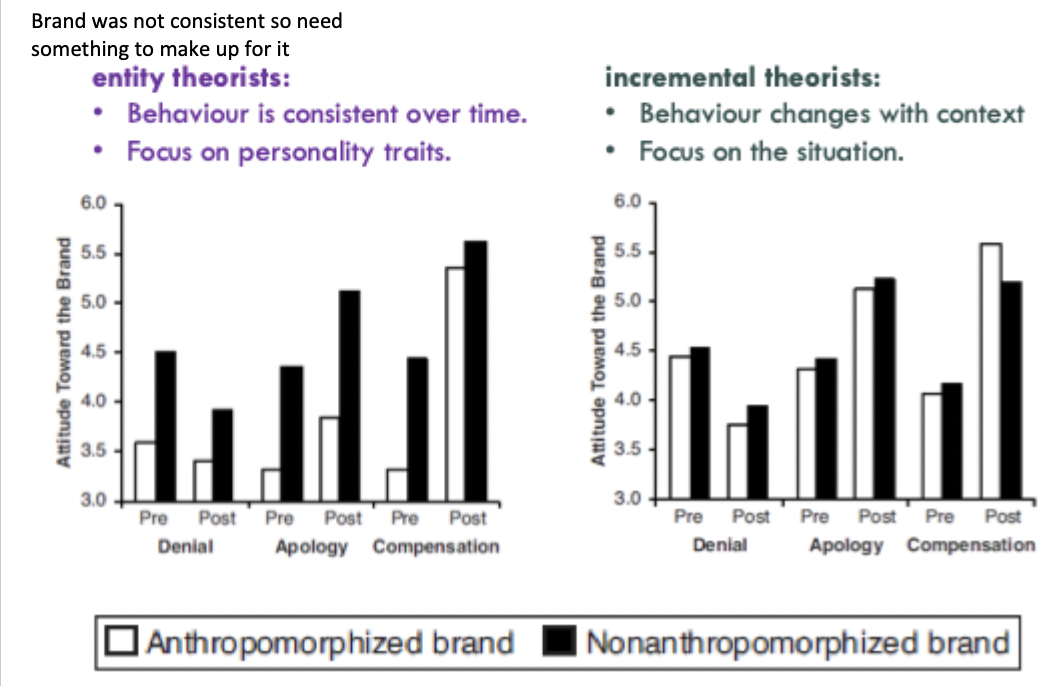
how did Puzakova study the effect of anthropomorphism
participants learned about a product that was either anthropomorphised or was not
then participants learned that product did not work - what are their attitudes toward the brand? might take it not working personally if cultivated relationship to anthropomorphised them
they hypothesised that it was depend on the social beliefs of the consumer: entity theorists will hold its mistakes against it, incremental theorists will not

entity theorists
expect behaviour to be consistent over time
characterise a person based on a single act
incremental theorists
believe that behaviour changes with context
do not expect behaviour to be stable over time
Results of Puzakova’s study of brand anthropomorphism

larger difference in attitude towards brand for entity theorists with anthropomorphised condition
In puzakova’s corporate response study leading on from anthropomorphised brands who failed, what were the three conditions? And what did they find
Denial
Apology
compensation

What are three strategies and their factors that audiences and use to resist persuasion?
avoidance: physical, mechanical, cognitive
contesting: content, source, tactics
empowering: attitude bolstering, social validation, self assertion
What are the resistance neutralising tactics that brands use against avoidance?
forced exposure
branded content
viral marketing
What are the resistance neutralising tactics that brands use against contesting?
two-sided advertising
cognitive depletion
distraction
safety cues
What are the resistance neutralising tactics that brands use against empowering?
self affirmation
freedom