IB ESS Topic 4.3 - Aquatic Food Production Systems
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
marine ecosystems
oceans, mangroves, estuaries, lagoons, coral reefs, deep ocean floor
very diverse and have high stability and resiliene
continental shelf
the extension of the continents under the seas and oceans - creates shallow water
important because:
- 50% of productivity in only 15% of its area
- upwellings bring nutirent-rich water to continental shelf
- higher light penetration/insolation
- countries can claim it as theirs to exploit and harvest
UNCLOS
The UN Convention on the Laws of the Sea - in 1982 they designated the continental shelf as belonging to the country from which they extend
phytoplankton
single-celled organisms that can photosynthesis and are the most important producer in in the oceans, producing 99% of primary productivty - crucial in supporting oceanic food webs
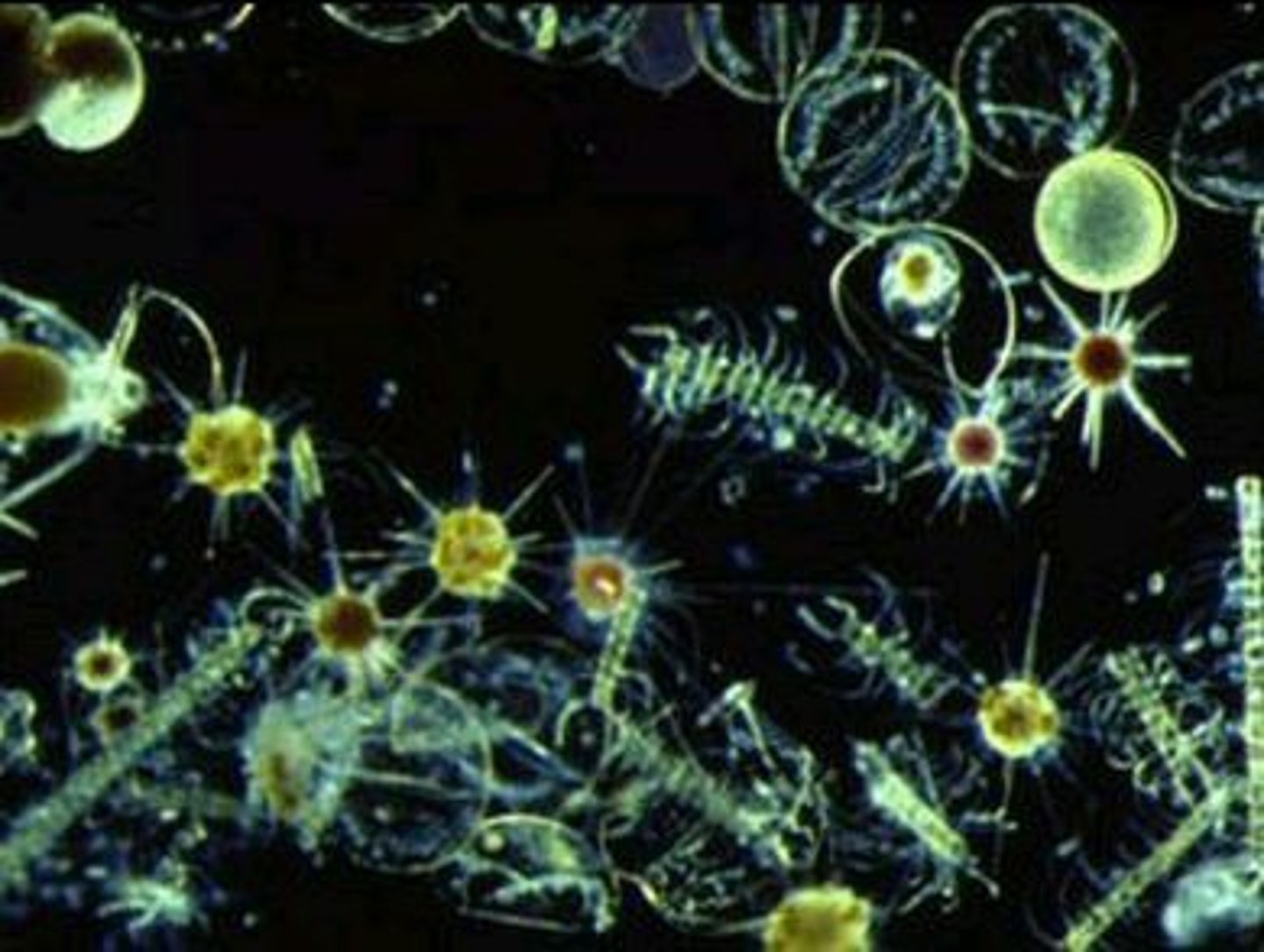
zooplankton
single-celled animals which feed off of phytplankton and their waste - crucial in supporting oceanic food webs
DOM
dead organic matter
waste created by living organisms as they grow and die
benthic
organisms living on or in the sea bed
pelagic
organisms living surrounded by water from above the sea bed to the surface
fishery
when fish are harvested in some way - includes capture of wild fish and aquaculture (fish farming)
90% is marine - 10% is freshwater
FAO
Food and Agriculture Organisation:
- more than 70% of world fisheries are fully exploited, in decline, seriously depleted or too low to allow recovery
aquaculture
the farming of aquatic organisms in both coastal and inland areas involving human intervention in the rearing process to enhance production (FAO)
benefits of fish
high in protein, contains important lipds (fats and oils), low in bad fats, provides
on average, people eat 20 kg of fish and only 8 kg of meat
vegetarian farmed fish
solution to sustainable aquaculture - the United States Department of Agriculture has proven that there are eight species of carnivorous fish which can gain enough nutrients on a diet excluding other fish
China's production of farmed fish
62% of all farmed fish - mostly carp or catfish - often grown in rice paddies (DOM and waste provides nutrients for the rcie)
rice - fish farming
a system whereby fish are reared in rice paddies - the fish eat insect larva and algae and produce waste which the rice uses as fertiliser
the tragedy of the commons
is an economic theory of a situation within a shared-resource system where individual users acting independently according to their own self-interest behave contrary to the common good of all users by depleting that resource through their collective action
e.g. individual countries using the ocean as a resource, and so over-exploitation is occuring
over-exploitation of fisheries
fishing at an unsustainable level - over-fishing (we are too good at catching fish)
- commercial fishing has high technology to aid in catching efficiency
- fishing fleeting are larger with modern refrigeration (to stay out longer)
- within a fishing fleet there are now also processing ships
- indiscriminate fishing gear catches all organisms whether they are the target species or not (by-catch)
- trawlers drag huge nets along the seabed destroying the benthic ecosystems
maximum sustainable yield (MSY)
the increase in natural capital that can be exploited each year without depleting the original stock or its potential to replenish itself - use of this leads to sustainability
SY = annual growth and recruitment - annual death and emigration
may lead to depletion of a population in bad breeding (recruitment) years
International waters
water that no country controls, outside the 200 nautical mile exclusion zone.
Fish farming
Cultivating fish in a controlled environment and harvesting when desired size is reached
By-catch
unwanted marine creatures that are caught in the nets while fishing for another species
Optimal sustainable yield
Half the carrying capacity. Safer margin than MSY but still may have an impact on population size with other environmental impacts.
Fishing quotas
Limits on the number and size of fish that can be caught in certain areas