Basics of Pharmacology - Flashcards
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the fundamentals of pharmacology, including pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and key definitions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Pharmacokinetics (PK) is defined as __.
What does the body does to the drug?
The four key processes in Pharmacokinetics are __.
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion (ADME)
Pharmacodynamics (PD) studies __.
What does the drug does to the body?
The relationship between plasma concentration and pharmacological effect is studied in __.
Pharmacodynamics (PD)
The process by which unchanged drug proceeds from the site of administration to the systemic circulation is called __.
Absorption
The extent of drug absorption is referred to as __.
Bioavailability
The main organ for metabolism of drugs is __.
Liver
The irreversible removal of intact drugs from the body is known as __.
Excretion (mainly through the kidneys)
The main factor impacting drug distribution in the body is __.
Plasma protein binding
The concept of how a drug interacts with its receptor is part of __.
Pharmacodynamics (PD)
What is the main graph used in Pharmacokinetics?
Plasma time-conc curve
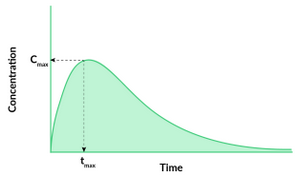
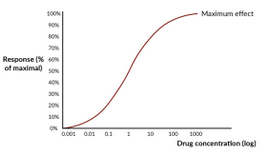
What is the main graph used in Pharmacodynamics?
Dose-response curve
Fill in the missing titles
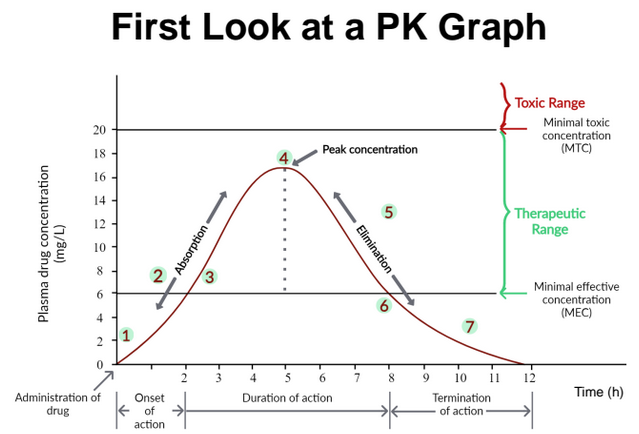
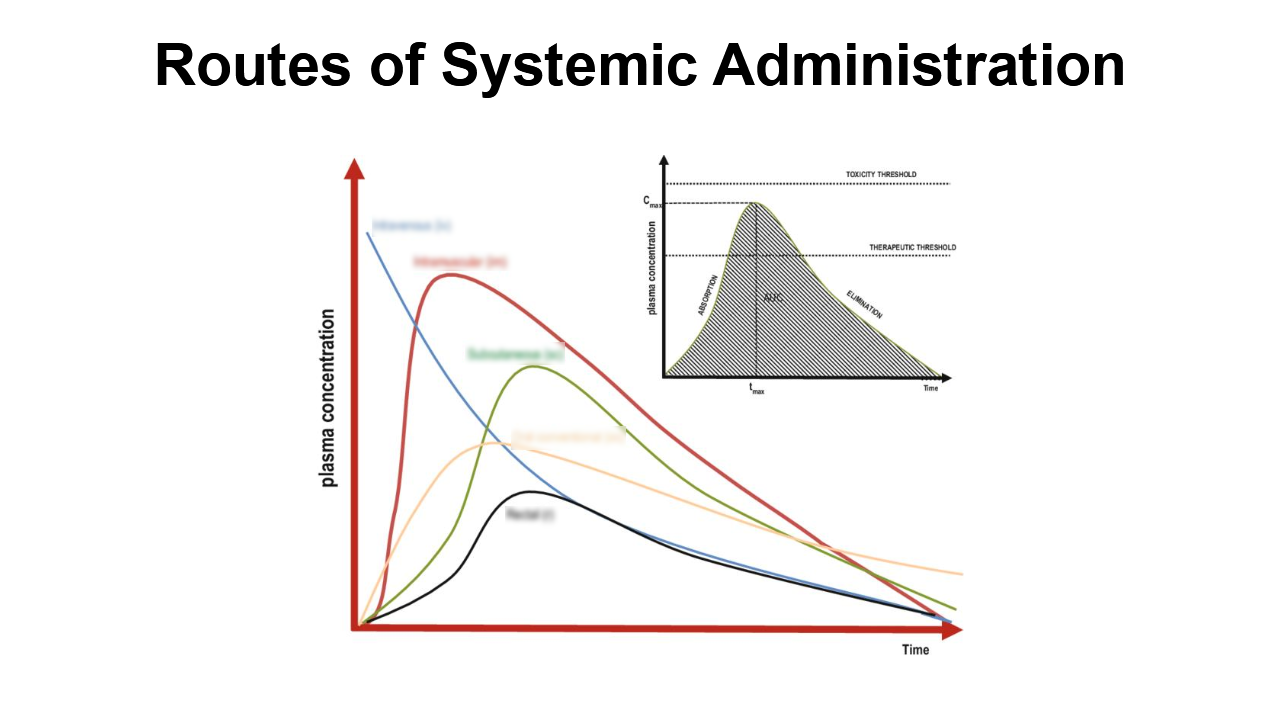
Inhalation is the second fastest route but not included in this graph
What are the 4 routes of ocular administration?
Topical, Periocular, Intraocular, and Systemic
Give 5 examples of Topical administration
Eye drops
Ointments
Gels
Ocuserts
Contact Lenses
Give 4 examples of Periocular administration
Subconjunctival (SC)
Subtenon (ST)
Retrobulbar (RB)
Perobulbar (PB)
Give 2 examples of Intraocular administration
Intravitreal (IVT)
Intracameral (IC)
Give 2 examples of Systemic administration
Intravenous (IV)
Oral (OS)
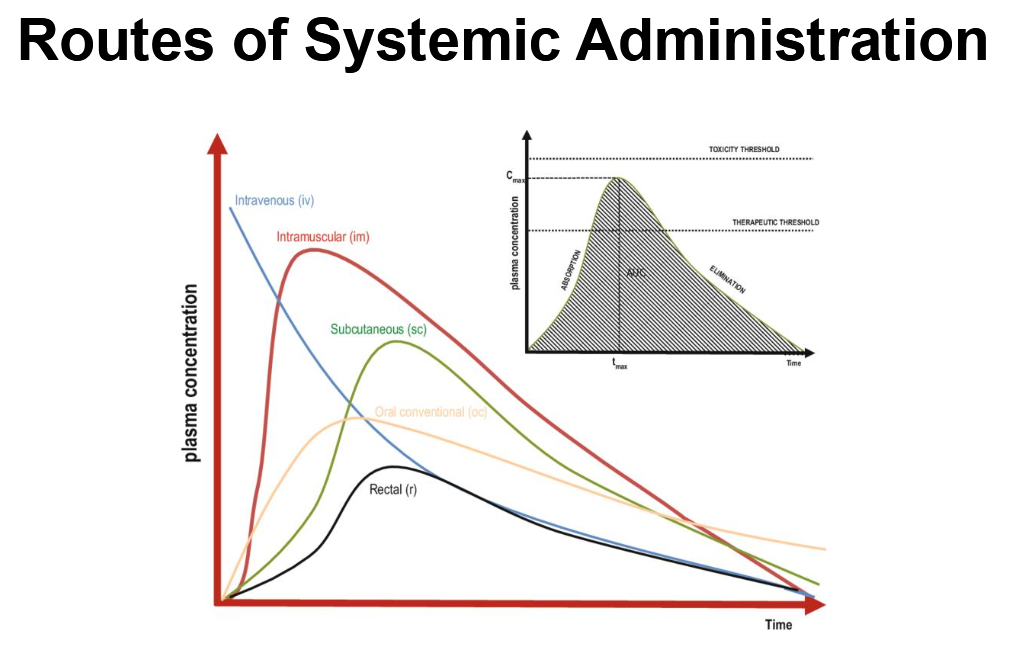
Which one of these absorptions is active transport?
Paracellular transport
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
ABC transporters
ABC transporters
__ is the most common absoprtion route.
Diffusion
To be successfully absorbed, a drug must be:
__ enough to dissolve in bodily fuilds.
__ enough to cross lipidic membranes.
Hydrophilic enough to dissolve in bodily fluids
Lipophilic enough to cross lipidic membranes
For oral dosing, it is mainly determined by the extent of hepatic __ - __ effect.
First-pass effect: The liver “takes a quote” of any drug taken orally, before it reached the systemic circulation.
__ is the chemical modification and/or breakdown of a xenobiotic/drug occuring in the body.
Metabolism
Sites contributing to drug excretion includes?
Bile
Sweat
Tears
Saliva
Lung exhalations
Milk
List 4 barriers for ocular delivery of a topically administered drug.
Tear protein binding, melanin binding
Intraocular metabolism
Pre-corneal fluid drainage
Crossing cornea and other absorption barries
The goal of metabolism is to make the drug as __ as possible for it to be dissolved and excreted through urine.
water soluable/hydrophillic
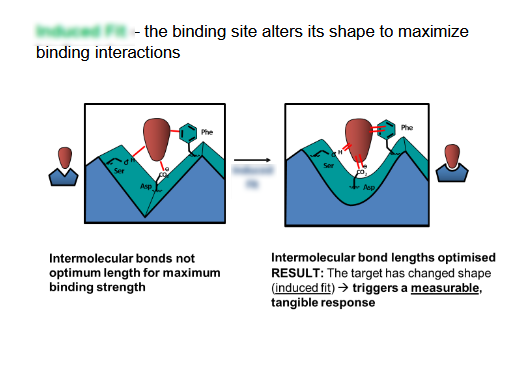
What is the basic principle of drug action?
Induced Fit
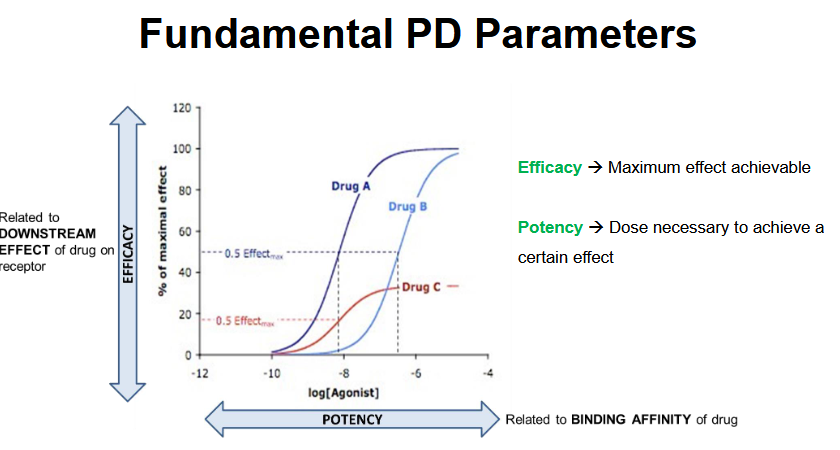
Between Drug A and Drug B, which drug is more potent?
Drug A because a lower conc is needed to acheive the same effect.
Potency is related to the __ interactions.
Binding
The better the drug binds to the target, the lower amount of drug needed to have a certain effect, therefore, more potent.
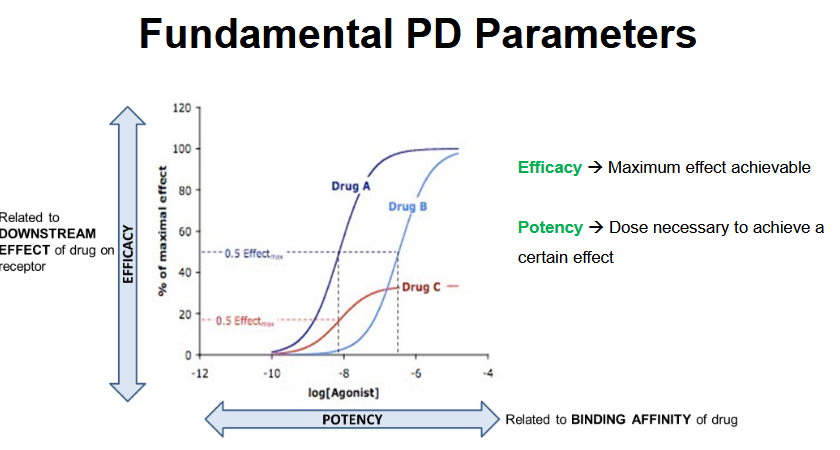
Which drugs have the same potency?
Drug A and Drug C
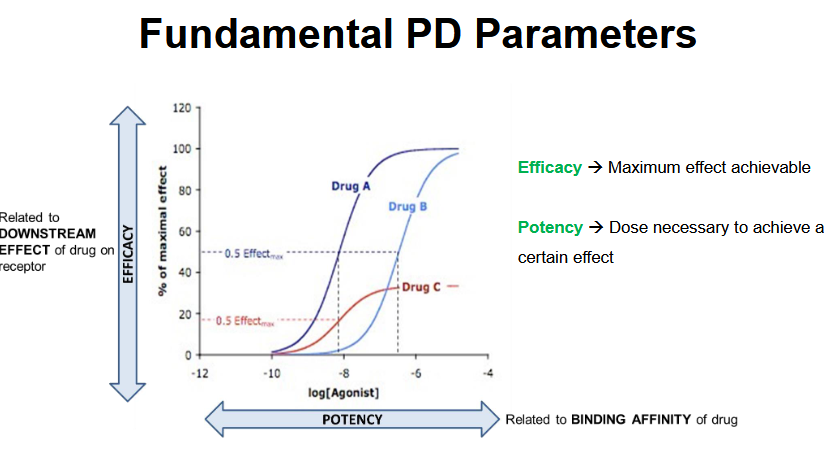
What drugs have the same efficacy?
Drug A and Drug B
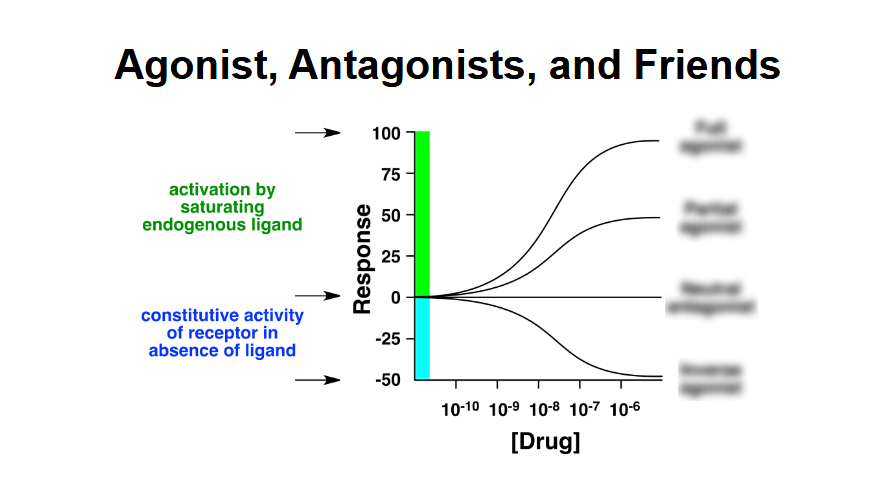
Fill in the missing titles
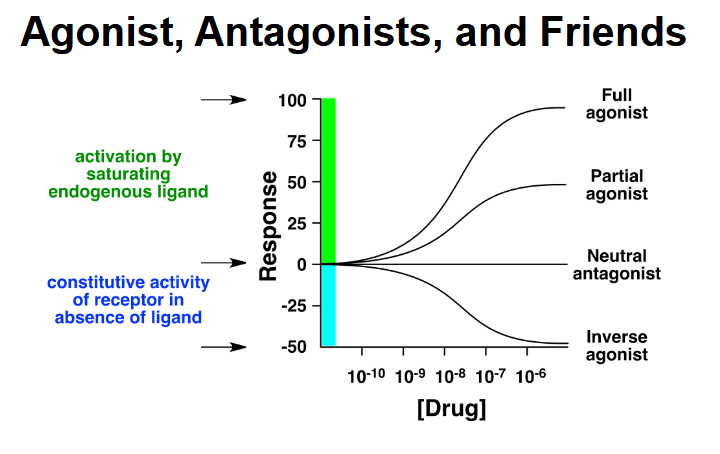
What are the 5 right-steps-follow” in drug administration?
Right Patient
Right Drug
Right Time
Right Route
Right Dose
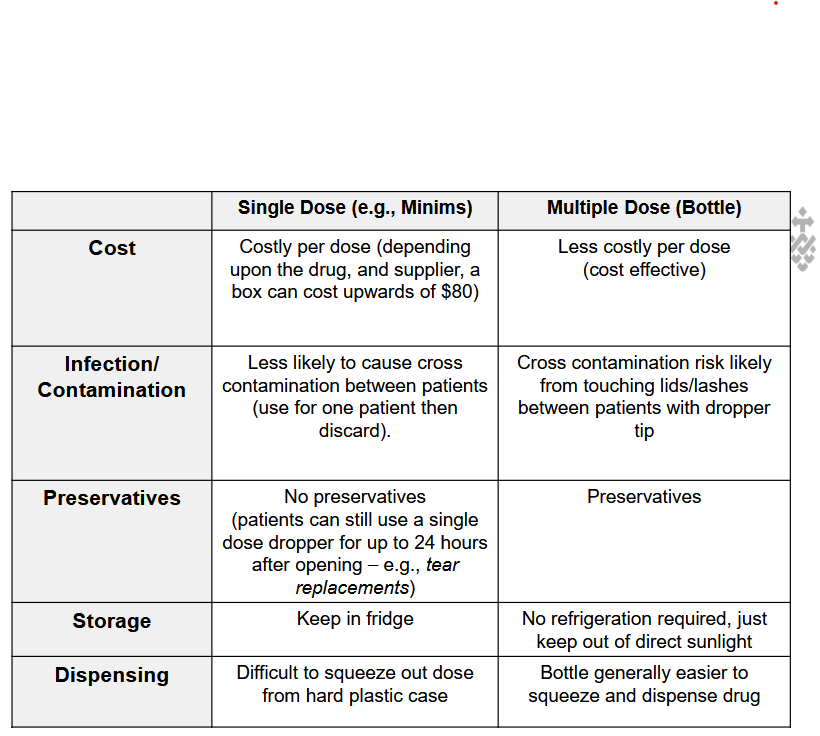
Fill in the blanks
What should you do before opening drop bottles?
What should you do after opening a new bottle?
Check the date of the bottle before opening and instilling to a patient
Upon opening - label it with date of opening