Animal Biology Lab 9 Flashcards
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about Animal Biology Lab.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Order Gymnophiona
Order of caecilians; characterized by a limbless, wormlike body, and small scales in some species.
Order Urodela
Order of salamanders; characterized by a body with head, trunk, and long tail, usually with two pairs of equal-sized limbs.
Order Anura
Order of frogs and toads; adults are characterized by a head and trunk fused, absent tail, elongated hindlimbs, and a large mouth.
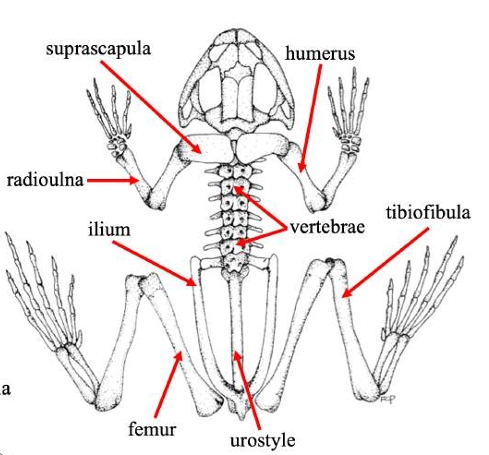
Suprascapula
A bone in some vertebrates that supports the shoulder girdle, often serving as an attachment for muscles, particularly in certain amphibians and reptiles.
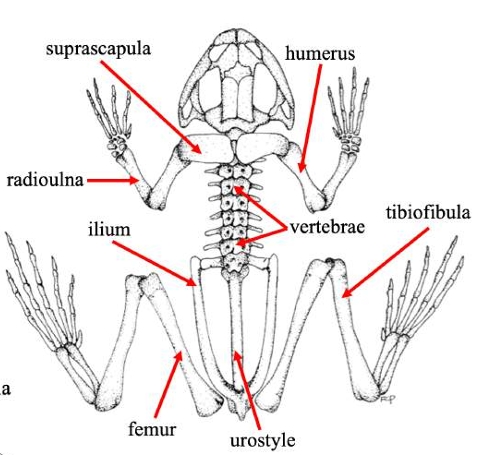
Scapula
A major bone in the shoulder region of vertebrates that articulates with the humerus and supports the upper limb.
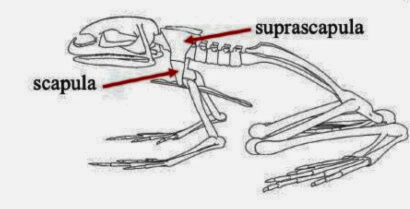
Humerus
The bone of the upper front limb in frogs, connecting the shoulder and the elbow.
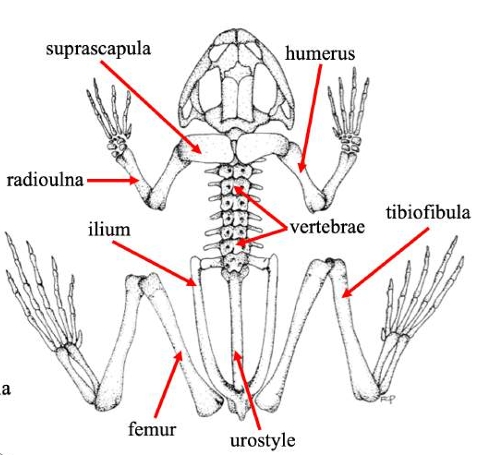
Radioulna
The fused bone in some vertebrates' forelimbs that combines the radius and ulna, playing a crucial role in forelimb movement and stability.
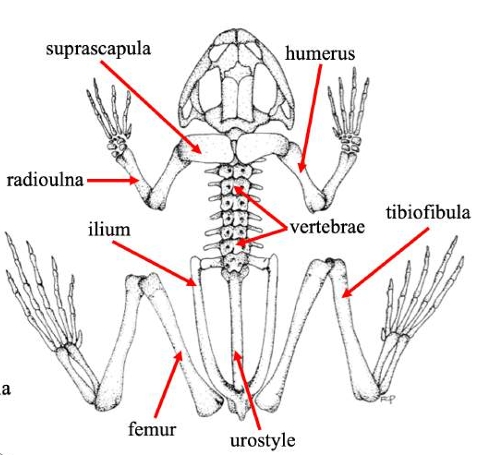
Vertebrae
The series of bones that make up the spine in vertebrates, providing structural support and protecting the spinal cord.
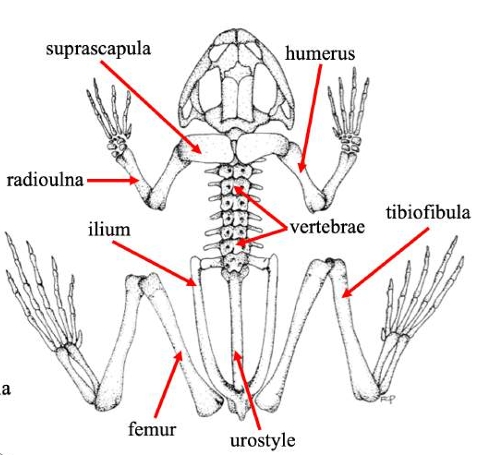
Ilium
The uppermost and largest bone of the pelvis, important for supporting the body and providing attachment for muscles.
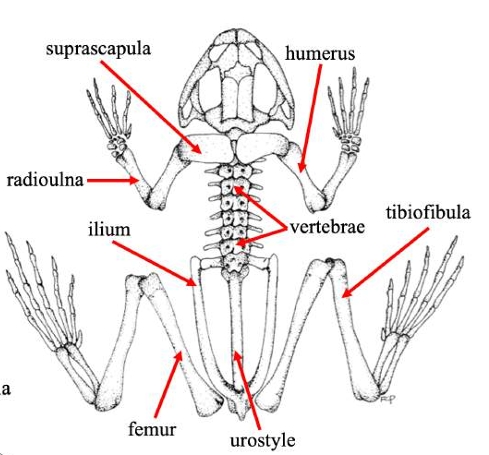
Urostyle
A fused skeletal element found in the vertebral column of some amphibians, particularly frogs, which aids in locomotion and body stability.
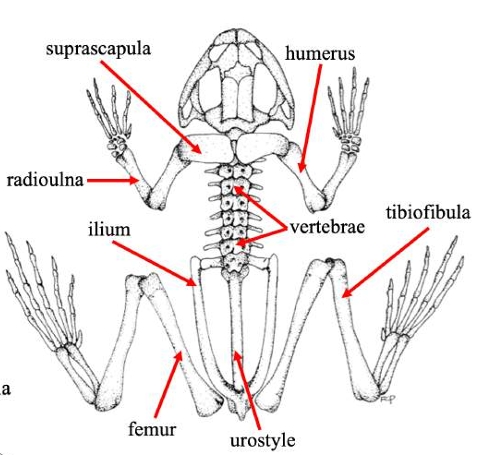
Femur (frog)
Thigh bonein frogs that supports weight and locomotion, connecting the hip to the knee.
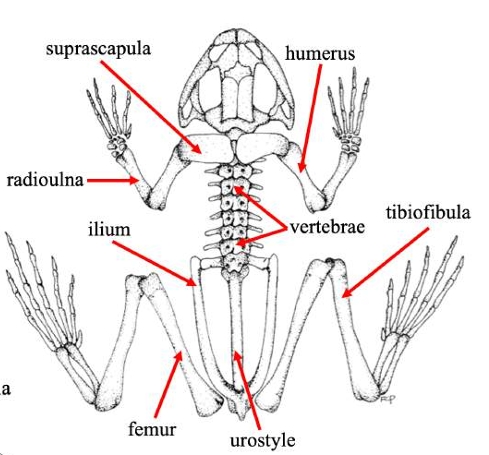
Tibiofibula
The bone in frogs that is a fusion of the tibia and fibula, supporting the lower limb and playing a key role in locomotion.
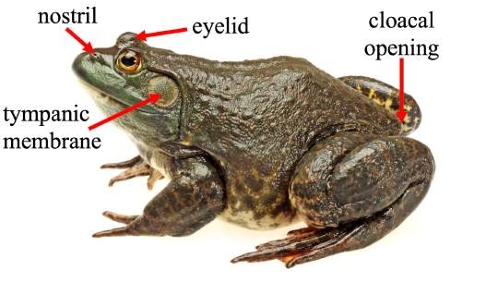
Cloacal opening
The posterior opening in amphibians, including frogs, through which excretion occurs and reproductive fluids are expelled.
Heart
Pumps blood throughout the body via blood vessels.
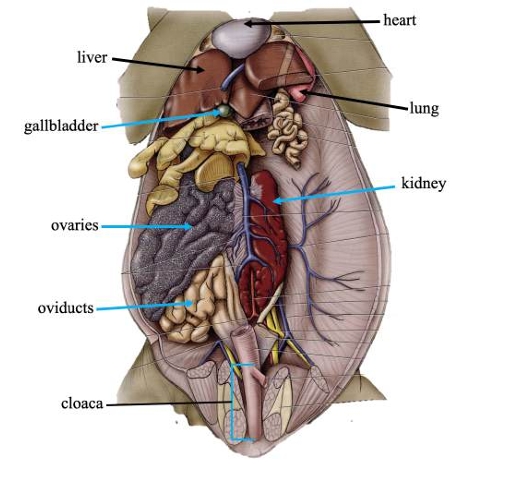
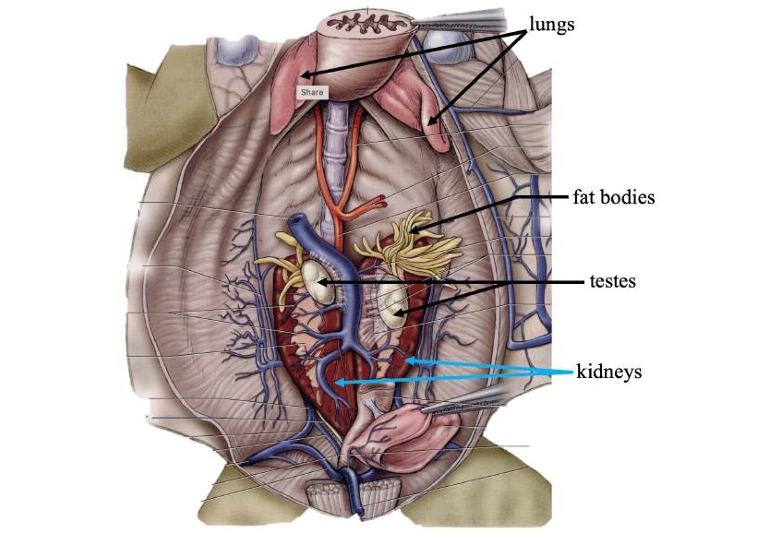
Lungs
Primary organs of respiration.
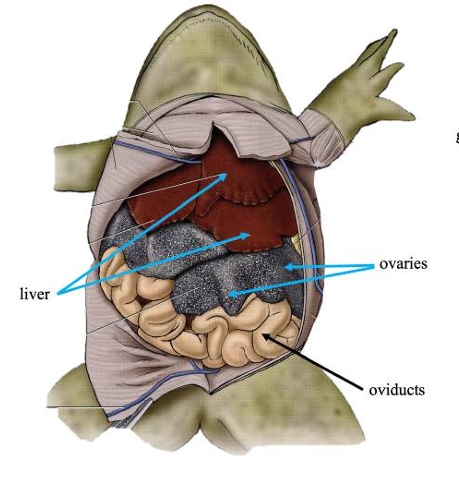
Liver
Detoxifies compounds from digested food; produces bile.
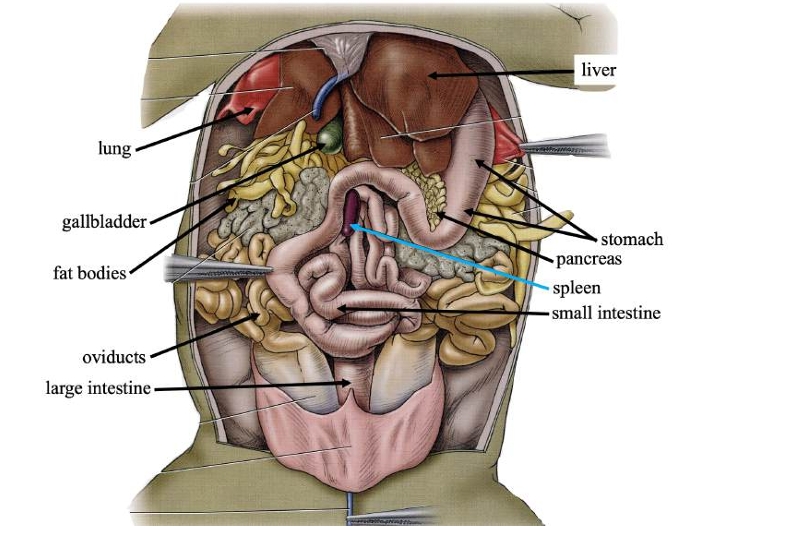
Gallbladder
Stores bile produced in the liver.
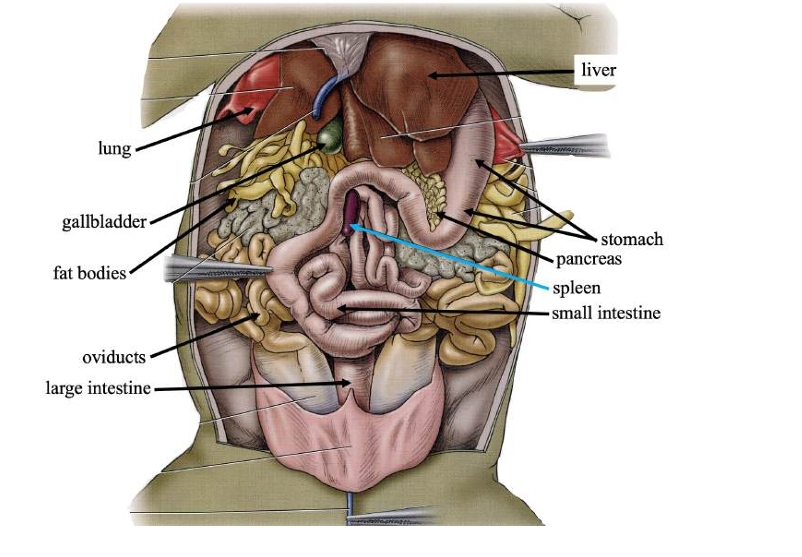
Pancreas
Produces digestive compounds & secrete them into the small intestine.
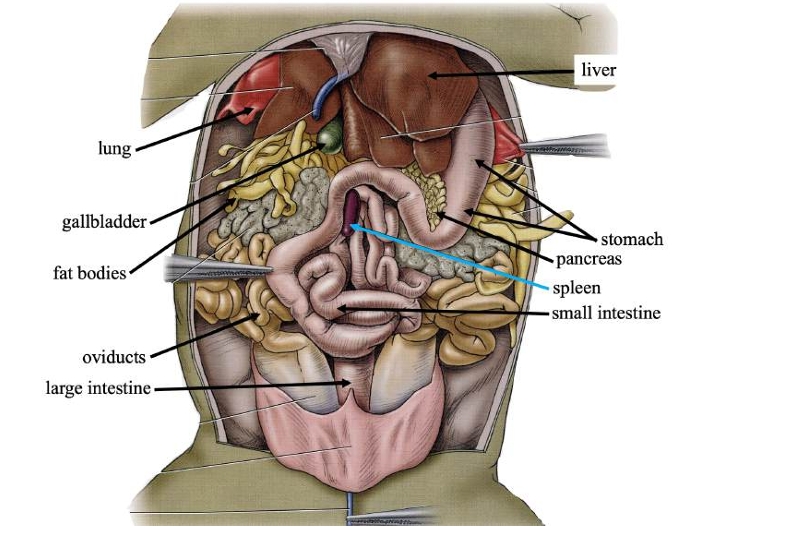
Spleen
Stores blood, recycles worn-out red blood cells, and makes white blood cells.
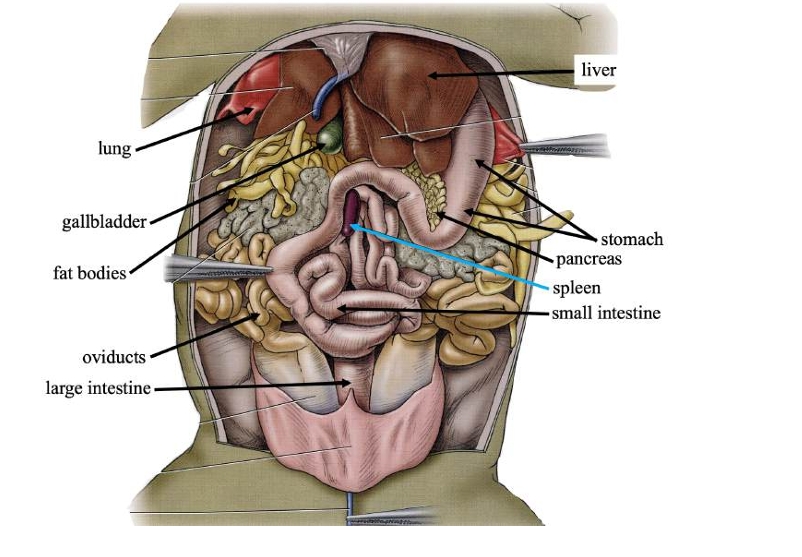
Stomach
Stores swallowed food and initiates digestion.
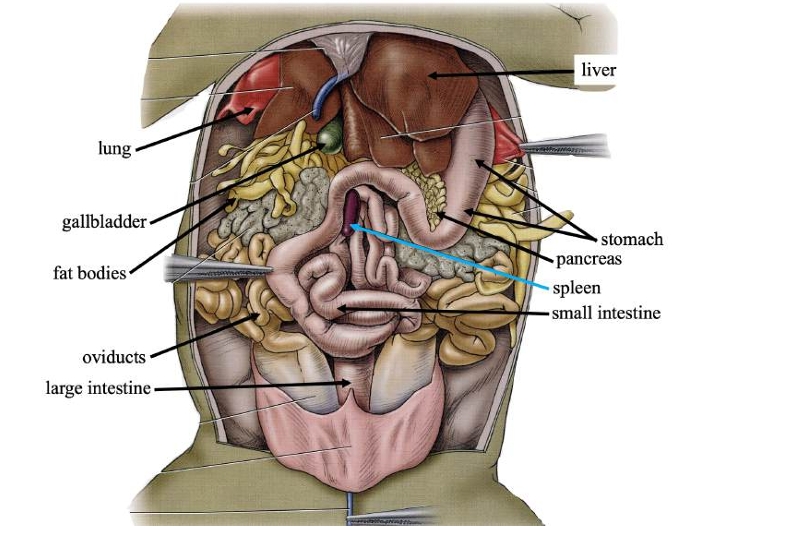
Small intestine
Completes food digestion and absorbs nutrients.
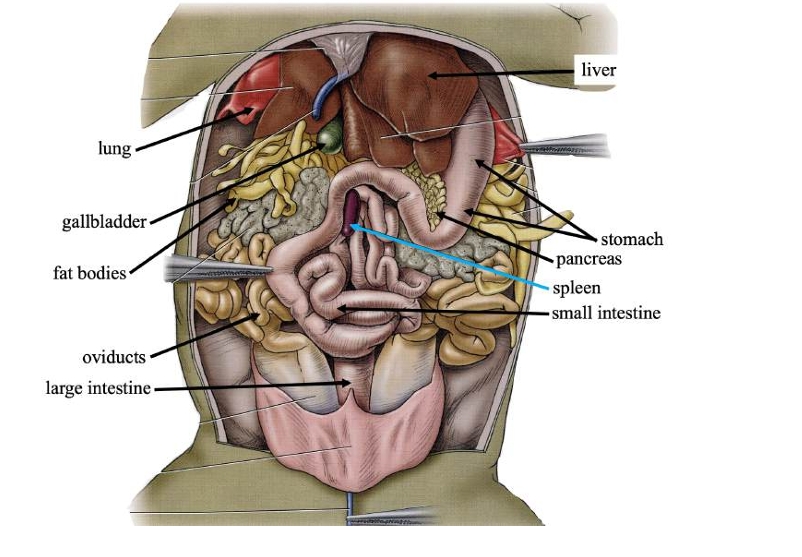
Large intestine
Absorbs water, ions, and some vitamins from digestive waste.
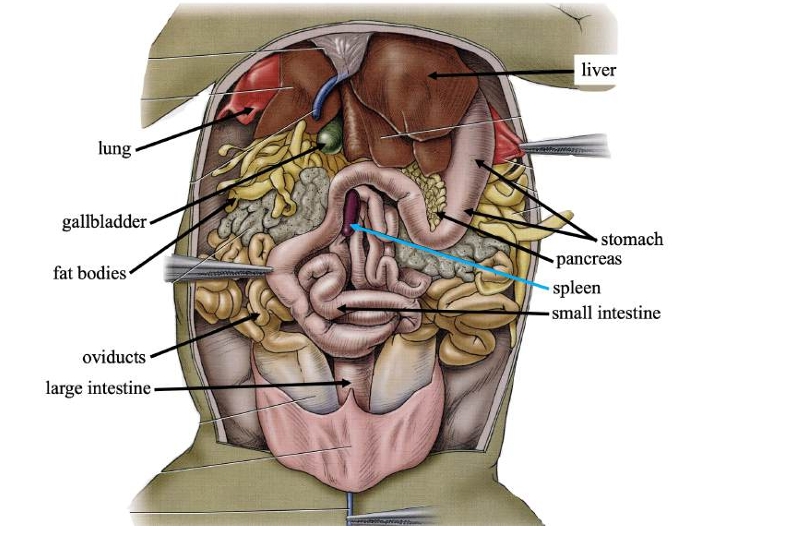
Fat bodies
Stores lipids (fats) for use when food is scarce.
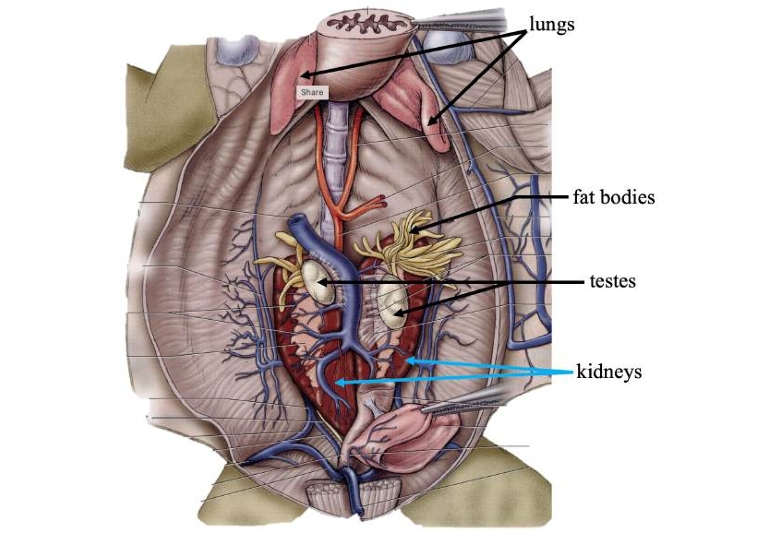
Kidneys
Filters nitrogenous waste out of the blood.
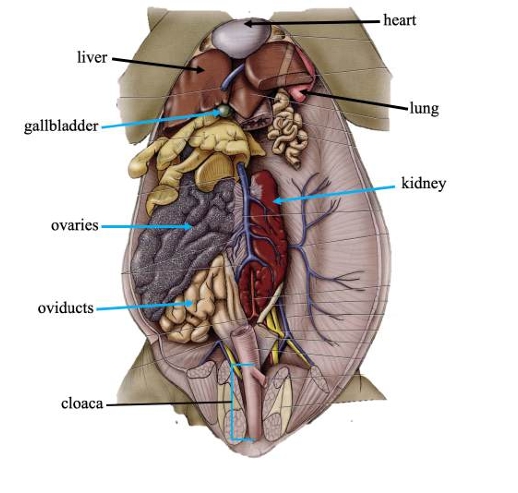
Cloaca
Common chamber for collection of urine, feces, and sperm or eggs.
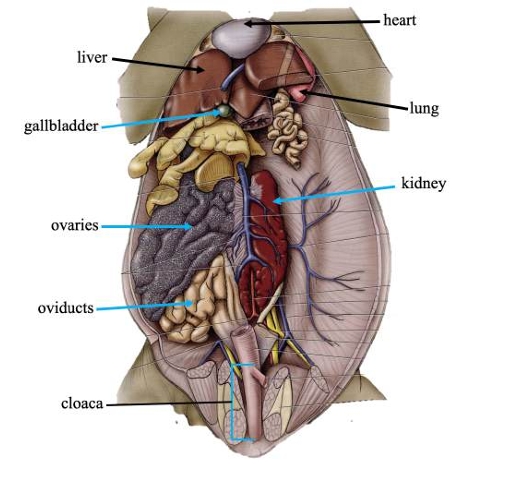
Ovaries
In females, produces eggs for reproduction.
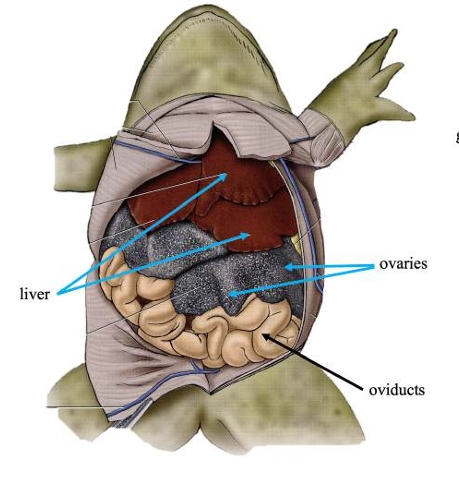
Oviducts
In females, transports eggs from ovaries and secrete protective coating.
Testes
In males, produces sperm for reproduction.