Metamorphic Rocks 2
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What’s metamorphism?
A process that converts one rock of any type (sedimentary, igneous, metamorphic) into another rock due to high pressure or temperature.
What’s a metamorphic rock?
A rock that forms when a pre-existing rock (protolith) undergoes a solid-state change in response to the modification of its environment.
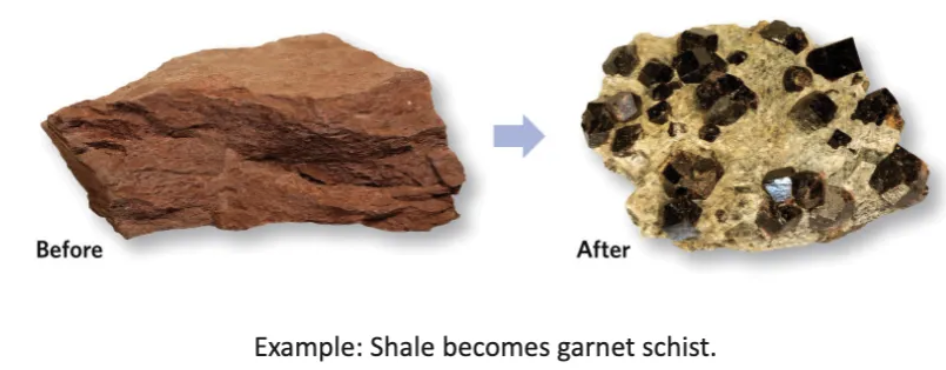
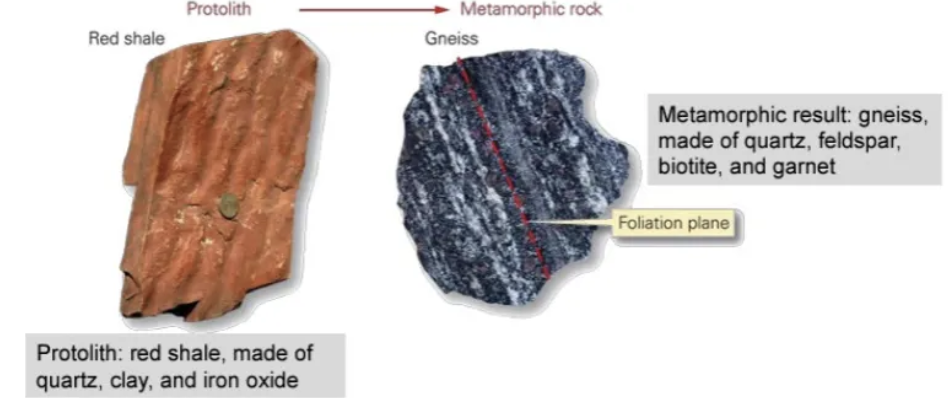
What’s a protolith?
A parent rock.
What changes happen during metamorphism?
New minerals grow at the expense of old minerals, changes:
Shape, size, texture and arrangement of grains in the rock
Occur in the solid state because melting doesn’t occur
Induced by heat, pressure, differential stress, hydrothermal fluids
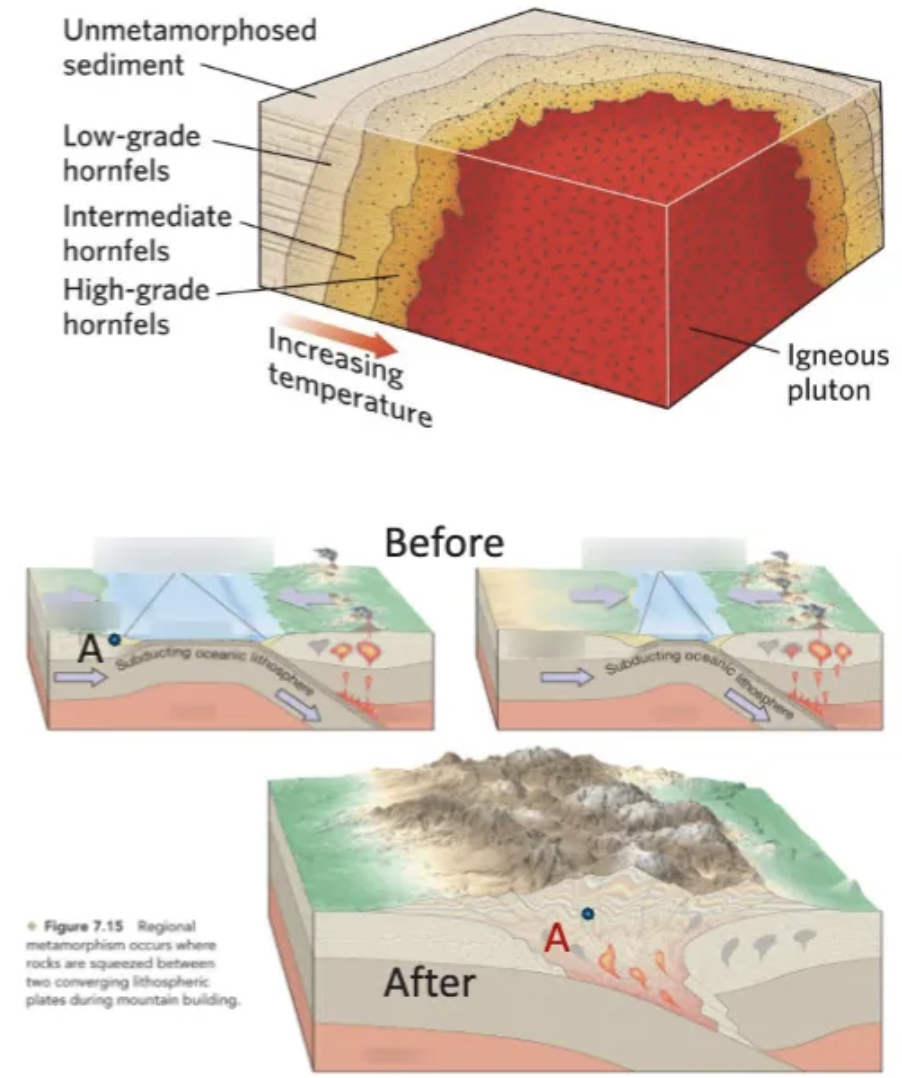
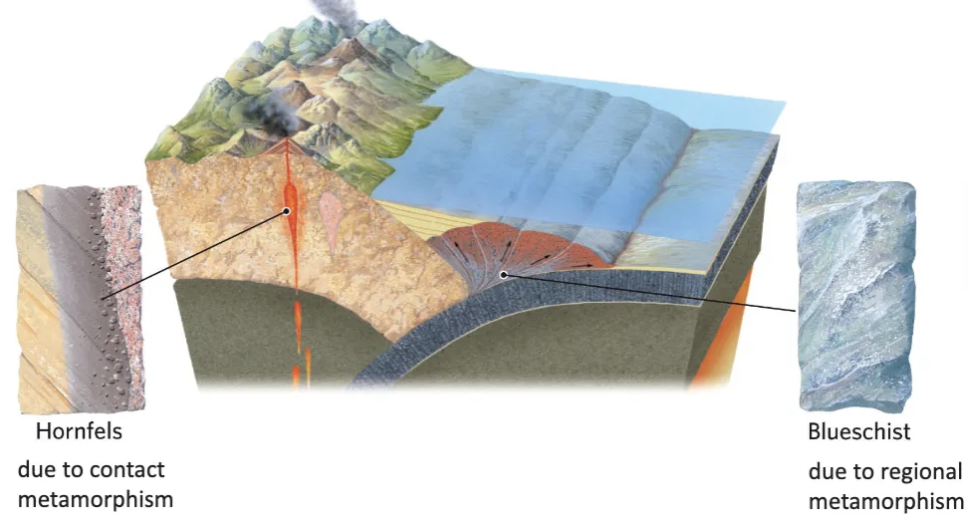
List 2 types of metamorphism and what causes them.
Contact (thermal) metamorphism—caused primarily by heat.
Occurs around igneous intrusions.
Regional metamorphism—caused primarily by pressure.
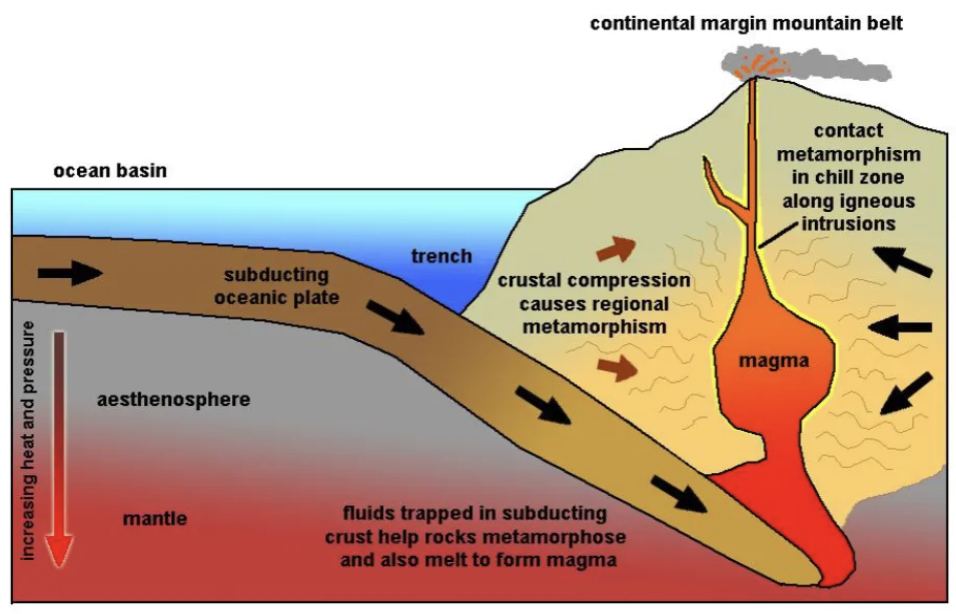
What’s metamorphism in subduction zones?
Metamorphism under extremely high pressure and relatively low temperature that only occurs in accretionary prisms.
List out the metamorphic processes.
Recrystallization
Phase change
Metamorphic reactions (neocrystallization)
Pressure solution
Plastic deformation
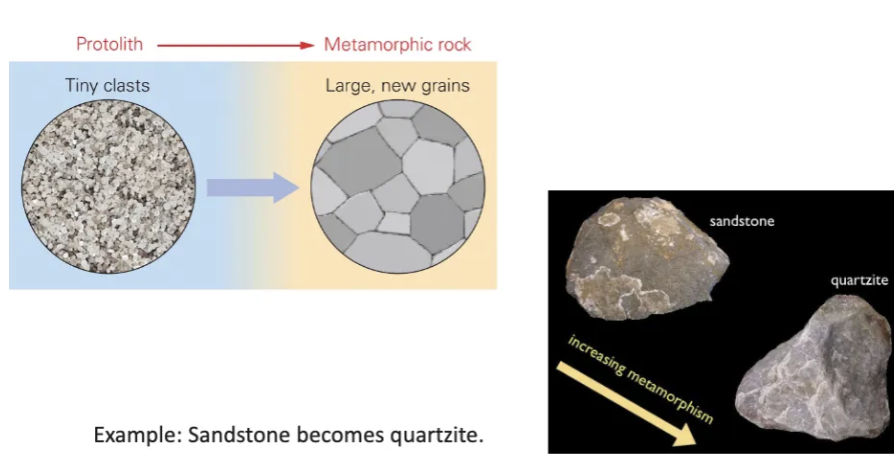
Describe recrystallization.
Involves changing the shape and size of certain mineral grains without changing the identity of the minerals.
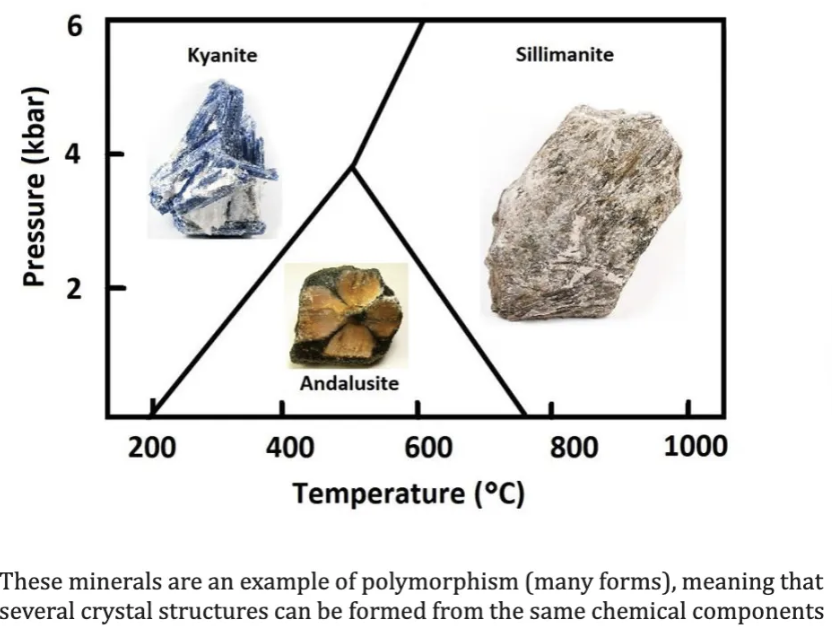
Describe phase change.
(polymorphic transformation/crystal structure change)
Transformation into another mineral with the same chemical composition but different crystal structure.
e.g. the transformation of graphite into diamond, both minerals are composed of pure carbon but have different crystal lattices
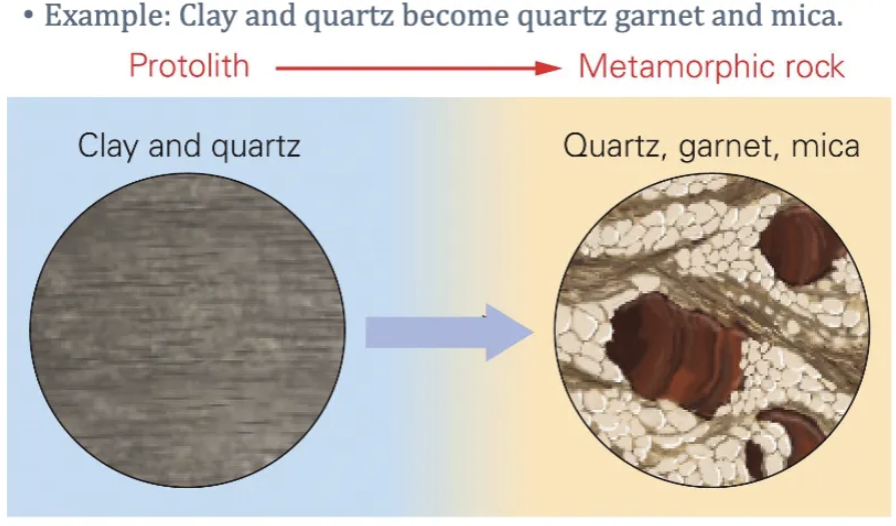
Describe metamorphic reactions.
(neocrystallization)
When atoms separate from the pre-existing minerals and re-bond to form new minerals.
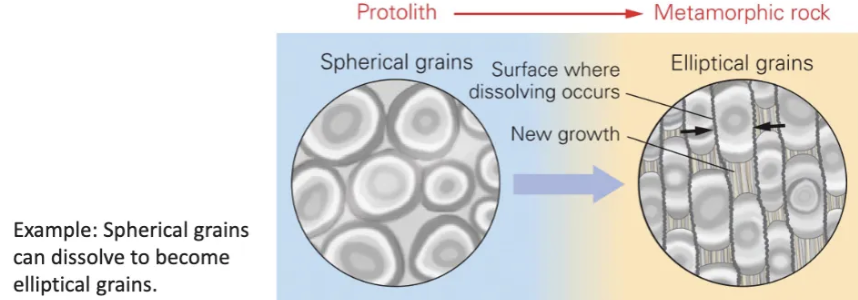
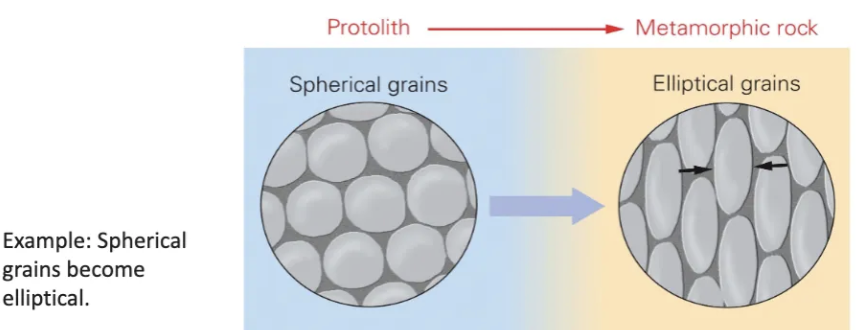
Describe pressure solution.
Dissolution that occurs more rapidly where pressure is being applied in the presence of water.
Mineral grains partially dissolve where their surfaces press together.
Ions from the dissolution migrate in the water film.
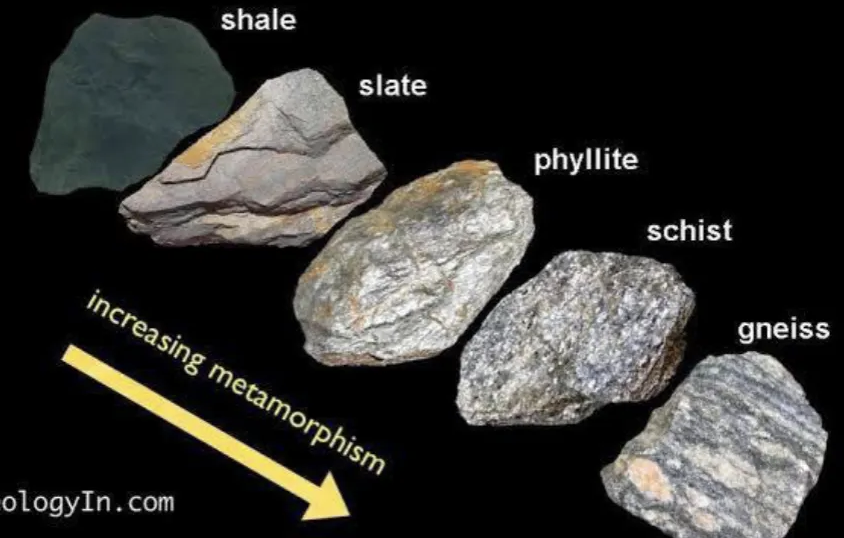
Describe plastic deformation.
Change of shape without breaking or dissolving.
Mineral grains that soften and deform are plastic
happens at elevated temperatures
Rock is squeezed or sheared

List agents/causes of metamorphism.
Temperature change
Pressure change
Both temperature and pressure change
Interaction with hydrothermal fluids
Application of stress
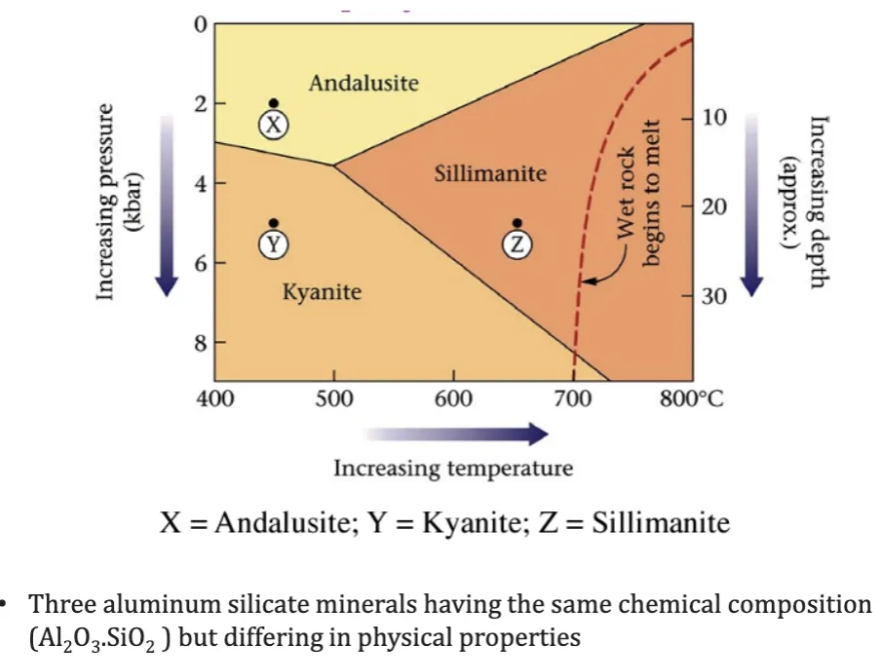
Describe the effect of increase in temperature and pressure on the minerals and the metamorphic process.
Heating of material adds energy to the rock → chemical bonds breaking and reforming in the minerals.
Pressure causes a material to collapse, forming different bonds and causing a phase change or metamorphic reaction.
Common cause of recrystallization, neocrystallization, phase transformation, neocrystallization.
What is stress?
Application of force over an area.
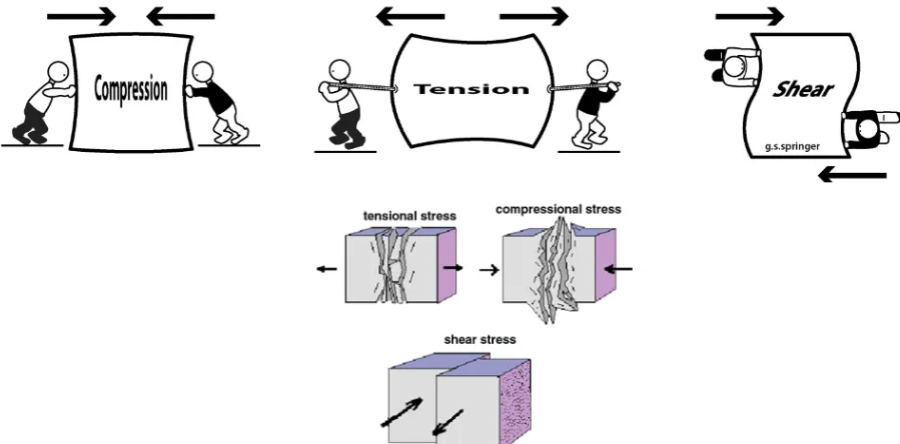
List and describe the different types of stress.
Compression—involves squeezing a material.
Tension—involves stretching a material.
Shear—an angle force that moves material sideways relative to another part.
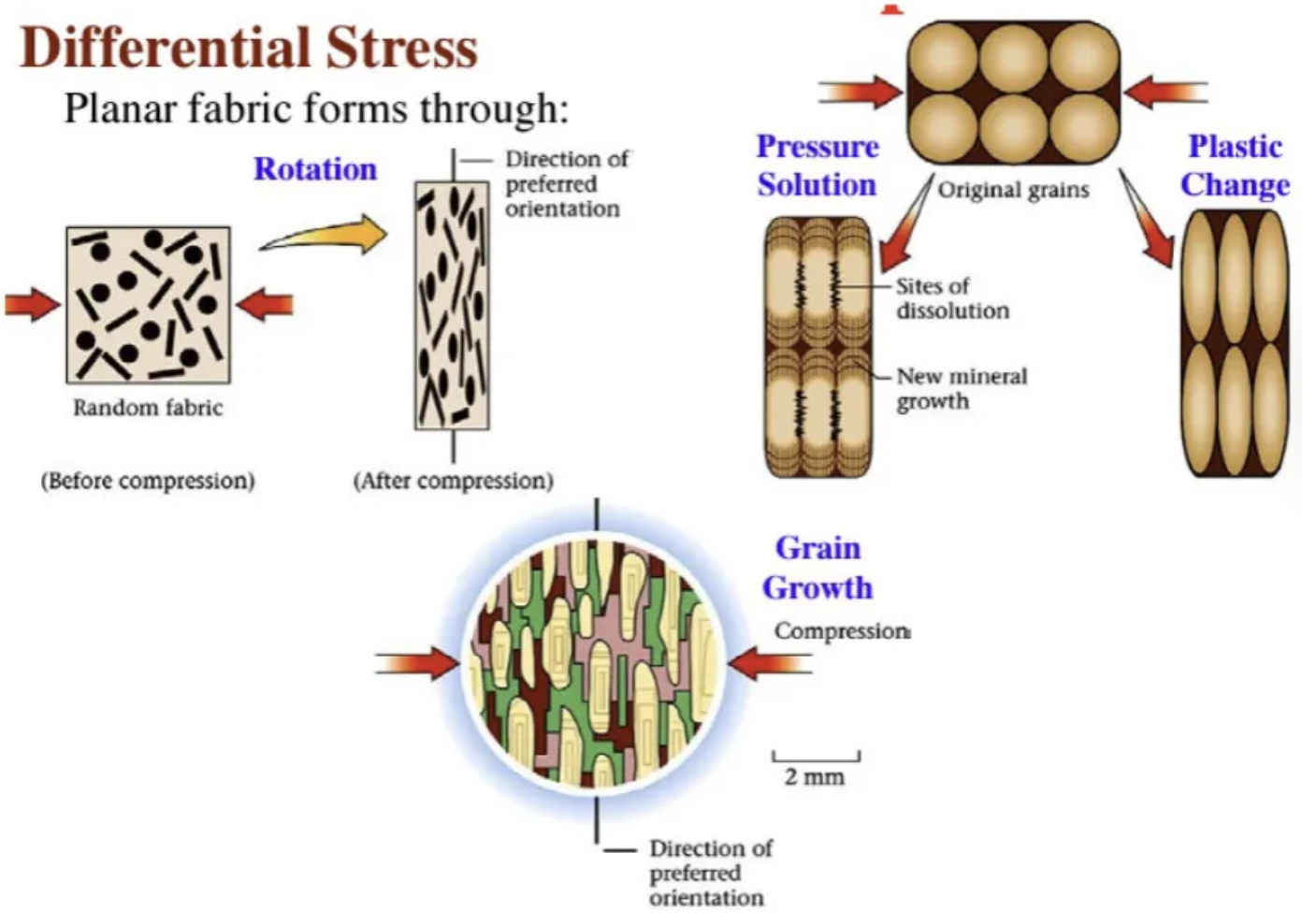
What is differential stress?
Occurs when the stress is not equal in all directions.
Describe differential stress and types of rock forms (result of differential stress).
In metamorphic rock, grains will align perpendicular to the direction of compression.
Rocks put under differential stress at high temperature deform plastically.
Forms
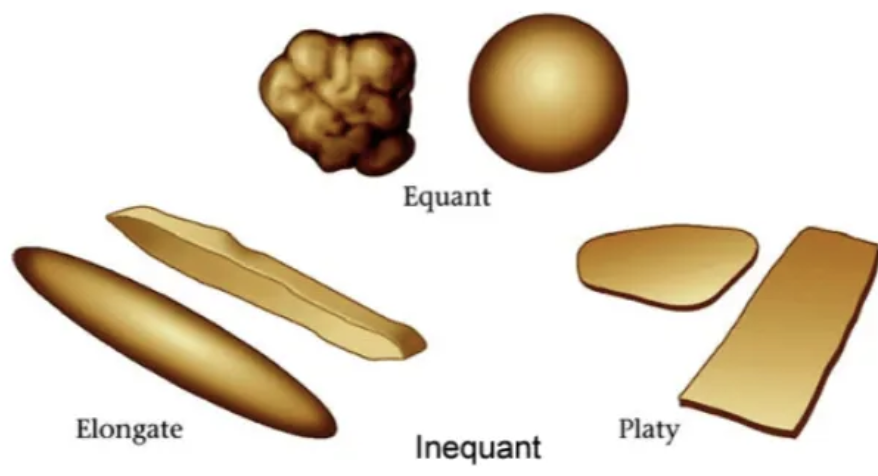
Inequant = platy and elongate minerals
Equant = equidimensional
Preferred orientation of inequant grains gives the rock a planar fabric
What’s hydrothermal fluids.
Very hot water solutions, contain water and steam (chemically active-can react with the rocks.
Describe interaction with hydrothermal fluids.
Speed up the metamorphic reactions by increasing the rate of diffusion.
Fluids will also carry dissolved material from one location to another.
They also move ions around (changing rock composition) this is metasomatism.
