GFR, renal flow, clearance
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
180, 1.5
Kidneys filter __ L of plasma daily and excrete about __ L of urine daily
Filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
Renal Stages
__ notes blood to lumen
__ notes lumen to blood
__ notes blood to lumen
__ notes lumen to external environment
20, non-selective
Renal Filtration
__% of plasma in glomerular capillaries is filtered into Bowman’s capsule
Filtration is __ (selective vs non-selective)
Filtrate composition resembles plasma minus most proteins
filtrate, peritubular, conserves
Renal Reabsorption
Many solutes and 99% of fluid reabsorbed from __ into the __ capillaries
Action __ substances (i.e. Na+, glucose, water)
Peritubular, lumen, excretion
Renal Secretion
Selective transfer of substances from __ capillaries to tubule __
Enhances __ (i.e. waste products, foreign substances, regulation of H+ and K+)
Mass, artery input, -, +, excreted
Fick’s Principle
__ is conserved in and out
Renal __ __ = ureter output + renal vein input
Amount filtered _ (+/-) amount reabsorbed _ (+/-) amount secreted = Amount of solute __
Membrane protein, not
Reabsorption and secretion of many solutes is mediated by __ __ transporters
Filtration __ (is/not) mediated by transport proteins
Low, transport, concentration, maximal transport rate
At __ (high/low) concentrations, the __ rate of substrate is proportional to the __ gradient
__ __ __ (Tmax): Occurs when all carriers are occupied (saturated)
Threshold, rate of transport
Renal __: Plasma concentration of substrate at which saturation occurs
When past threshold = No longer able to increase __ of __
200 mg/dL
Renal threshold for glucose reabsorption
SGLT, Tmax, excreted
Glucose Handling
When plasma [glucose] rises above threshold, __ transporter in nephron is saturated and reaches __
Glucose that could not be reabsorbed is __ in urine
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Volume of fluid that enters Bowman’s capsules per unit time
All, hydrostatic, oncotic, surface area, glomeruli
GFR is a sum of filtration rate of __ nephrons
Net Filtration Pressure (deltaP) = Net __ and __ forces in glomerular capillary and Bowman’s capsule
Filtration Coefficient (Kf) = __ __ and permeability
More __ area = more filtration
Net filtration pressure x Kf
GFR Equation
Increase, increase, decrease, decrease, increase, decrease, decrease, increase
Answer 1-4
RBF (increase/decrease), GFR (increase/decrease)
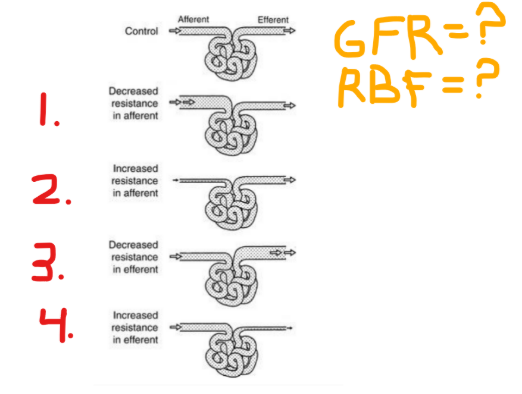
Net, relative
The effects on RBF depend on __ changes in renal resistance
The effects of GFR depend on __ rates of glomerular inflow vs outflow
(relative/net)
Dilate, constrict, dilate
Factors increasing renal blood flow
ANP and BNP
__ afferent arterioles; __ efferent arterioles
Prostaglandins
__ afferent arterioles (and efferent a. to lesser degree)
Afferent, efferent, hypotension, stenosis
Factors decreasing renal blood flow
Sympathetic system
Constricts both efferent < __
Angiotensin II
Constricts both __ > afferent
Severe __ - outside myogenic autoregulation zone
Renal artery __
Increase, increase, decrease, increase, decrease, decrease
How does each stimulus affect GFR?
ANP + BNP __ GFR
Prostaglandins __ GFR
Sympathetic NS __ GFR
Angiotensin II __ GFR at steady levels, at high levels __ GFR
Severe hypotension or renal stenosis __ GFR
Sympathetic, high
Renal vasculature has little __ tone
Renal sympathetic activity must be __ in order to reduce renal blood flow
Filtration fraction (FF), 0.17, increase
__ __ is the fraction of renal plasma flow that is filtered
Normally around __
Increase in glomerular capillary pressure, __ in FF
GFR / RPF
Filtration fraction formula
Renal Clearance
Rate at which solute is removed from plasma by kidneys
Affected by GFR, reabsorption, and secretion
Renal clearance of solute X
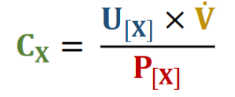
Inulin, filtered
__ is a plant polysaccharide that is freely__, NOT reabsorbed, NOT secreted
Excreted, tubules, GFR
Inulin
100% of filtered inulin is __ → Inulin Excretion = Inulin Filtration
All fluid reabsorbed from __ is “cleared” of inulin
Therefore Inulin = __ (rate which plasma is filtered)
0.02, 100, 126, 600
Renal clearance numbers
Glucose: __ mL/min (largely reabsorbed)
Inulin: __ mL/min
Creatinine: __ mL/min
PAH: __ mL/min (largely secreted)
Creatinine (Cr)
Endogenous substance that is freely filtered
Reabsorbed, muscle, constant, increases
Creatine
Not __ (filtered/reabsorbed) → Small amount secreted to tubules
Byproduct of __ metabolism; produced at steady state
Plasma [Cr] remains relatively __ for given muscle mass
Small amount of creatinine secretion __ (increases/decreases) clearance rate
Rise (increase)
What will happen to plasma [Cr] over time if GFR falls?
young, lean, serum
Creatinine clearance
directly proportional to __ age and __ body weight
inversely proportional to __ creatinine levels
Secreted, reabsorbed
Determining net renal handling of solutes
If amount excreted > filtered → difference was __
If amount excreted < filtered → difference was __
Filtration only
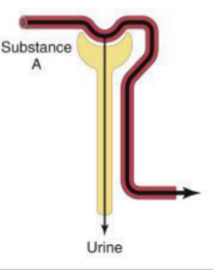
Filtration, partial reabsorption
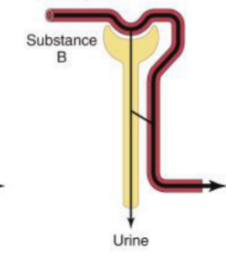
Filtration, complete reabsorption
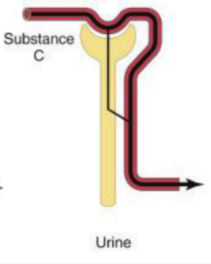
Filtration, secretion
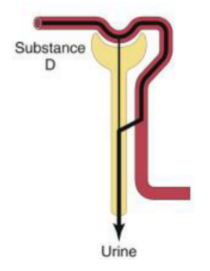
Reabsorbed, 0
Renal clearance of glucose
All glucose is __
No plasma is “cleared” of glucose → Glucose clearance = _
clearance of solute / clearance of inulin
Clearance ratio formula
greater, secretion
Clearance ratio > 1
Clearance of solute __ than GFR
Solute undergoes net __
less, reabsorption
Clearance ratio < 1
Clearance of solute __ than clearance of inulin
Solute undergoes net __
PAH
__ clearance can be used to estimate renal plasma flow (RPF)
nearly 100% of renal plasma flow is cleared of this
RPF = C PAH
Rate which PAH enters (via artery) ~ rate which PAH leaves (as urine)
(Equation)
RPF / (1-HCT)
Renal blood flow formula
Hematocrit, 1-HCT
RBF Components
__ is the fraction of blood composed of blood cells
Fraction of blood composed of plasma = ___ (formula)