Glycolysis (carbohydrate metabolism I)
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
what is the type of dietary carbs found in animals?
glycogen
three types of dietary carbs in plants?
starches, fibers and sugars
what are the three types of starches in plants (which are different combinations of amylose and amylopectin)?
rapidly digested, slowly digested and resistant starch
which enzyme is glycogen digested by?
alpha amylase
which enzyme are rapidly and slowly digested starches digested by?
alpha amylase
resistant starch cannot be digested because of its GRANULAR STRUCTURE but what happend in the gut?
it is fermented by gut microbiota
what are the two types of fibers found in plants and fruits?
insoluble and soluble
both soluble and insoluble fibers are not digestable but are…?
fermentable by gut microbiota
example of soluble and insoluble fibers, respectively?
inulin and cellulose
three types of simple sugars found in plants and fruits?
mono, di and trisaccharides
example of trisaccharide?
maltotriose
example of disaccharide?
maltose
example of monosaccharides?
glucose and fructose
what is the monomer for both maltose and maltotriose?
glucose
name of the 6 membered ring of simple glucose?
glucopyranose
which glucose form (L or D) is synthetic?
L
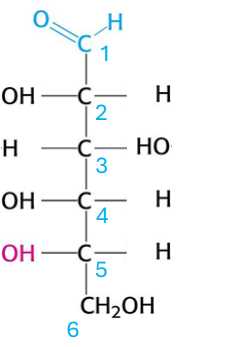
which glucose form is this?
L
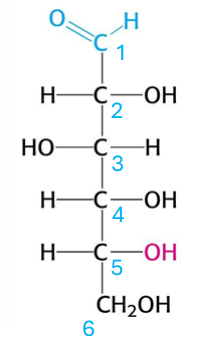
which glucose form is this?
D
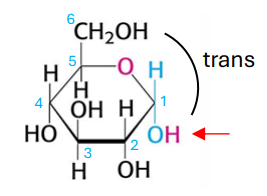
which glucose form is this?
alpha D glucopyranose
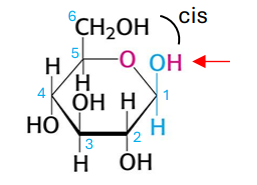
which form of glucose is this?
beta D glucopyranose
which form (alpha or beta) of D glucopyranose is more common?
beta (2/3)
name of sugars which contain a ketone group?
ketoses
examples of ketoses?
fructose, ribulose, xylulose and sedoheptulose
name of sugars with an aldehyde group?
aldoses
out of ribose and ribulose which is an aldose?
ribose
out of ribose and ribulose which is a ketose?
ribulose
examples of aldoses?
glucose, galactose, glyceraldehyde and ribose
what monomers is sucrose made of and what is the bond connecting them?
glucose and fructose (alpha 1,2)
what monomers is maltose made of and what is the bond connecting them?
glucose (alpha 1,4)
what monomers is lactosemade of and what is the bond connecting them?
glucose and galactose (beta 1,4)
examples of two branched glucose polysaccharides?
glycogen and amylopectin
which bonds in glycogen and amylopectin confer linearity?
alpha 1,4 glycosidic
which bonds in glycogen and amylopectin confer branching?
alpha 1,6 glycosidic
which is more branched glycogen or amlyopectin?
glycogen
is amylose branched or unbranched?
unbranched
two examples of unbranched glucose polysaccharides
amylose and cellulose
bonds in amylose?
alpha 1,4 glycosidic
bonds in cellulose?
beta 1,4 glycosidic
bonds in inulin?
beta 1,2 glycosidic
what monomers is inulin made of?
beta fructose
beta 1,4 and beta 1,2 glycosidic bonds in cellulose and inulin confer what?
compactness
what type of bonds form between hydroxyl groups within and between chains of cellulose?
hydrogen bonds
which bonds are the reason amylose adapts a helical structure?
hydrogen bonds
starch consumption shapes our genetic makeup by?
increasing amylase gene duplication
what is the main glucose transporter in animals?
GLUT1
what does the Michaelis constant Km represent?
it represents the concentration of substrate at which the enzyme works at half its max velocity
does glut1 have a low or high Km?
low
what does low Km mean in terms of affinity for substrate?
it means the enzyme has a high affinity for the substrate
what is the Km for glut1?
1mM
where in the body is glut1 found?
everywhere
where in the body is glut2 found? leap card
liver, kidneys, intestines and pancreas (LIPK)
does glut2 have a low or high Km?
high
glut2’s high Km and low affinity for glucose allow it to act as…?
a glucose sensor
what is the Km for glut2?
15-20mM
“low Km meaning high sensitivity allowing it to constantly take up glucose across the physiological range” —> which glucose transporters is this about?
glut1 and glut3
“high Km meaning low sensitivity allowing it to be a glucose sensor” —> which glucose transporter is this about?
glut2
where is glut3 found?
mainly neurons
which has a higher affinity for glucose, glut1 or glut3?
glut3
Ensures a constant glucose supply to cells (especially where glucose is the main energy source) —> which glucose transporter?
glut1
Ensures neurons get enough glucose even when blood sugar is low —> which glucose transporter?
glut3
where is glut4 found? mama
muscles and adipose tissue
which glucose transporter is highly regulated by insulin?
glut4
glut4 moves from intracellular vescicles to the cell surface in response to which hormone?
insulin
what happens to glut4 on cell surface when insulin levels drop?
it moves back to the cell’s interior
what is the Km for glut4?
5mM
what is the Km for glut5?
5mM
where is glut5 found?
jejunum
which sugar does glut5 transport?
fructose
what is the main glucose transporter in the gut?
SGLT1
SGLT1 full name
sodiu glucose transporter 1
does sglt1 use atp?
no
what other transporter does sglt1 rely on?
Na/K ATPase
which two sugars does sglt1 transport from the gut lumen?
glucose and galactose
is sglt1 located on the apical or basolateral side of enterocytes?
apical
what is the transporter located on the basolateral side of enterocytes and transports glucose from enterocytes into the bloodstream?
glut2
is the sodium concentration higher in the intracellular or extracellular space in enterocytes?
extracellular
in enteroendocrine cells what channels does a high level of glucose (and thus atp) inhibit?
ATP gated potassium channels
inhibition of K channels in enteroendocrine cells leads to what?
depolarisation of the cells and calcium influx
influx of calcium in enteroendocrine cells leads to what?
hormone secretion
GLP1 stimulates secretion of which hormone?
insulin
GLP1 inhibits secretion of which hormone?
glucagon
which glucose transporter transports glucose into pancreatic beta cells?
glut2
describe the general mechanism of how high blood glucose level results in secretion of insulin in pancreatic beta cells
glut2 transports glucose from the bloodstream into pancreatic beta cells, high levels of glucose in the cells results in high levels of ATP, ATP inhibits ATP gated potassium channels, this results in the depolarisation of the cell, which results in the release of insulin
describe the general mechanism of how insulin stimulates glucose absorption in muscle cells via glut4
when insulin binds to the insulin receptor, glut4 vescicles fuse with the plasma membrane to translocate glut4 from the cell’s interior to the surface, when insulin levels fall glut4 vescicles are retrieved back into the cell
what does AMPK stand for?
AMP activated protein kinase
is AMPK insulin dependent or independent?
independent
what are the two molecules which stimulate glut4 translocation to the cell surface?
insulin and AMPK
when is AMPK activated and responsible for glut4 translocation?
during exercise
generally describe the mechanism through which glucose uptake stimulates GLP1 release in enteroendocrine cells
glucose is transported into the cell by sglt1, a higher level of glucose means a higher level of ATP, ATP then inhibits the ATP gated potassion channel, this leads to the depolarisation of the cell, which in turn leads to the uptake of calcium, calcium then stimulates secretion of GLP1
which enzyme converts pyruvate to lactate?
lactate dehydrogenase
what coenzyme is used by lactate dehydrogenase?
NADH
what is pyruvate converted to in yeast cells under anaerobic conditions?
ethanol
what are the two enzymes used in conversion of pyruvate to acetaldehyde and then ethanol?
pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase
what coenzyme is used in conversion of pyruvate to ethanol (and what is released as a side product)?
NADH and CO2
first step of glycolysis
glucose to glucose 6 phosphate (hexokinase)
second step of glycolysis
glucose 6 phosphate to fructose 6 phosphate (phosphoglucose isomerase)
third step of glycolysis
fructose 6 phosphate to fructose 1,6 bisphosphate (phosphofructokinase)
fourth step of glycolysis (last in the investment phase)
fructose 1,6 bisphosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate (aldolase)
which enzyme converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate
triose phosphate isomerase
how many molecules of ATP are used in the investment phase of glycolysis and which enzymes use them?
2, hexokinase and phosphofructokinase