MGT 131_Values, Attitudes, and Job Satisfaction
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
values
represent basic convictions that “a specific mode of conduct or end-state of existence is personally or socially preferable to an opposite or converse mode of conduct or end-state of existence”
They lay the foundations for the understanding of attitudes and motivation and because they influence perception. They tend to be relatively stable and enduring. (Robbins)
milto rokeach
the two types of values is terminal and instrumental. someone based a study on this—who was it?
terminal and instrumental
what are the two types of values by milto rokeach?
terminal values
refers to desirable end-states of existence; goals that a person wants to achieve in his or her lifetime
a comfortable life, an exciting life, a world at peace, equality, salvation, social recognition
instrumental
refers to preferable modes of behavior or means of achieving the terminal values
ambitious, open-minded, cheerful, courageous, loving,
polite
veterans
boomers
x’ers
nexters
4 dominant work values in today’s workforce
veterans
entered the workforce at 1950s-1960s
hardworking, conservative, conforming, loyal to org
boomers
entered the workforce at 1965s-1985s
success, achievement, ambition, dislike authority, loyalty to career
x’ers
entered the workforce at 1985-2000s
work/life balance, team-oriented, dislike of rules, loyalty to relationships
nexters
(entered workforce at 2000 to present)
confident, self-reliant but team-oriented, entrepreneurial, with loyalty to both self and relationships, financial success; like feedback, entitled
power distance
individualism vs collectivism
masculinity vs femininity
uncertainty avoidance
long-term vs short-term orientation
indulgence vs restraint
hofstede’s six value of dimensions of national culture
power distance
degree to which people in a country accept that power in institutions and orgs is distributed unequally
individualism vs collectivism
degree to which people in a country prefer to act as indivs. than grp members
masculinity vs femininity
degree to which values such as achievement, assertiveness, competition, acquisition of money and mat goods prevail
degree to which people value relationships and show sensitivity and concern for others’ welfare. preference for cooperation, modesty, caring for weak and quality of life
masculinity
degree to which values such as achievement, assertiveness, competition, acquisition of money and mat goods prevail
femininity
degree to which people value relationships and show sensitivity and concern for others’ welfare. preference for cooperation, modesty, caring for weak and quality of life
uncertainty avoidance
degree to which ppl in a country prefer structured over unstructured situations
long-term vs short-term orientation
cultures look to the future and value thrift and persistence while the other one values the here and now
indulgence vs restraint
stands for a society that allows free gratification of basic and natural human drives to enjoy life & have fun
stands for a society that suppresses gratification of needs and regulates it by means of strict social norms
attitudes
evaluative statements–either favorable or unfavorable– concerning objects, people or events
cognition, affect, behavior
3 components of attitude
cognition
value statement
discrimination is wrong
affect
emotional segment of an attitude
behavior
an intention to behave in a certain way towards someone or smth
attitudes are less stable than values
affect
which component of attitude is this?
“i dislike my superior!”
cognition
which component of attitude is this?
“my superior gave a promotion to a coworker who deserved it less than me. my supervisor is unfair”
behavior
which component of attitude is this?
“i’m looking for other work. i’ve complained abt my superior to anyone who listened.”
consistency
people seek ________ among their attitudes and between their attitudes and their behavior
cognitive dissonance
– any incompatibility that an individual might perceive between two or more of his/her attitudes or between his/her behavior and attitudes.
importance, specificity, accessibility, social pressure, direct experience
5 attitude-behavior relationship: moderating variables
importance
important attitudes tend to show a strong relationship to behavior
specificity
the more specific the attitude, the more specific the behavior
accessibility
attitudes that are easily remembered are most likely to predict behavior
social pressure
discrepancies between attitudes and behavior likely to happen due to this to behave in a certain way that hold exceptional power
direct experience
attitude-behavior rel is stronger if the person has a _____ personal ______ with.
attitudes are used to understand an action
does behavior influence attitude?
productivity
leads to satisfaction
happy organizations (not necessarily employees) are more of this.
consistent negative rel between job satisfaction and absenteeism but correlation is moderate
consistent ______ rel between ______ and _______ but correlation is _______
negatively related
whats the rel between satisfaction and turnover?
satisfaction level
what is less important in predicting turnover for
superior performers since they get pay raises and recognition?
organizational citizenship behavior
OCB means?
customer satisfaction and loyalty
Satisfied employee increase what 2 things?
employee’s job dissatisfaction
dissatisfied customers also increase..?
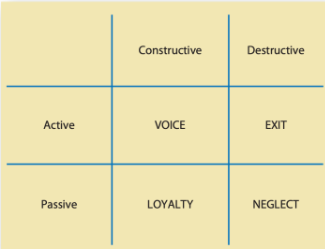
exit, voice, loyalty, neglect
4 ways that employees express dissatisfaction
exit
employee dissatisfaction expression
leaving the org
voice
employee dissatisfaction expression
suggesting improvements, discussing problems w/ superior or some union activity
loyalty
employee dissatisfaction expression
passively but optimistically waiting for conditions to improve
neglect
employee dissatisfaction expression
passively allowing conditions to worsen, including chronic absenteeism or lateness, reduced effort and increased error rate
sonic
rmr it. say sonic for next