Solutions, Enthalpy Changes, Acid-base Equilibria
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Define ionic bonding
The electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions
What two processes occur when an ionic solid dissolves
The ionic lattice breaks into gaseous ions
- Energy is required to overcome forces of attraction between ions
- This is the reverse of lattice enthalpy
Gaseous ions dissolve in water (hydration) due to the attraction between ions and polar water molecules (ion-dipole bonds)
What factor impacts if an ionic solid will dissolve
Solid will dissolve if more (or similar ) energy is released when bonds form, than is needed to break bonds
Bonds broken = ionic bonds in solid and hydrogen bonds in water
Bonds formed = ion-dipole bonds between ions and polar water molecules
What is Lattice Enthalpy and what does its magnitude depend on
The enthalpy change on formation of 1 mole of an ionic solid from gaseous ions
Is always exothermic (negative) because ionic bonds are being made
Magnitude (more exothermic) depend on strength of ionic bonds which depends on the charge and size of ions involved
What is Enthalpy change of hydration and what does its magnitude depend on
The enthalpy change on dissolving 1 moles of gaseous ions in water
Always exothermic (Negative) as ion-dipole bonds are being made between ions and polar water molecules
Ions become hydrated
Magnitude (more exothermic) depends on ability of the ions to attract the polar water molecules forming ion-dipole bonds
The attraction is strongest with ions with high charge density
What is enthalpy change of solution
The enthalpy change on dissolving 1 moles of a solute forming an infinitely dilute solution
Can be exothermic or endothermic
Lattice enthalpy, enthalpy change of hydration and enthalpy change of solution can be linked with a Born Habor cycle. Draw a Born Habor Cycle for calcium chloride (CaCl2)
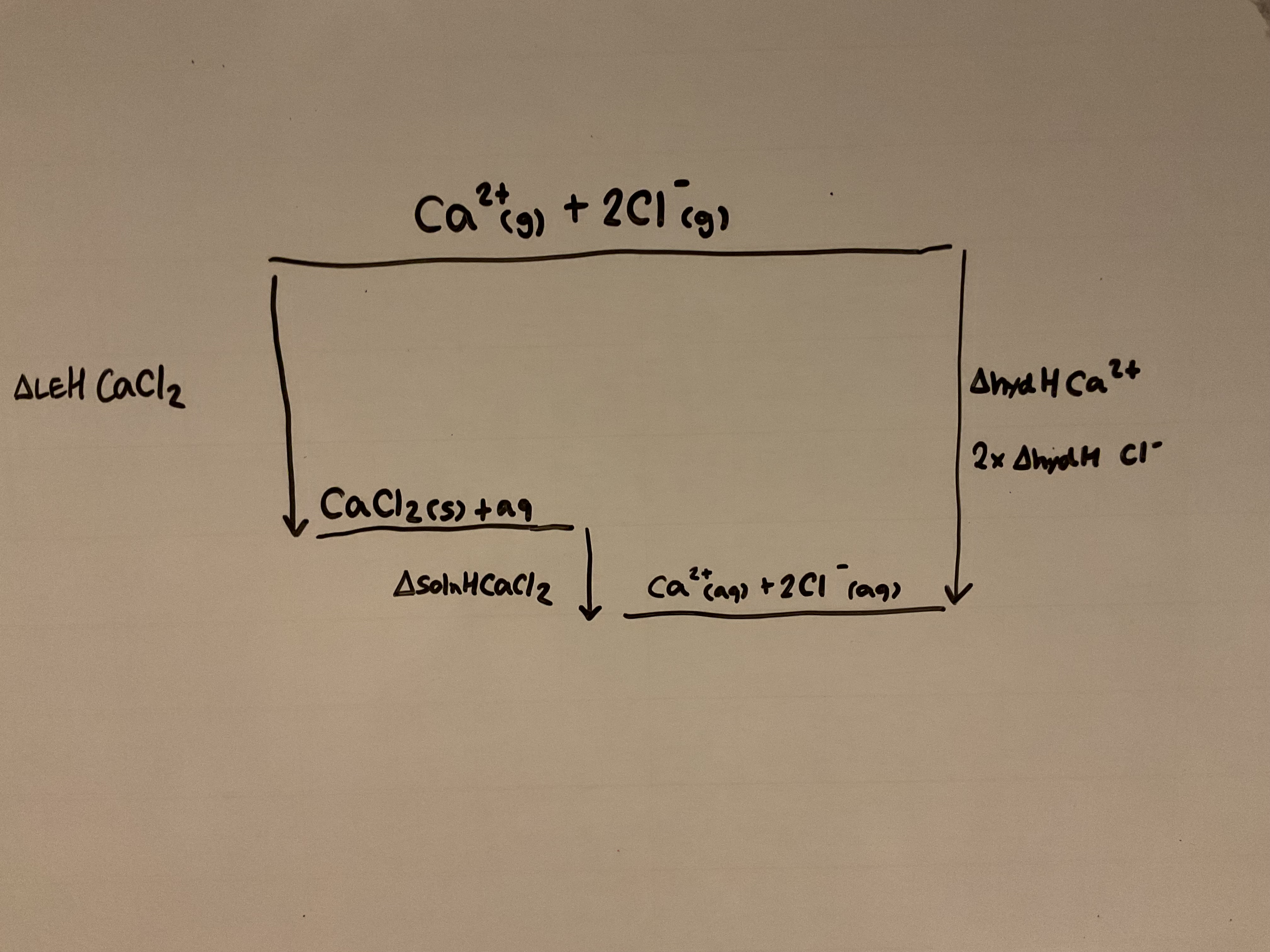
If enthalpy change of a solution is exothermic, what will the solubility of the solid be
Almost always soluble
Providing enthalpy change of hydration is more exothermic than lattice enthalpy, the enthalpy change of solution will be negative and the solid will dissolve
The energy needed to break up the ionic lattice is more than compensated for by the exothermic enthalpy of hydration
If enthalpy change of a solution is endothermic, what will the solubility of the solid be
Solubility depends on how endothermic the enthalpy of solution is
Insoluble - enthalpy of solution is large and endothermic (lattice enthalpy must more exo than enthalpy of hydration)
Usually soluble - enthalpy of solution is small and endothermic. Heat energy taken in from surroundings
Use enthalpy changes to explain why Group 2 hydroxides increase in solubility down the group
Controlled by lattice enthalpy of M(OH)2
Lattice enthalpy decreases (less exo) down the group because charge density decreases
Enthalpy of hydration also decreases (less exo) down the group due to lower charge density
Lattice enthalpy decreases more rapidly, so as cation size increases, Enthalpy of hydration becomes > lattice enthalpy and solubility increases
According to Bronsted-Lowry Theory, an acid is _____ and a base is ____
Acid - proton donor
Base - proton acceptor
What is the difference between an alkali and a base
A base - a proton acceptor
An alkali - Dissolves in water to form OH- ions
All alkalis are bases but not all bases are alkaline
Acids contain _____ atoms bonded ______ to an _________ atom. They are polar molecules
In water, acid molecules collide with ______ water molecules and a _____ bond forms between the O on water and the H of the acid.
The _____ ion that is formed is called a __________ ion. These are present in every dilute acid and responsible for the behaviour of all acids.
In terms of equations, we simplify and use ____ instead
Acids contain hydrogen atoms bonded covalently to an electronegative atom. They are polar molecules
In water, acid molecules collide with polar water molecules and a dative bond forms between the O on water and the H of the acid.
The H3O+ ion that is formed is called a hydroxonium ion. These are present in every dilute acid and responsible for the behaviour of all acids.
In terms of equations, we simplify and use H+ instead
What is a strong acid/base
A strong acid fully dissociates into ions in solutions
E.g. HCl → H+ + Cl-
A strong base fully dissociates into ions in solutions
E.g. NaOH → Na+ + OH-
What is a weak acid/base
A weak acid partially dissociates into its ions in solutions
E.g. CH3COOH <=> H+ + CH3COO-
A weak base partially dissociates into its ions in solutions
E.g. NH3 + H2O <=> NH4+ + OH-
Acid + Metal →
Salt + H2
Acid + Base →
Salt + Water
Acid + Metal Carbonate →
CO2 + Salt + H2O
Acid + Alkali →
Salt + Water
What is the general equation for an acid + base equilibrium
HA + H2O <=> H3O+ + A-
How do acid base indicators work
Indicators are weak acids
HA <=> H+ + A-
Either HA or A- must be coloured
Addition of acid causes concentration of H+ to increase
Equilibrium shifts to LHS
The colour of HA appears
Addition of alkali cause H+ to react and therefore to decrease in concentration
Equilibrium shifts to RHS
The colour of A- appears
What is a conjugate acid-base pair
a conjugate acid–base pair consists of two substances that differ only by the presence of a proton (H⁺). A conjugate acid is formed when a proton is added to a base, and a conjugate base is formed when a proton is removed from an acid.
Will conjugate bases be strong or weak if the acid is strong
Conjugative base will be weak
Acid is strong so dissociates fully
Reactions complete
Equilibrium fully to RHS, reverse reaction will not occur
Conjugative base does not act as a base in its reaction (reverse reaction)
Will conjugate bases be strong or weak if the acid is weak
Conjugate base will be strong
Weak acid partially dissociates
Reaction doesn’t go to completion
Equilibrium position to left as reverse reaction occurs
Conjugate base acts as a base in its reactions (reverse)
What is the expression for the Acid Dissociation Constant, Ka
Ka = [H+] [A-] / [HA]
What is the only factor that can change Ka
Temperature
For strong acids:
Equilibrium is to the ______
Because the dissociate _____ in water
Therefore the magnitude of Ka would be _____
And the magnitude of pKa would be _____
For strong acids:
Equilibrium is to the RHS
Because the dissociate fully in water
Therefore the magnitude of Ka would be Large
And the magnitude of pKa would be Small
For weak acids:
Equilibrium is to the _____
Because the dissociate _____ in water
Therefore the magnitude of Ka would be _____
And the magnitude of pKa would be _____
For weak acids:
Equilibrium is to the LHS
Because the dissociate partially in water
Therefore the magnitude of Ka would be Small
And the magnitude of pKa would be Large
What is the equation that links Ka with pKa
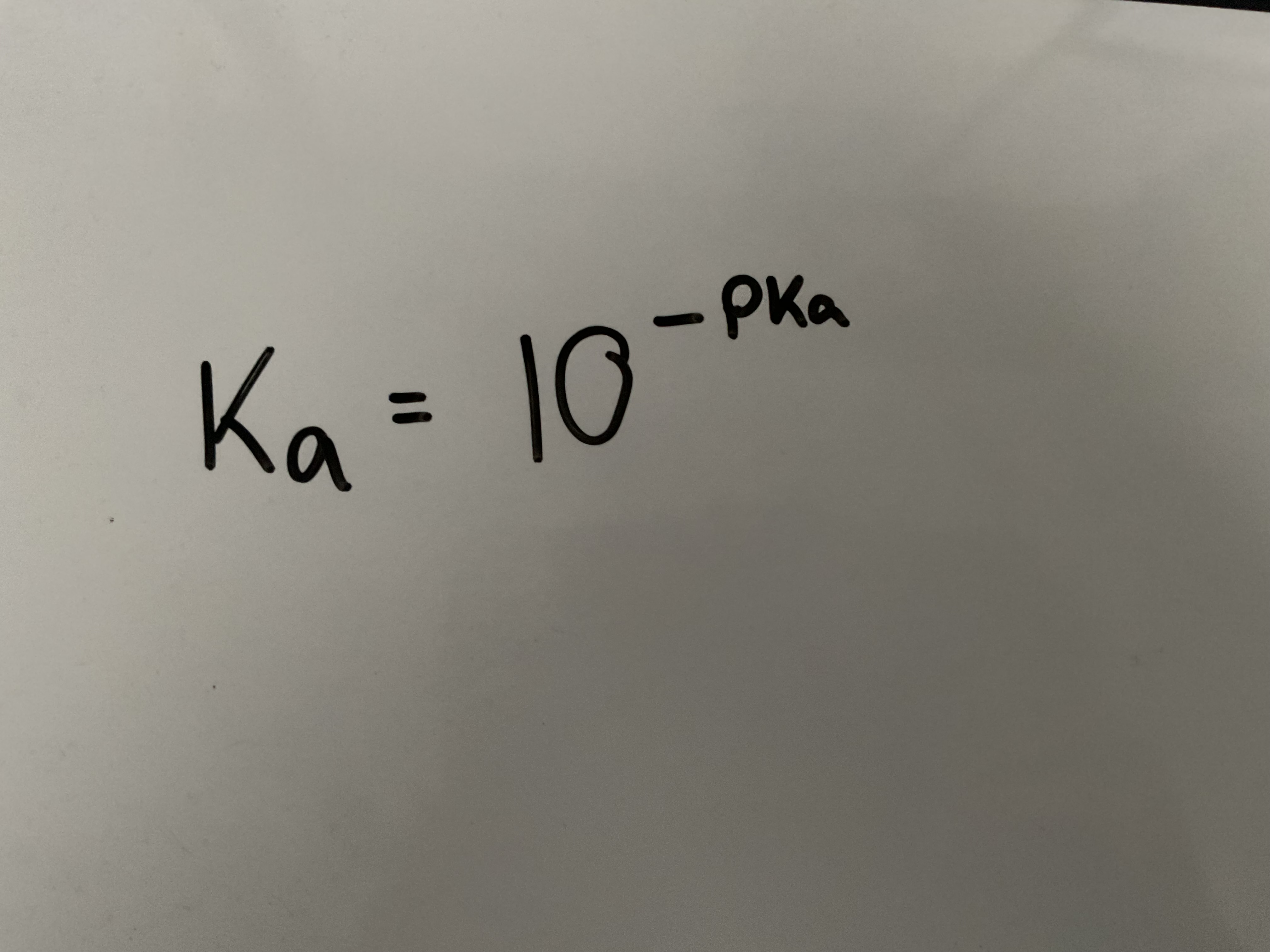
What is the equation for the ionic product of water, Kw
What is the value for Kw at room temp (on data sheet)
Kw = [H+] [OH-]
At room temp Kw = 1.00 × 10^-14 mol2 dm^-6
Why can pure water carry electrical current
Pure water will conduct electric current due to the small amount of dissociation
H2O <=> H+ + OH-
How can pH be calculated using the H+ concentration
Use water as an example which has a H+ concentration of 1 × 10^-7 mol dm-3
PH = -log10 [H+]
Water pH = -log10 (1 × 10^-7)
= 7
How do acidic buffers work, use ethanol acid and sodium ethanoate as an example
A buffer doesn’t stop the pH from changing completely, but it minimises it
Acidic buffers are made by mixing a weak acid with its conjugate base (salt)
In this example, sodium ethanoate fully dissociates in water
Ethanoic acid only partially dissociates in water
Therefore the buffer solution contains lots of CH3COO- and lots of CH3COOH
On addition of acid
The equilibrium position shifts to the LHS
CH3COO-(aq) + H+(aq) → CH3COOH
CH3COO- reacts with additional H+ so the change in pH is minimised
On addition of alkali
H+ ions are removed when they react with OH- to form water
The equilibrium position shifted to the RHS to replace H+
OH- + H+ → H2O
Change in pH is minimised
Overall
PH change is counteracted as the concentrations of weak acid and conjugate base are both large
How do buffers play a role in maintains the blood plasma pH
H2CO3(aq) <=> H+(aq) + HCO3(aq)
NaHCO3 (aq) → Na+(aq) + HCO3-(aq)
On addition of an acid
Concentration of H+ increases
H+ reacts with HCO3-
Equilibrium over to the LHS
On addition of an alkali
Concentration of OH- increases
OH- reacts with H+ to form H2O
Equilibrium over to the RHS
What happens to the pH of a buffer if you dilute it
Remains unchanged
If the buffer solution is diluted, the concentration of both acid (HA) and conjugate base (A-) will change by the same factor
On dilution, the value of [A-] / [HA] will be unchanged
As Ka is a constant, [H+] must be unchanged too
What happens to the pH of an acid when you dilute it
The concentration of H+ decreases
As the [H+] concentration of water is 1 × 10^-7 mol/dm³, the more water that is added to the acid, the closer [H+] becomes 1 × 10^-7
The pH of the acid tends towards 7
Give an equation for the lattice enthalpy of sodium chloride
Na+(g) + Cl-(g) → NaCl(s)
Give an equation for the enthalpy of solubility for NaCl
NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Give the equation for the enthalpy of hydration of a sodium ion
Na+(g) → Na+(aq)