Community Planning and Health Promotion Final
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
theory
a set of interrelated concepts, definitions, and propositions that presents a systematic view of events or situations by specifying relations among variables in order to explain or predict the events of the situations
provide a framework for generating testable hypotheses for health education specialists, as well as, integrative empirical evidence that overtime provides a roadmap for the design and implementation of intervention strategies
concepts: primary elements of theories (building blocks)
construct: a concept developed, created, or adopted for use with a specific theory
variable: operational/practical use form of a construct
how a construct will be measured
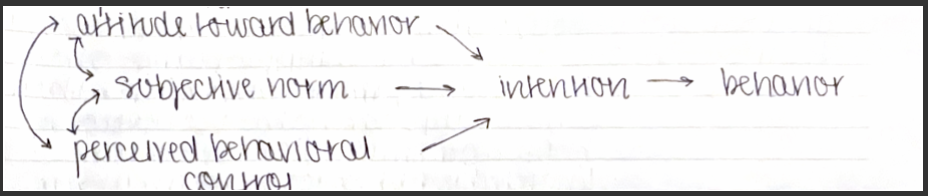
Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB)
attitude toward behavior: degree to which performance of behavior is positively or negatively valued
subjective norm: an individual’s perceived social pressure to engage or not engage in a behavior
perceived behavioral control: a person’s perceptions of their ability to perform a given behavior
immediate antecedent of behavior
Human Belief Model (HBM)
perceived susceptibility: belief of a person regarding the possibility of acquiring a disease or harmful state as a result of a particular behavior
perceived severity: belief of a person regarding the extent of harm that can result from the acquired disease or harmful state as a result of a particular behavior
perceived benefits: belief of a person regarding usefulness of the methods suggested for reducing risk or seriousness of the disease or harmful state resulting from a particular behavior
perceived barriers: belief of a person regarding actual and imagined costs of performing new behavior
cues to action: precipitating force that makes the person feel the need to take action
self-efficacy: the belief or confidence in performing behavior

Transtheoretical Model (TTM)/ “Stages of Change Model”: an integrative framework for understanding how individuals and populations progress toward adopting and maintaining health behavior change for optimal health
precontemplation: no plans to change behavior
contemplation: plan to change within 6 months
preparation: plan to change within 30 days
action: has changed behavior
maintenance: has changed behavior for > 6 months
termination: behavior change = permanent (no change of relapse)
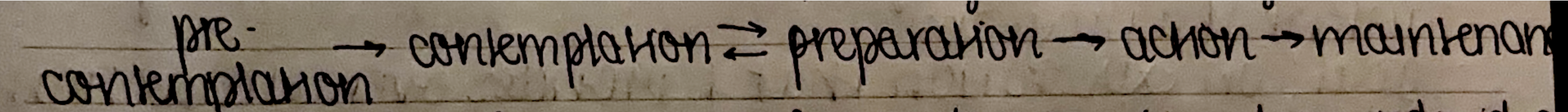
objectives
represent smaller steps that lead to reaching goals
more precise than goals
outline specific changes to occur
written in measurable terms
several levels:

need to be SMART:
S: specific
M: measurable
A: achievable
R: realistic
T: time
who, what
how much/many
time-line
can it be realized in a reasonable time frame
can the objective be realistically achieved
does the program have enough resources to obtain the objective
is it consistent with policies and procedures
do the objectives violate any of the rights of those who are involved
does it reflect the cultural characteristics of the priority group and the changes sought
DO NOT USE THE WORD AND
WHO is going to do WHAT, WHEN, and to WHAT EXTENT
Must only be ONE sentence
logic model
a systematic and visual way for planners to share and present their understanding of the relationship among the resources they have to operate a program, the activities they plan to implement, and the outputs and outcomes they hope to achieve
can help all stakeholders understand the “big picture” of how planning, implementing, and evaluating all fit together
inputs (resources)
outputs (activities)
outcomes (results of effects)
short-term, mid-term, and long-term
.
.