9a. transport system in mammals
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
1
New cards
mass transport system
a transport system in which the bulk moment of fluid occurs in one direction
2
New cards
closed system
blood is contained within the heart and blood vessels and doest’t come into contact directly with tissue cells
3
New cards
tissue fluid
fluid which exchange of substances with tissues occur in
4
New cards
open system
system with open ended blood vessels where blood bathes the tissues directly
5
New cards
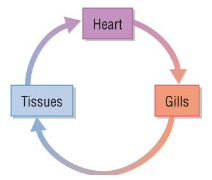
single circulatory system
system where the blood flows through the heart once in a complete circuit eg fish
6
New cards
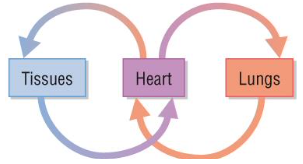
double circulatory system
systems where good travels those though heart in one compete circuit around the body, one circuit to longs one to body eg mammals
7
New cards
different pressures
in the pulmonary and systemic circulation prevents capillaries and alveoli getting damaged, and make sure blood reaches all of the body
8
New cards
blood supply
addicted by vasodilation and vasoconstriction depending on how their respiring
9
New cards
metabolic rate
determines if an animal requires a closed double circulatory system or single open system
10
New cards
capillary
smallest blood vessel, are cross section SA fro exchange with cells, wall only one cell think made from squamous epithelium form networks called beds
11
New cards
artery
carry blood from the heart, thick layer of collagen to withstand pressure and prevent bursting, smooth muscle and elastic fibre maintain pressure, carry oxygenated blood except pulmonary
12
New cards
vein
returns blood to heart, very little elastic fibre or smooth muscle, semilunar velvets prevent back flow, contraction of skeletal muscles helps maintain blood flow, cary deoxygenated blood except pulmonary
13
New cards
venule
slightly wider then capillaries very thin walls of smooth muscle and elastic fibres, cary blood from capillaries to veins
14
New cards
arteriole
smaller vessels divided from arteries, thin wall of smooth muscle and elastic fibres, divert blood flow to different areas of the body by contraction of smooth muscle in wall to restrict blood flow (vasoconstriction), or relaxation of smooth muscle to allow blood flow into capillaries (vasodilation)
15
New cards
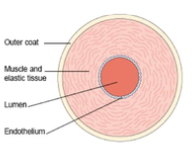
artery structure
* high pressure
* thick wall
* narrow lumen
* tunica intima, folded endothelium (allow expansion) of smooth squamous epithelium
* tunica media, thick layer of smooth muscle and elastic fibres
* tunica externa, more collagen to prevent busting
* no valves
* thick wall
* narrow lumen
* tunica intima, folded endothelium (allow expansion) of smooth squamous epithelium
* tunica media, thick layer of smooth muscle and elastic fibres
* tunica externa, more collagen to prevent busting
* no valves
16
New cards
capillary structure
* low pressure
* singe layer of cells make up the wall
* narrow lumen 7µm in diameter
* tunica intima, endothelium of single later of smooth squamous epithelium
* singe layer of cells make up the wall
* narrow lumen 7µm in diameter
* tunica intima, endothelium of single later of smooth squamous epithelium

17
New cards
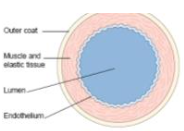
vein structure
* low pressure
* thin wall that can be compressed
* wide lumen
* tunica intima, endothelium of smooth squamous epithelium
* tunica media, thin layer of smooth muscle and elastic fibres
* tunica externa, less collagen
* semilunar valves to prevent back Flow
* thin wall that can be compressed
* wide lumen
* tunica intima, endothelium of smooth squamous epithelium
* tunica media, thin layer of smooth muscle and elastic fibres
* tunica externa, less collagen
* semilunar valves to prevent back Flow
18
New cards
tunica intima
inner layer of blood vessel
19
New cards
tunica media
middle layer of blood vessel
20
New cards
tunica externa
outer layer of blood vessel
21
New cards
elastic fibres
stretch to accommodate the volume of blood ejected into arteries during ventricular systole, then recoil during ventricular diastole to maintain pressure and smooth blood flow
22
New cards
smooth muscle
contracts to narrow lumen and maintain pressure during ventricular diastole
23
New cards
vasodilation
relaxation of smooth muscle on wall of arterioles and pre capillary sphincter to increase blood flow in capillaries
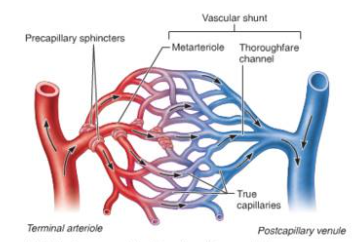
24
New cards
vasoconstriction
constriction of smooth muscle in walls of arterioles and pre capillary sphincters to reduce blood flow in capillaries
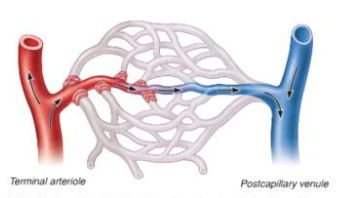
25
New cards
skeletal muscle
if it contracts it compresses veins , increasing pressure to more blood goes back to the heart
relaxation decompresses veins and reduces pressure which allows greater blood flow from capillaries
relaxation decompresses veins and reduces pressure which allows greater blood flow from capillaries
26
New cards
smooth endothelium
reduces friction and provides and short diffusion distance in capillaries
27
New cards
low power plan diagram
used to show arrangement of tissues in walls of artery or vein, no internal details or structure of cells shown
28
New cards
high power drawing
used to show individual cells in walls of capillary
29
New cards
increase exchange efficiency
* capillary bed has large total cross sectional surface area
* short diffusion distance
* steep contraction gradient marinated by blood flow
* short diffusion distance
* steep contraction gradient marinated by blood flow
30
New cards
plasma
forced out capillaries into tissues at arteriole end due to high hydrostatic pressure, and enters at venule end due to lower hydrostatic pressure, forms tissue fluid
31
New cards
lymphatic system
drain for excess tissue fluid
32
New cards
colloid osmotic pressure
caused by plasma proteins remaining in blood as their to large to pass though the pores in capillaries, leads to return of water to blood
33
New cards
fenstrations’s
pores in capillary endothelium
34
New cards
oedema
build up of tissue fluid due to body break down of own plasma proteins so colloid osmotic pressure is less
35
New cards
velocity
starts high with blood pressure in arteries but falls as surface area increases at capillaries, increases Adrian in veins due to skeletal muscles
36
New cards
sphygmomanometer
measures blood pressure in kilopascals (kPa) or mmHg
37
New cards
120/80 mmHg
average blood pressure
38
New cards
systolic pressure
due to contraction of muscle in left ventricle in systole, produces a higher reading
39
New cards
diastolic
when the muscle in the left venture id relaxed, produces a lower reading
40
New cards
inflatable cuff
used when measuring blood pressure manually and electronically, inflated until blood flow stops then gradually deflated
41
New cards
1, 3, 2, 4, 6, 5
order statement for how to measure blood pressure:
1. The person should have been sitting down with legs uncrossed for five to ten minutes.
2. Inflate cuff until it exerts sufficient pressure to stop blood flow in the brachial artery.
3. Securely attach the cuff (not too tightly) to the upper left arm which is held supported at heart level
4. Use the stethoscope to listen for the sounds of blood flow and slowly release the pressure from the cuff.
5. When the pulsing sounds disappear the pressure is equal to that in the artery at diastole (diastolic pressure)
6. When pulsing sounds (Korotkoff sounds) are first heard the pressure is equal to that in the artery at systole (systolic pressure)
1. The person should have been sitting down with legs uncrossed for five to ten minutes.
2. Inflate cuff until it exerts sufficient pressure to stop blood flow in the brachial artery.
3. Securely attach the cuff (not too tightly) to the upper left arm which is held supported at heart level
4. Use the stethoscope to listen for the sounds of blood flow and slowly release the pressure from the cuff.
5. When the pulsing sounds disappear the pressure is equal to that in the artery at diastole (diastolic pressure)
6. When pulsing sounds (Korotkoff sounds) are first heard the pressure is equal to that in the artery at systole (systolic pressure)
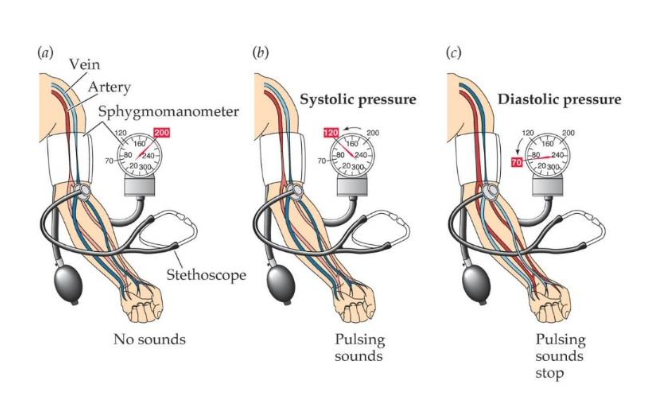
42
New cards
ABPM ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
patient wears a portable blood pressure monitor in their arm
43
New cards
HBPM home blood pressure monitoring
patient measures own blood pressure at regular intervals at home
44
New cards
hypotension
persistently low blood pressure, typically below 90/0 mmHg
risks of; tiredness and weakness, dizziness and fainting, coma and death
risks of; tiredness and weakness, dizziness and fainting, coma and death
45
New cards
hypertension
persistently higher tax average blood pressure, typically above 140/90 mmHg
risks of; premature morbidity and mortality, damage to endothelium, thrombus formation, damage to blood valves, kidney damage
risks of; premature morbidity and mortality, damage to endothelium, thrombus formation, damage to blood valves, kidney damage
46
New cards
prehypertension
120/80 mmHg
47
New cards
stage 1 hypertension
140/90 mmHg
48
New cards
stage 2 hypertension
160/100 mmHg
49
New cards
severe hypertension
180/110 mmHg
50
New cards
increases risk of hypertension
* smoking
* been obese
* alcohol
* stress
* age
* make
* sedentary life style
* been obese
* alcohol
* stress
* age
* make
* sedentary life style
51
New cards
decreases risk of hypertension
* regular exercise
* low salt diet
* low stress
* low salt diet
* low stress