Lecture 7: Community & Ecosystem Ecology
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
what is ecology?
the study of the relationship of organisms to the environment and to other organisms
what are the 5 trophic levels?
primary producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers, apex predator
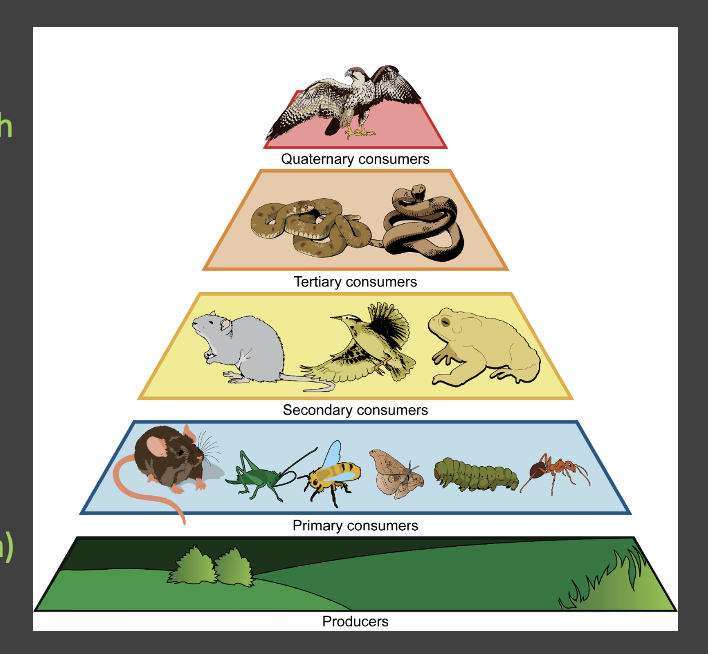
what are primary producers? what is another name for them?
organisms that make their own food through photosynthesis (plants) or using chemicals (some bacteria). another name: autotrophs
what does autotroph mean?
self feeding (plants)
what does heterotroph mean?
feeds off of others (primary/secondary/tertiary consumers, apex predator)
what are primary consumers? what word describes their diets?
organisms that eat the primary producers (plants). they are herbivores
what are secondary/tertiary consumers?
secondary consumers: eat the primary consumers (carnivores, heterotroph)
tertiary consumers: eat the secondary consumers (carnivores, heterotroph)
what are quaternary consumers? what is another name for them?
apex predators: predators at the top of the food chain with no natural predators
eg. lions, bears, tigers, crocodiles
what is the 10% rule?
energy flow is inefficient from one tropic level to another. when energy is passed in an ecosystem from one trophic level to the next, only 10% of the energy will be passed on. 90% of that energy will be lost as heat, etc. to the environment
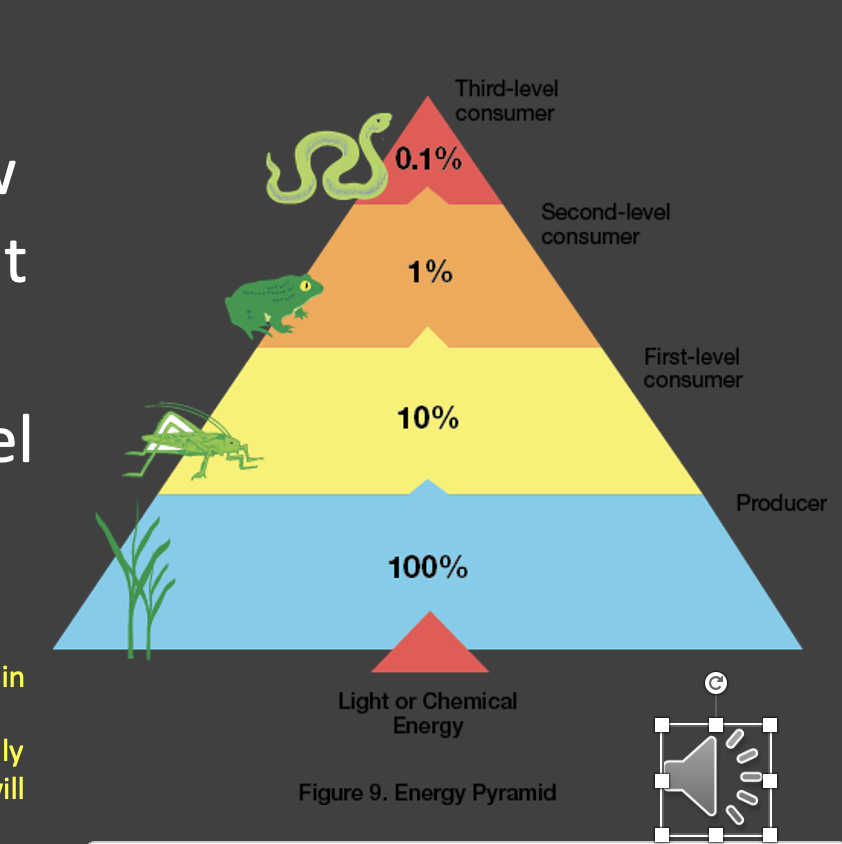
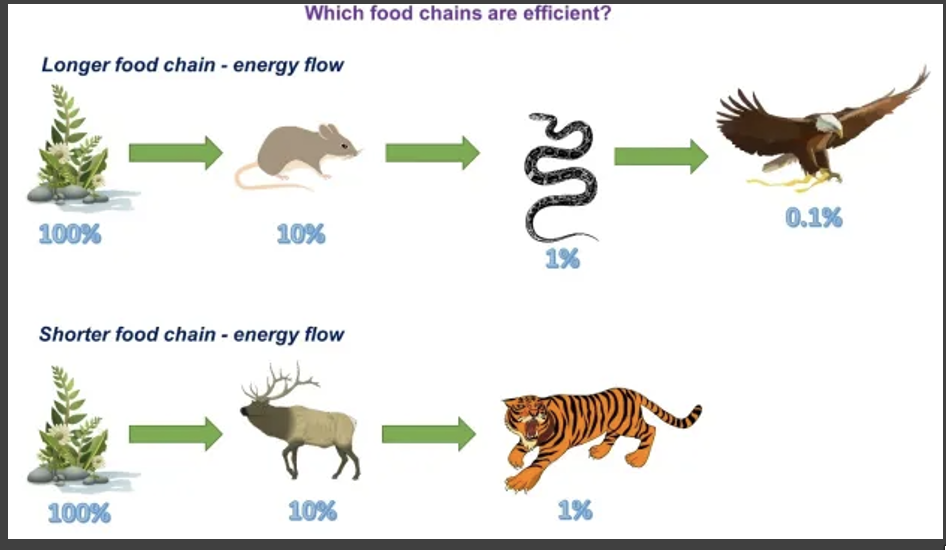
why are shorter food chains more efficient?
in shorter food chains, there are less trophic levels for the energy to transfer through, so less energy is lost
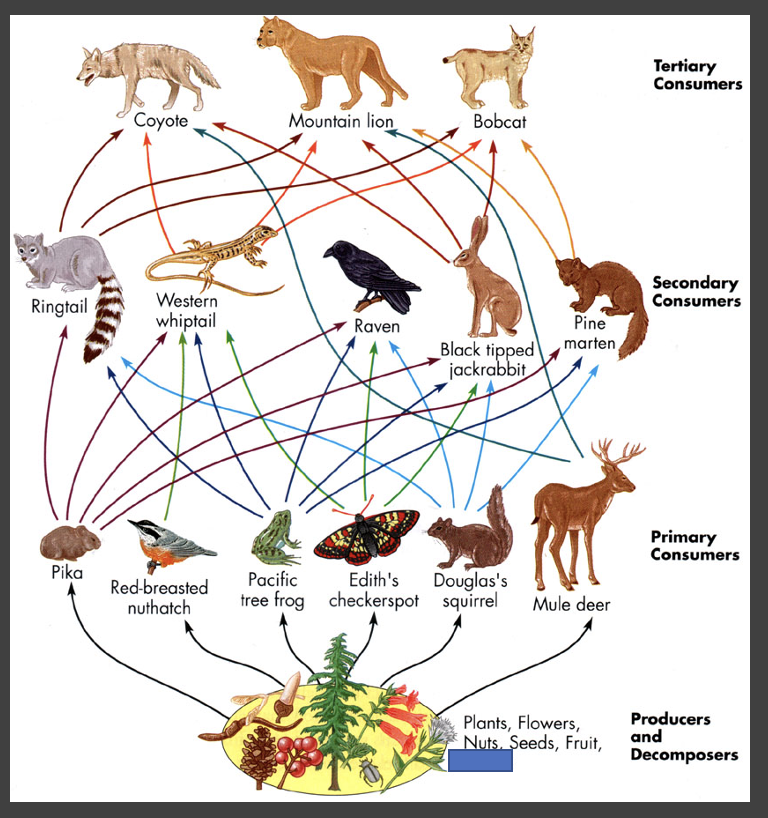
why are food webs a more realistic representation of the food chain?
there are many complex interactions between the organisms of an ecosystem
what are 3 main community/ecosyetem interactions?
predation: where one individual is eating another individual
competition: 2 individuals are fighting for the same resource
symbiosis: close interaction between 2-3 different organisms that live in close association with one another
name 3 prey defenses
aposematic coloration: bright colors that warn predators that an organism is poisonous (poison dart frog, monarch caterpillar)
batesian mimicry: when a non-poisonous animal mimics the appearance of an animal that is poisonous
camouflage: an organism blends into its environment
what are the 2 kinds of competition?
intraspecific: competition within the same species (fighting for a mate)
interspecific: competition between 2 different species (fighting for food)
what does the competitive exclusion principle state?
2 species competing for the same resource in the same location cannot coexist
if 2 organisms are fighting for the same resource, an organism might find a different resource or a different location
what is resource partitioning?
when 2 species use the same resource differently, so that they are not fighting for the same resource in the same location.
eg: brown creeper and white breasted nuthatch - white breasted nuthatch always walks down a tree to look for food, while the brown creeper always walks up a tree to look for food
what is symbiosis? what are the 3 types of symbiosis?
any relationship where 2 or more species live closely together.
3 types: mutualism, commensalism, parasitism
what is mutualism? give examples
a +/+ association, where all species involved are benefitting from the association
eg. oxpecker and impala, cleaner shrimp and eel, bees and flowers
what is commensalism? give examples
a +/0 association, where one species benefits, and the other species is not affected
eg. shark and remora, whale and barnacle
what is parasitism? give examples
a + / - association where one individual benefits and one individual is harmed
eg. ant and roundworms, hornworm and wasp
what is a keystone species?
a species that when present keeps biodiversity high in that area. the extinction of a keystone species would consequently lead to the extinction of many other species
eg. wolf, sea star, otter, prairie dogs
eg. Thomas Payne’s experiment with sea stars in the Pacific Northwest: sea stars retain biodiversity. when they are taken away, mussels outcompete all other species
what are biomes? name examples
large scale environments that are distinguished by characteristic temps and precipitation levels, which lead to different animals and plants
forests
grasslands
deserts
tundra
aquatic
what factors most impact terrestrial biomes? what affects these factors?
precipitation and temperature (impacted by latitude and longitude)
describe the 3 forest biomes
forests are dominated by trees and contain a lot of the world’s biodiversity
3 types:
tropical: warm and high precipitation. at equatorial region. most biodiverse terrestrial biome. temp and sunlight are stable with high annual rainfall, so they have year-round plant growth
temperate: middle temperature, 4 seasons. lower annual temp than tropical rainforests. distinct growing seasons rather than year-round growth
boreal: high latitude, cold and dry, most precipitation in form of snow. cold, dry winters with short, cool, wet summers. pines, spruce, fir trees.
describe the 2 types of grassland biomes
grasslands are dominated by grass with a warm, dry climate
savannas (tropical grasslands): scattered trees, hot and tropical, annual rainfall higher than temperate grasslands. extremely dry seasons where fire is common and helps the biome survive
temperate grasslands (prairie or steppe): no trees because they receive very little precipitation
name the 4 kinds of desert biomes
characterized by dry areas with less than 20 inches of annual rainfall, low biodiversity, animals and plants with adaptations to survive the lack of rain
4 types:
subtropical
semiarid
coastal
cold
describe the 2 kinds of tundra biomes
characterized by simple, low-lying vegetation with no trees. lowest temp of any biome and low annual precipitation. short summer = short growing season. plants and animals must be adapted to extreme conditions. low biodiversity
2 types:
arctic: high latitudes close to the arctic
alpine: high elevations in mountains
describe the 2 kinds of aquatic biomes
freshwater: inland bodies of water surrounded by land with a salt content of less than 1%. eg. lakes and ponds, river and streams, wetlands
marine: often open area with higher salt content. eg. ocean, coral reefs, estuaries, mangrove forests
describe rivers and streams
bodies of freshwater flowing in one direction
start at headwaters and travel great distances, often ending in the ocean
provide habitat and food for many aquatic/terrestrial species
describe lakes and ponds
landlocked bodies of freshwater
ponds are usually smaller and more shallow
provide habitat and food for many aquatic and terrestrial species
describe wetlands
places in which the land is covered by water permanently or seasonally
often recognized by the distinct plants found there
high biodiversity and critical habitat for many species
important for cleaning water, shoreline and storm protection, storing carbon from the atmosphere and food security
what are mangrove forests?
a type of wetland
made up of salt tolerant trees along coastlines
high biodiversity
estimated that the world has already lost over ½ of mangrove forests
breeding ground for many fish and other marine organisms
protect coastal areas from extreme weather, such as hurricanes and tsunamis