Unl Anatomy lab 6
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
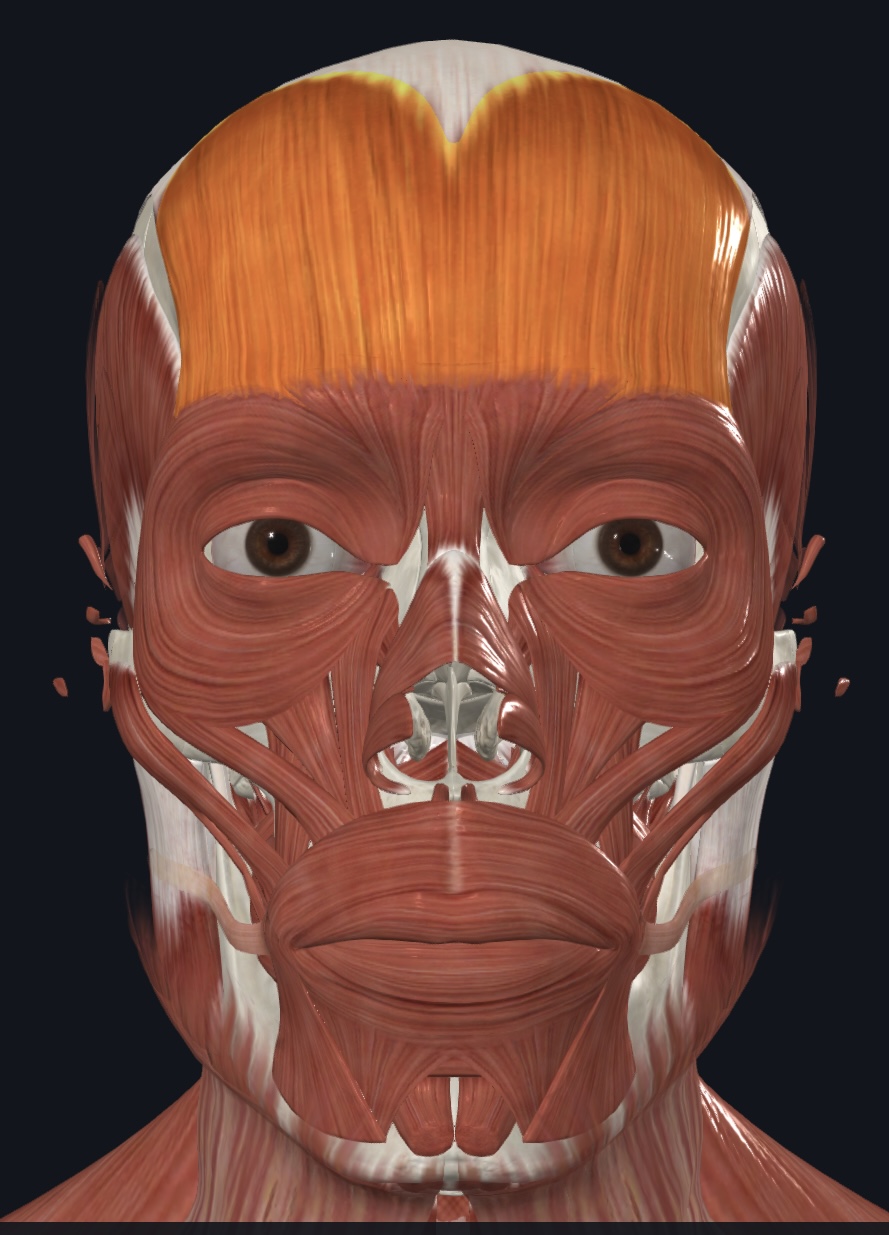
Epicranius: Frontalis (Frontal Belly)
O=galea aponeurotic
I=skin of eyebrows, bridge of nose
A=elevates eyebrows (when galea fixed);wrinkles forehead skin
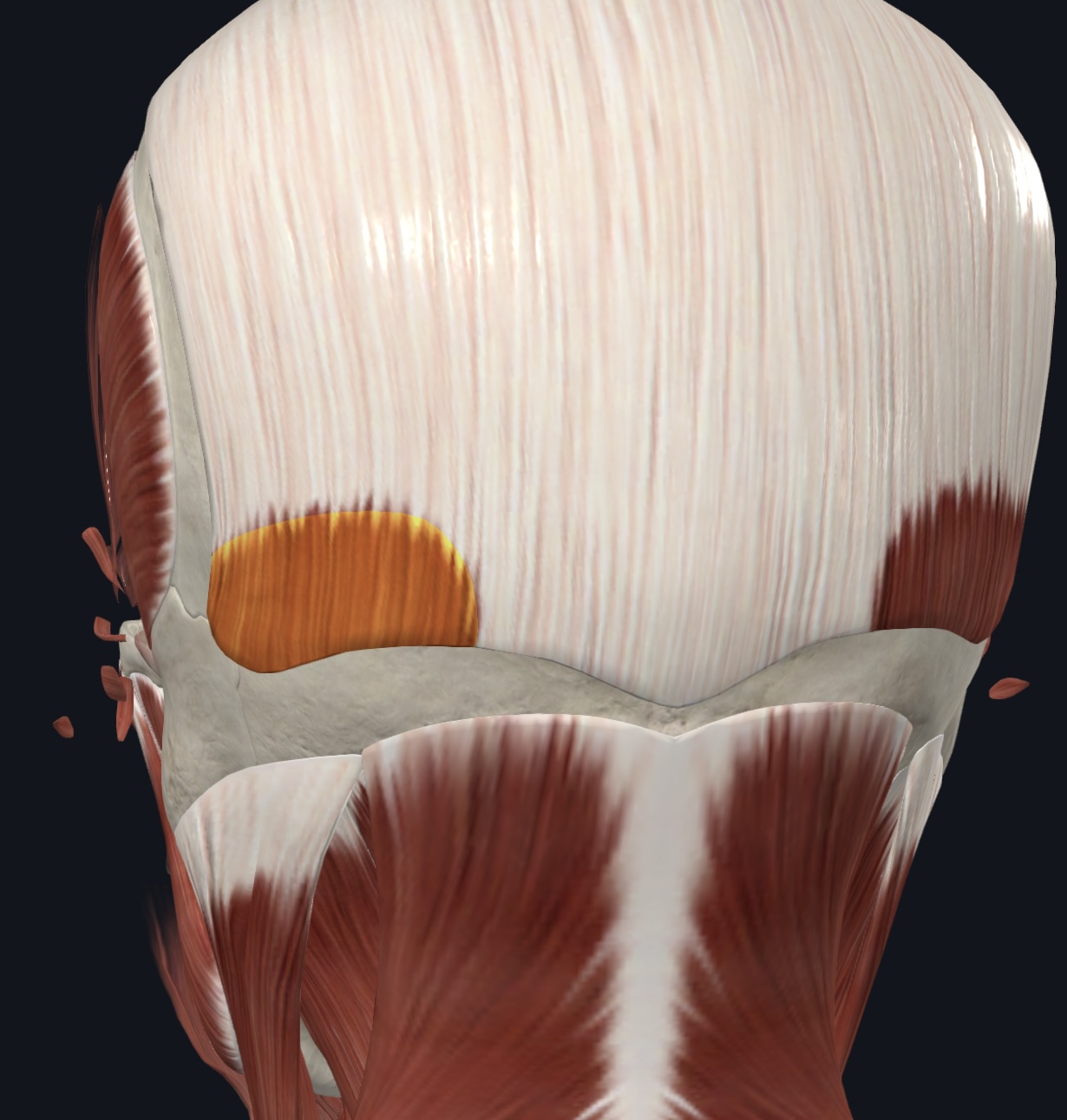
Epicranius: Occipitalis (Occipital belly)
O= superior nuchal line (occipital bone)
I= galea aponeurotica
A=Tenses and retracts scalp
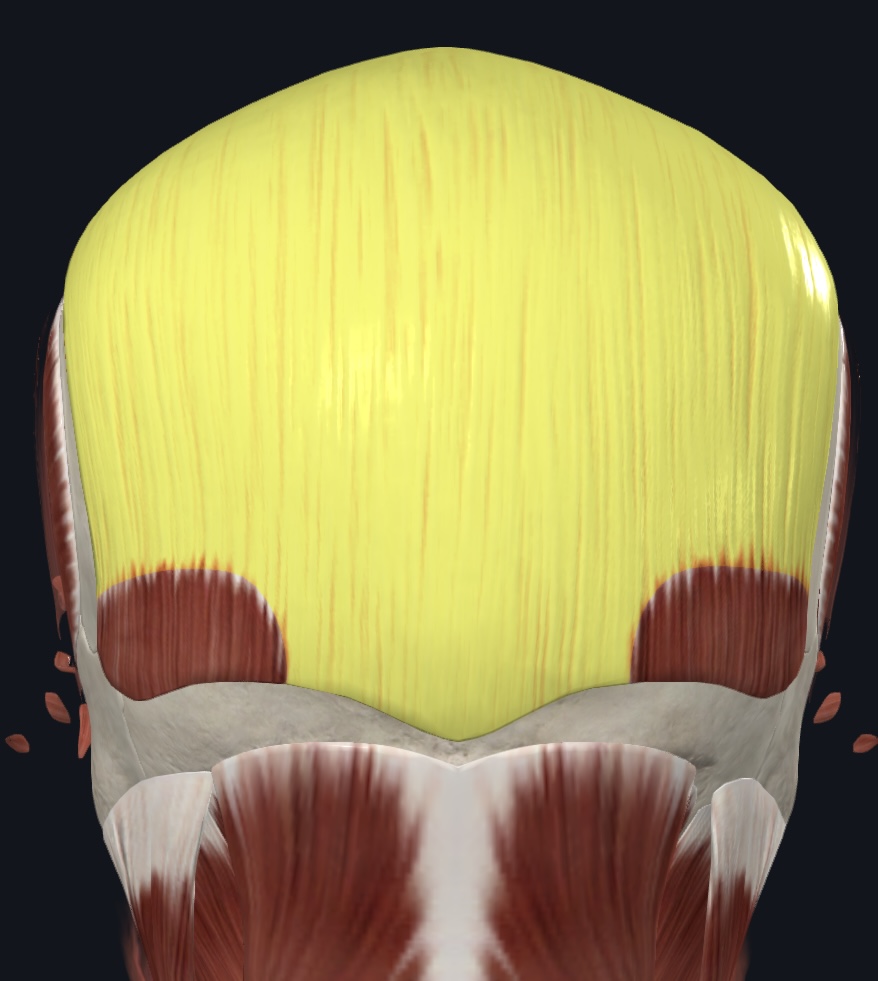
Galea aponeurotica (aponeurosis, ID only)
Muscles of Facial Expression (13)
All innervated by the Facial Nerve (CN VII)
Corrugator supercilii
Orbicularis oculi
Nasalis
Orbicularis oris (“kissing muscle”)
Levator labii superioris
Zygomaticus major (“smiling muscle”)
Zygomaticus minor (“smiling muscle”)
Risorius (“grinning muscle”)
Buccinator (“blowing muscle”)
Depressor anguli oris
Depressor labii inferioris
Mentalis (“pouting muscle”)
Platysma
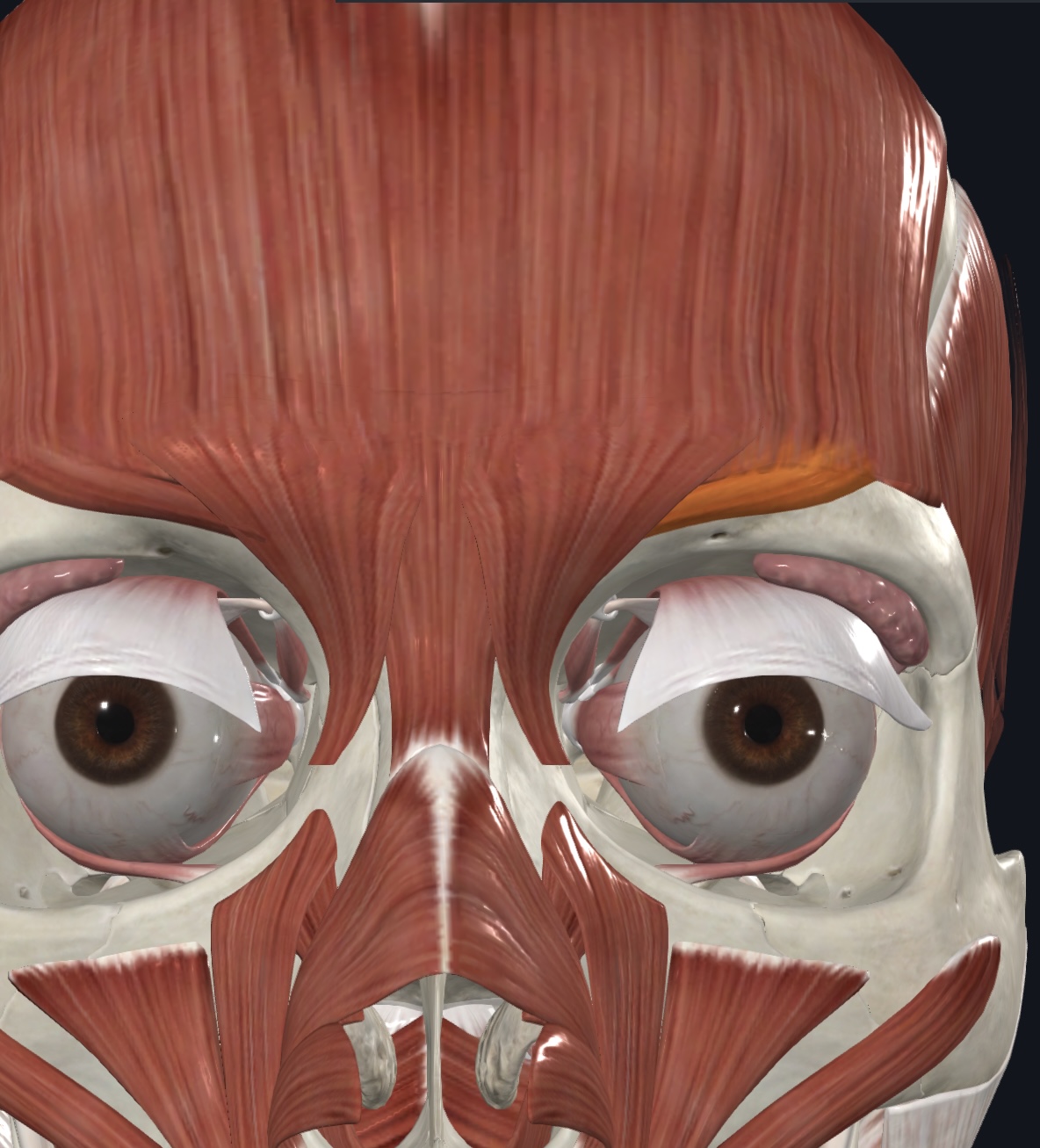

Corrugator supercilii
- O=arch of frontal bone above nasal bone
- I=skin of eyebrow
- A=draws eyebrow medially & inferiorly, - wrinkles skin of forehead vertically
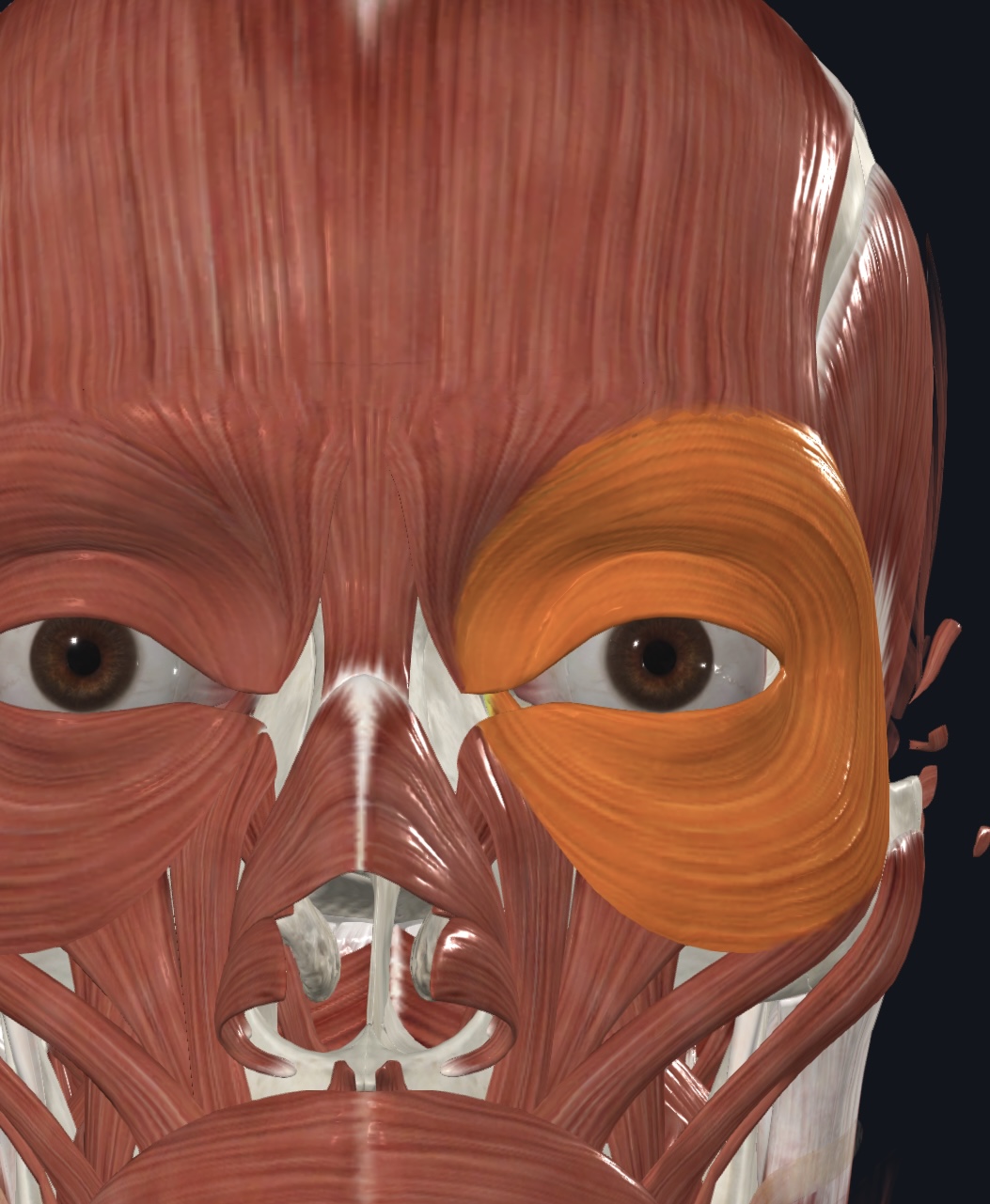
Orbicularis oculi,
- O = frontal and maxillary bones (medial margin of orbit)
- I = skin around eyelids
- A = closes eyelids; draws eyebrows inferiorly
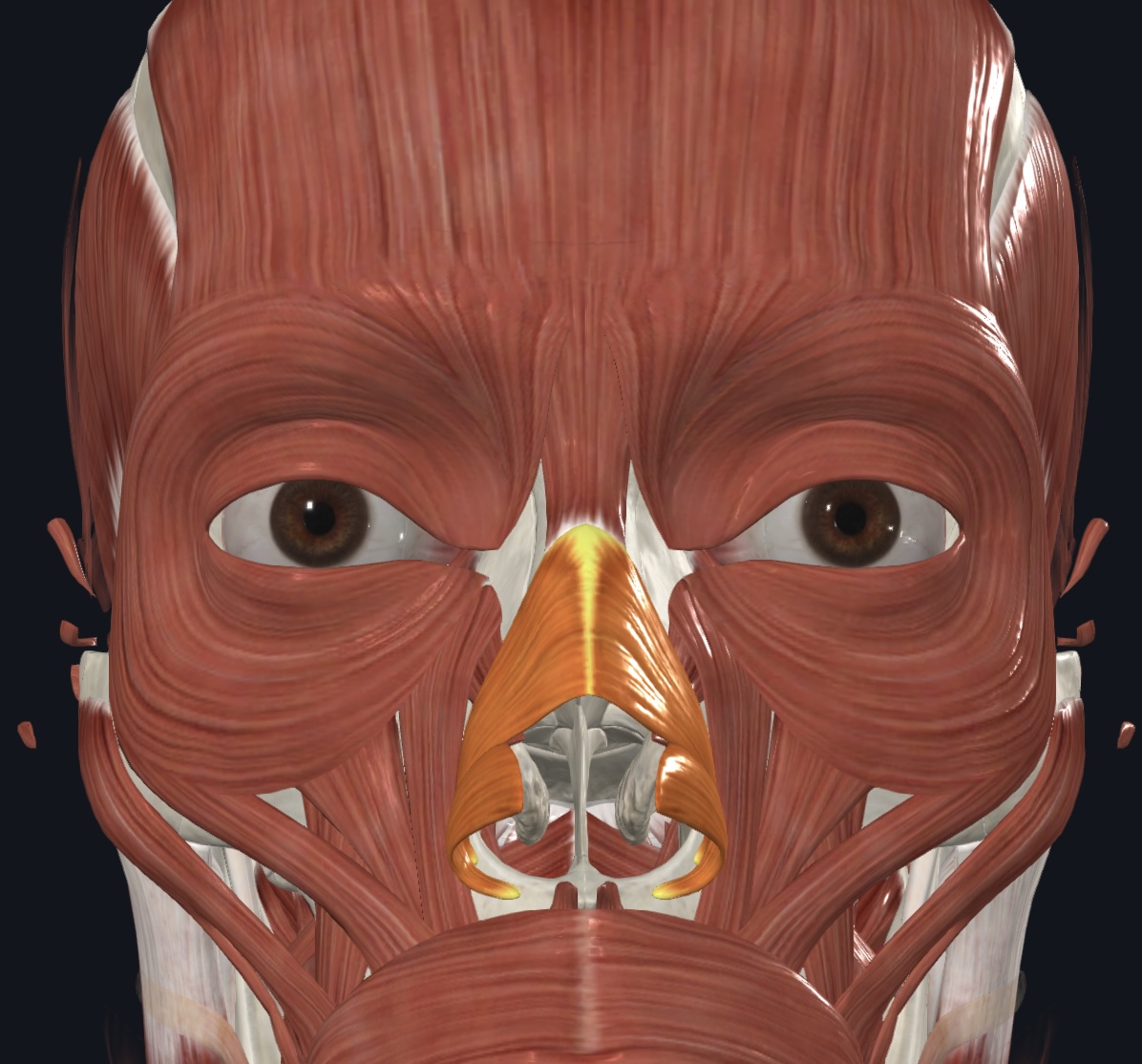
Nasalis,
- O = maxilla and nasal cartilage
- I = bridge of the nose
- A = compresses nostrils, depresses tip of nose, elevates corners of nose
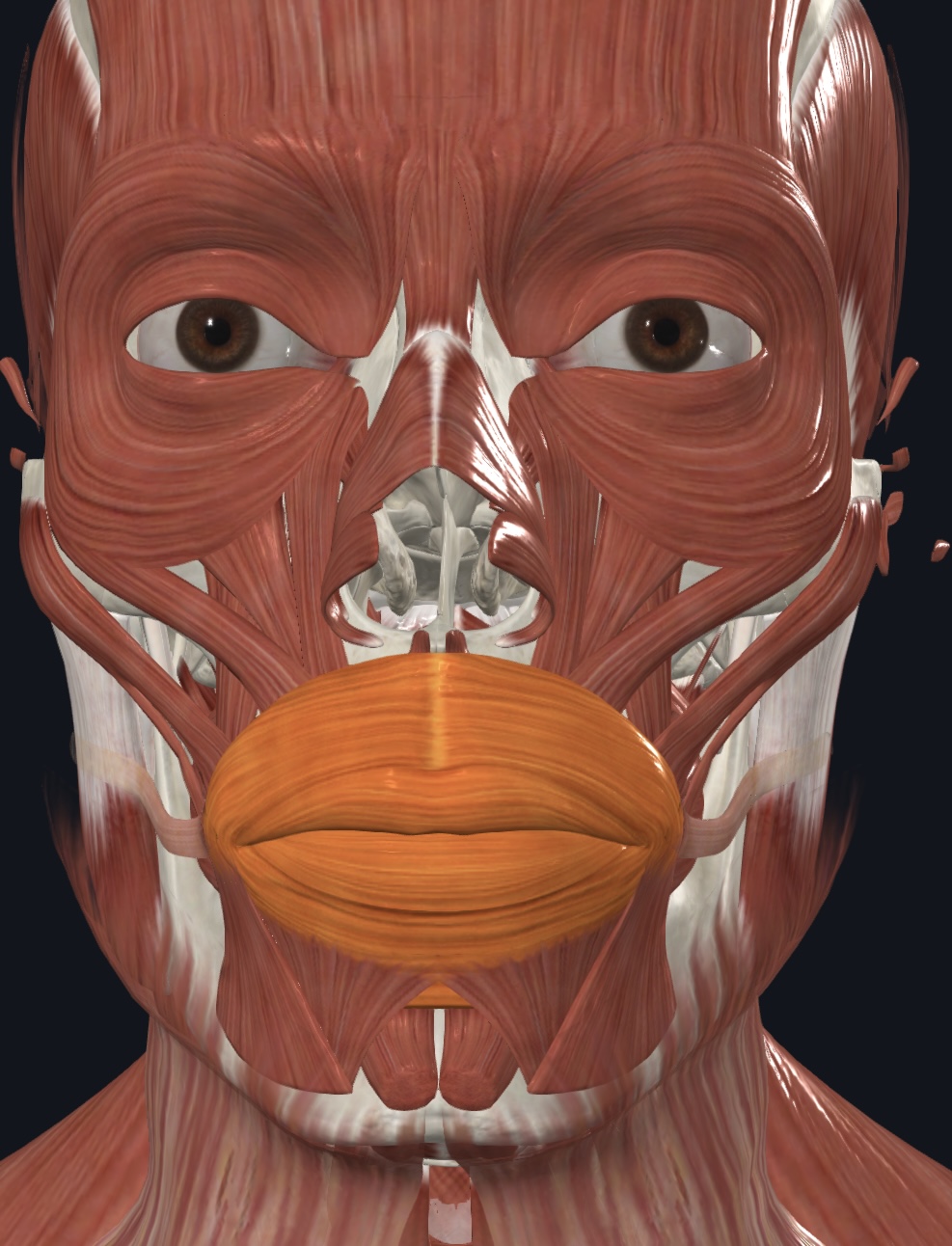
Orbicularis oris (“kissing muscle”),
- O = maxilla and mandible via surrounding facial muscles
- I = lips
- A = closes, purses, and protrudes lips
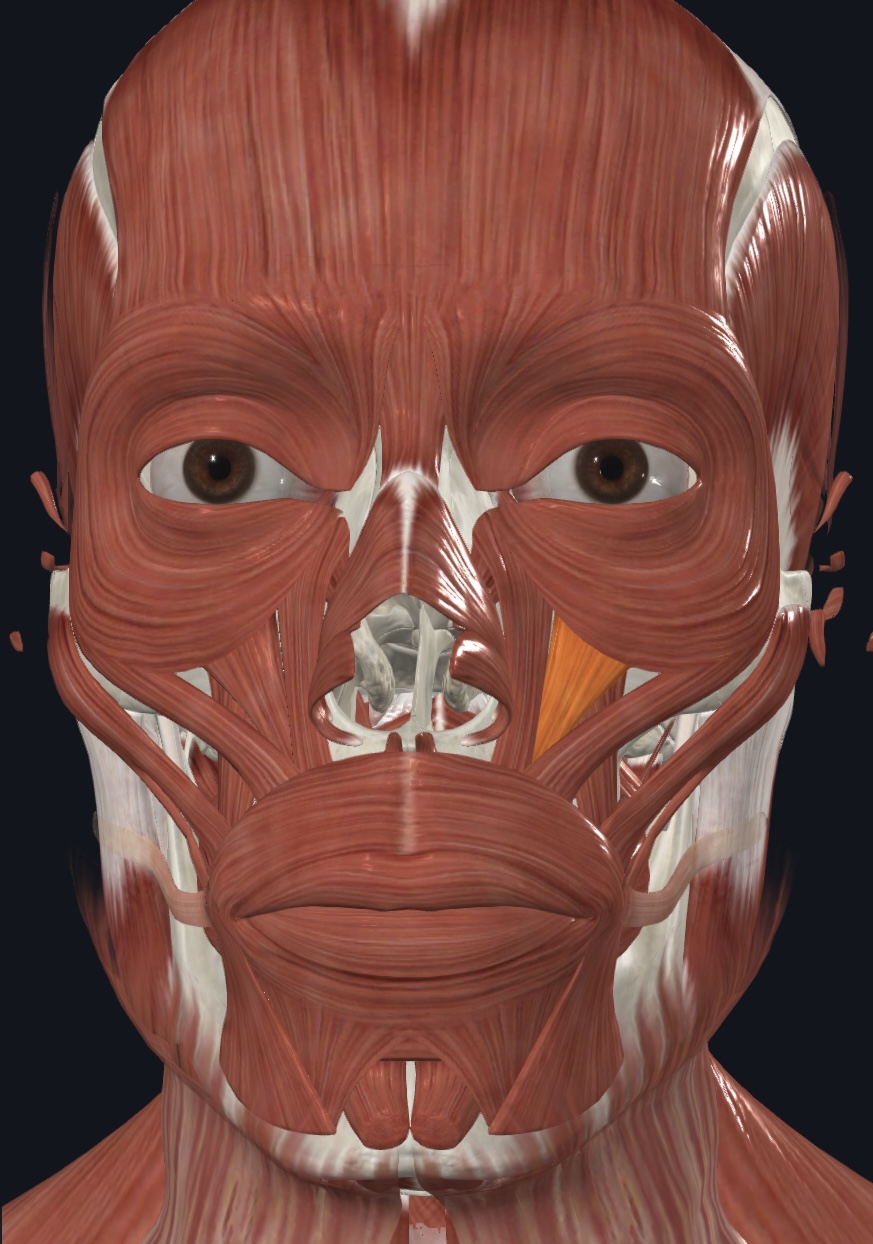
Levator labii superioris,
- O = zygomatic bone and infraorbital margin of maxilla
- I = orbicularis oris
- A = raises and furrows upper lip
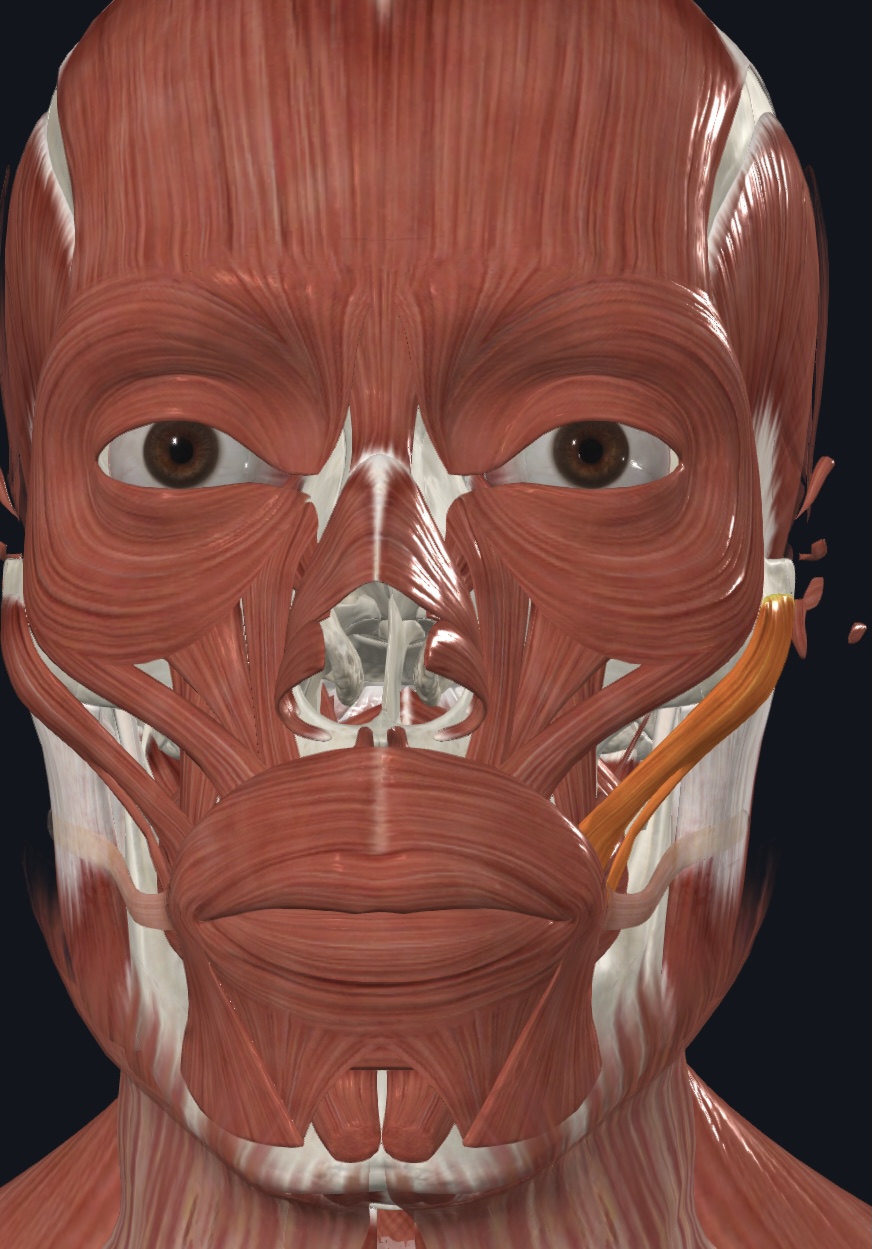
Zygomaticus major (“smiling muscle”),
- O = zygomatic bone (lateral to zygomaticus minor)
- I = skin and muscle at angle of mouth
- A = retracts and elevates lateral angle of the mouth
Zygomaticus minor (“smiling muscle”),
- O = zygomatic bone (medial to zygomaticus major)
- I = skin and muscle of upper lip
- A = retracts and elevates lateral angle of mouth
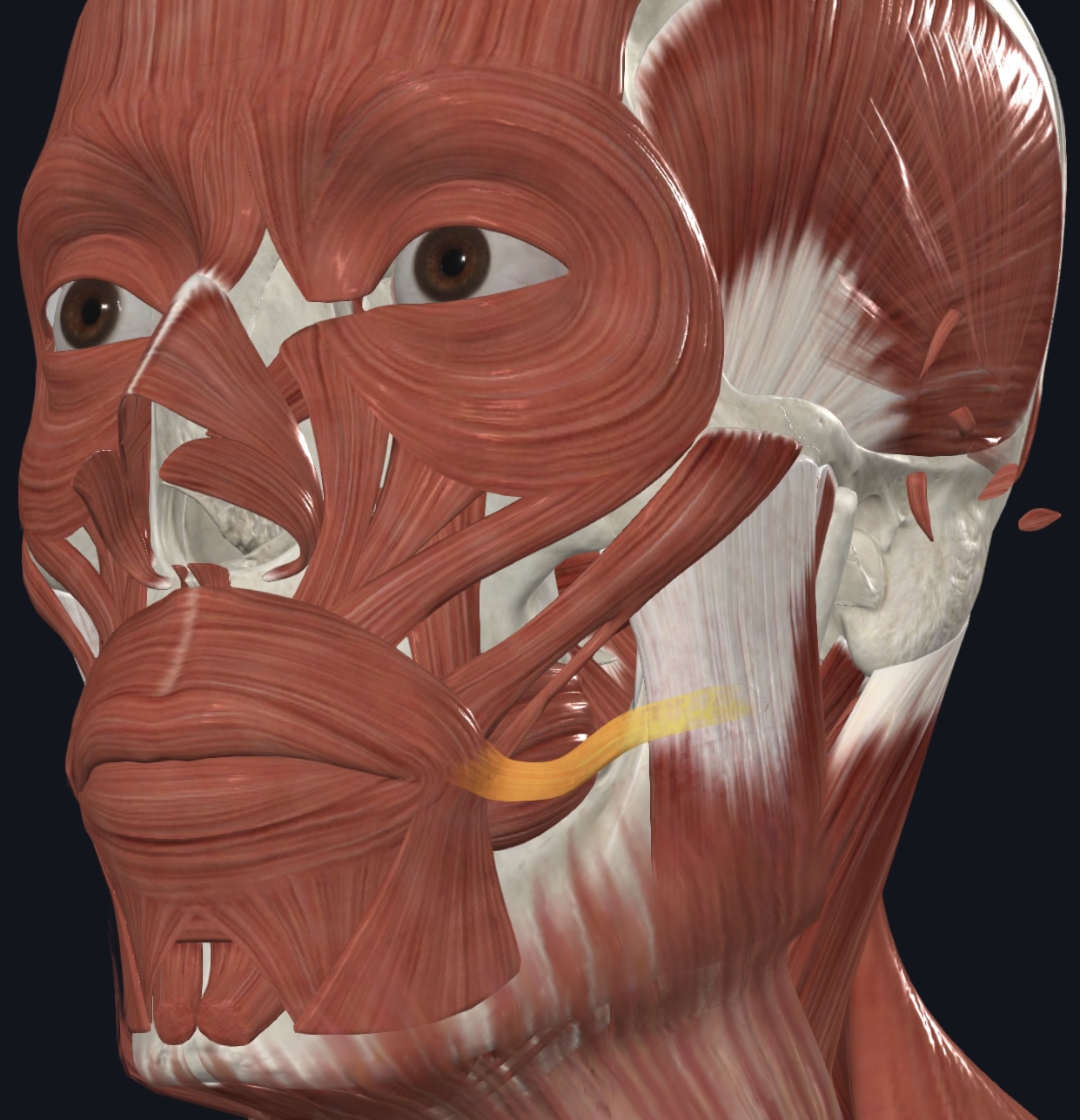
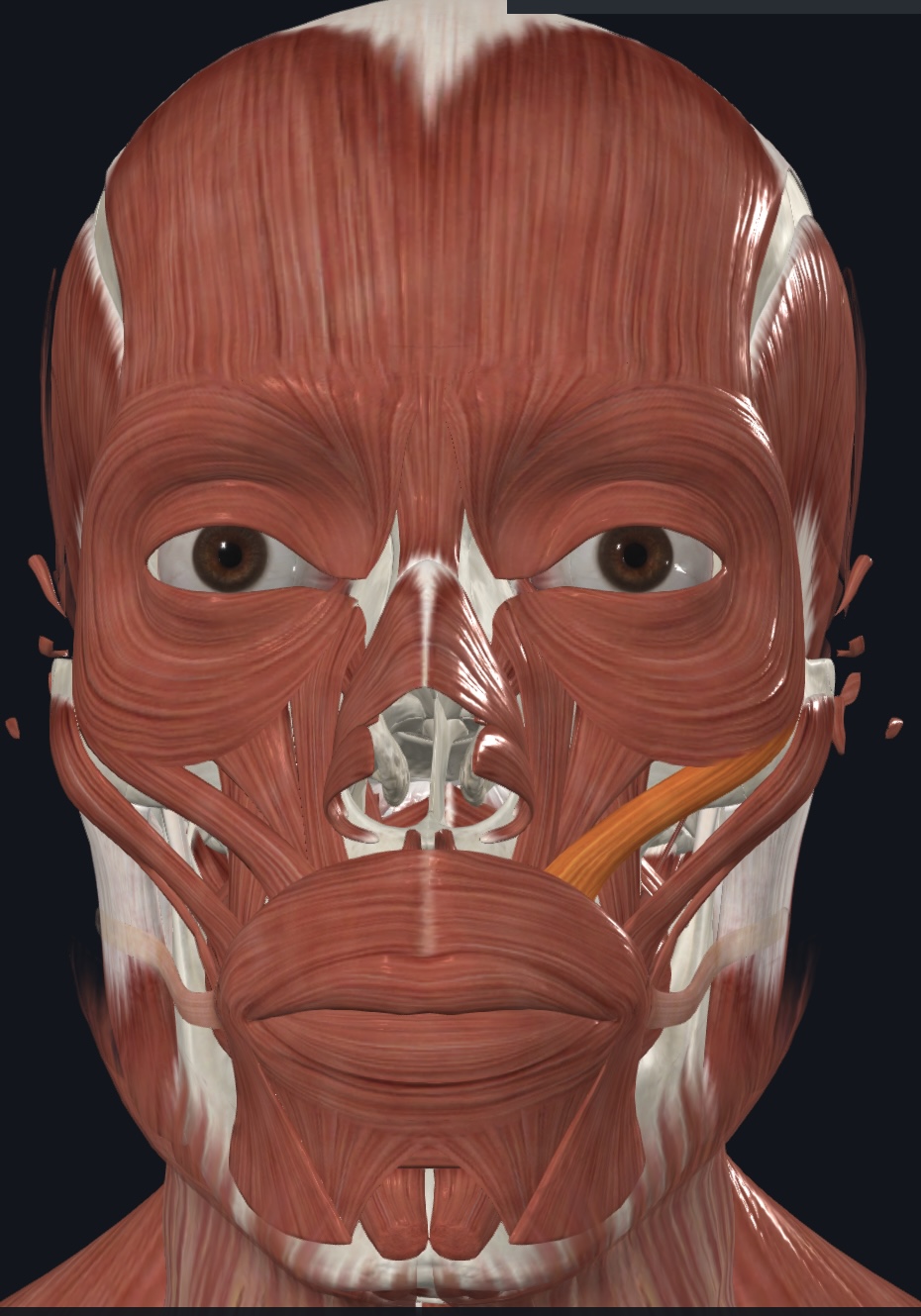
Risorius (“grinning muscle”),
- O = lateral fascia of masseter muscle and parotid salivary gland
- I = skin at angle of mouth
- A = draws angle of mouth laterally; synergist with zygomaticus muscles
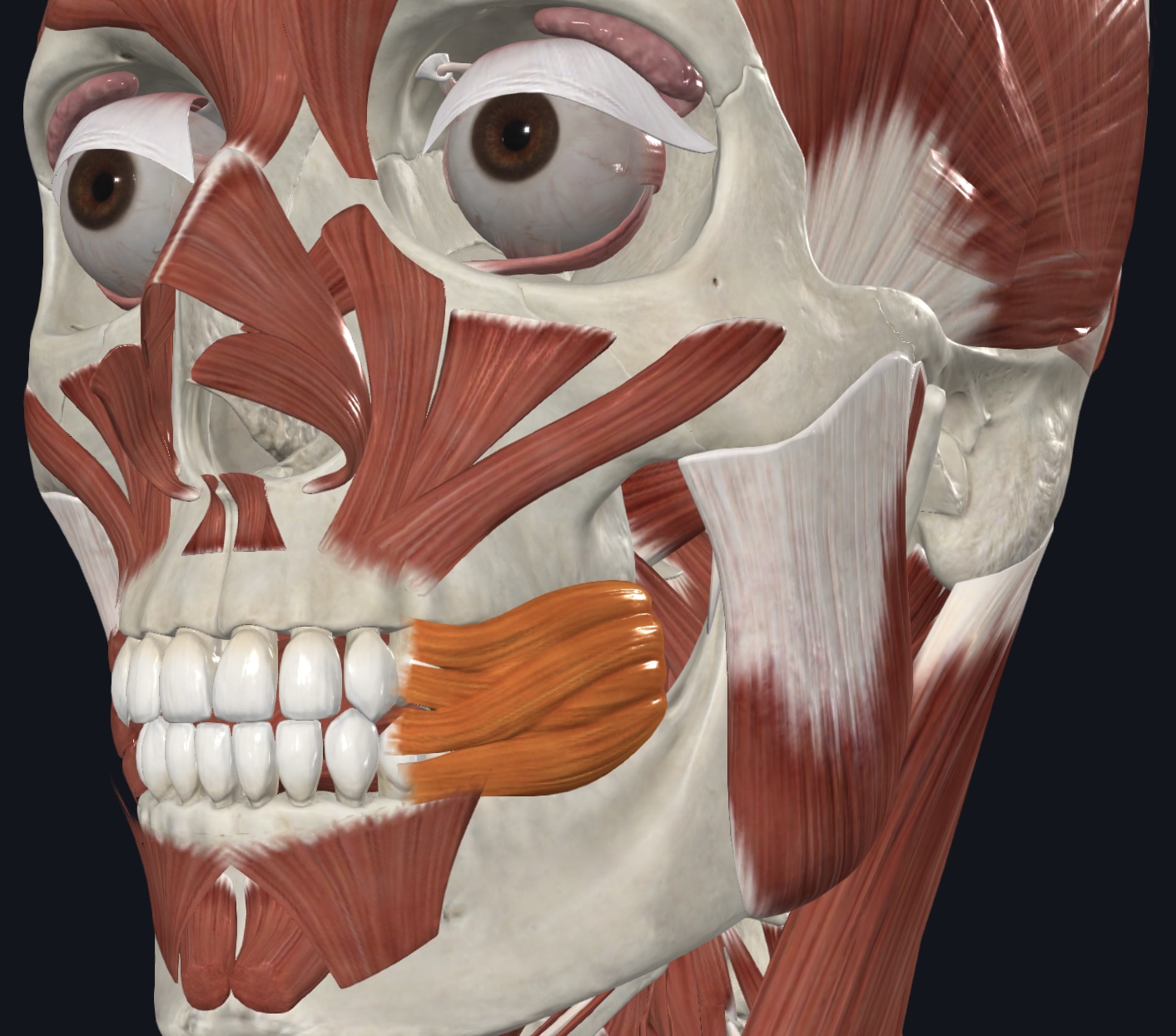
Buccinator (“blowing muscle”),
- O = molar region of maxilla and mandible
- I = orbicularis oris
- A = compresses cheek; holds food between teeth during chewing (thus, is
considered an accessory muscle to the muscles of mastication, in
addition to its primary role as a muscle of facial expression)
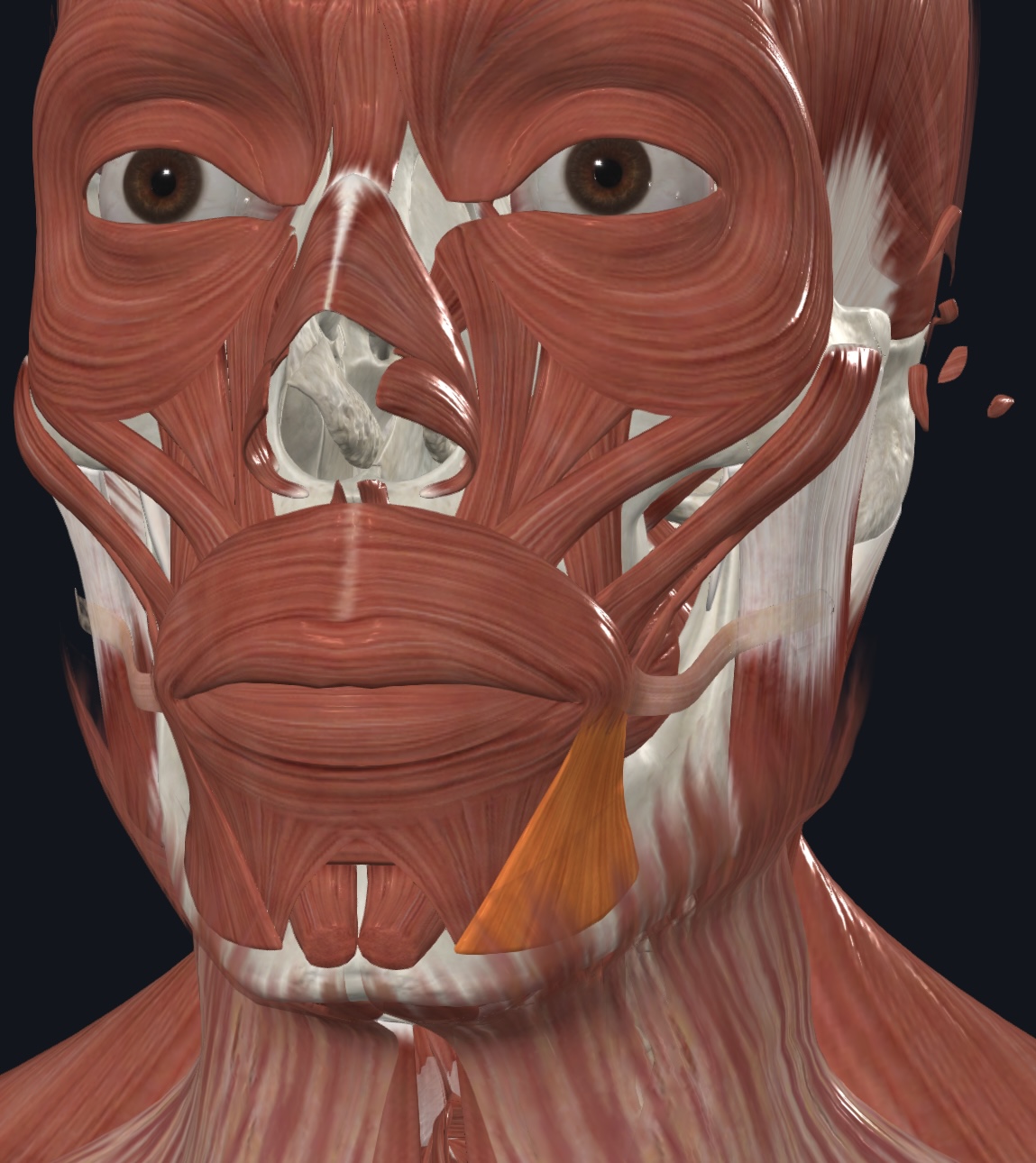
Depressor anguli oris,
- O = anterolateral surface of body of mandible, inferior to incisors
- I = skin and muscle at inferior angle of mouth,
- A = draws angle of mouth inferiorly and laterally; zygomaticus antagonist
Depressor labii inferioris,
- O = body of mandible, lateral to midline
- I = skin and muscle of lower lip
- A = draws lower lip inferiorly
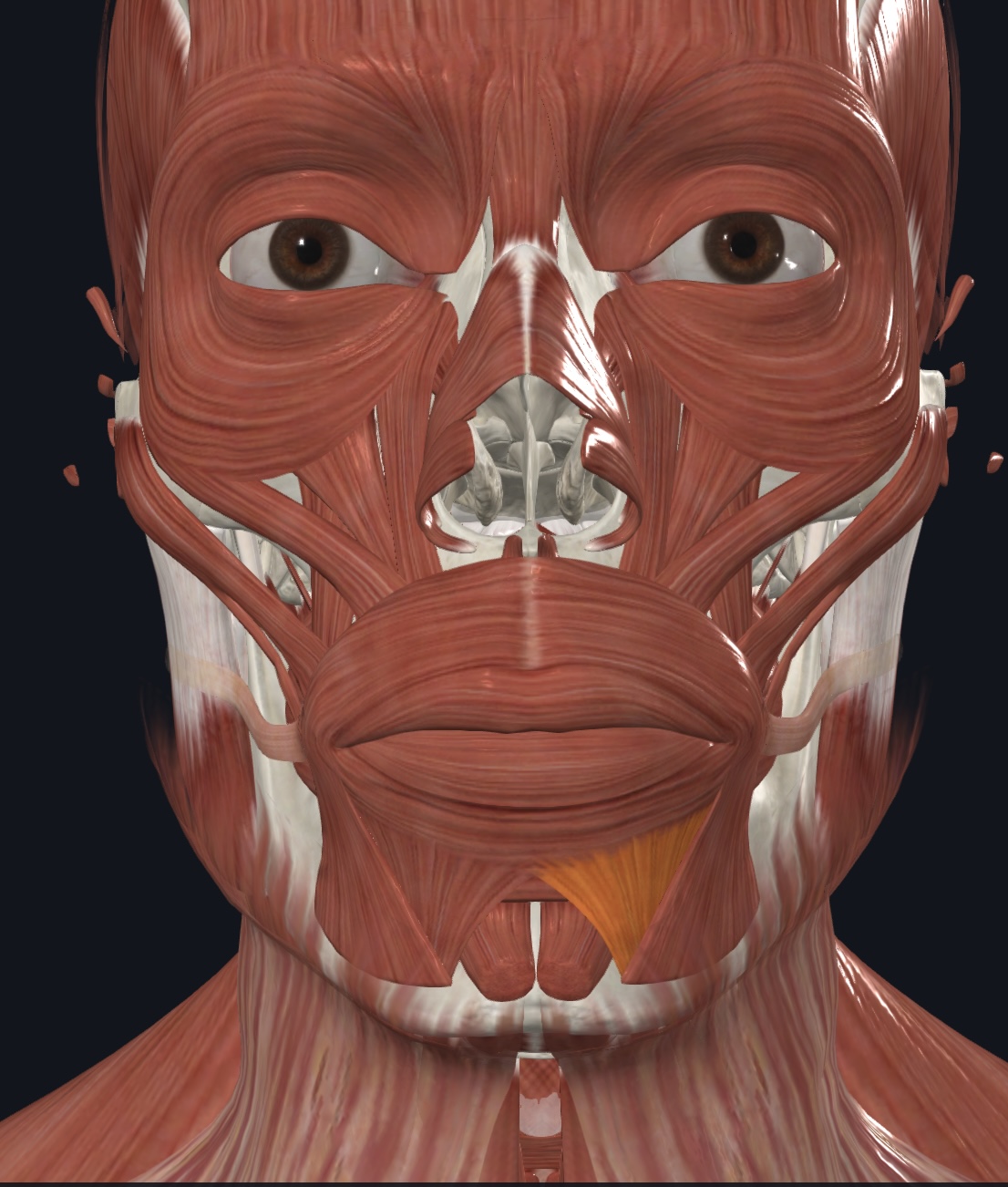
Mentalis (“pouting muscle”),
O = incisive fossa of mandible
I = skin of chin
A = elevates and protrudes lower lip; wrinkles chin
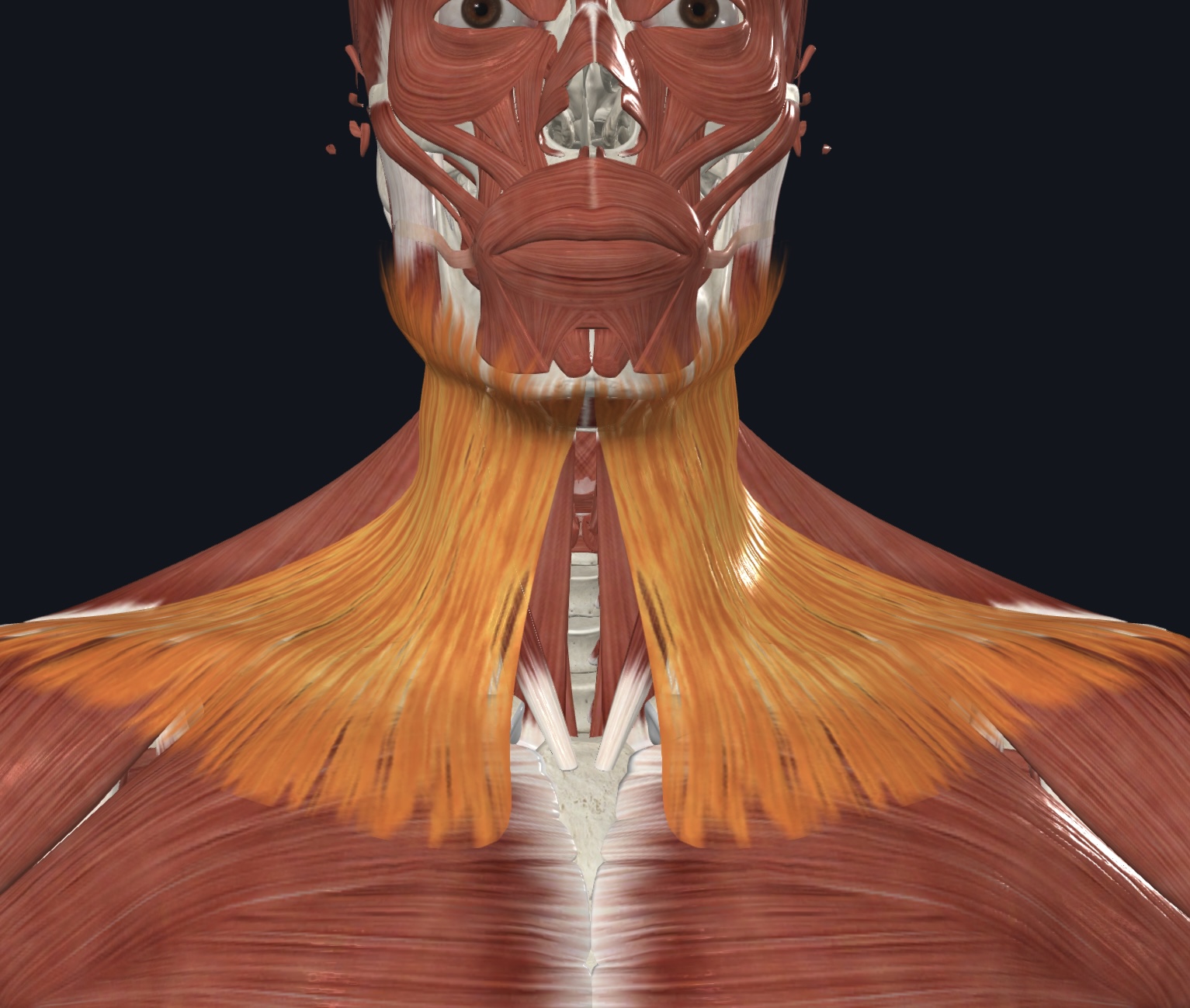
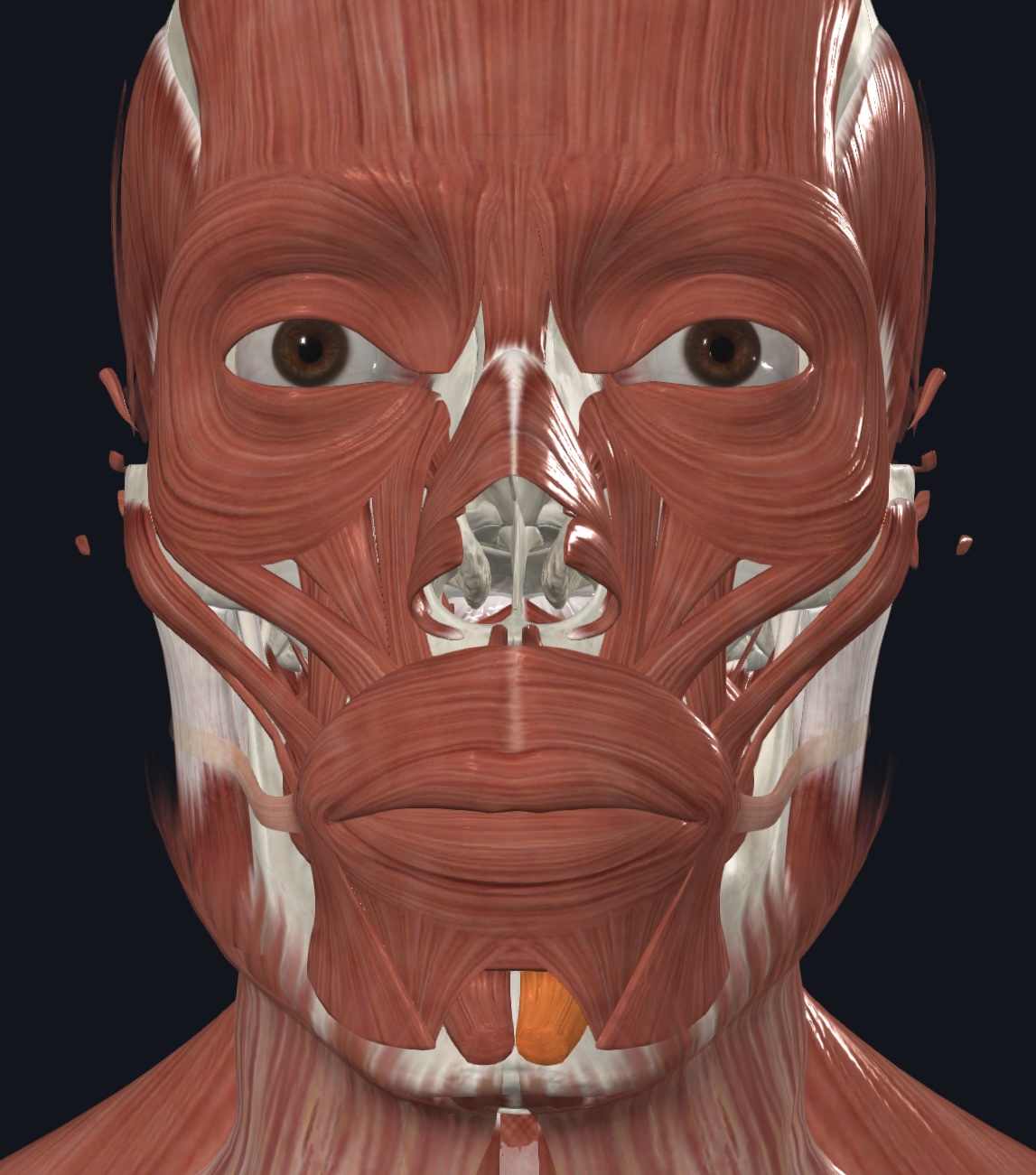
Platysma,
O = fascia of pectoralis major and deltoid muscles
I = inferior margin of mandible, and skin and muscle at angle of mouth
A = depresses mandible; tenses skin of neck
Muscles of Mastication
(4) *All are innervated by the Mandibular Branch of the Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
Masseter
Temporalis
Medial Pterygoid (“grinding muscle”)
Lateral pterygoid (“grinding muscle”)
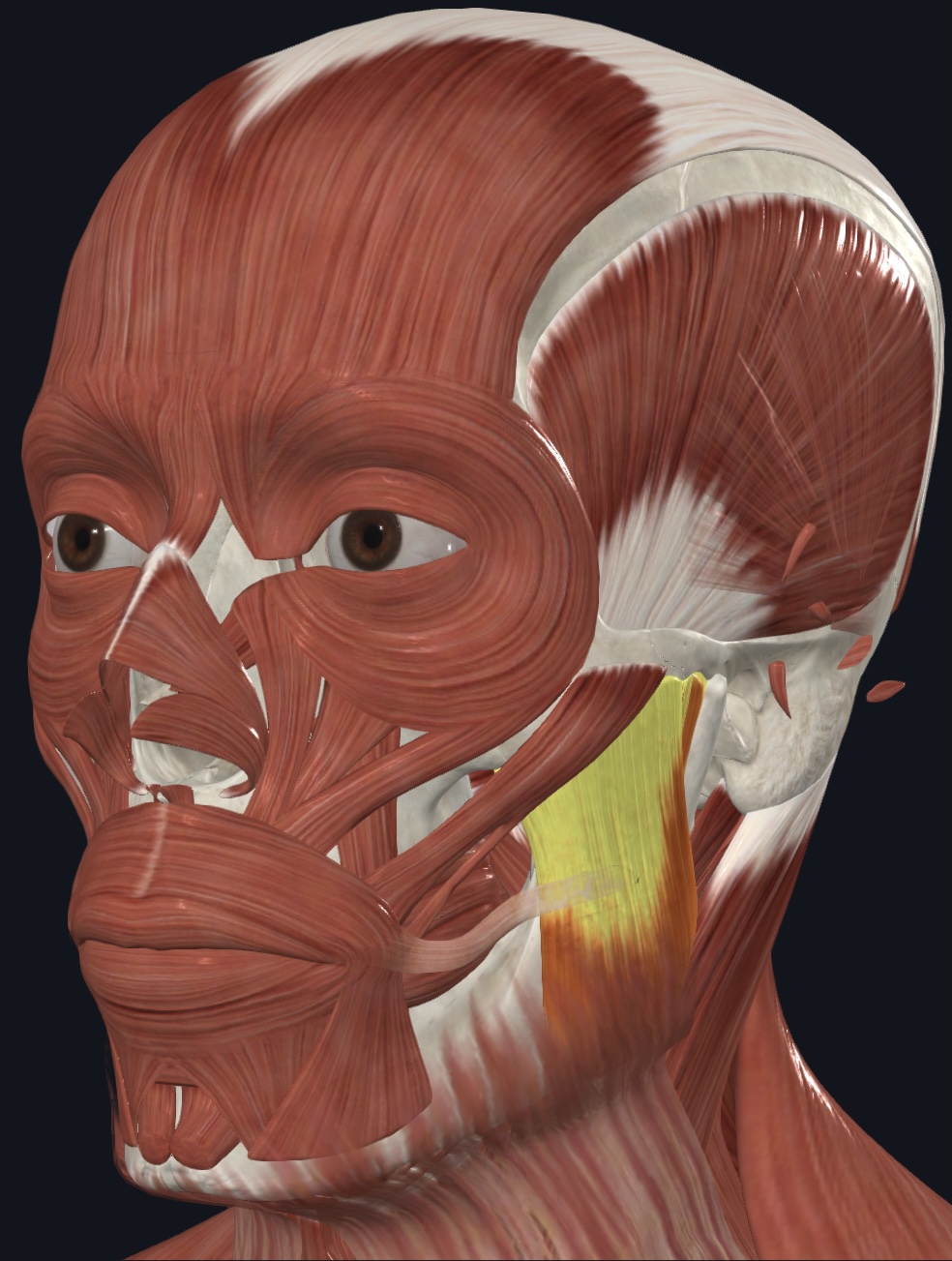
Masseter,
O = zygomatic arch
I = lateral surface of ramus of mandible
A = prime mover of mandibular elevation
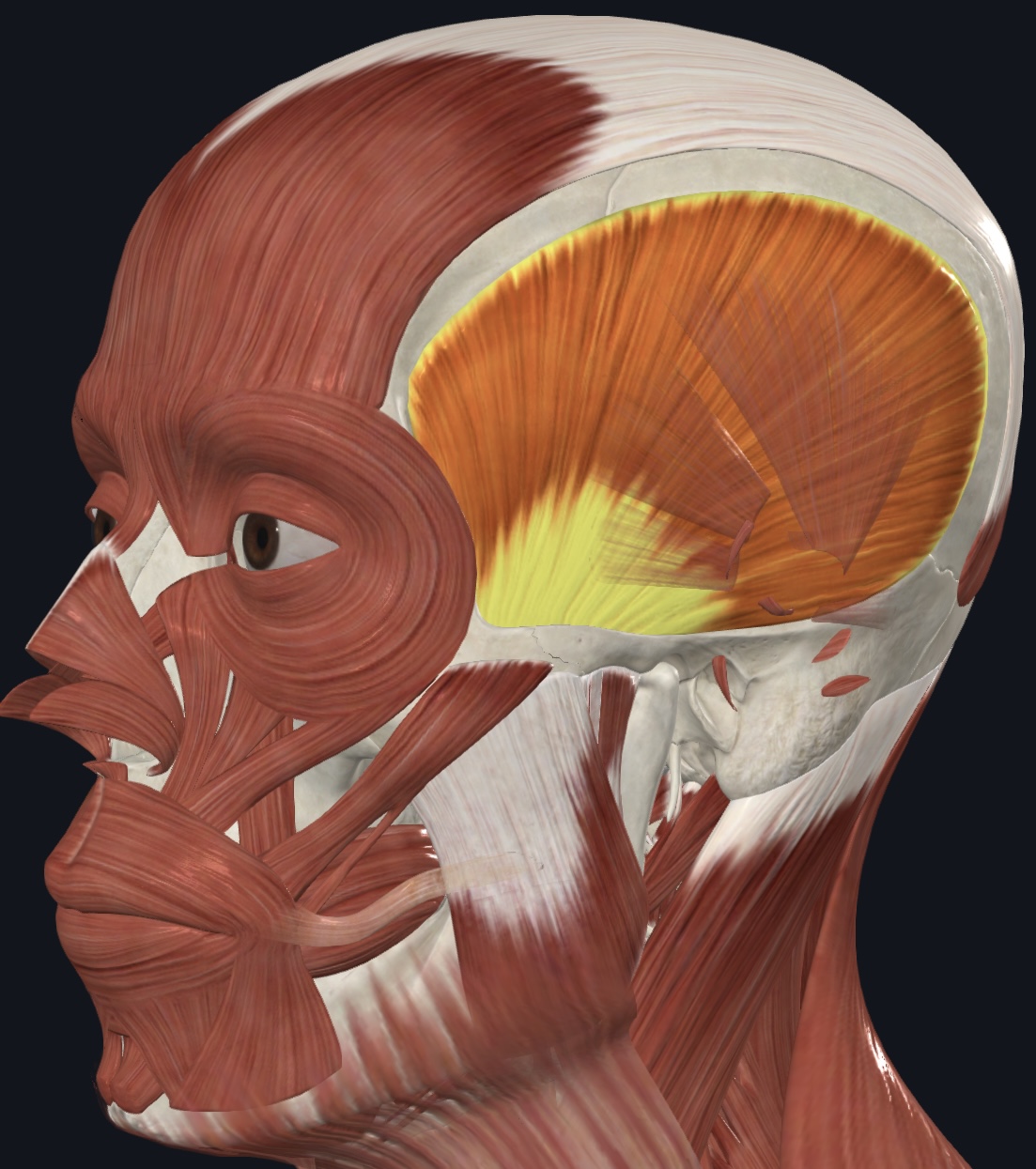
Temporalis,
O = temporal fossa
I = coronoid process of mandible
A = elevates and retracts mandible (closing the jaw); maintains resting position of the mandible
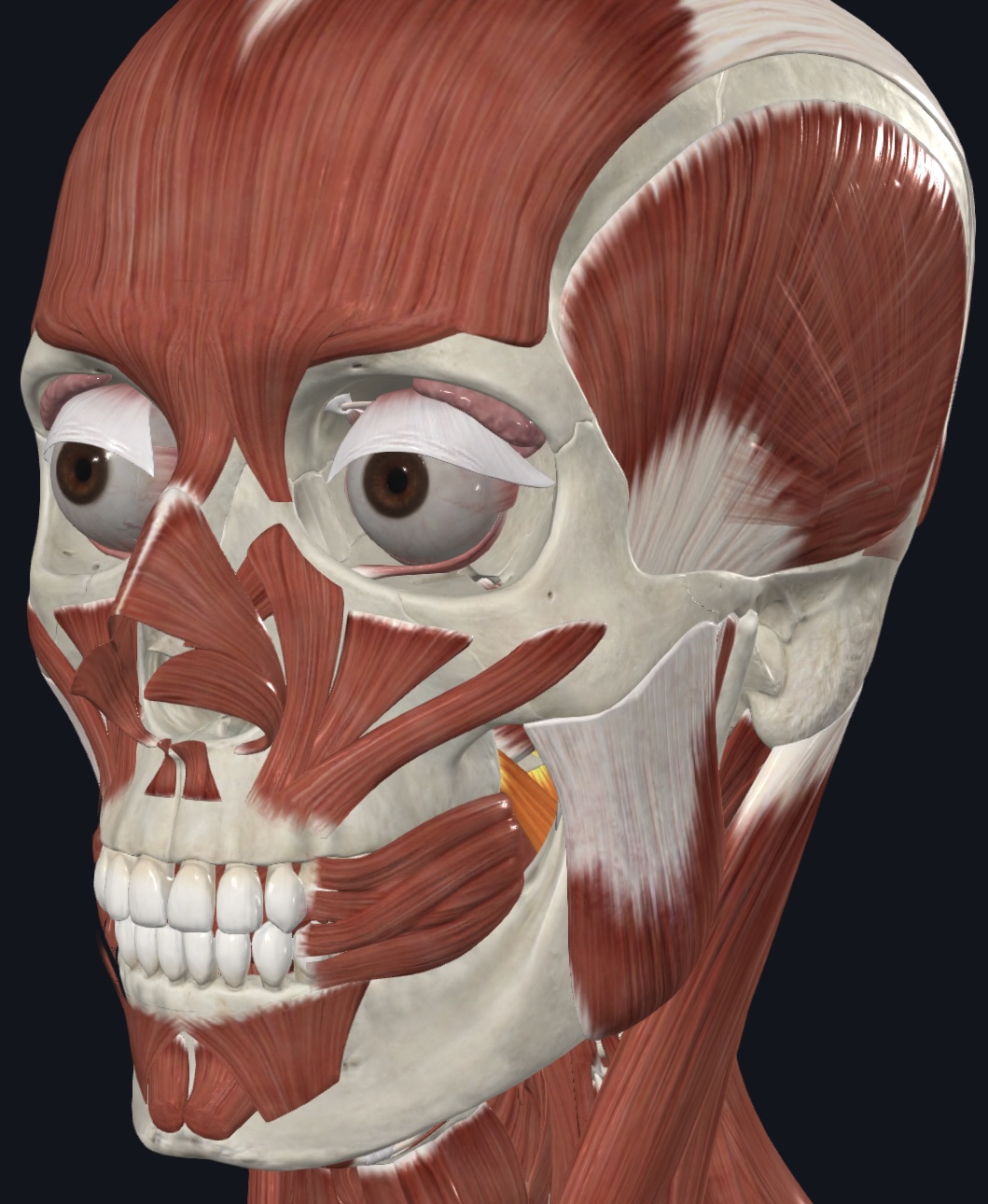
Medial pterygoid (“grinding muscle”),
O = maxilla, palatine bone, and medial surface of lateral pterygoid process of sphenoid bone
I = near angle of medial mandibular surface
A = synergist to temporalis and masseter in mandibular elevation; synergist to lateral pterygoid in side-to-
side movement of mandible
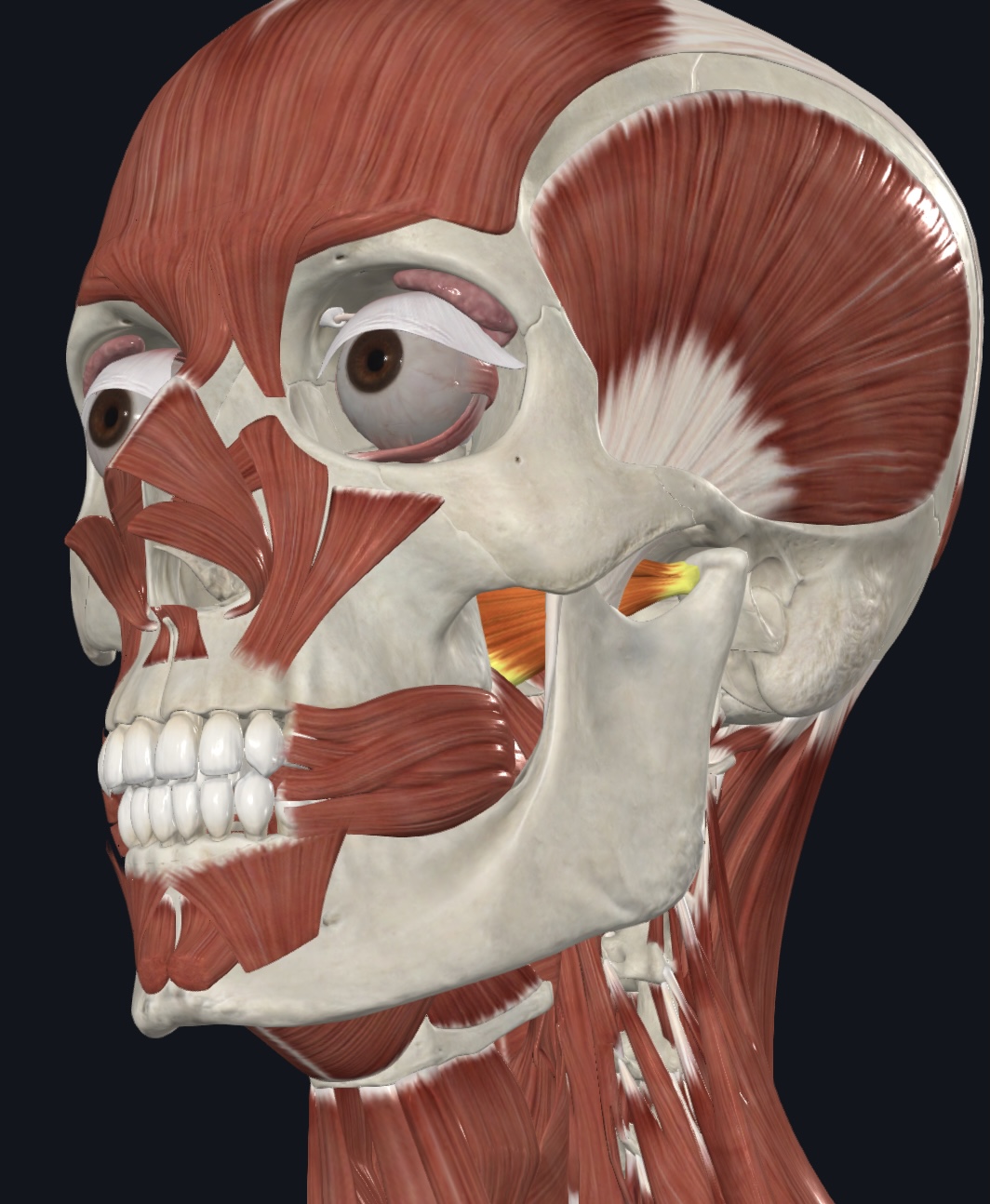
Lateral pterygoid (“grinding muscle”),
O = greatser wing and lateral pterygoid process of sphenoid bone
I = mandibular condyle and capsule of temporomandibular joint
A = protrudes, elevates and depresses mandible; synergist to medial
pterygoid in side-to-side movement of mandible
Anterior muscles of the Neck:
Digastric (both anterior and posterior bellies),
Stylohyoid
Geniohyoid
Mylohyoid
Omohyoid - strap-like muscle with a superior and inferior belly, united by an intermediate tendon - strap-like muscle with a superior and inferior belly, united by an intermediate tendon
Sternohyoid
Sternothyroid
Thyrohyoid
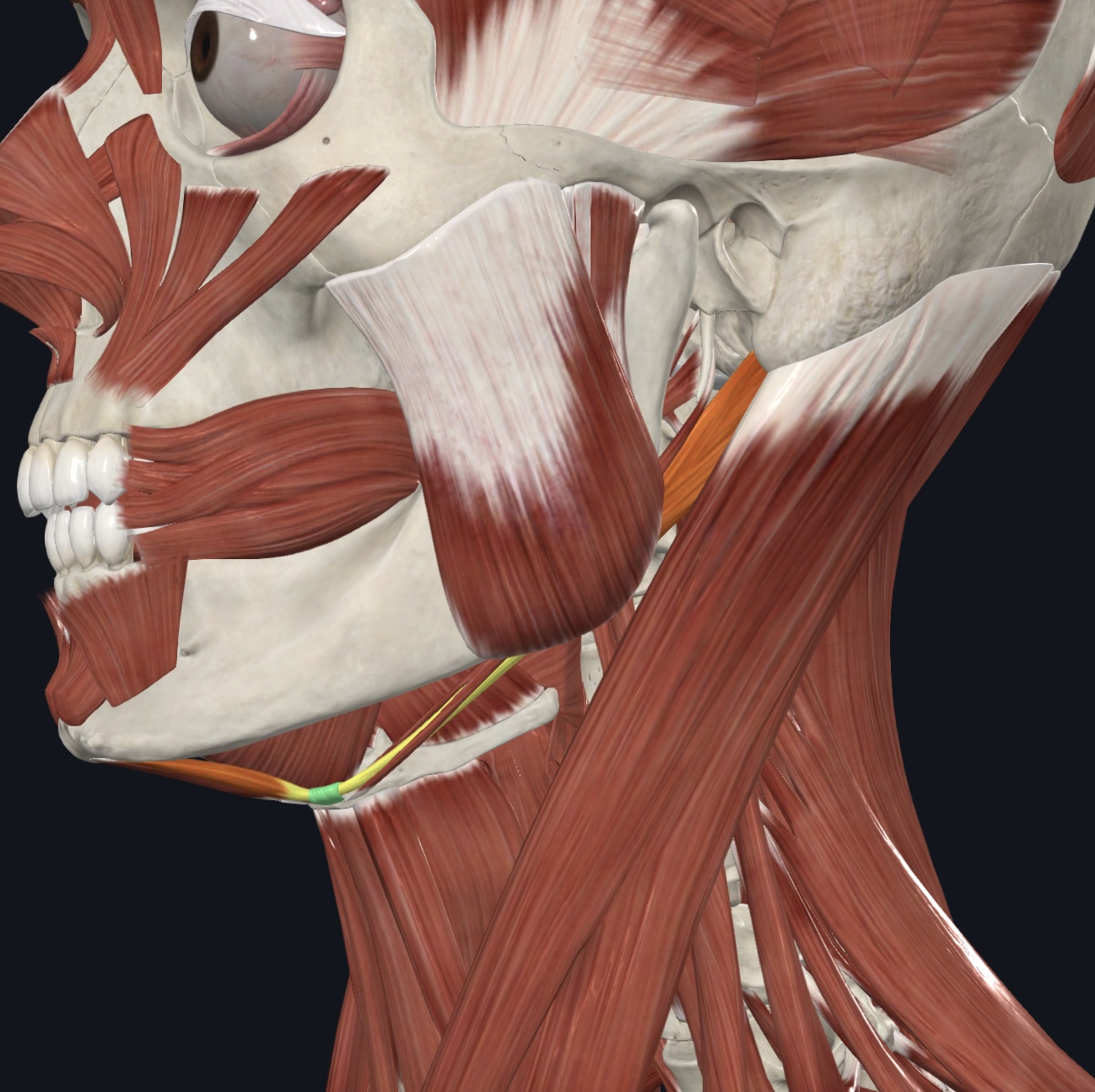
Digastric (both anterior and posterior bellies),
O = anterior belly--inferior margin of mandible; posterior belly--mastoid process of temporal bone
I = hyoid bone via an intermediate tendon
A = prime mover of mandibular depression; elevate and fix hyoid bone during swallowing and speech
N = anterior belly--Mandibular Branch of the Trigeminal Nerve (CN V); posterior belly--Facial Nerve
(CN VII)
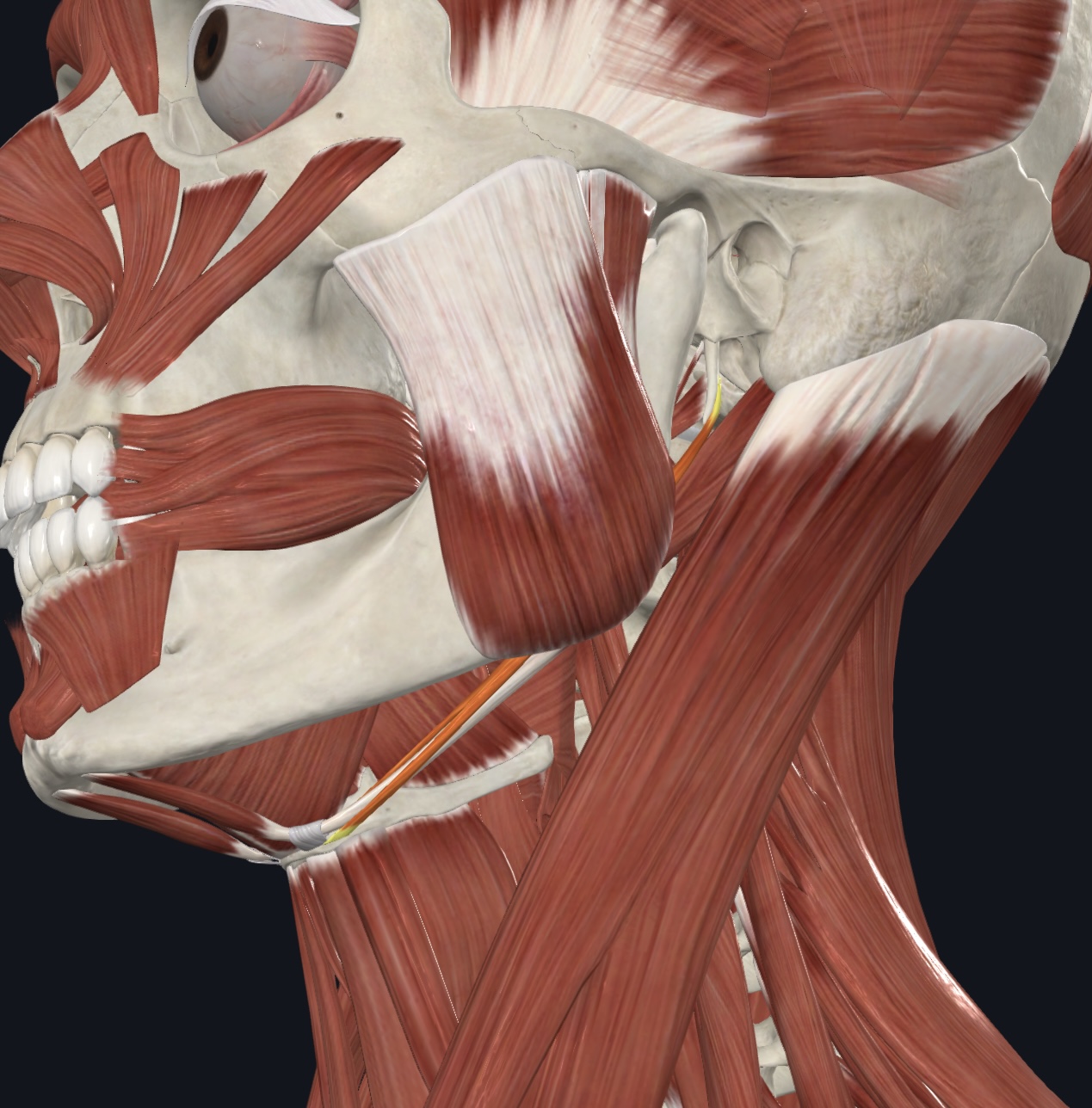
Stylohyoid,
O = styloid process of temporal bone
I = hyoid bone
A = elevates larynx
N = Facial Nerve (CN VII)
Geniohyoid,
O = medial surface of mandibular symphysis
I = hyoid bone
A = pulls hyoid bone anteriorly and superiorly, depresses mandible when
hyoid is fixed
N = Spinal Nerve C1
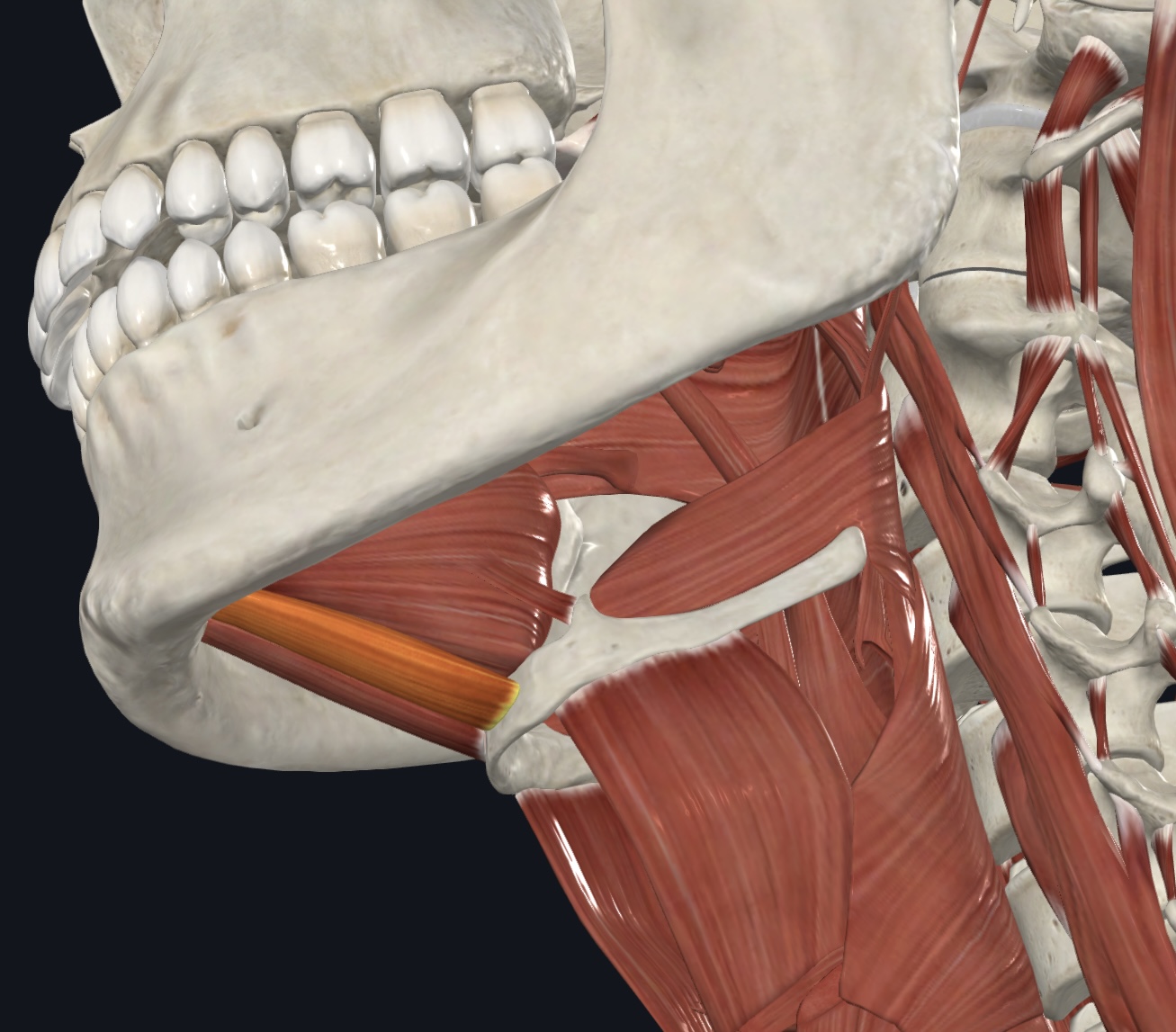
Mylohyoid,
O = mylohyoid line of mandible
I = hyoid bone via median raphe
A = elevates hyoid bone and floor of mouth during swallowing; may also
depress mandible
N = Mandibular branch of the Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
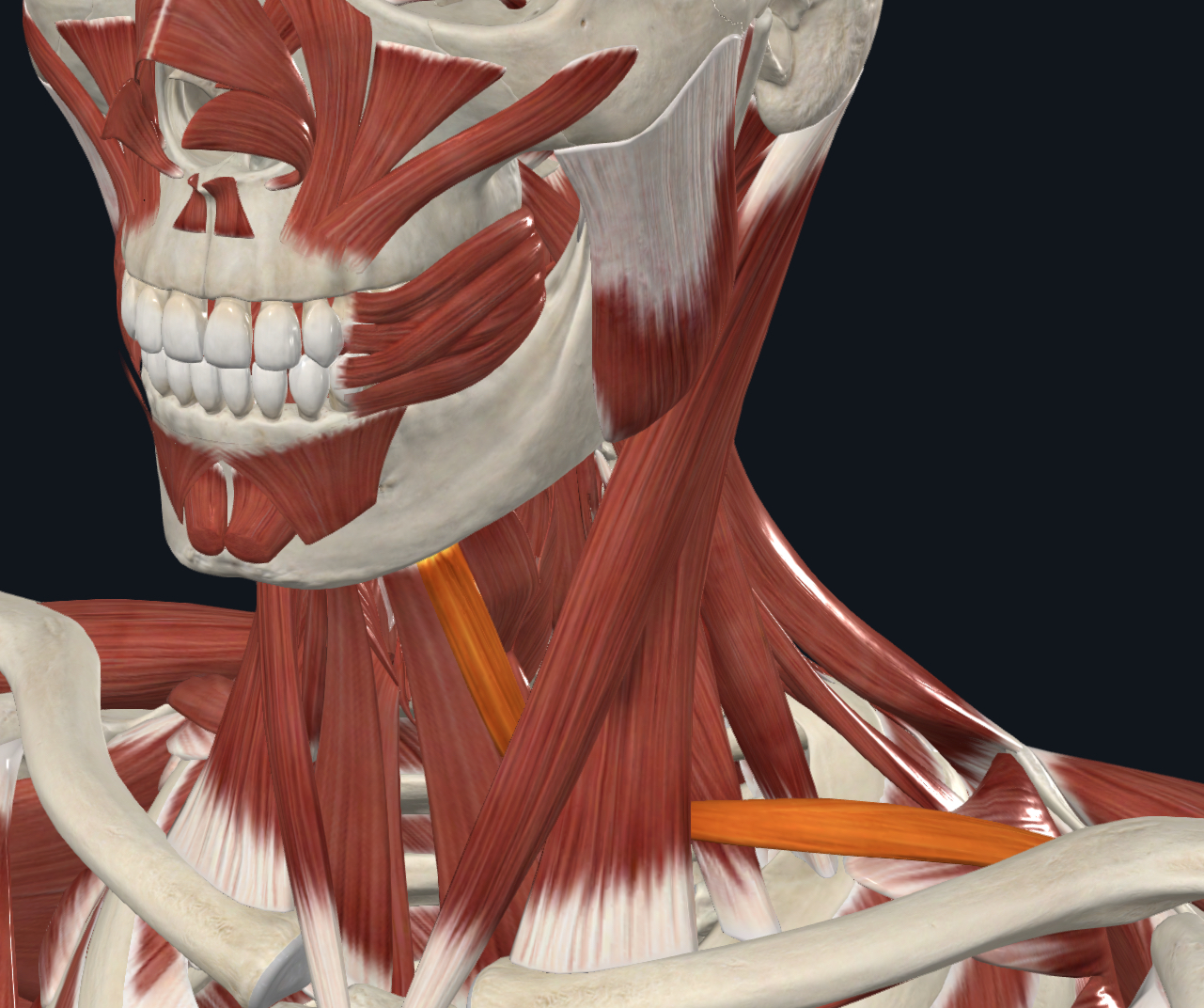
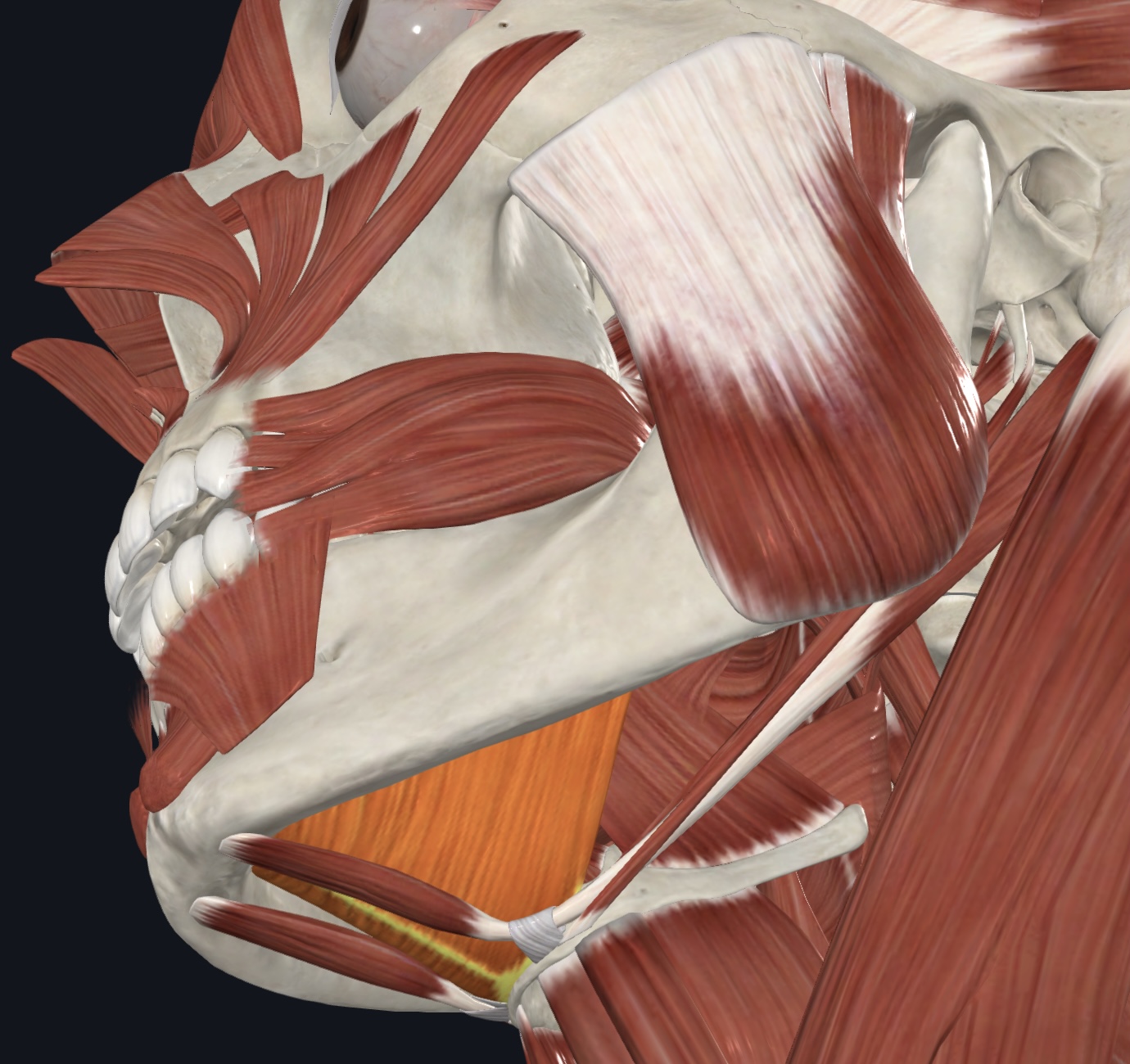
Omohyoid - strap-like muscle with a superior and inferior belly, united by an intermediate tendon,
O = intermediate tendon attached to clavicle and first rib
I = superior belly—hyoid bone, inferior belly-superior margin of scapula
A = depresses and retracts hyoid bone
N = Spinal Nerves C1-C3/Ansa cervicalis
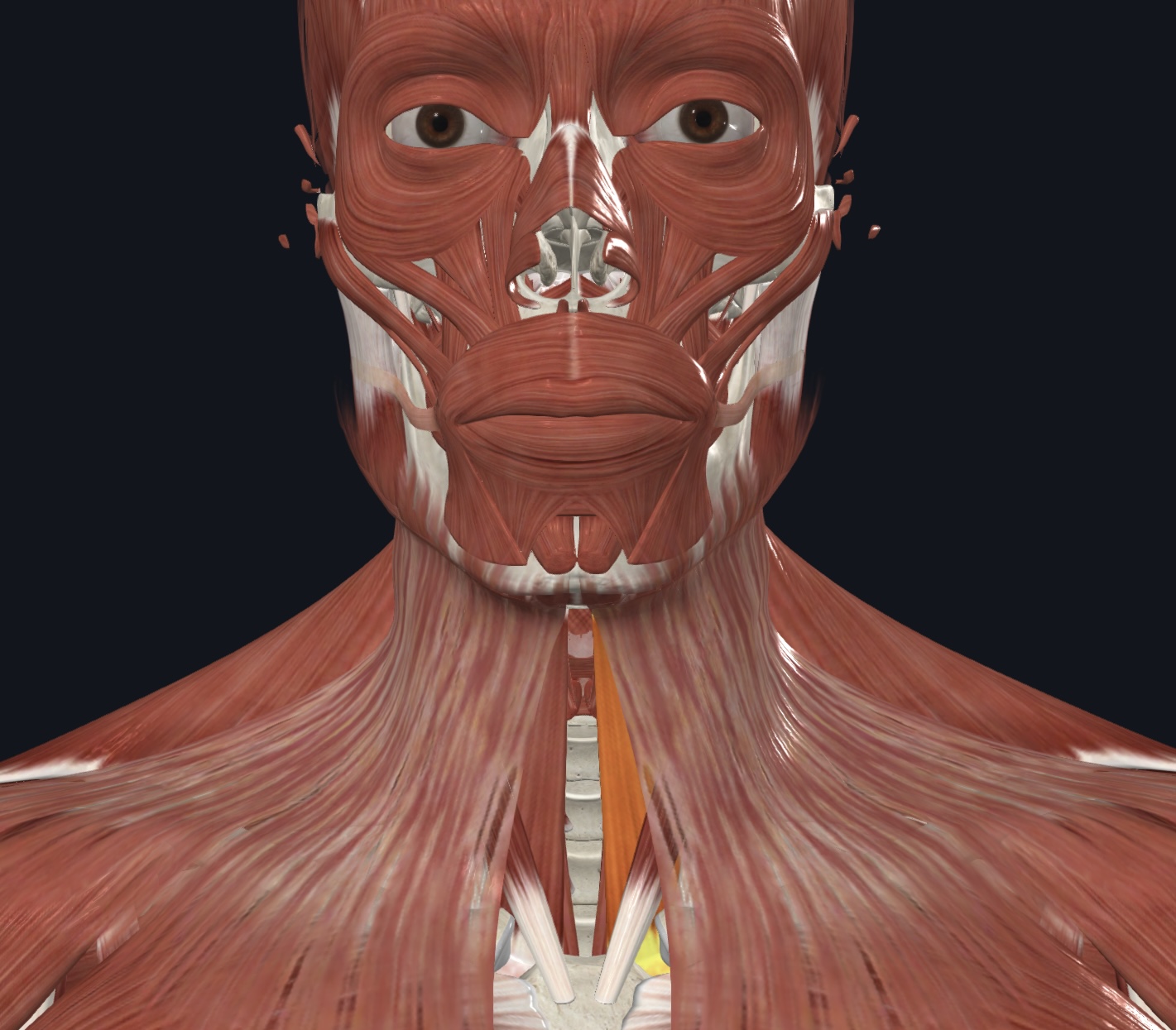
Sternohyoid,
O = manubrium and medial (sternal) end of clavicle
I = hyoid bone
A = depresses larynx and hyoid bone if mandible is fixed
N = Spinal Nerves C1-C3/Ansa cervicalis
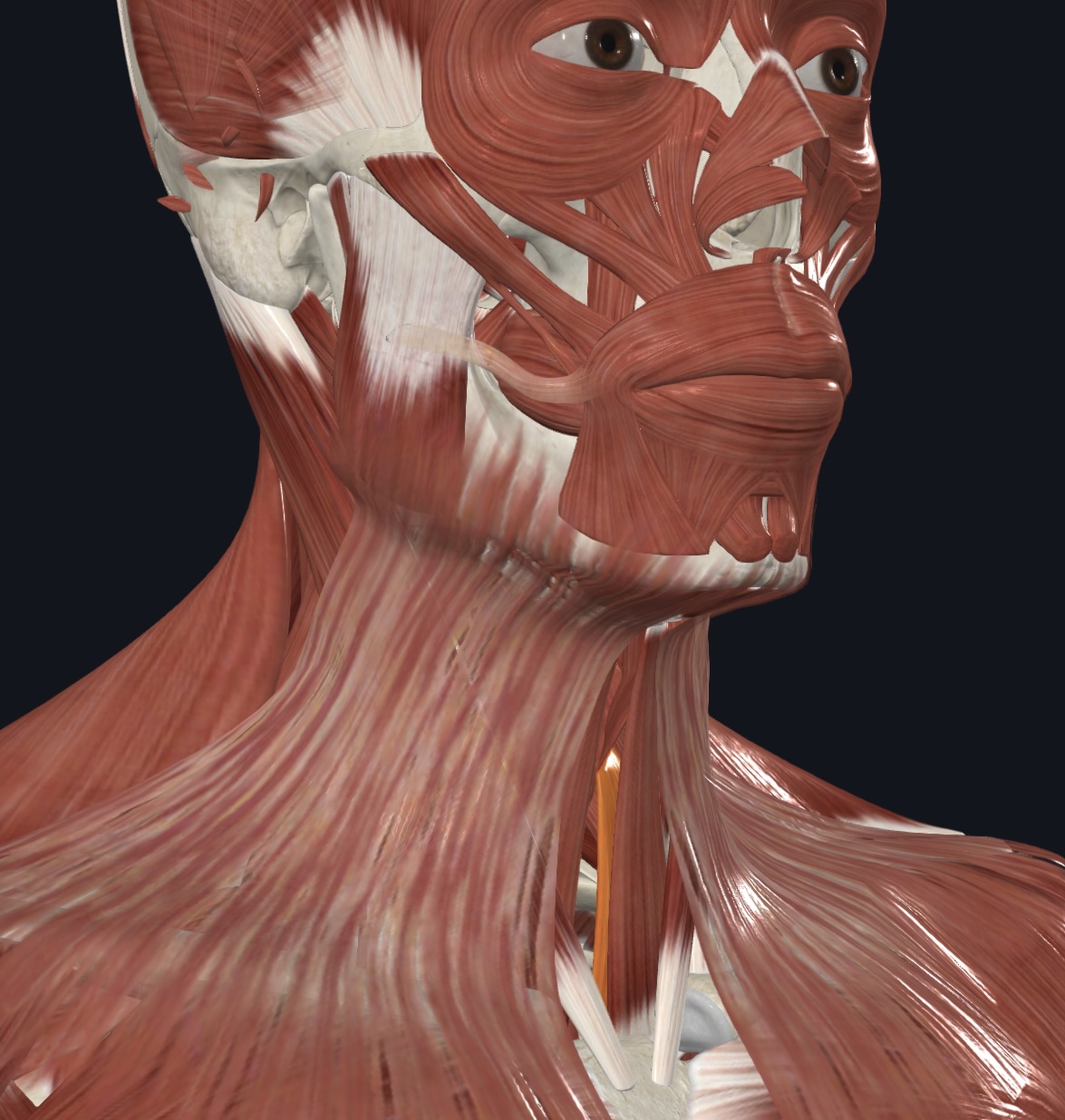
Sternothyroid,
O = posterior surface of manubrium and first costal cartilage
I = thyroid cartilage of larynx
A = depresses larynx and hyoid bone
N = Spinal Nerves C1-C3/Ansa cervicalis
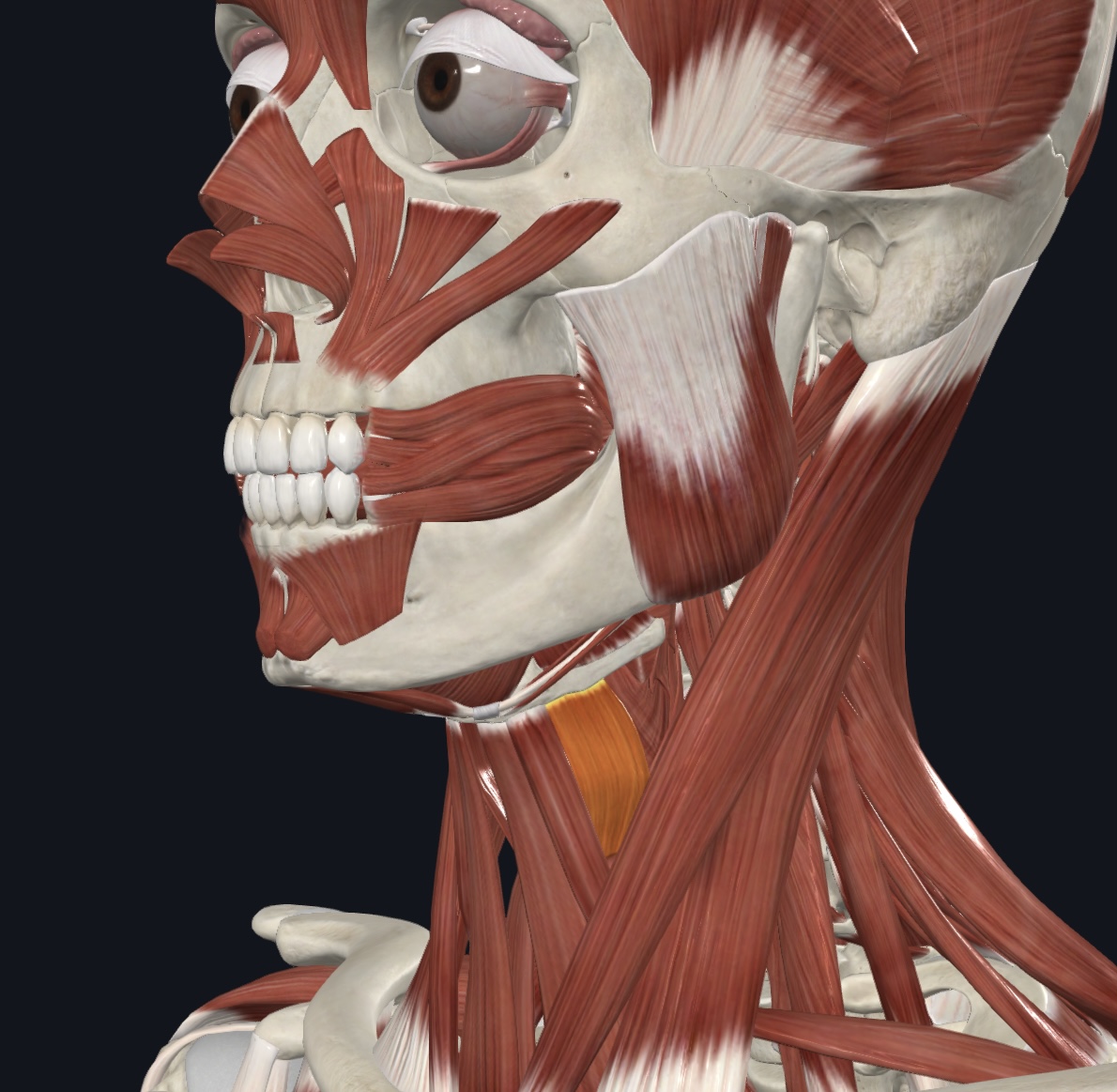
Thyrohyoid,
O = thyroid cartilage
I = hyoid bone
A = depresses hyoid bone; elevates thyroid cartilage
N = cervical spinal nerves C1 & C2 via hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
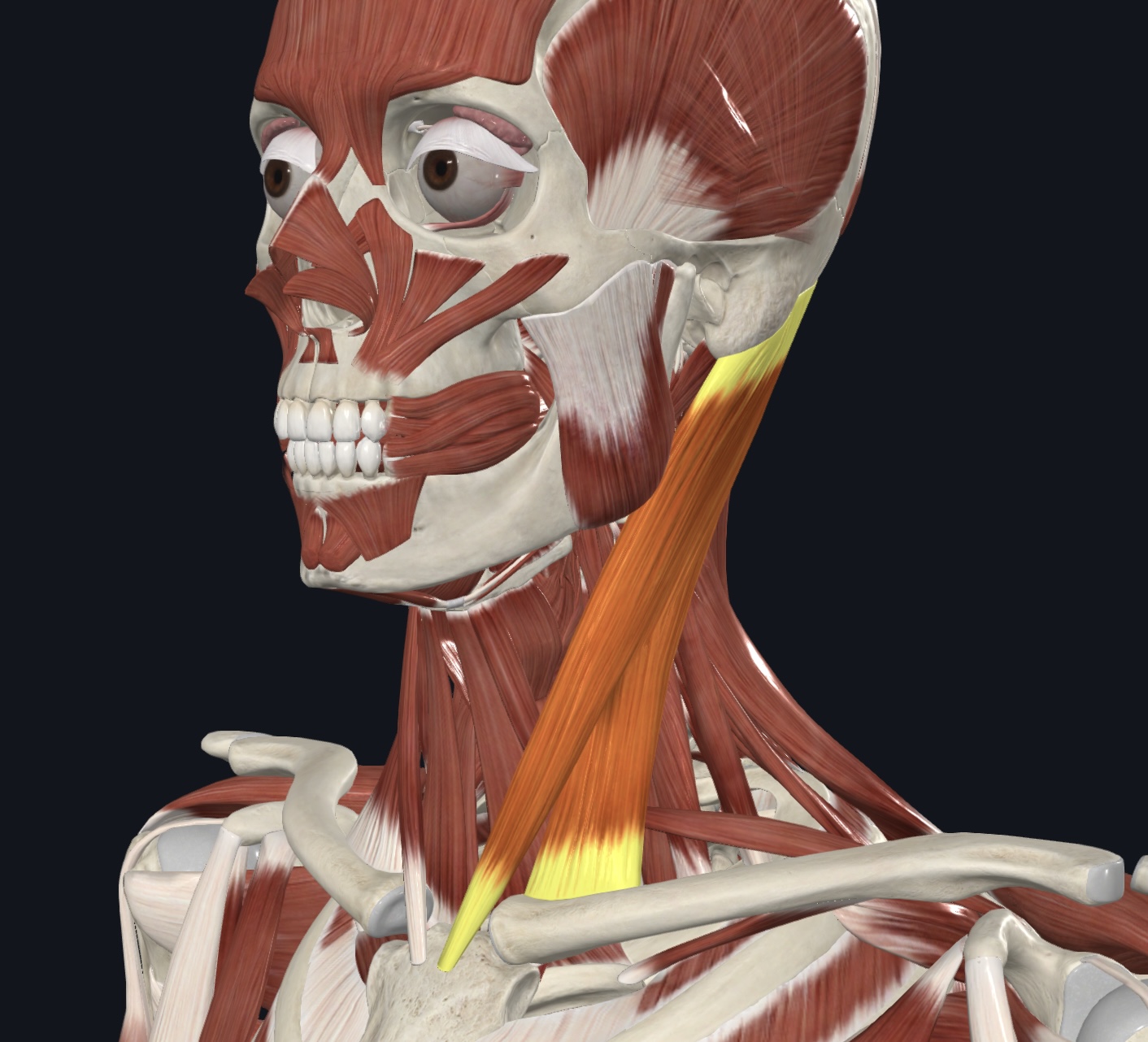
Muscle of the Anterolateral Neck
Sternocleidomastoid - sternal and clavicular heads,
O = sternal head--manubrium; clavicular head--medial end of clavicle
I = mastoid process of temporal bone
A = prime mover of skull flexion (simultaneous bilateral contraction); skull rotation to opposite side
and tilts or laterally rotates skull toward same side (unilateral contraction)
N = Accessory Nerve (CN XI) and cervical spinal nerves C2 & C3
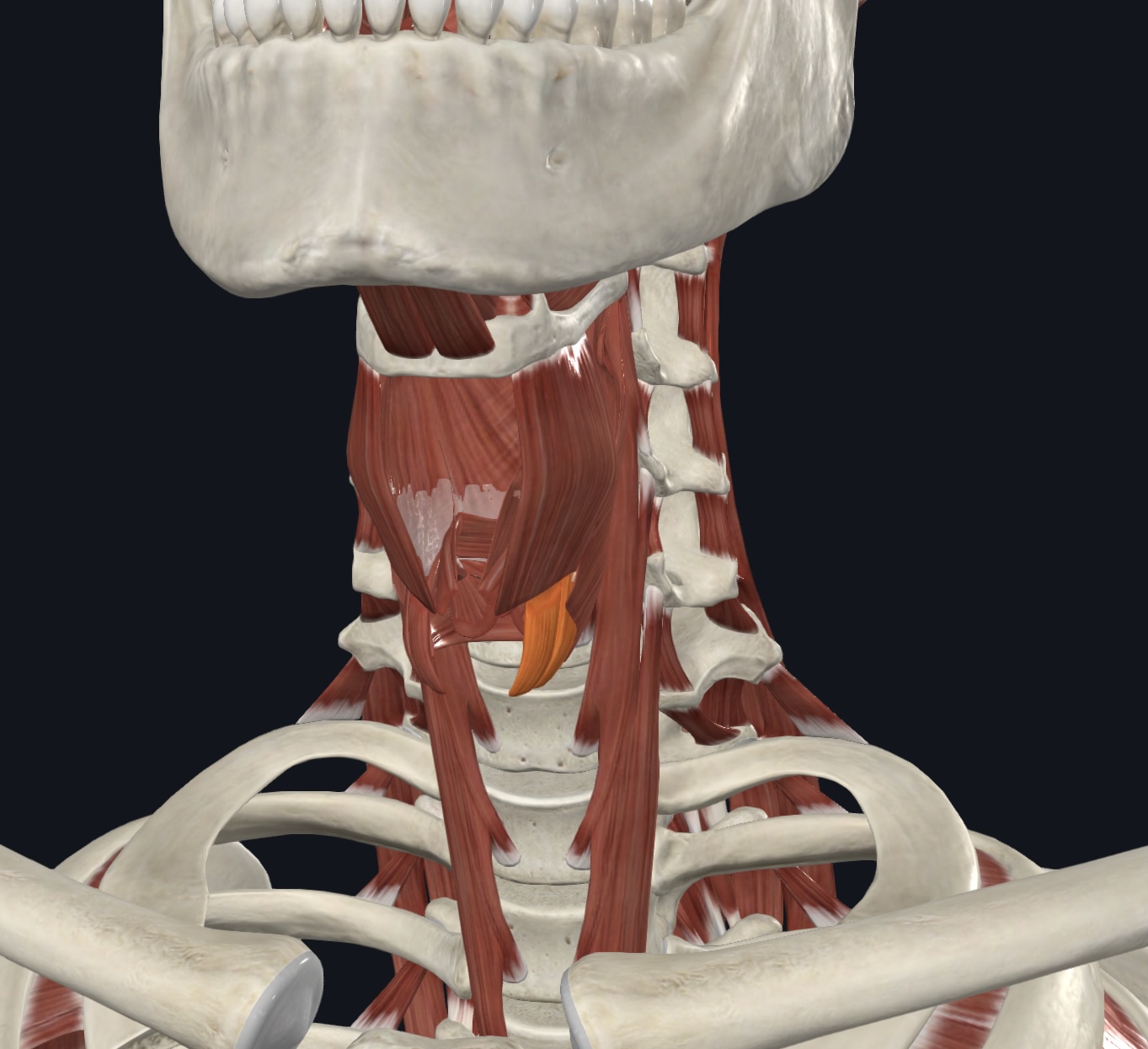
Intrinsic Muscle of the Larynx
Cricothyroid,
O = cricoid cartilage
I = thyroid cartilage
A = elevates cricoid cartilage during swallowing; depresses thyroid cartilage and tilts it forward during phonation
N = Vagus Nerve (CN X)
Muscles of the Anterolateral Abdominal Wall: (I.D. Only; note direction of the fibers)
(7). External oblique
Internal oblique
Transversus abdominis
Rectus abdominis
Linea alba
Rectus sheath
Tendinous intersections/Tendinous Inscriptions, (pg. 336) “six-pack”
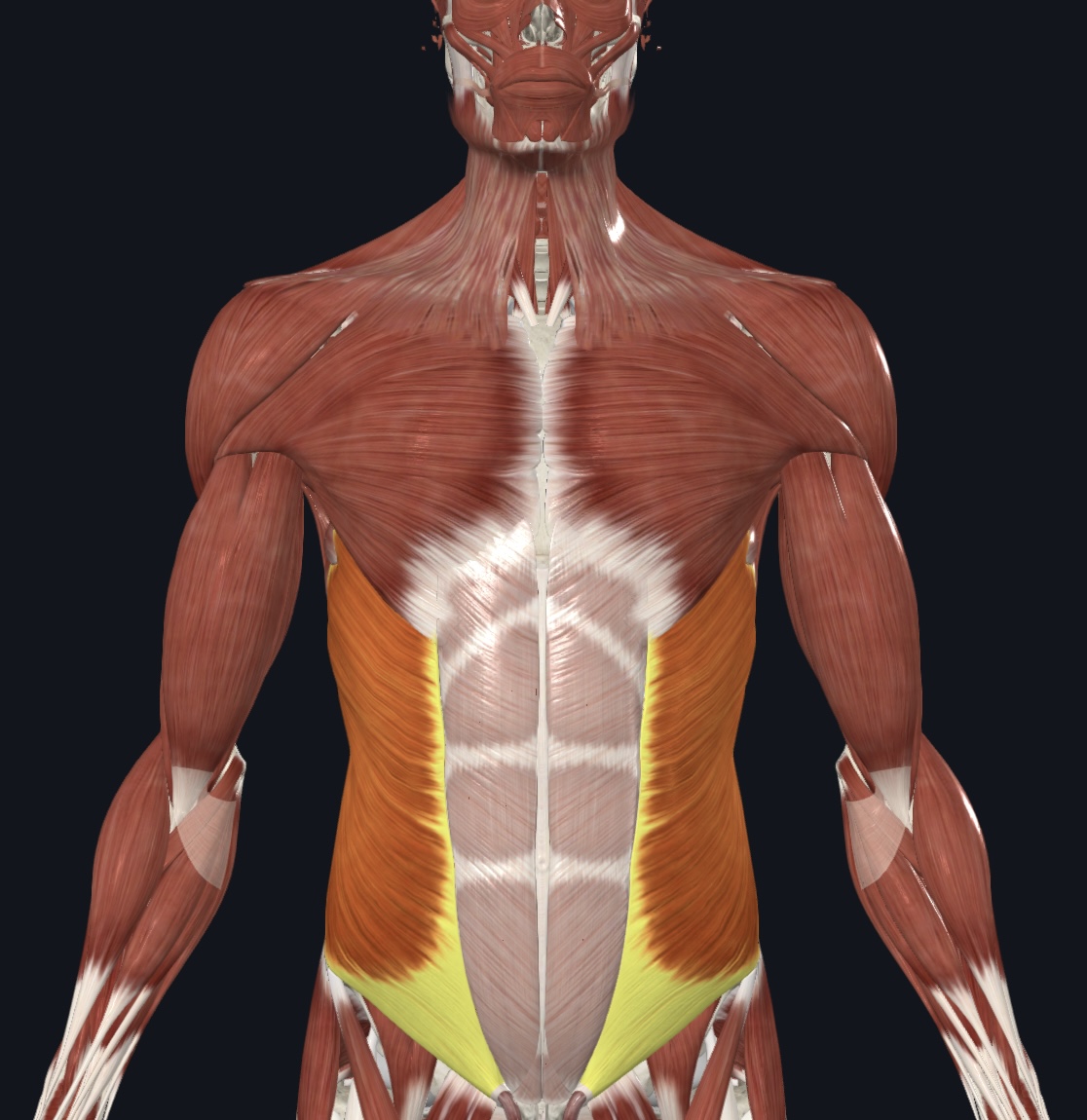
External Oblique
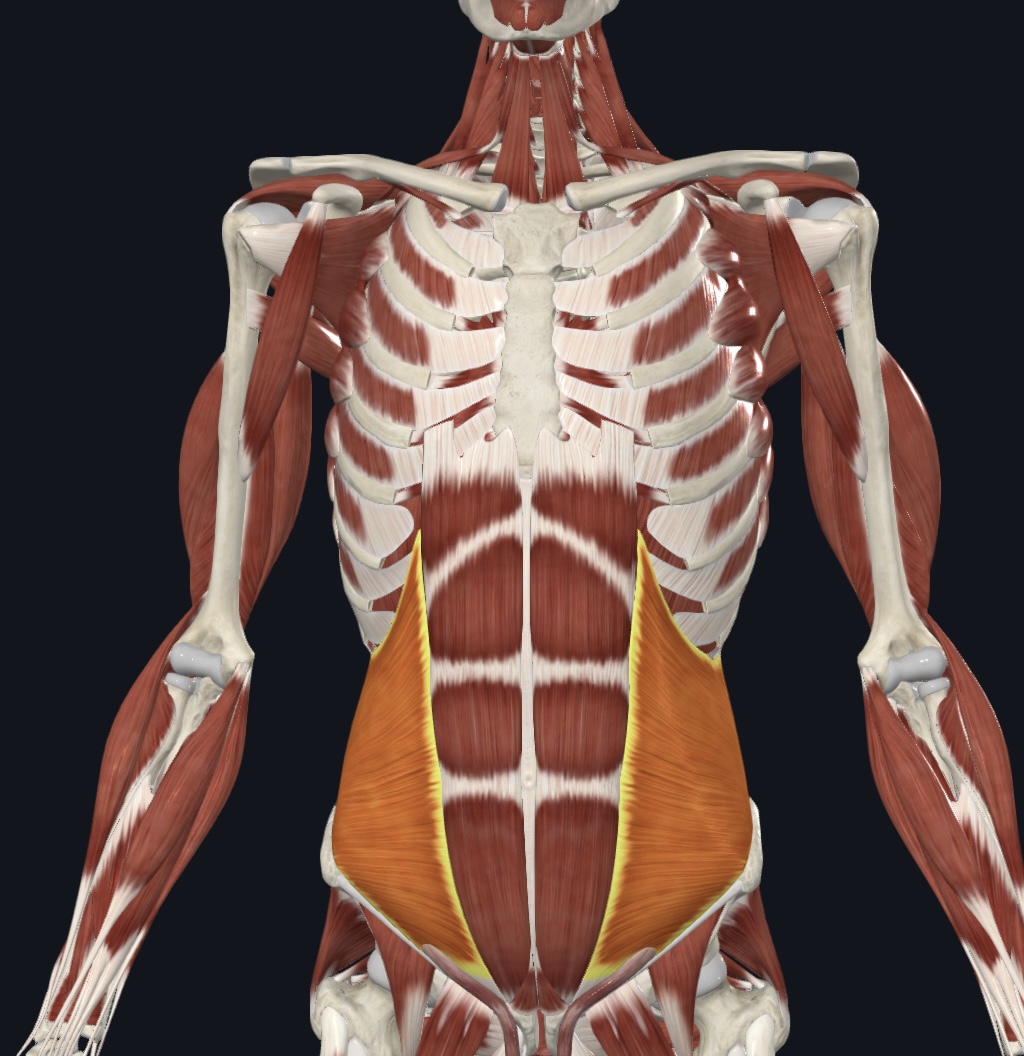
Internal Oblique
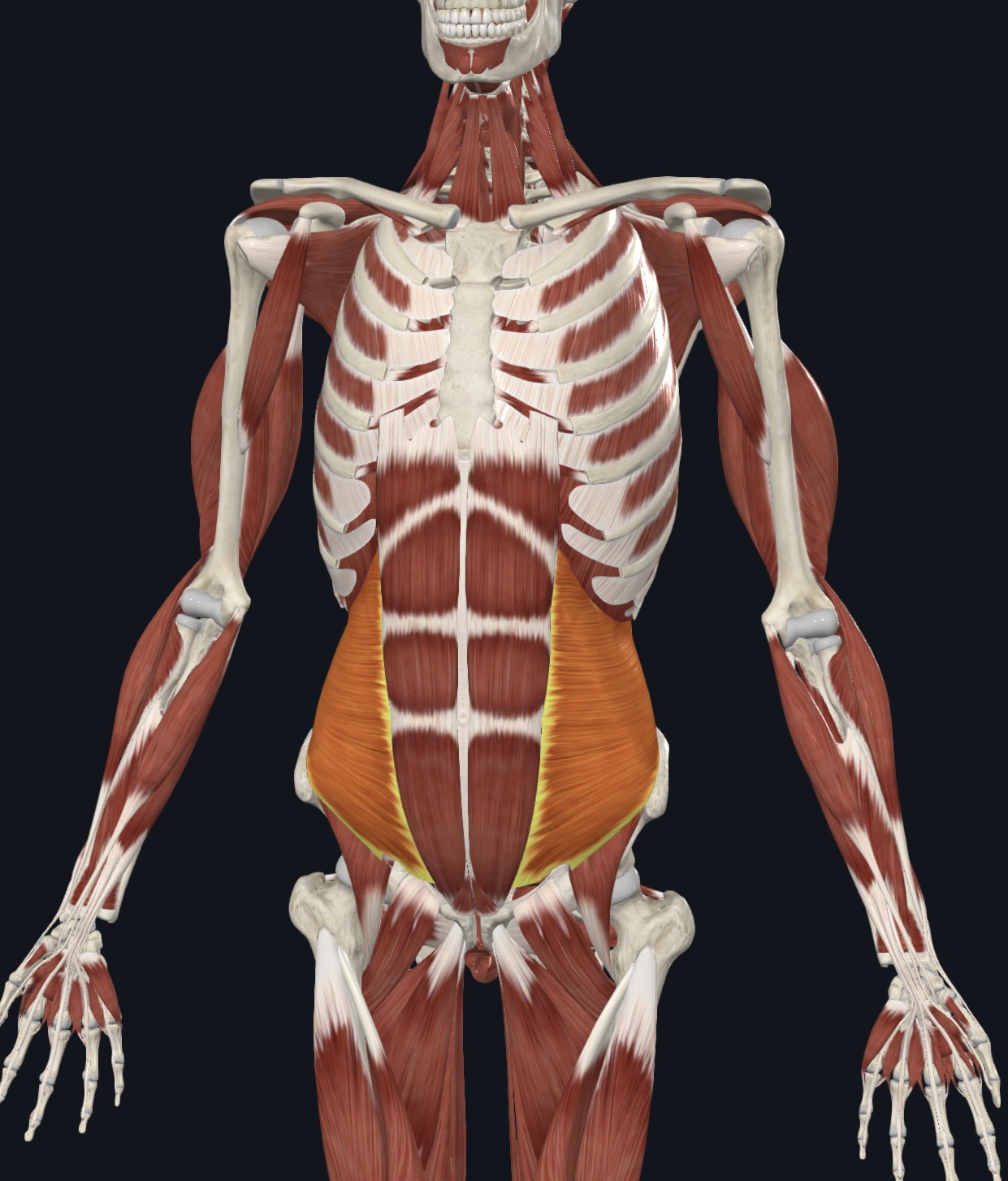
Transverse abdominis
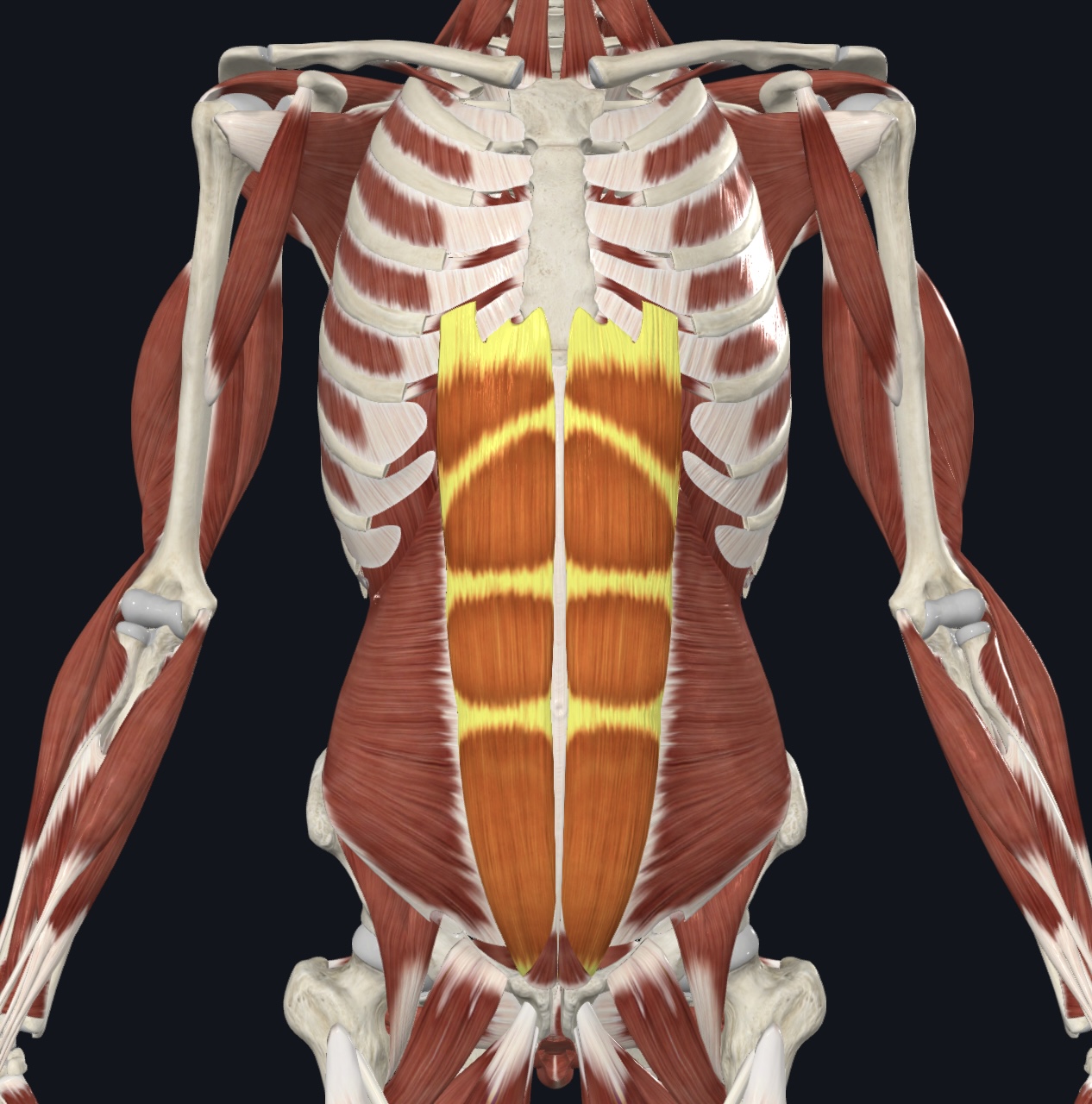
Rectus abdominis
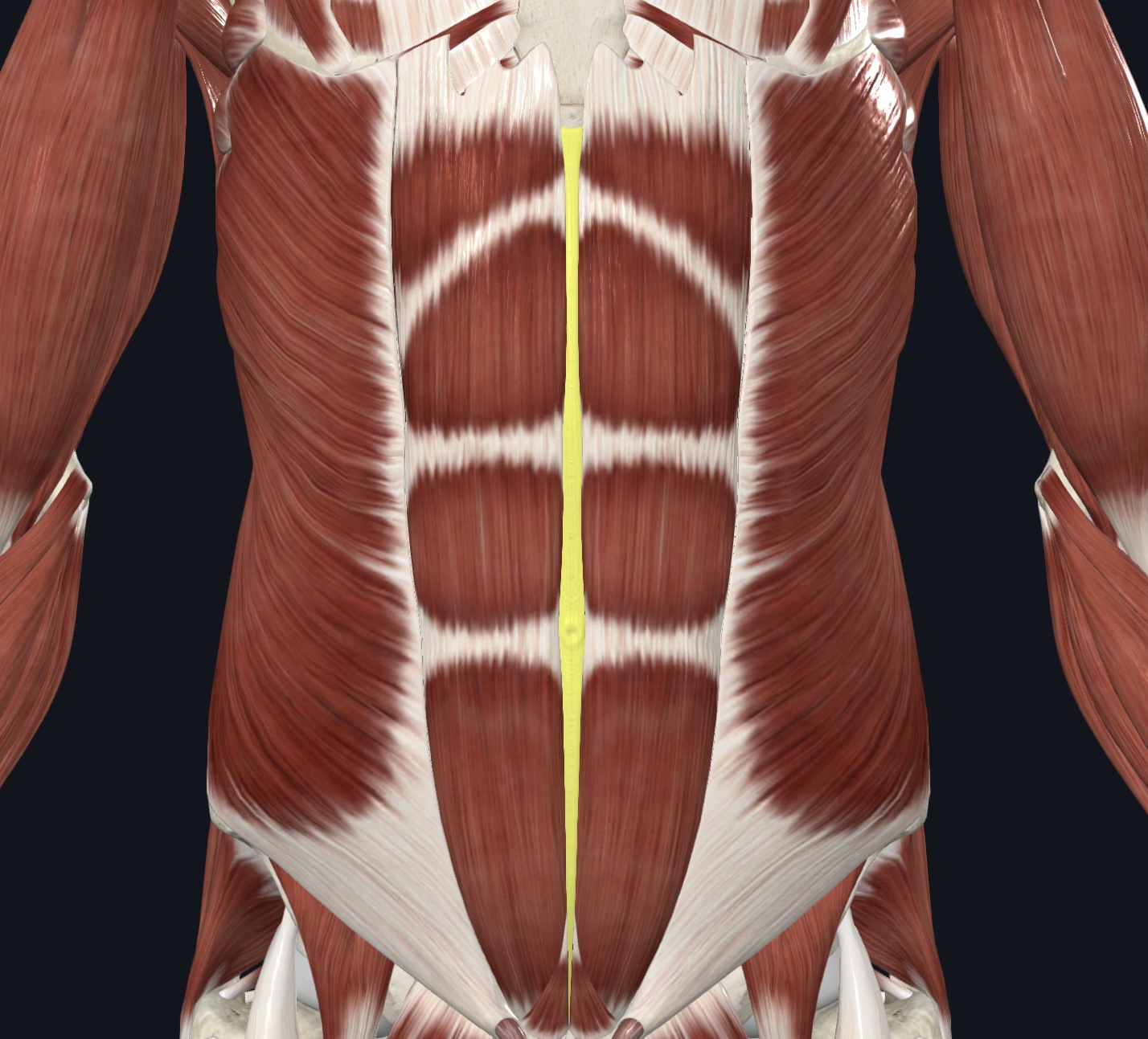
Linea abla
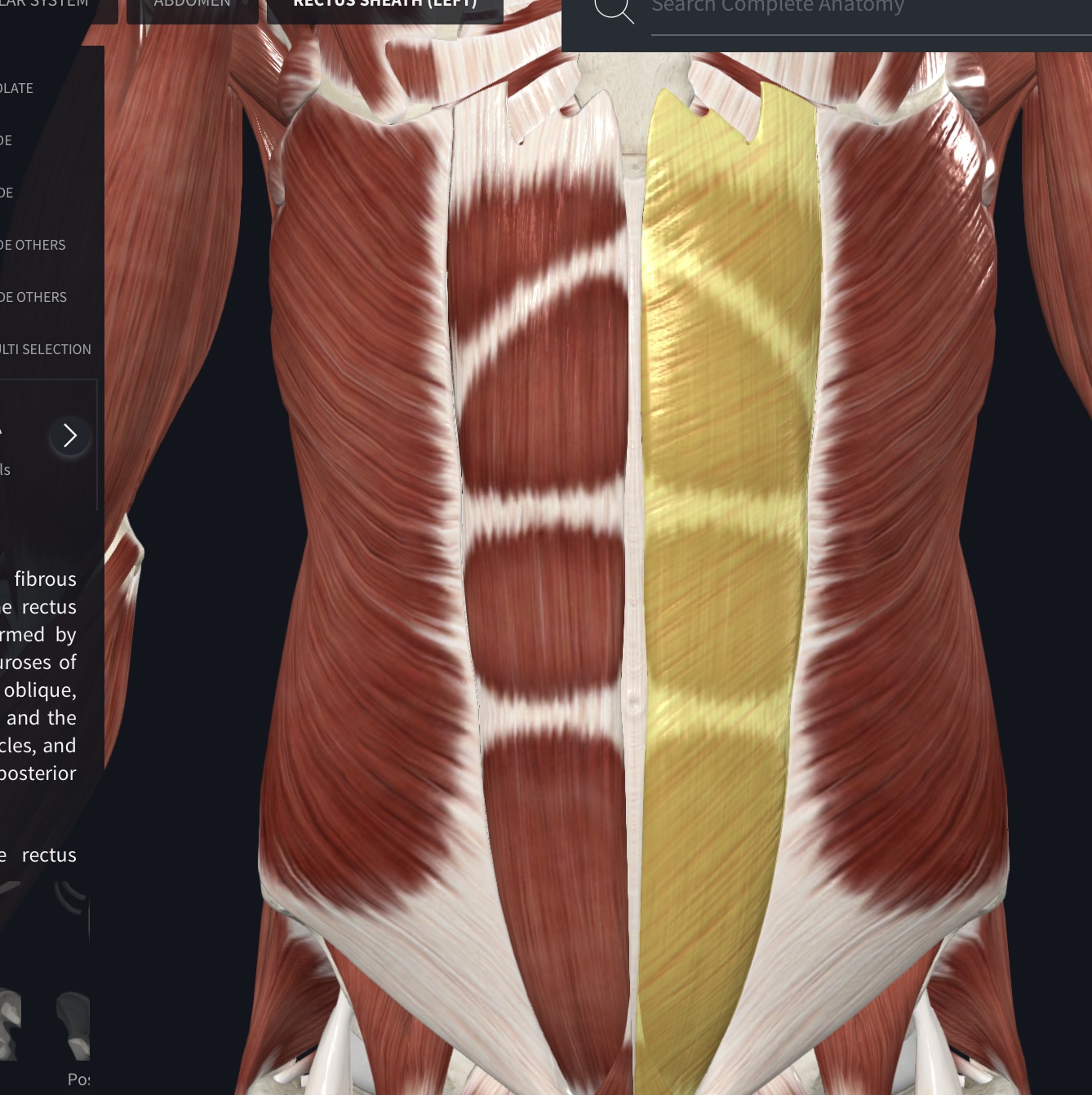
Rectus sheath
Fibrous bands that cross the rectus abdominis muscle, dividing it into distinct segments
Tendinous intersections/Tendinous Inscriptions (pg. 336) “six-pack”[There should be 19 muscles .]
Muscles of the Anterior Shoulder Joint: Movements of the Humerous
(3)
Pectoralis major - both sternocostal and clavicular head
Deltoid
Coracobrachialis
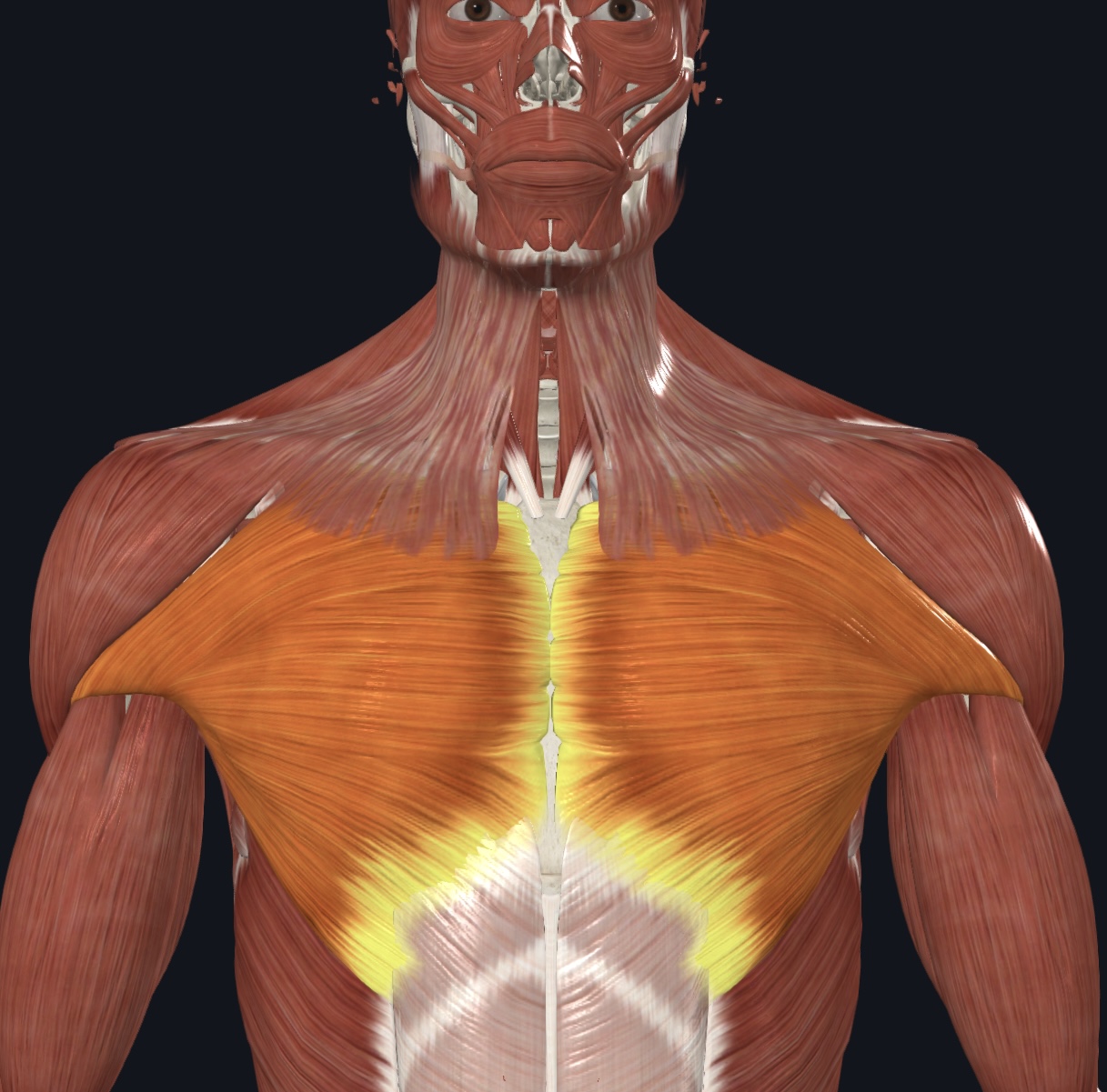
Pectoralis major - both sternocostal and clavicular head,
O = clavicular head--clavicle; sternocostal head--sternum and costal cartilages 1-6
I = greater tubercle of humerus
A = prime mover of arm flexion; adducts and medial rotates arm
N = Medial and Lateral Pectoral Nerves
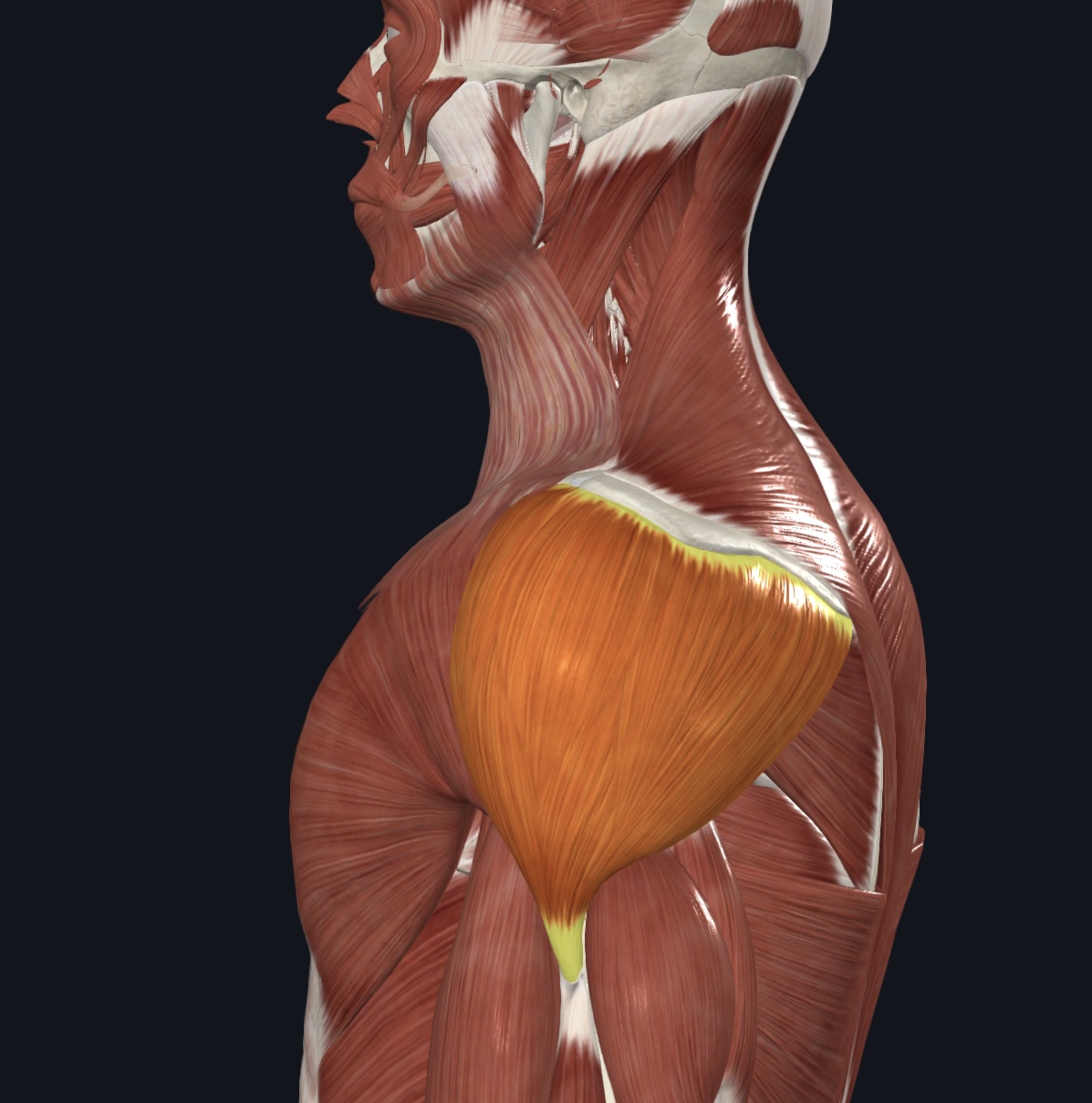
Deltoid,
O = spine and acromion process of scapula, lateral 1/3 of clavicle
I = deltoid tuberosity of humerus
A = prime mover of arm abduction; synergist in flexion & extension of arm
N = Axillary Nerve
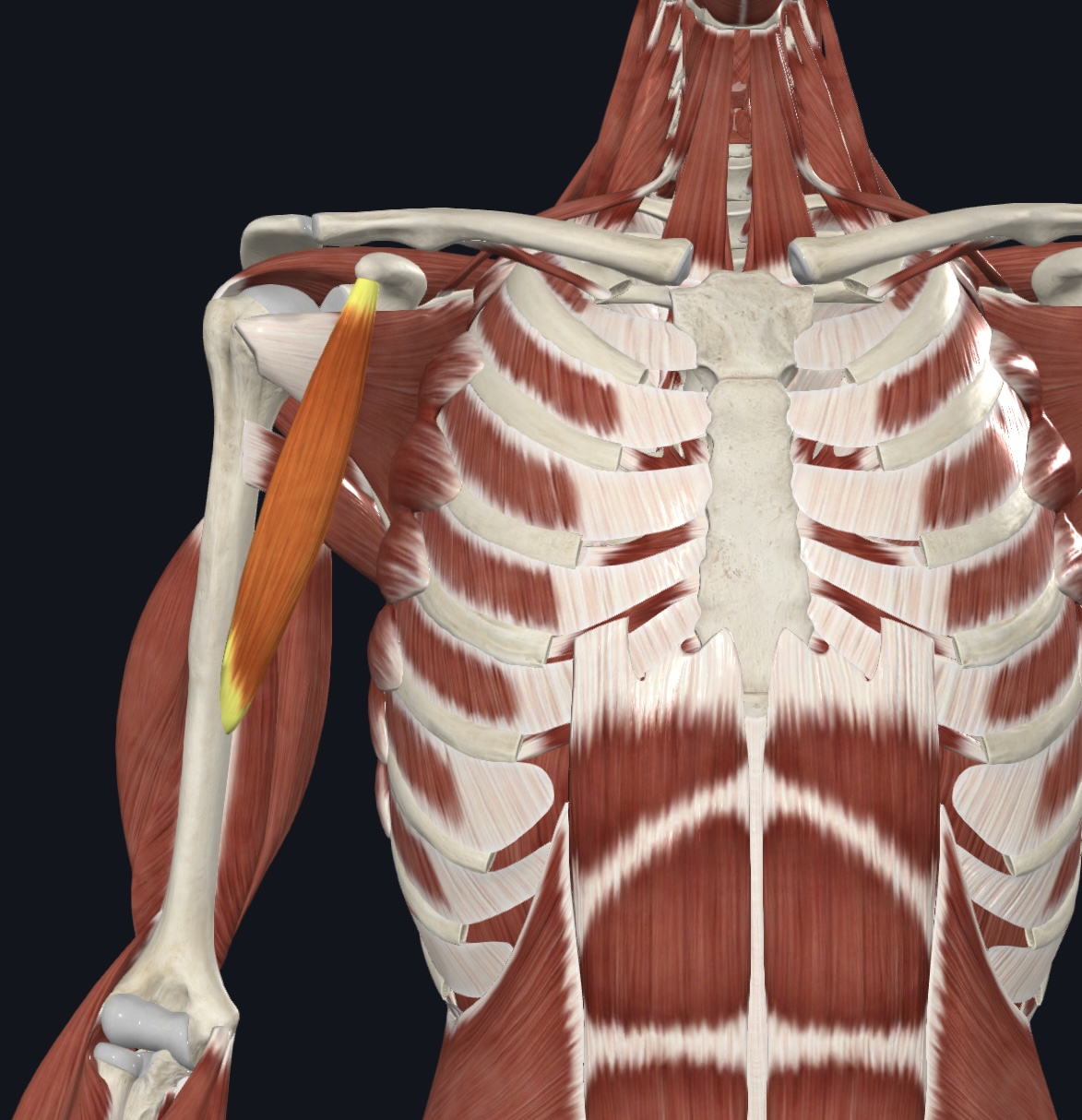
Coracobrachialis,
O = coracoid process of scapula
I = mid-medial shaft of humerus
A = flexes and adducts arm
N = Musculocutaneous nerve
Muscles of the Anterior Thorax: Movements of the Scapula
(2)
Serratus anterior (‘boxer’s muscle")
Pectoralis minor
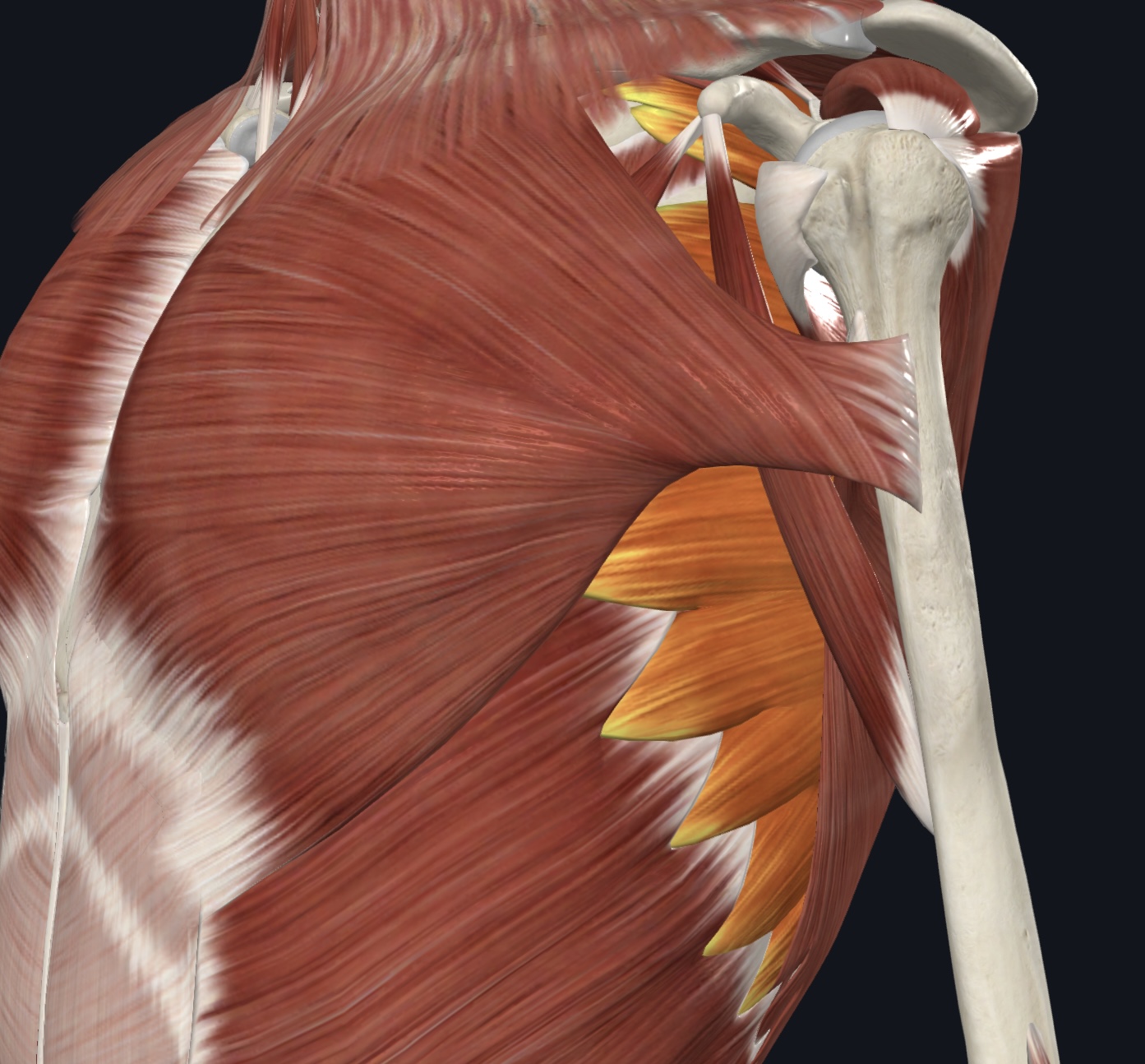
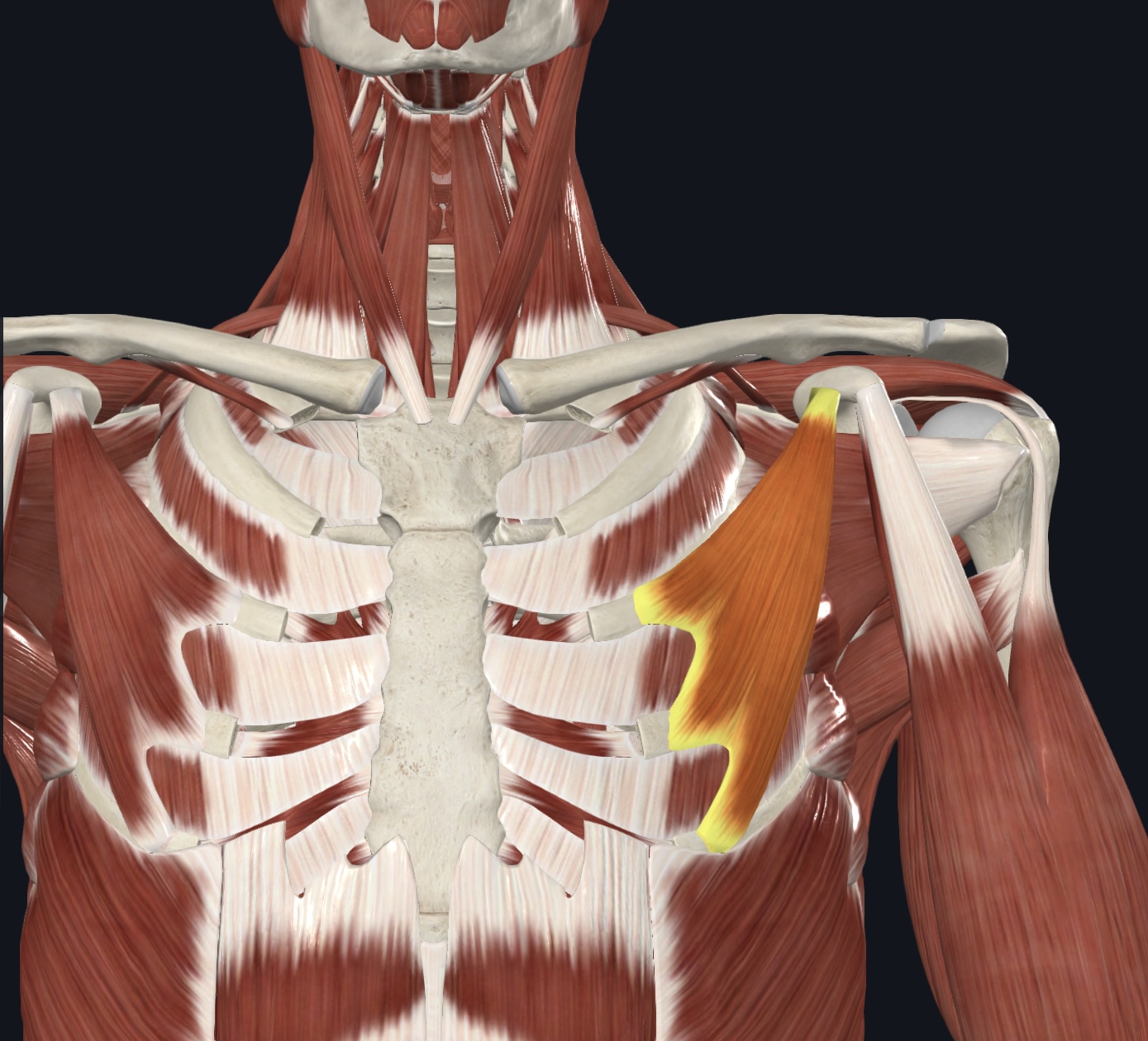
Serratus anterior (“boxer’s muscle”),
O = ribs 1-8 (or 9)
I = vertebral border of scapula (ventral surface)
A = Protracts shoulder; rotates scapula so glenoid cavity moves superiorly (upward rotation)
N = Long Thoracic Nerve
Pectoralis minor,
O = ribs 3-5 (ventral surface)
I = coracoid process of scapula
A = Depresses and protracts shoulder; rotates scapula so glenoid cavity move inferiorly (downward rotation);
elevates ribs if scapula is stationary.
N = Medial & Lateral Pectoral Nerve
Muscles of the Anterior Humerus
(3)
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
Brachioradialis
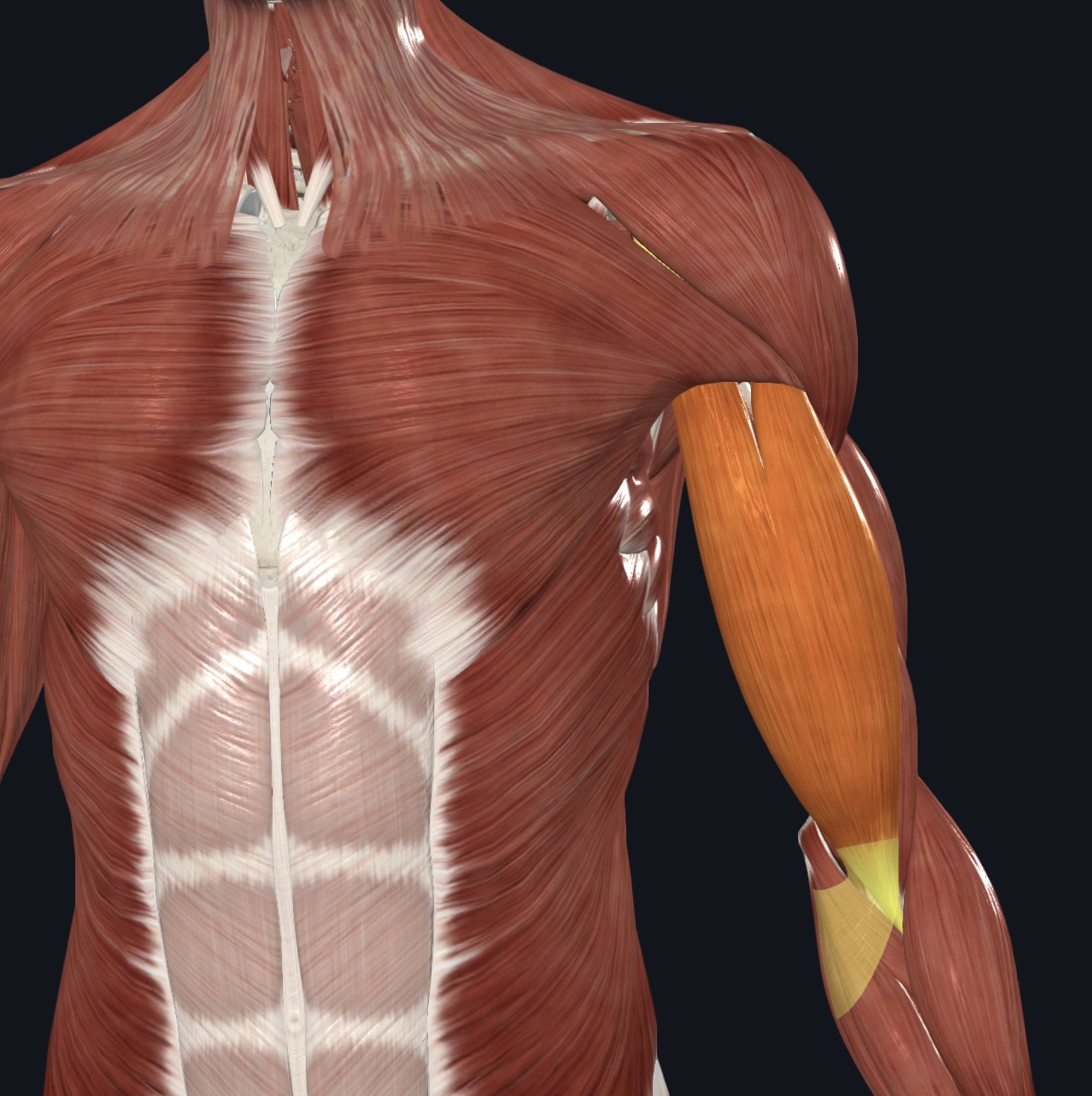
Biceps brachii - long and short heads,
O = long head--supraglenoid tubercle of scapula (descends within intertubercular groove of humerus);
short head--coracoid process of scapula
I = radial tuberosity of radius
A = major forearm flexor; supinates forearm; weak flexor of arm
N = Musculocutaneous Nerve
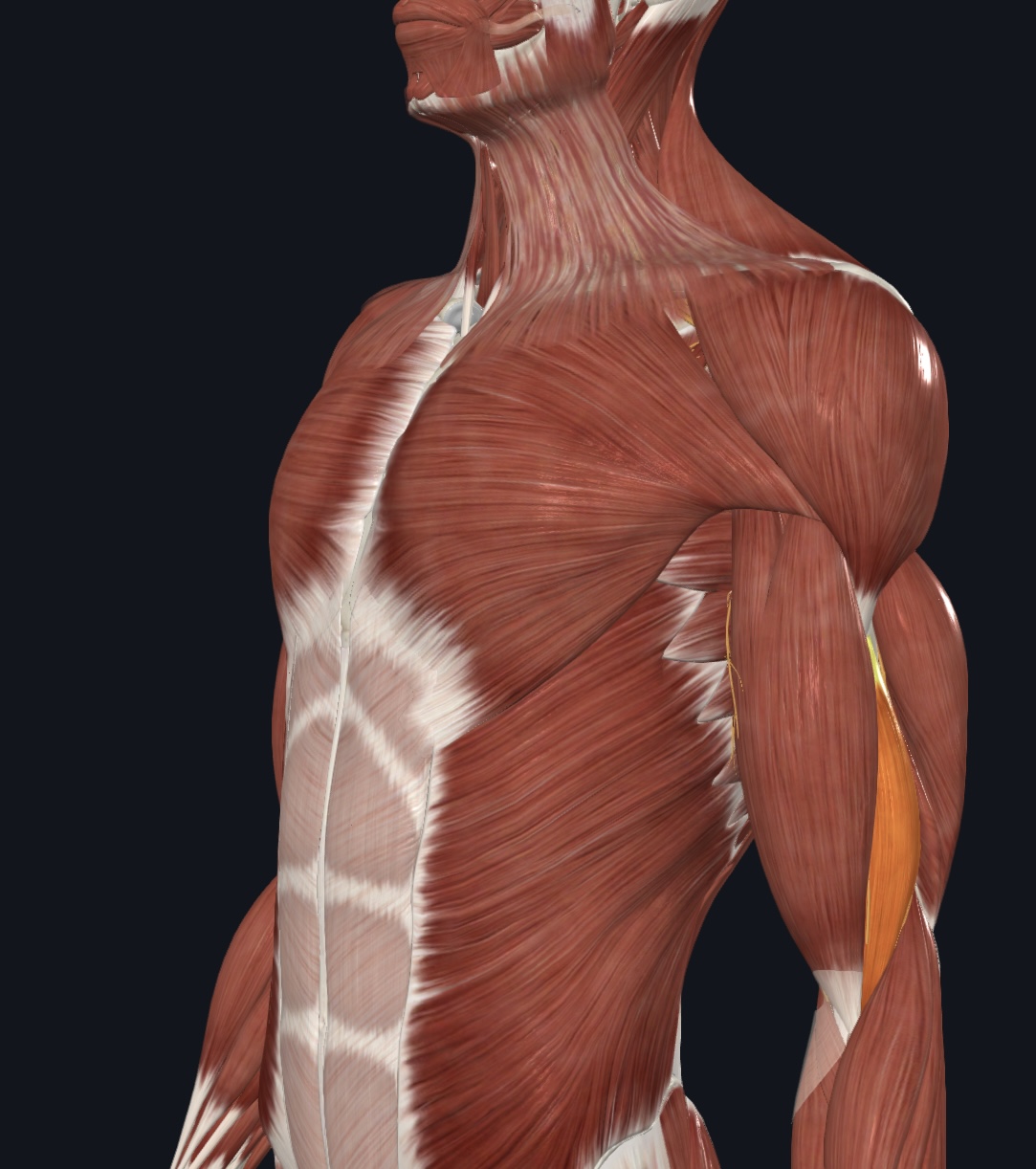
Brachialis,
O = anterior, distal surface of humerus
I = coronoid process and tuberosity of ulna
A = major forearm flexor
N = Musculocutaneous Nerve
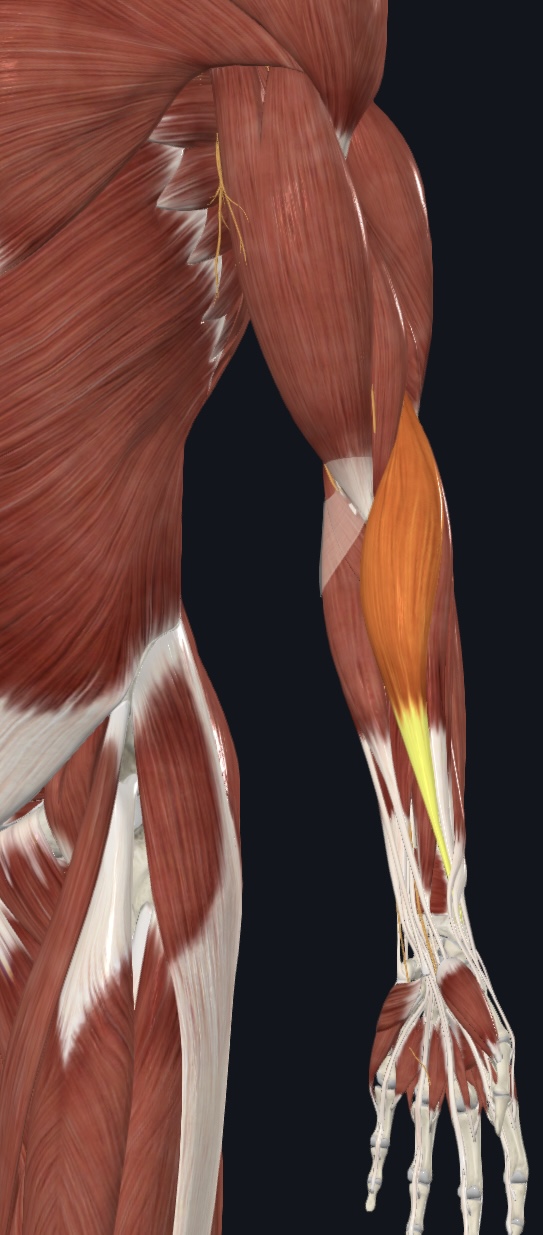
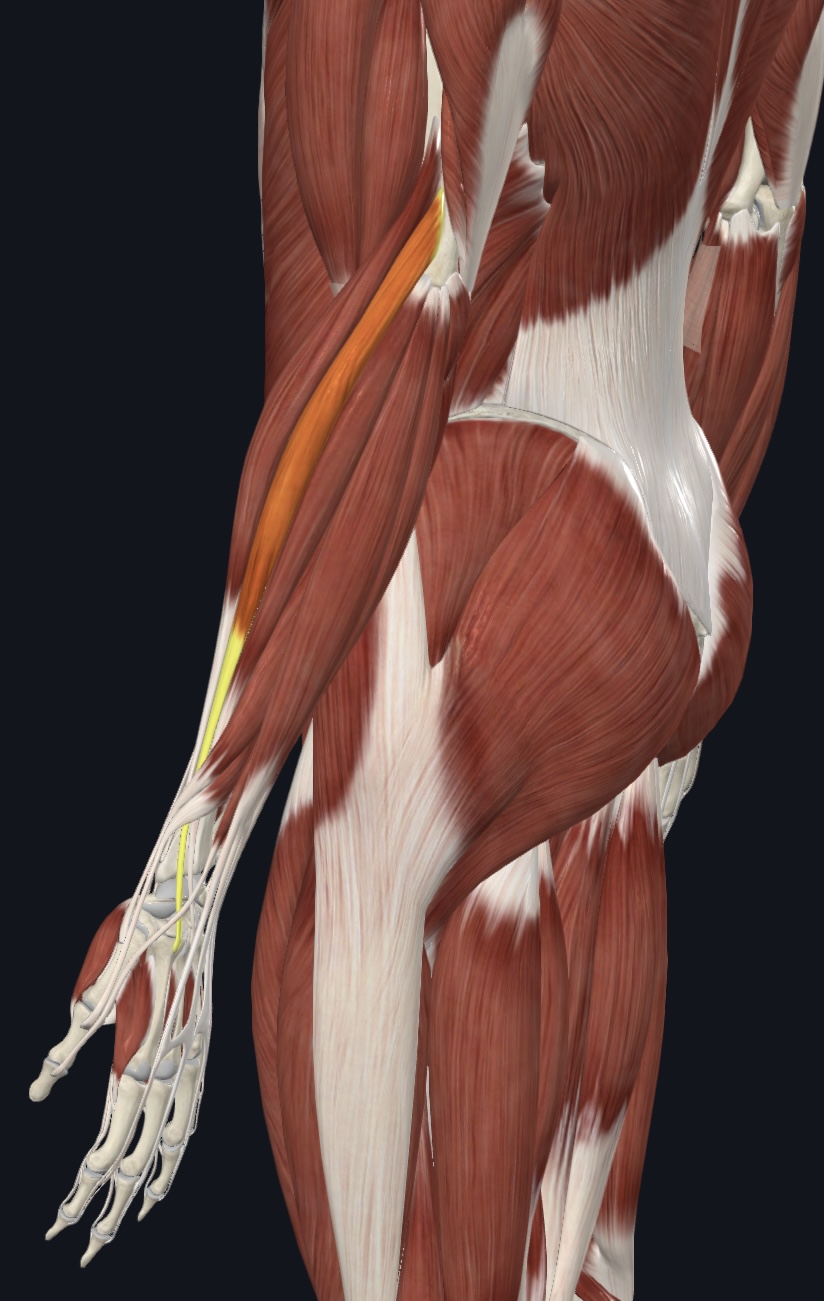
Brachioradialis,
O = lateral epicondyle of humerus
I = styloid process of radius
A = forearm flexion
N = Radial Nerve
Muscles of the Posterior Forearm
(10) All are innervated by the Radial Nerve
Extensor carpi radialis longus
Extensor carpi radialis brevis
Abductor pollicis longus
Extensor pollicis brevis
Extensor pollicis longus
Extensor indicis
Extensor digitorum
Extensor digiti minimi
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Extensor retinaculum (dense fascia, I.D. only)
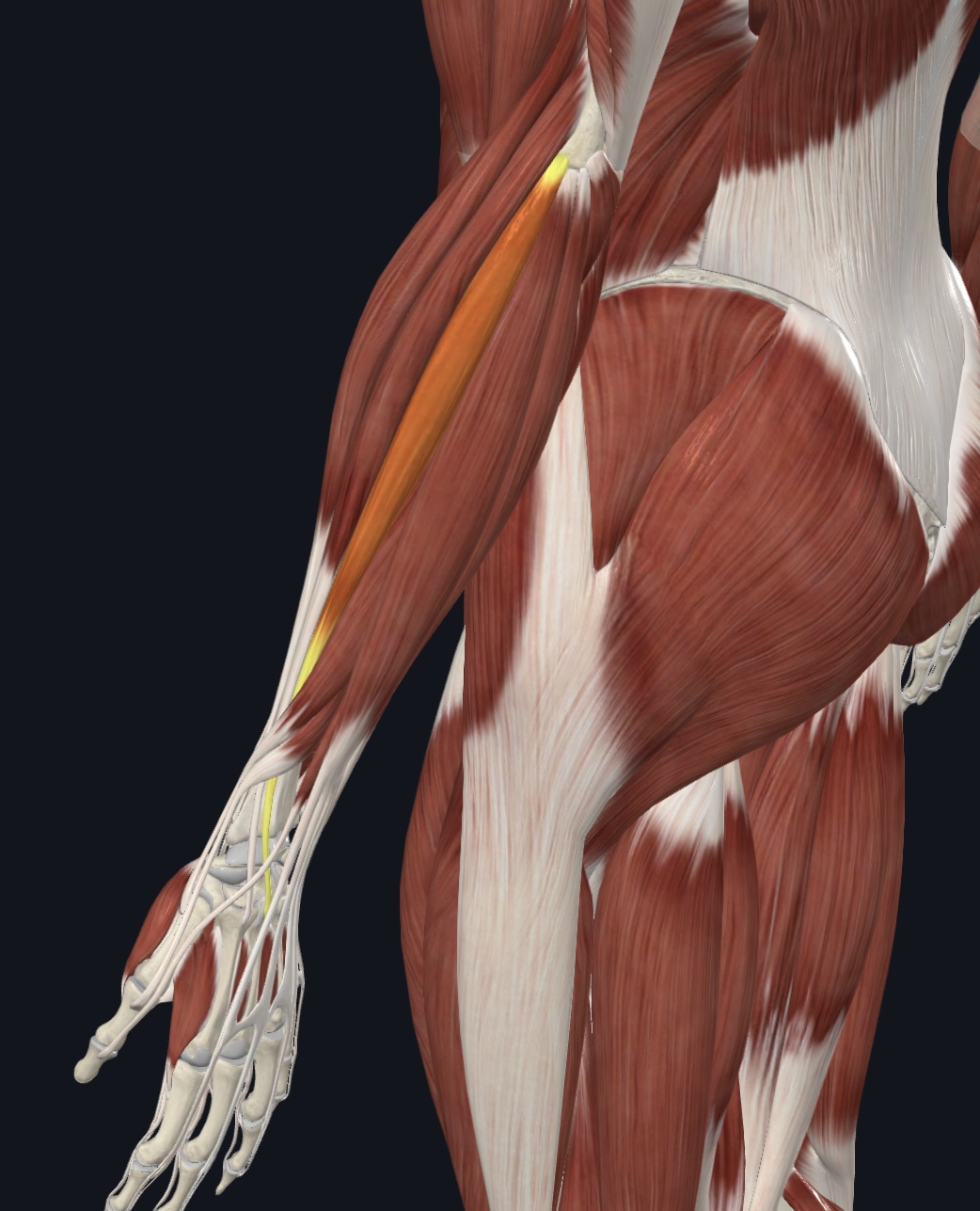
Extensor carpi radialis longus,
O = lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus
I = base of metacarpal 2
A = extends and abducts hand
Extensor carpi radialis brevis,
O = lateral epicondyle of humerus
I = base of metacarpal 3
A = extends and abducts hand
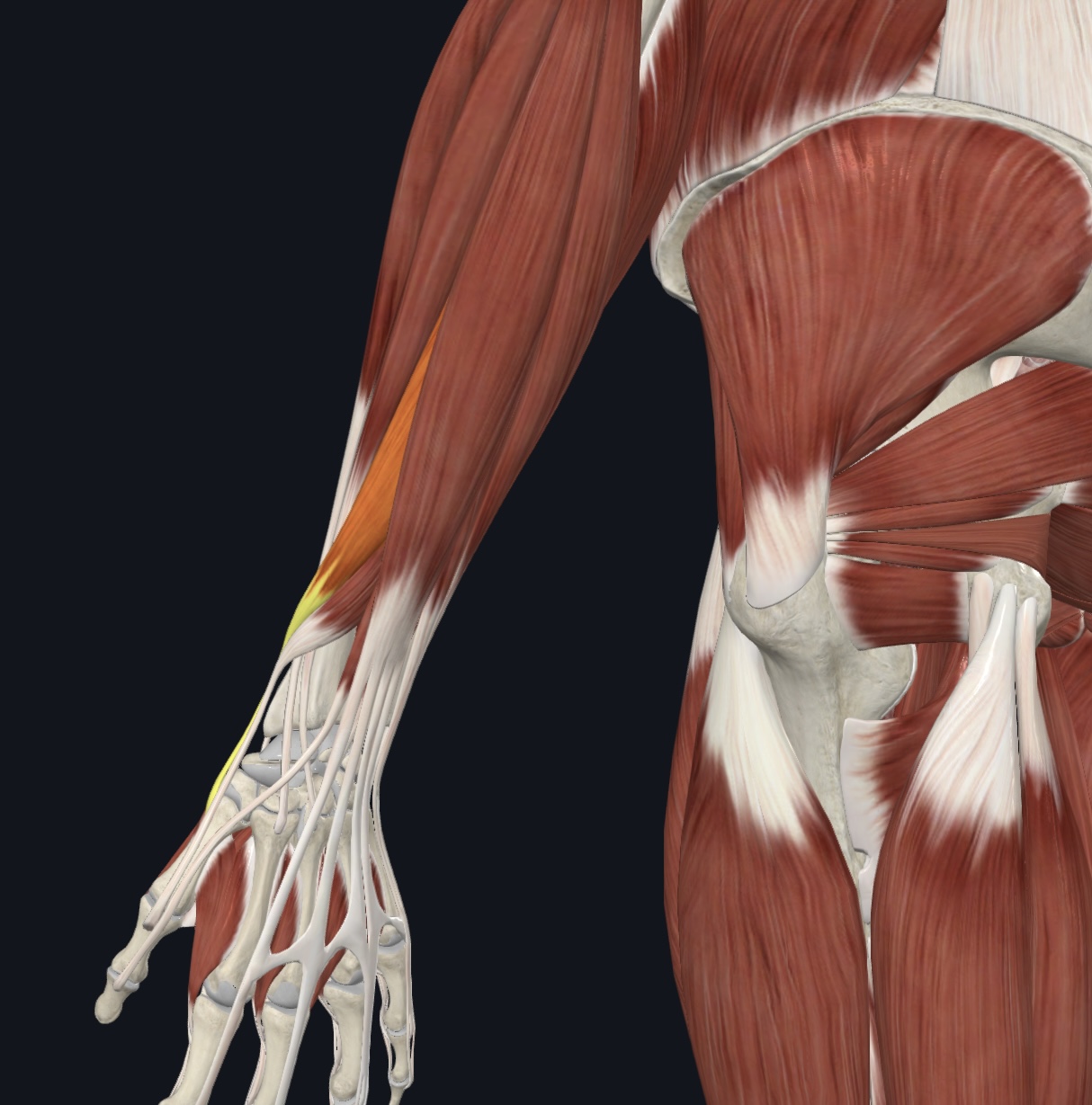
Abductor pollicis longus,
O = proximal posterior shafts of ulna and radius
I = lateral margin of metacarpal 1
A = extends and abducts thumb; weak abductor of hand
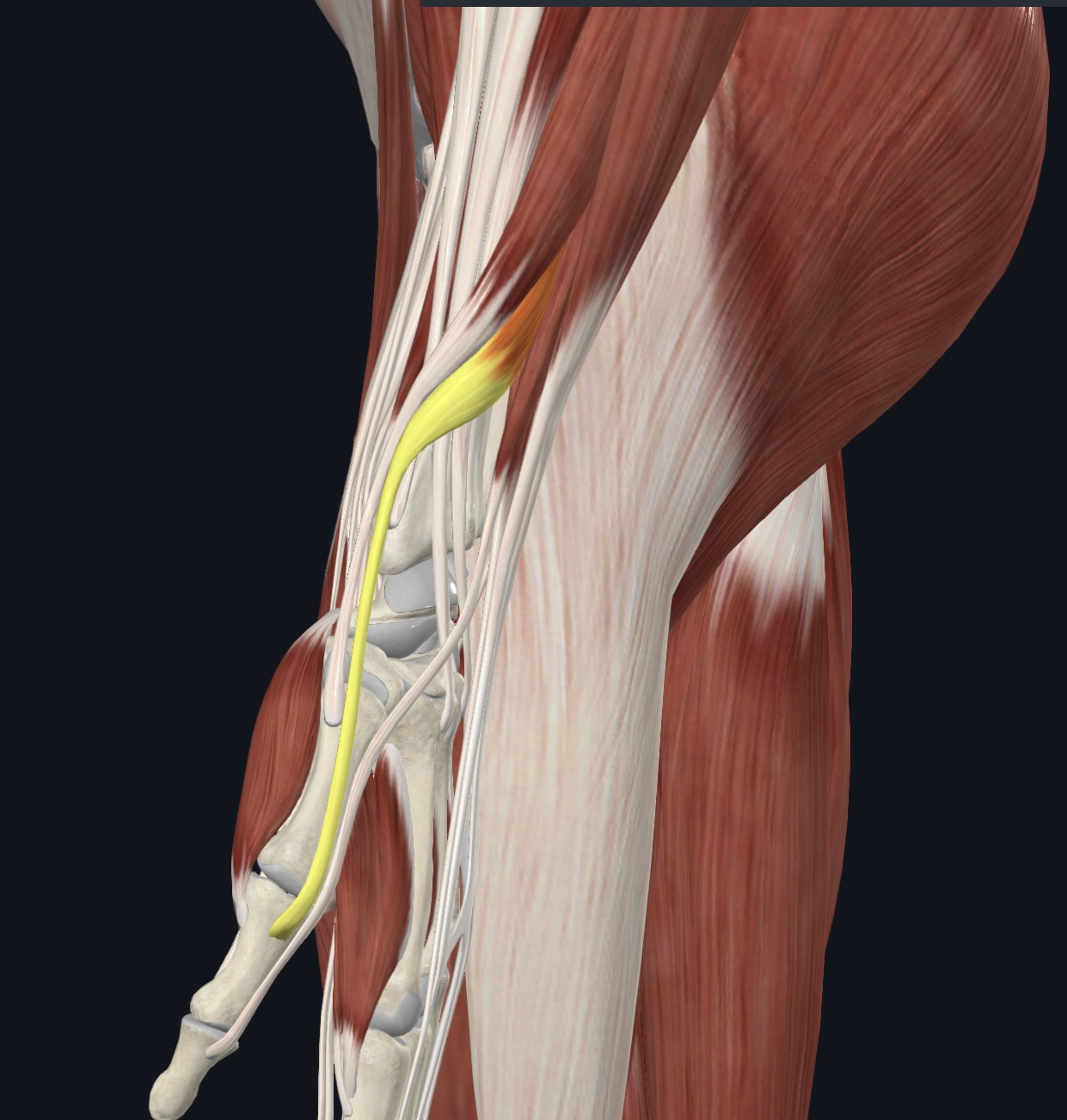
Extensor pollicis brevis,
O = posterior distal radial shaft and interosseous membrane
I = base of proximal phalanx of pollex
A = extends thumb; weak abductor of hand
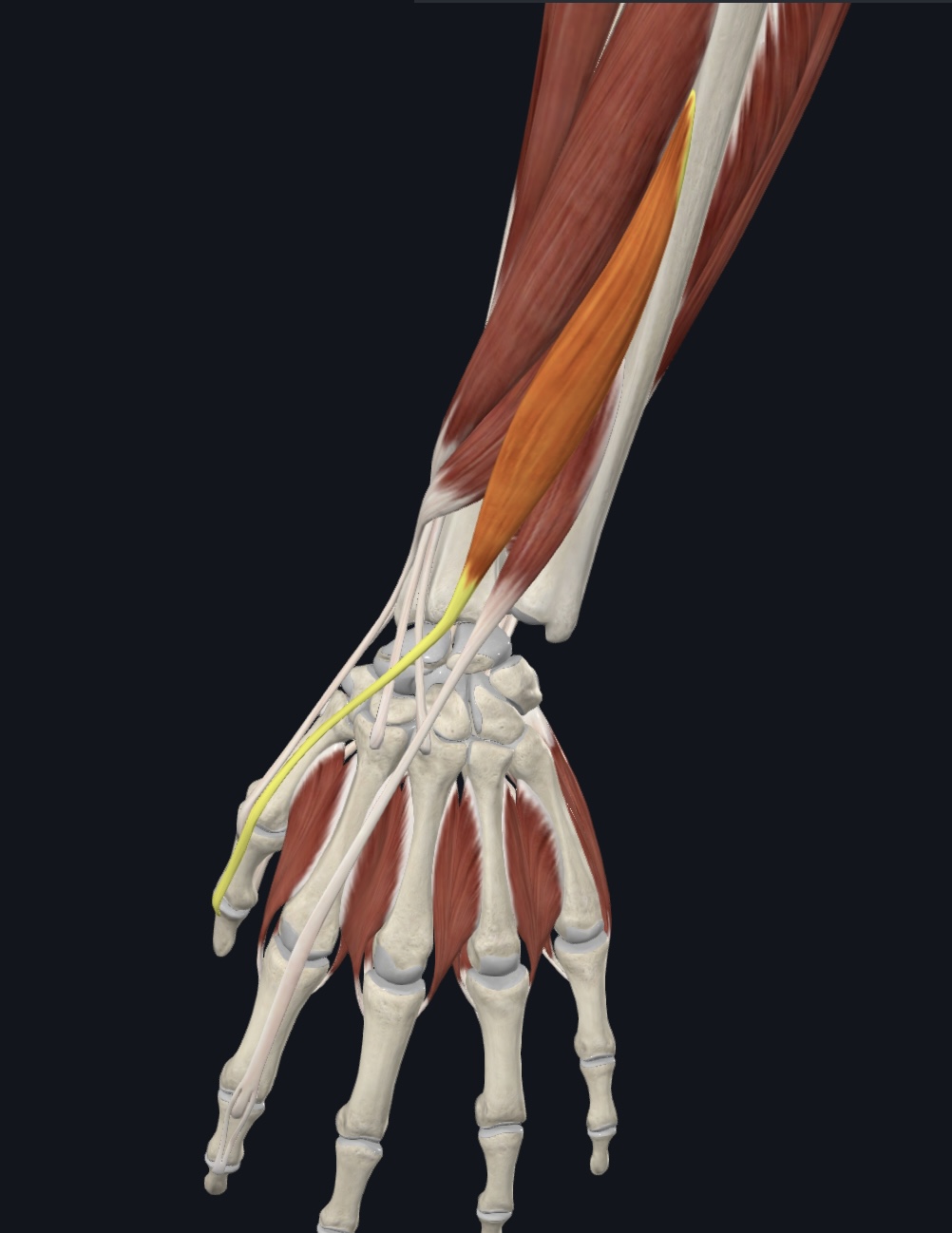
Extensor pollicis longus,
O = posterolateral surface of ulna and interosseus membrane
I = base of distal phalanx of pollex
A = extends thumb; weak abductor of hand
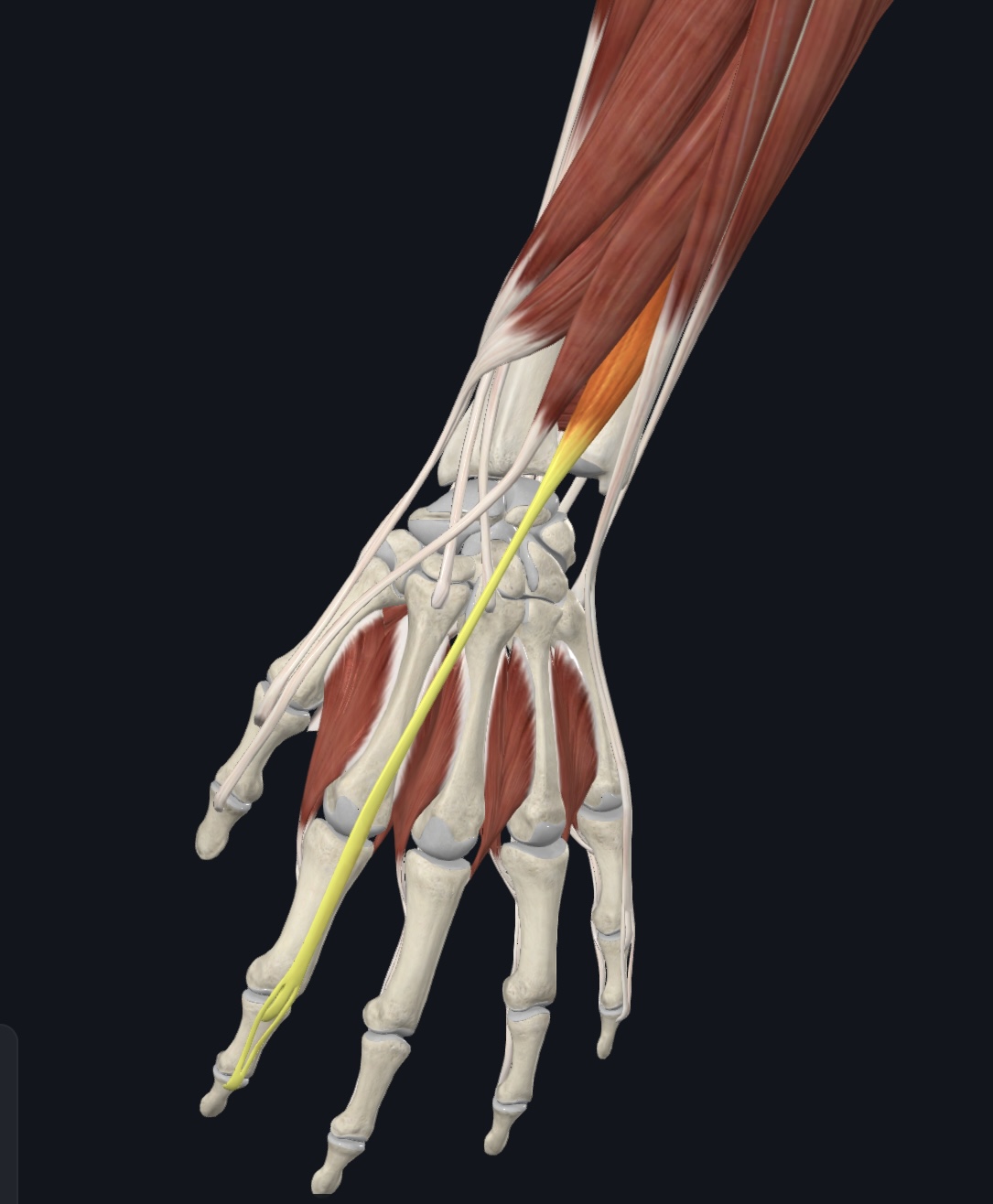
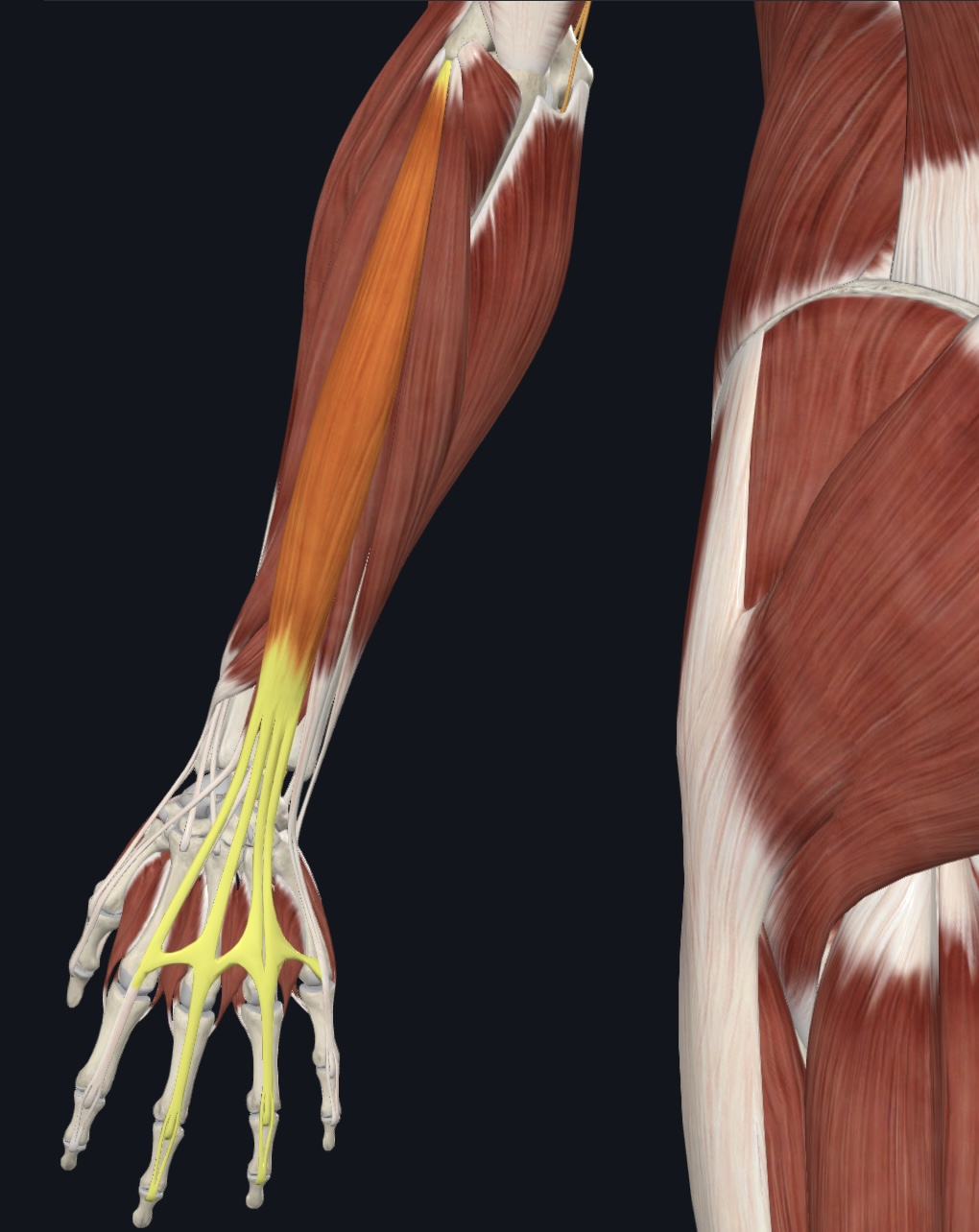
Extensor indicis,
O = posterior distal ulnar shaft and interosseous membrane
I = distal phalanx of digit 2
A = extends index finger
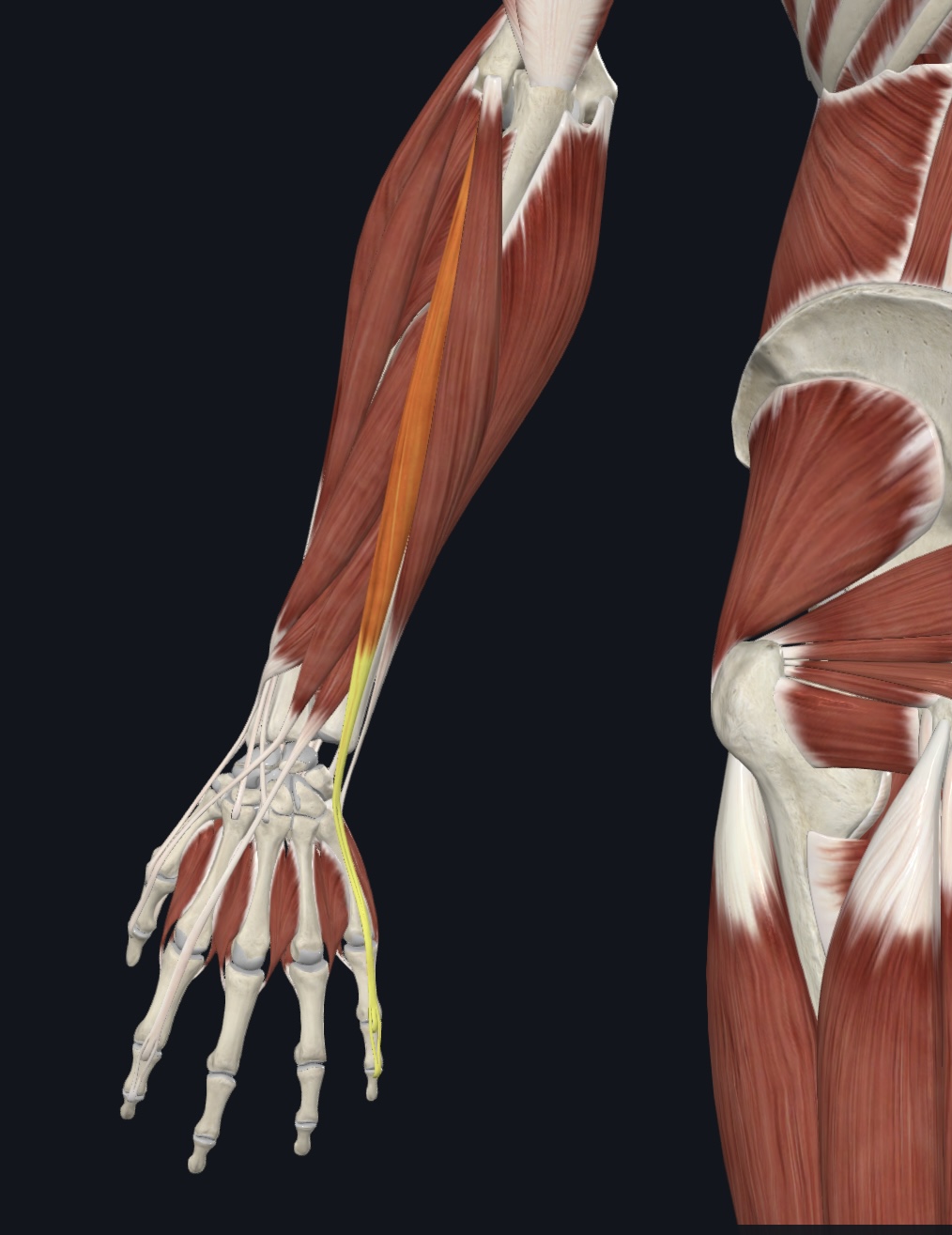
Extensor digitorum,
O = lateral epicondyle of humerus
I = posterior surface of distal phalanges 2-5
A = prime mover finger extension, extends hand
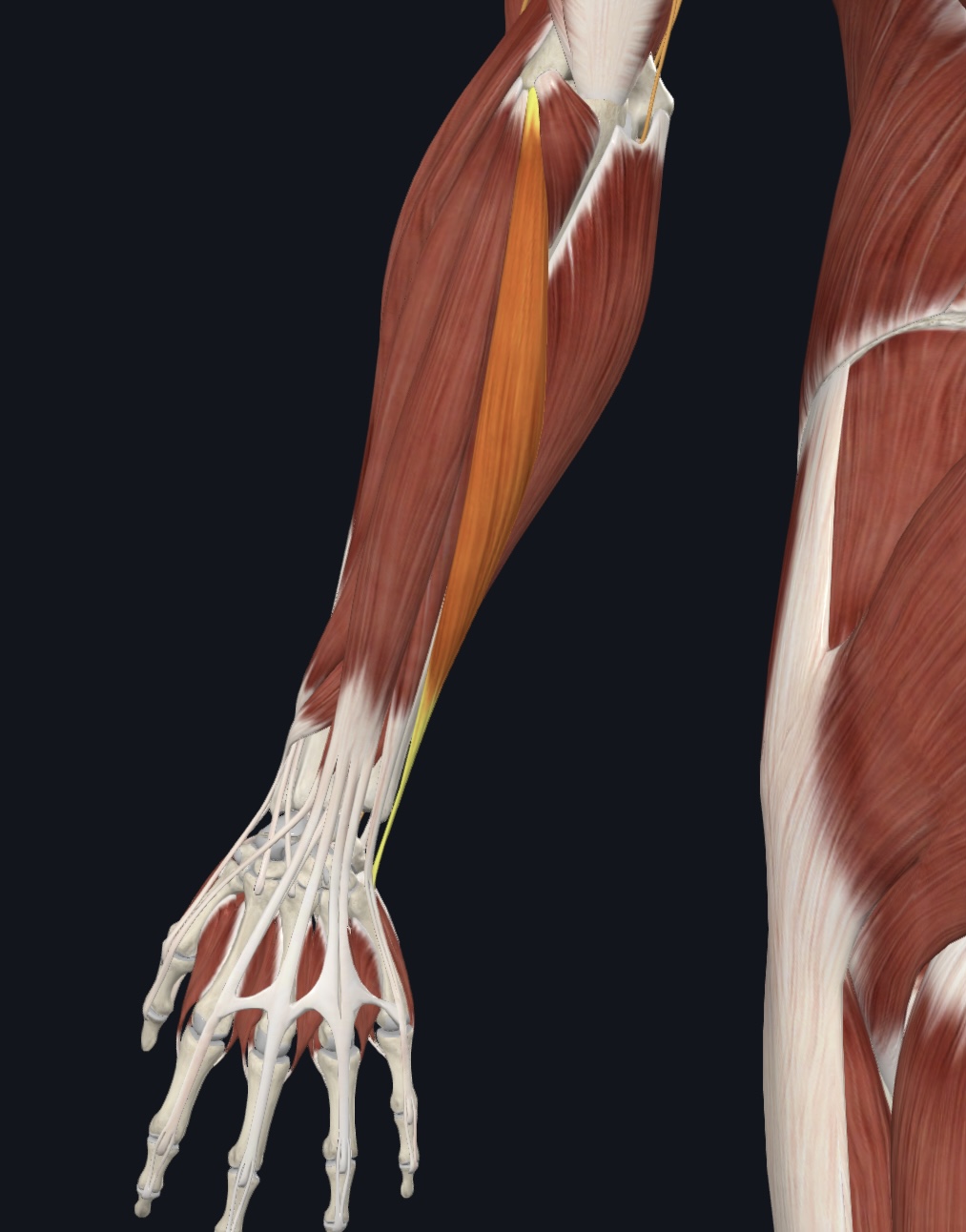
Extensor digiti minimi
O = via extensor tendon to lateral epicondyle of humerus, and from intramuscular septa
I = posterior surface of proximal phalanx of 5th finger (with tendon of extensor digitorum)
A = extends fifth finger
Extensor carpi ulnaris,
O = lateral epicondyle of humerus and posterior border of ulna
I = base of metacarpal 5
A = extends and adducts of hand
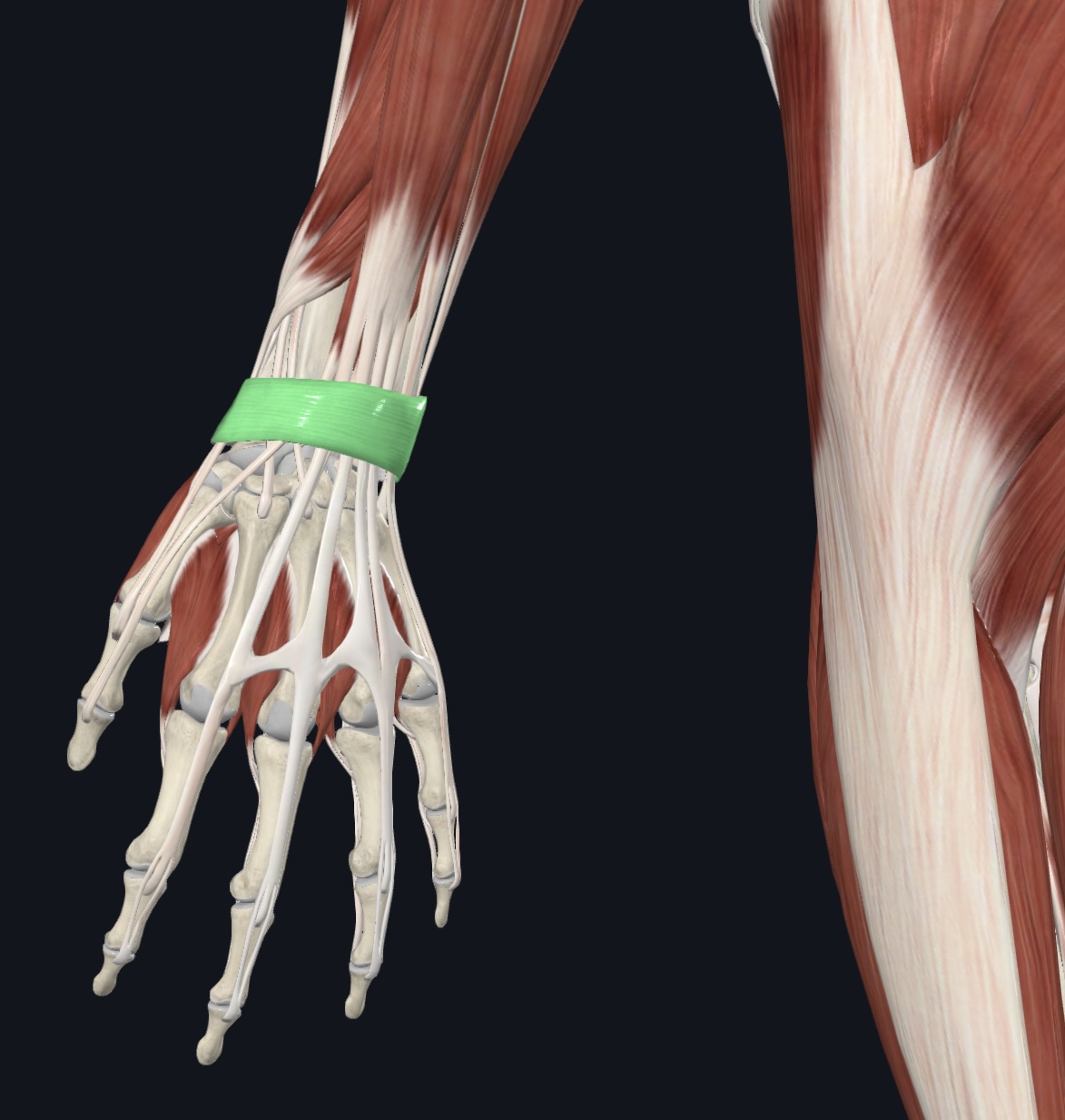
Extensor retinaculum (dense fascia, I.D. only)
Pronators/Supinators
(3)
Supinator
Pronator teres
Pronator quadratus
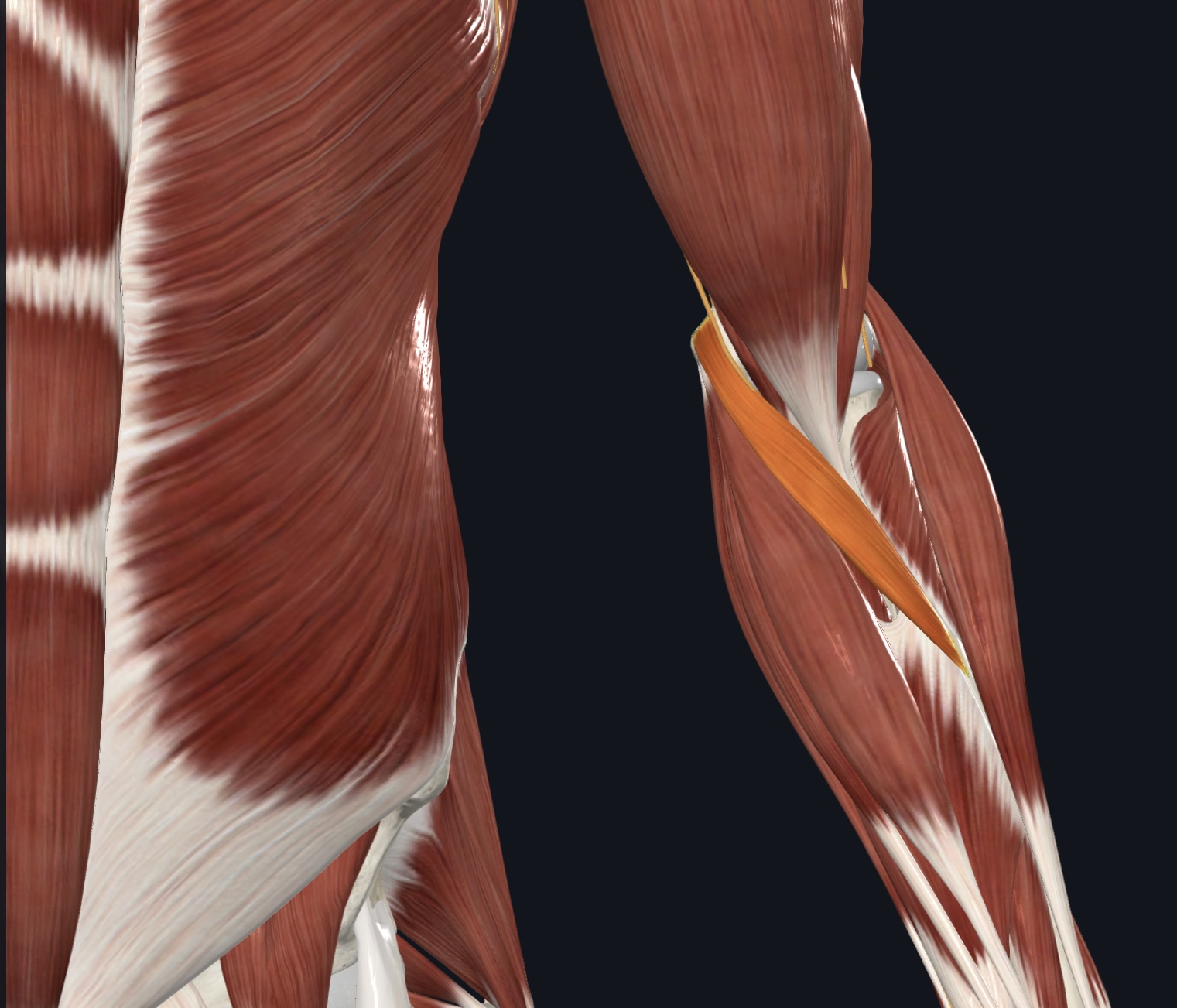
Supinator,
O = lateral epicondyle of humerus and proximal ulna
I = anterolateral surface of proximal radius
A = supinates forearm
N = Radial Nerve
Pronator teres,
O = medial epicondyle of humerus and coronoid process of ulna
I = lateral midshaft of radius
A = pronates forearm; weak forearm flexor
N = Median Nerve
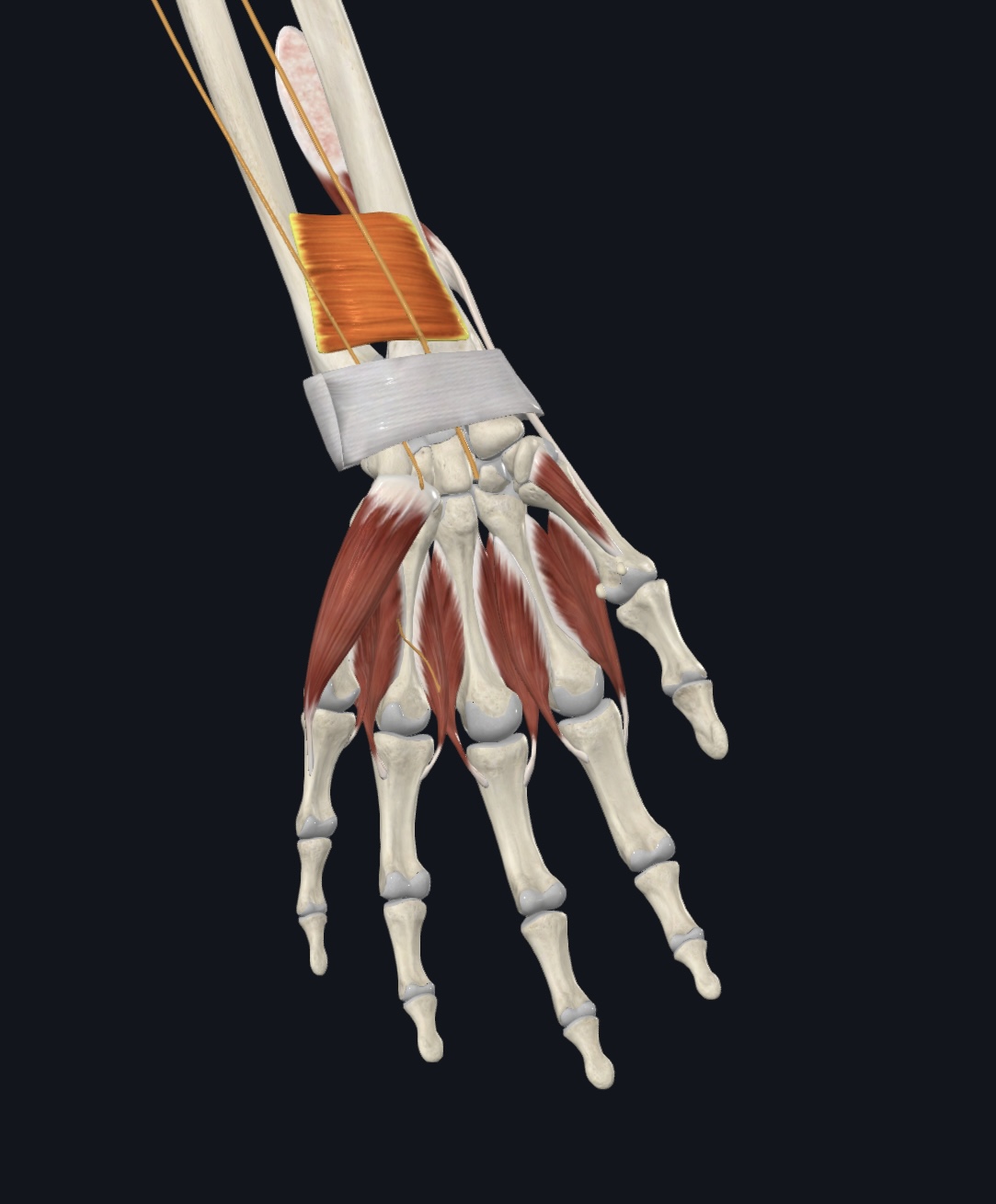
Pronator quadratus,
O = distal anterior and medial ulnar shaft
I = distal anterior and lateral radial shaft
A = pronates forearm
N = Median Nerve
Anterior & Medial Muscles that Originate on the Os Coxae
(4)
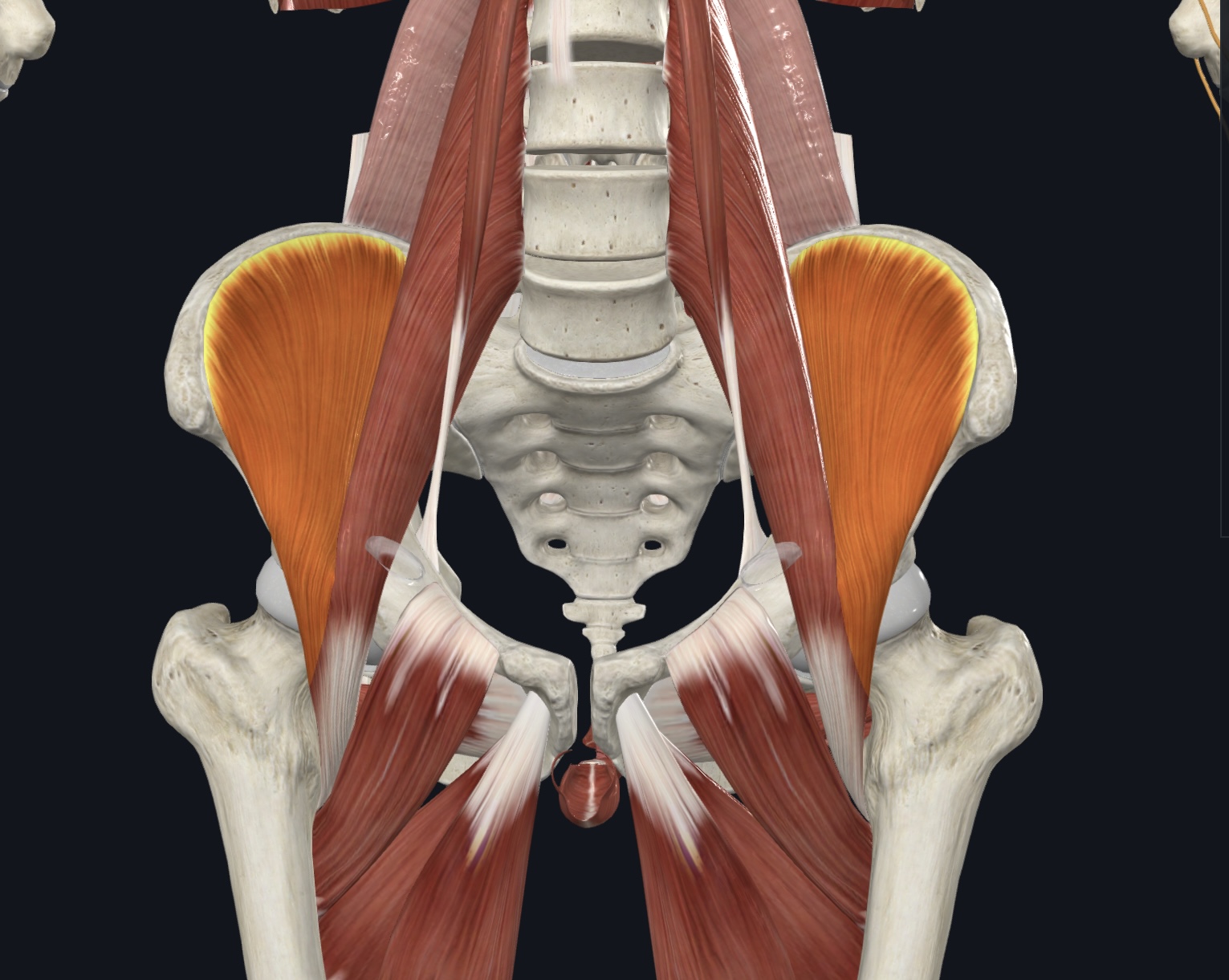
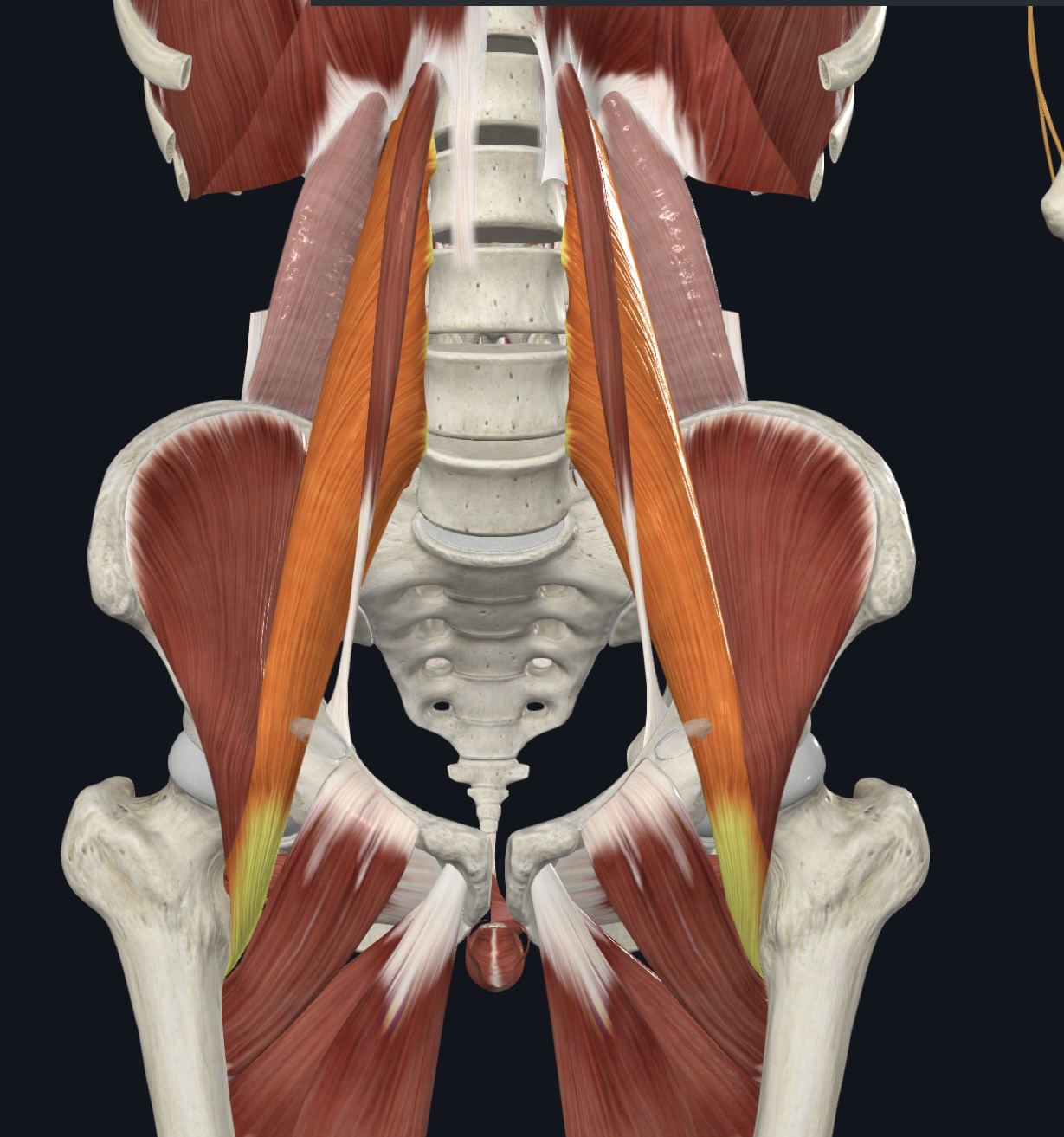
Iliopsoas
Iliacus
Psoas major (note: does not originate on the pelvis!)
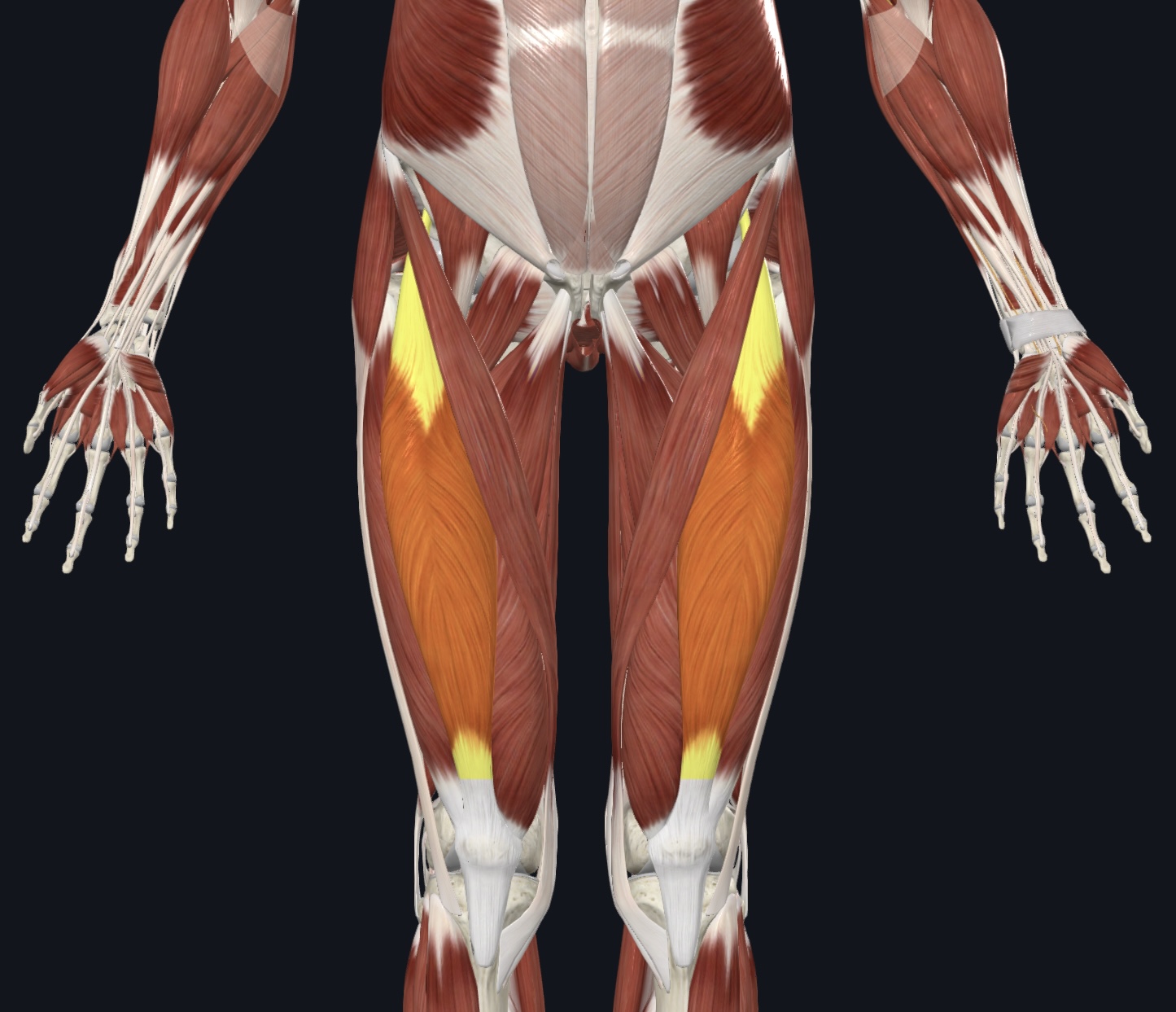
Sartorius (“tailor’s muscle”)
Iliopsoas:
Iliacus,
O = iliac fossa of the os coxa, ala of sacrum
I = lesser trochanter of femur
A = prime mover of thigh flexion, postural muscle (fibers converge into tendon of psoas major)
N = Femoral Nerve (L2 & L3)
Iliopsoas:
Psoas major, Note: does not originate on the pelvis!
O = vertebrae T12-L5
I = lesser trochanter of femur
A = prime mover of thigh flexion, postural muscle
N = Ventral Rami L1-L3
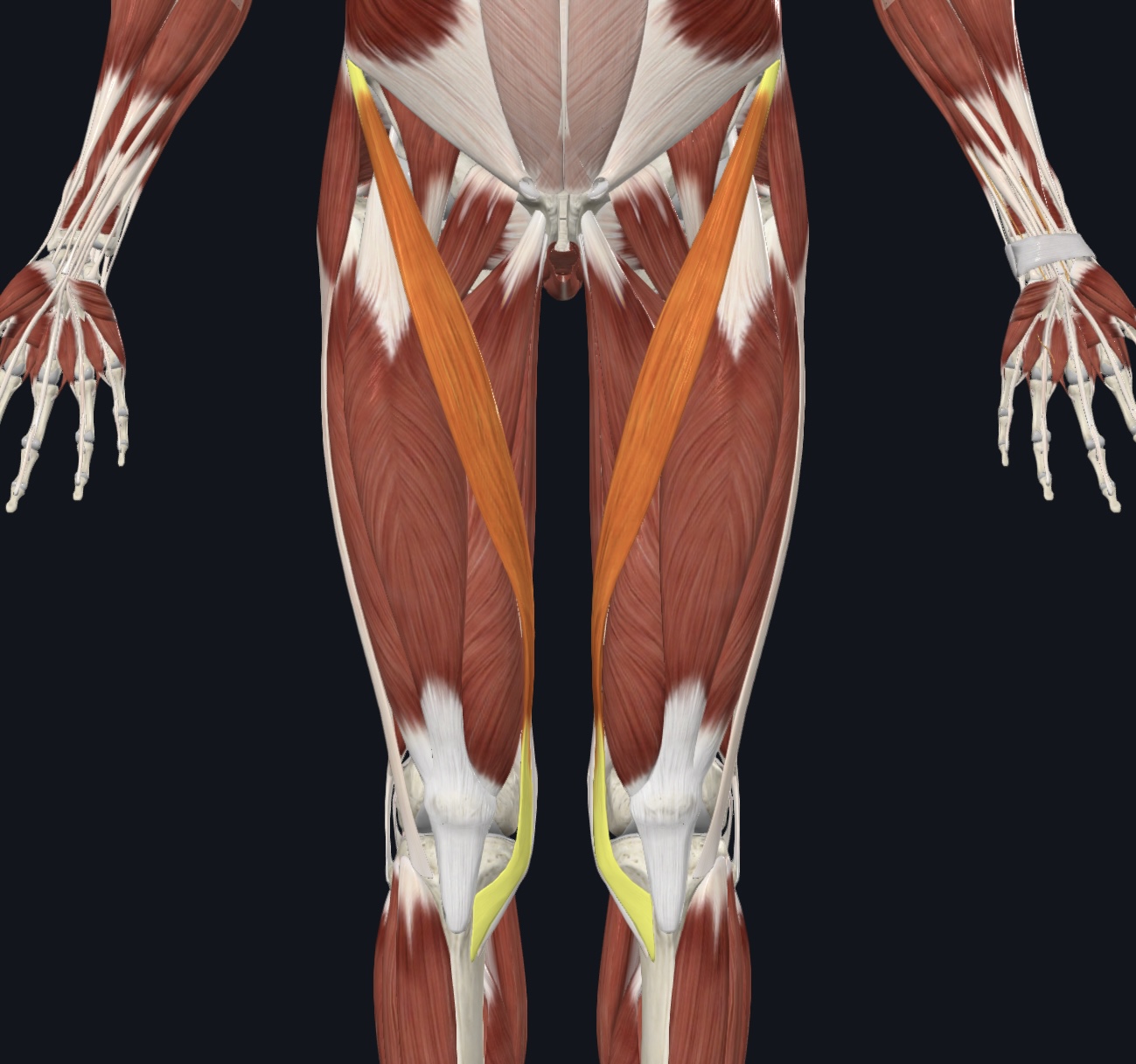
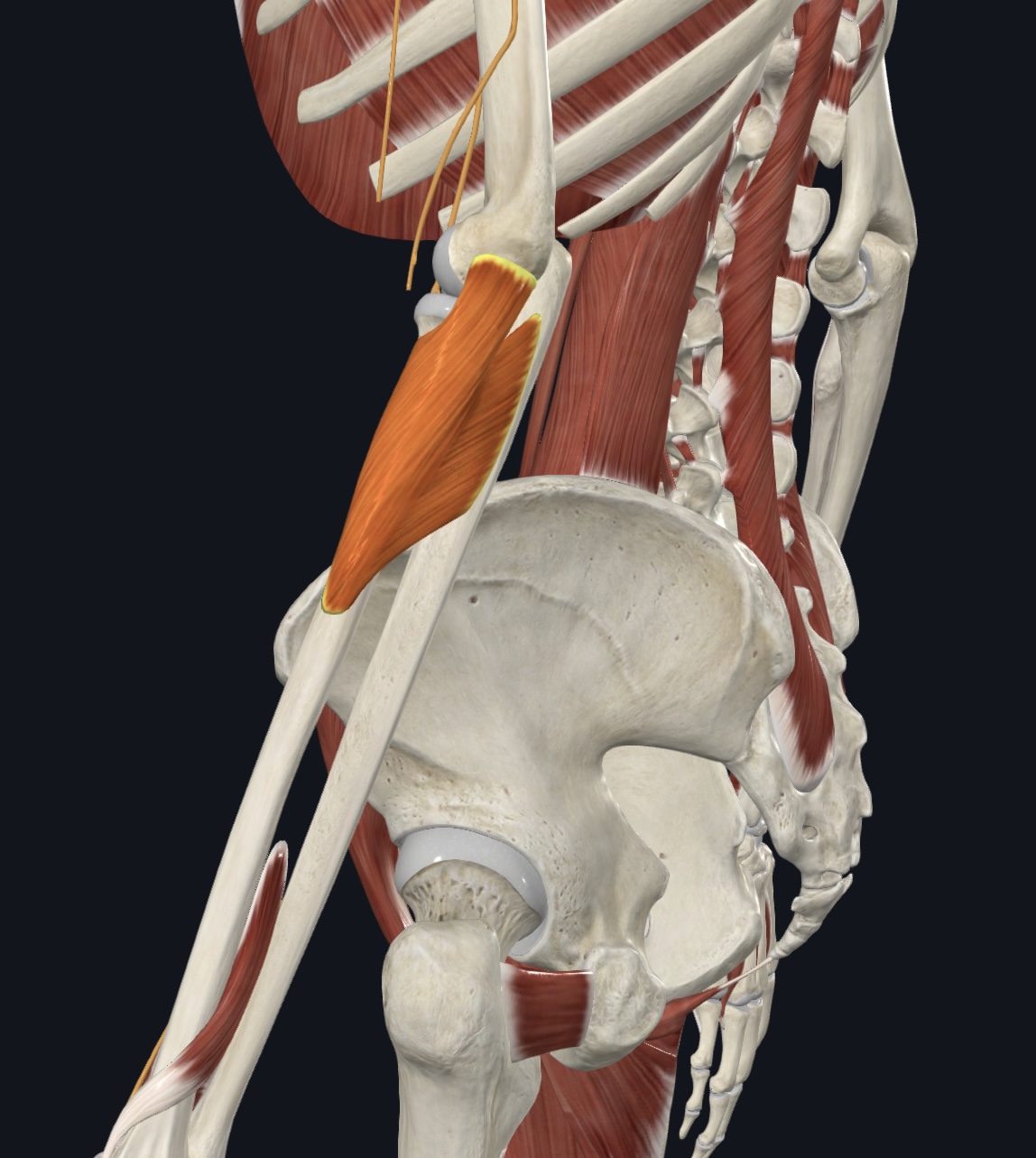
Sartorius (“tailor's muscle”),
O = anterior superior iliac spine of the os coxa
I = medial proximal tibial shaft
A = flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates thigh; flexes lower leg
N = Femoral Nerve (L2 & L3)
Muscles of the Anterior Compartment of the Thigh
(8)
Quadriceps femoris (All are innervated by the Femoral Nerve)
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis
Vastus intermedius
Patellar ligament (O & I given —I.D.)
Tensor fasciae latae
Iliotibial tract (I.D. only)
Rectus femoris,
O = anterior inferior iliac spine and superior margin of acetabulum of the os coxa
I = patella via quadriceps tendon
A = flexes thigh, extends lower leg
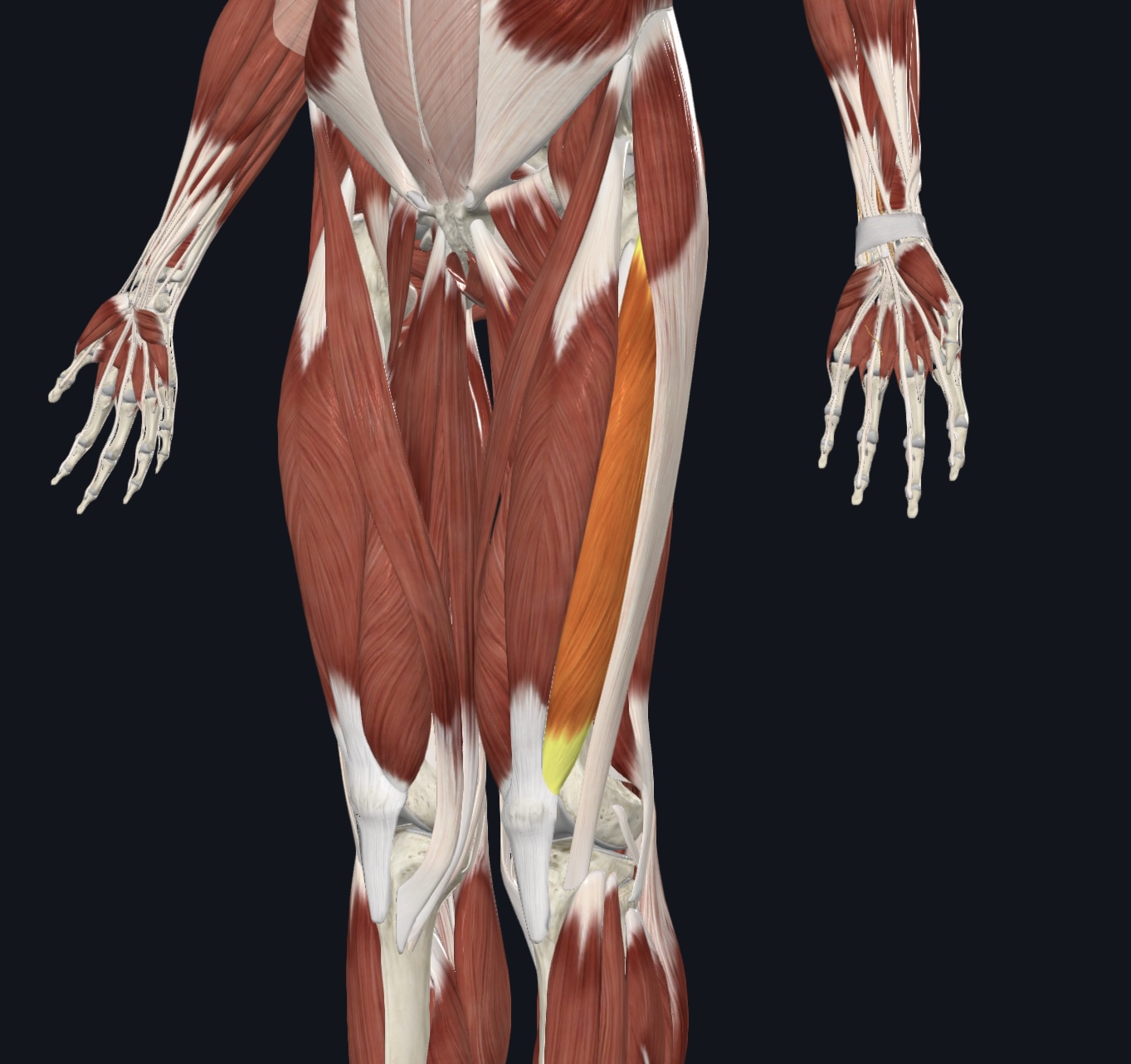
Vastus lateralis,
O = greater trochanter, intertrochanteric crest, and linea aspera of femur
I = patella via quadriceps tendon
A = extends lower leg; stabilizes patella
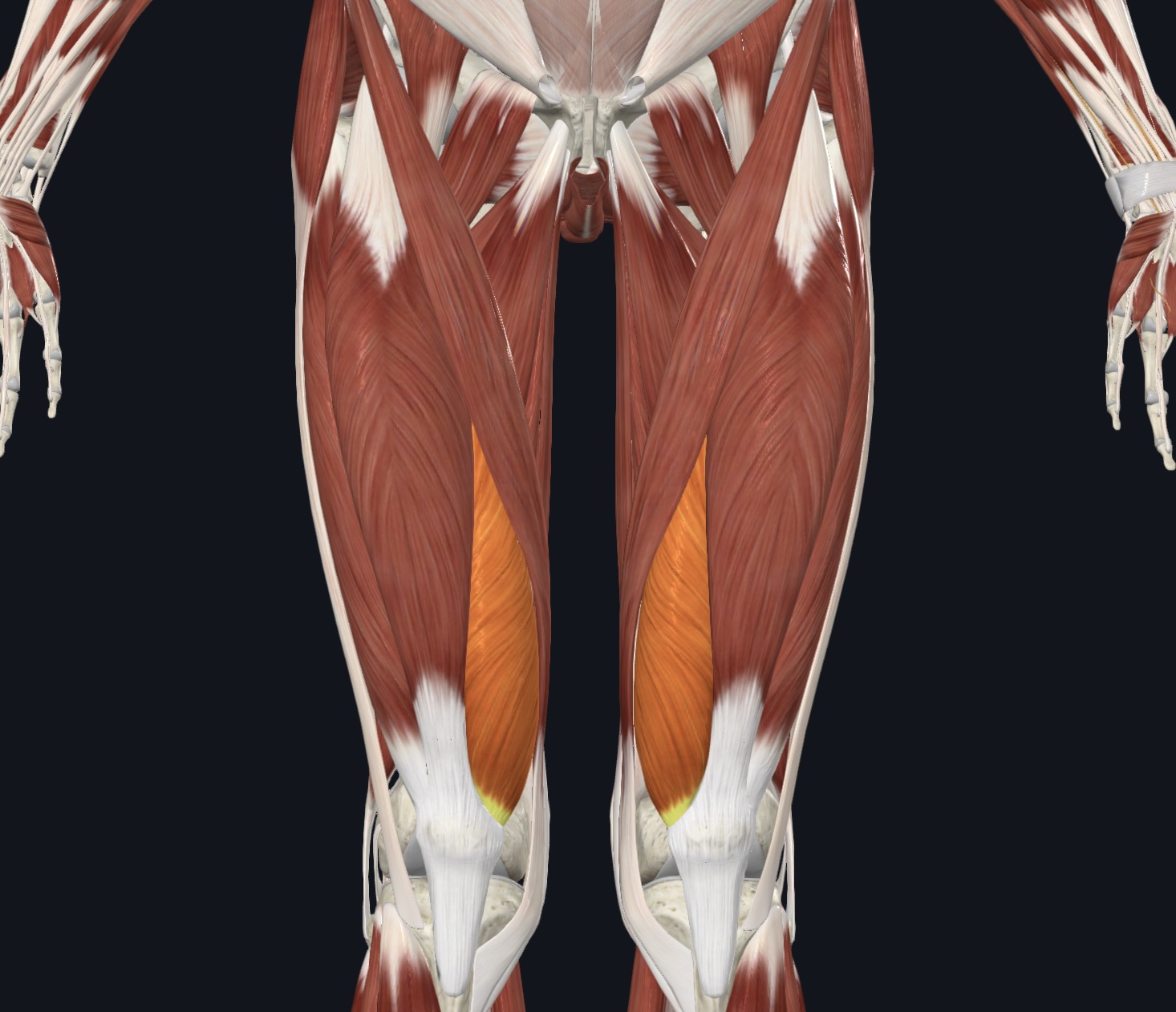
Vastus medialis,
O = linea aspera and intertrochanteric crest of femur
I = patella via quadriceps tendon
A = extends lower leg; stabilizes patella
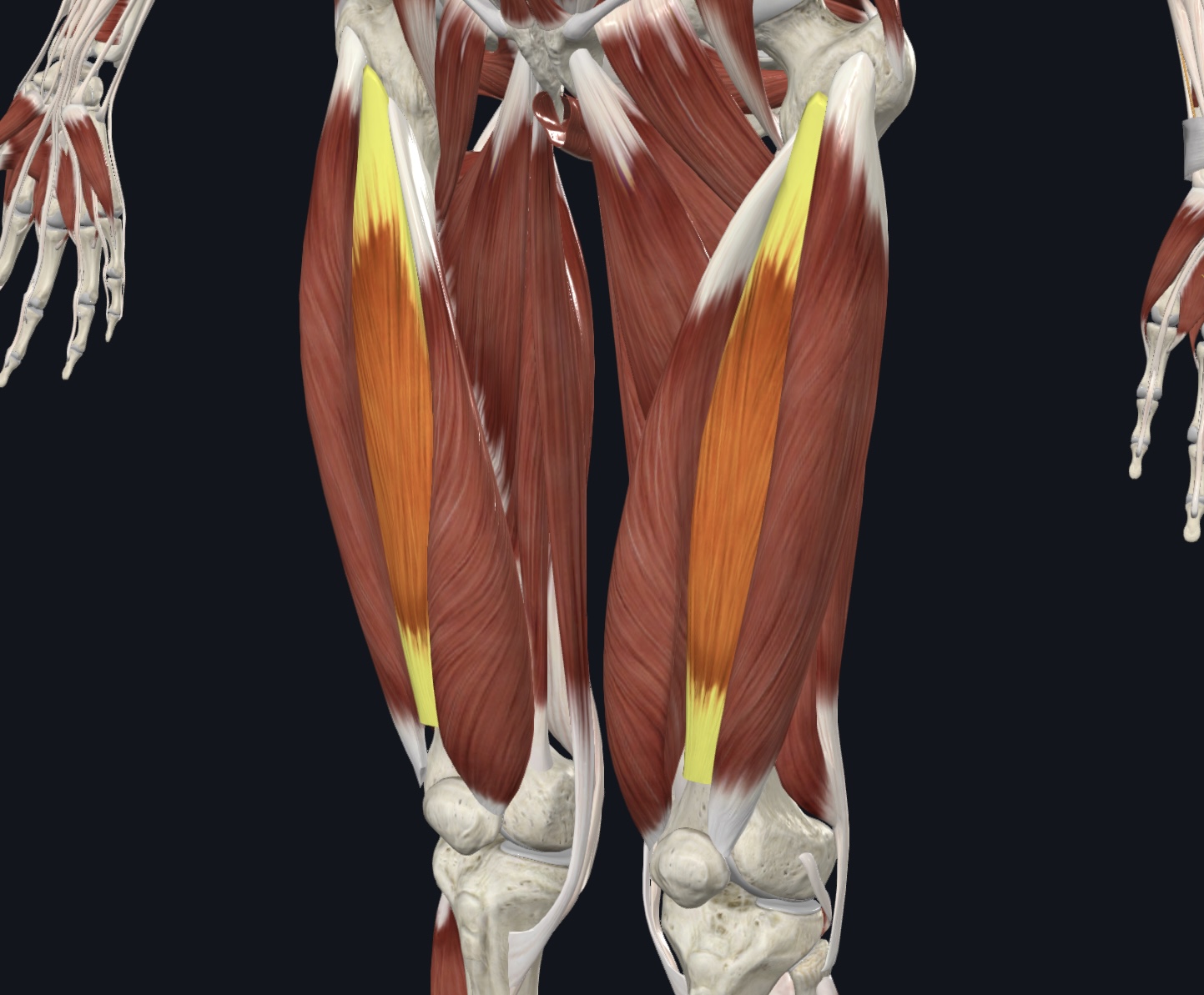
Vastus intermedius,
O = proximal anterolateral femoral shaft
I = patella via quadriceps tendon
A = extends lower leg
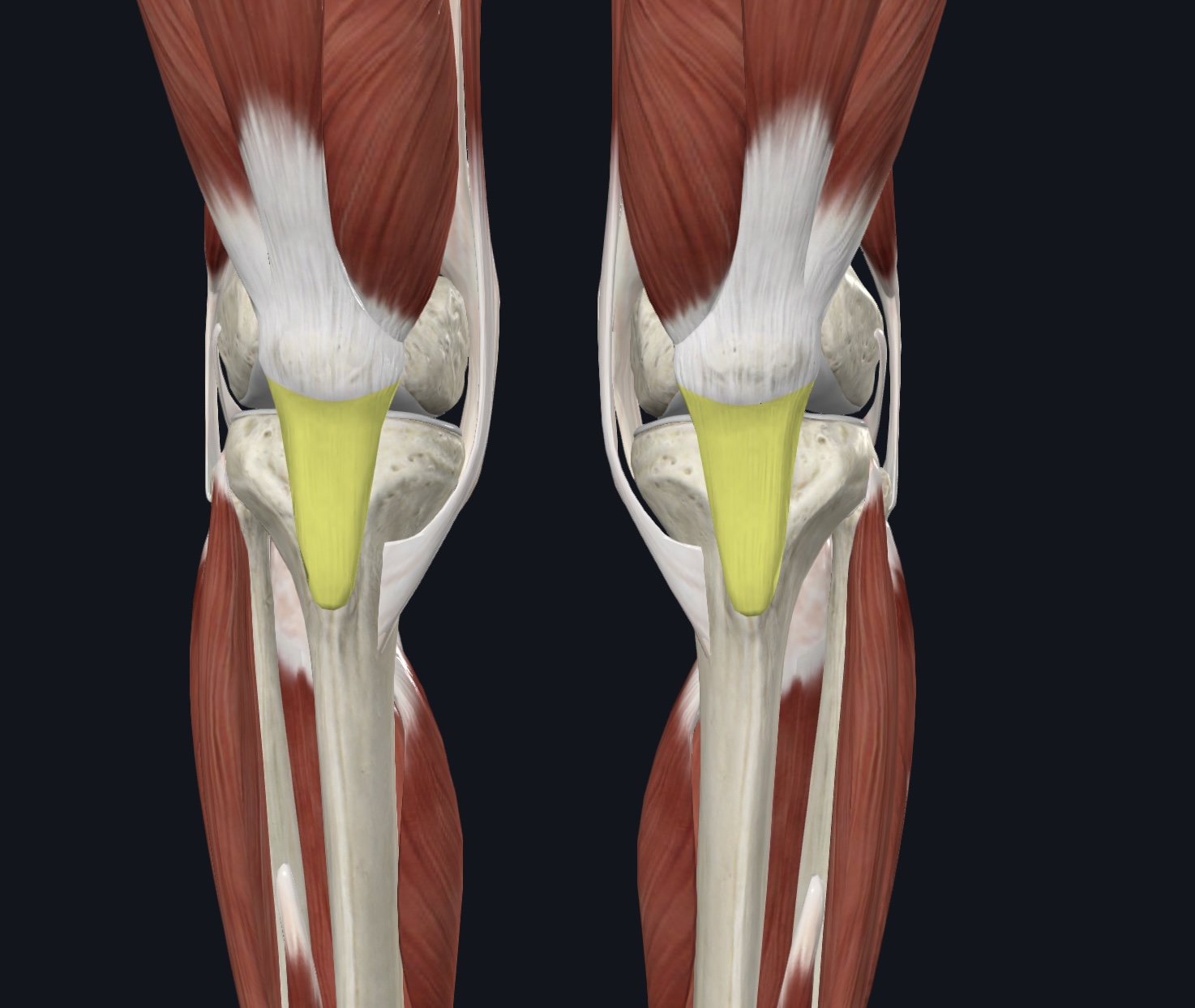
Patellar ligament (O & I given--I.D.),
O = patella
I = tibial tuberosity of the tibia
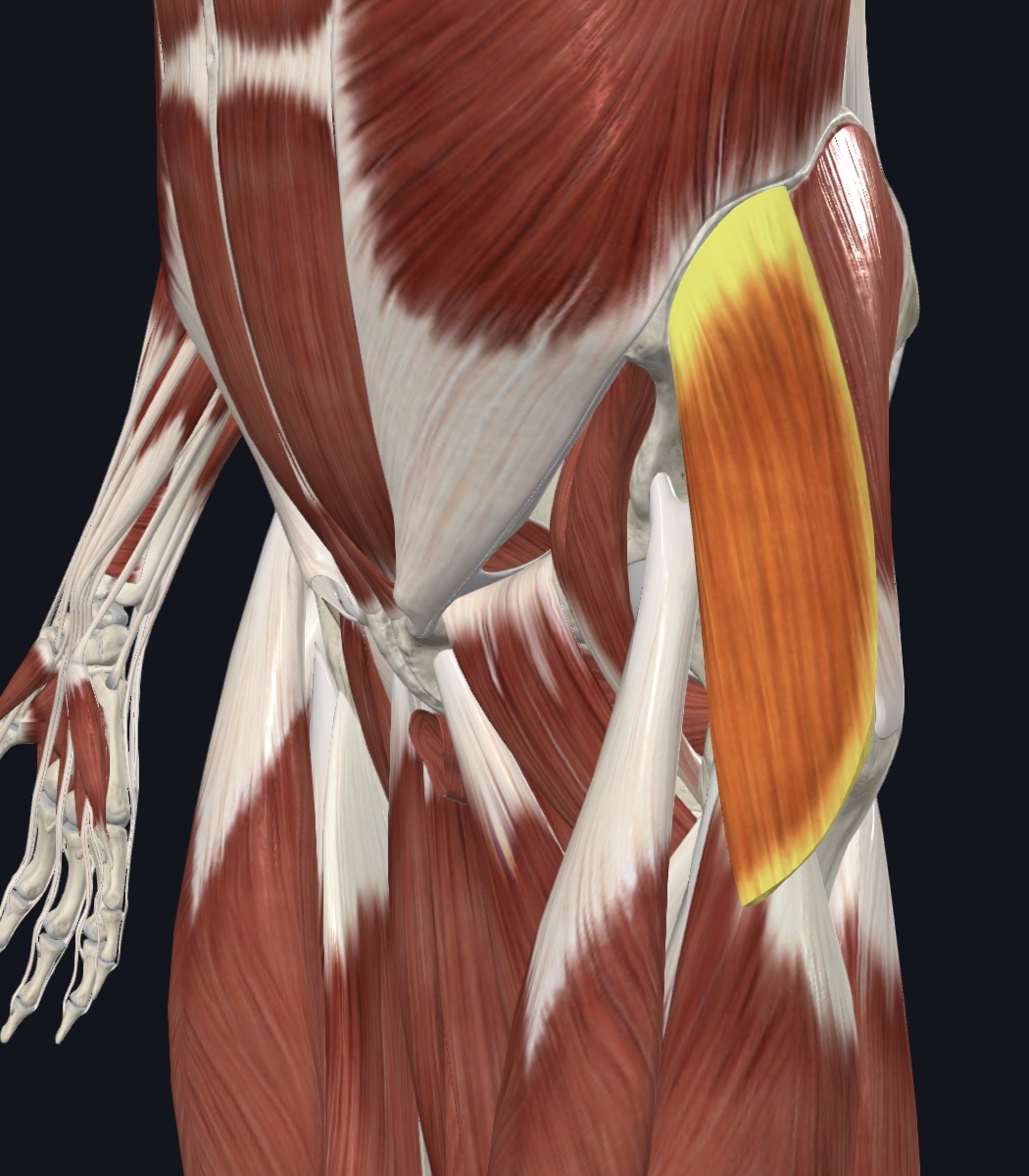
Tensor fasciae latae,
O = anterior aspect of iliac crest and anterior superior iliac spine of the os coxa
I = iliotibial tract
A = abducts, flexes, and medially rotates thigh
N = Superior Gluteal Nerve
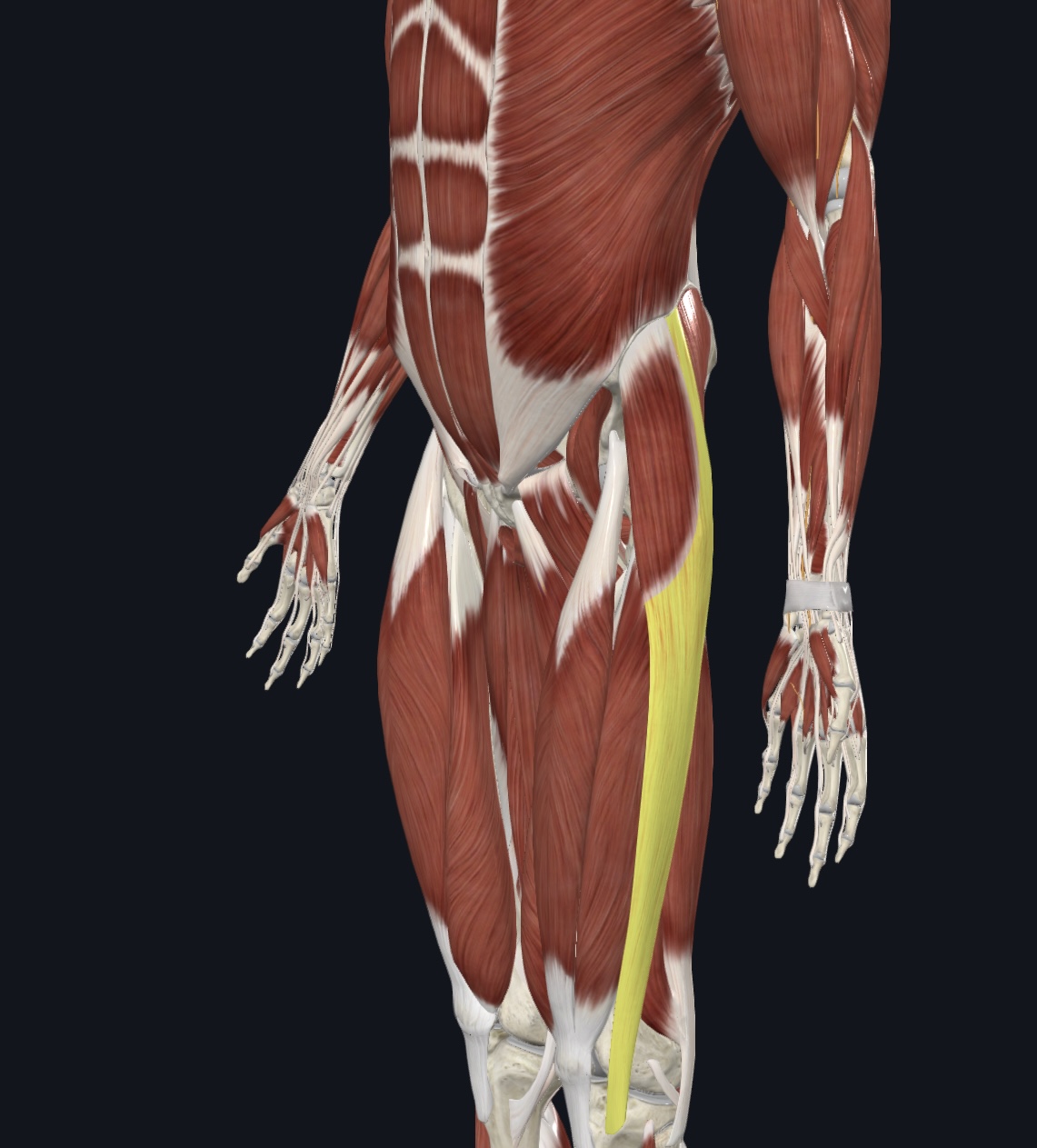
Iliotibial tract (I.D. only)
Muscles of the Medial Compartment of the Thigh
(4)
Pectineus
Gracilis
Adductor longus, (note adductor brevis also present-you will not be required to identify it)
Adductor magnus
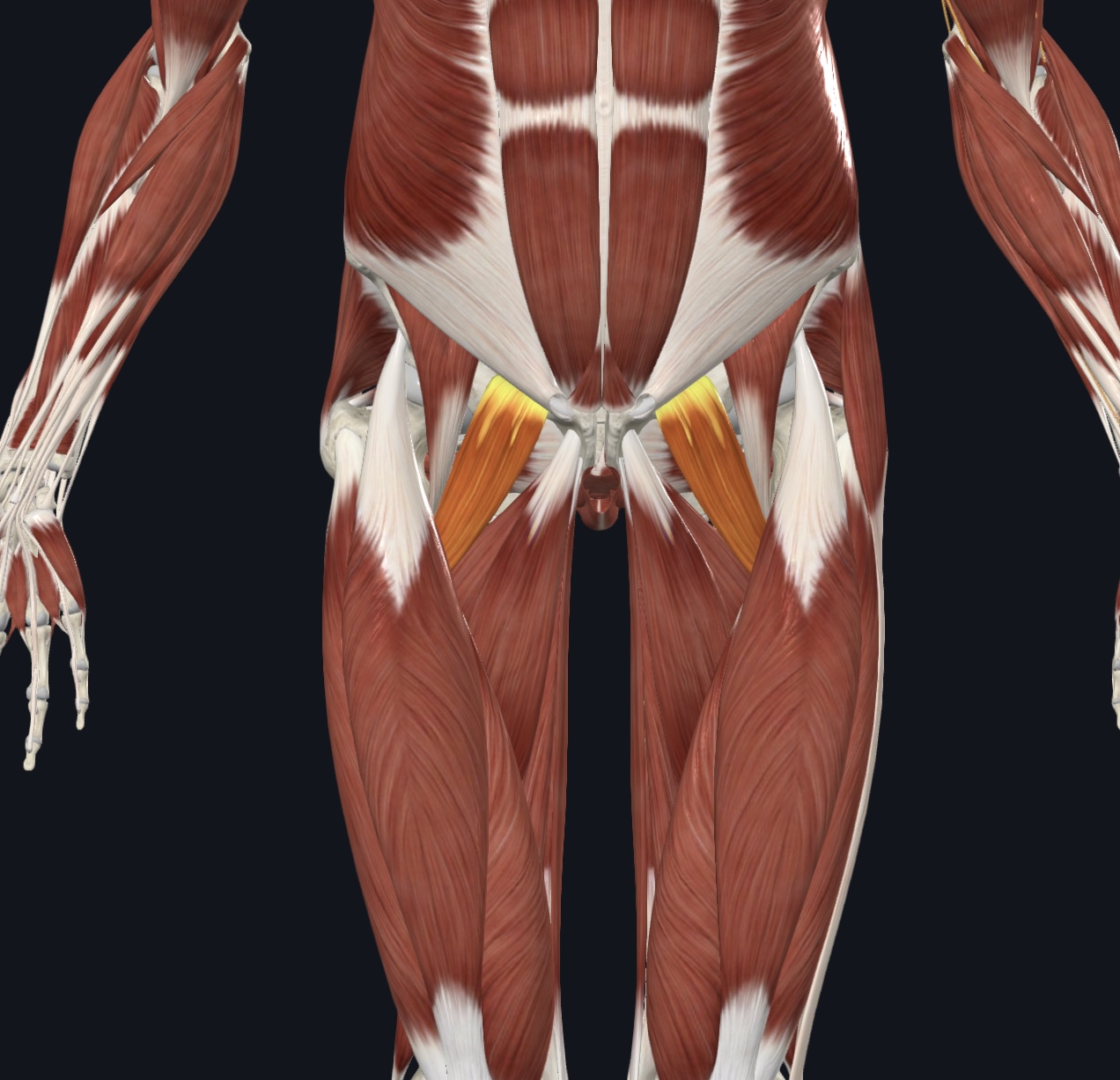
Pectineus,
O = pubis of the os coxa
I = pectineal line of femur
A = adducts, flexes, and medially rotates thigh
N = Femoral Nerve (L2 & L3) and sometimes Obturator Nerve
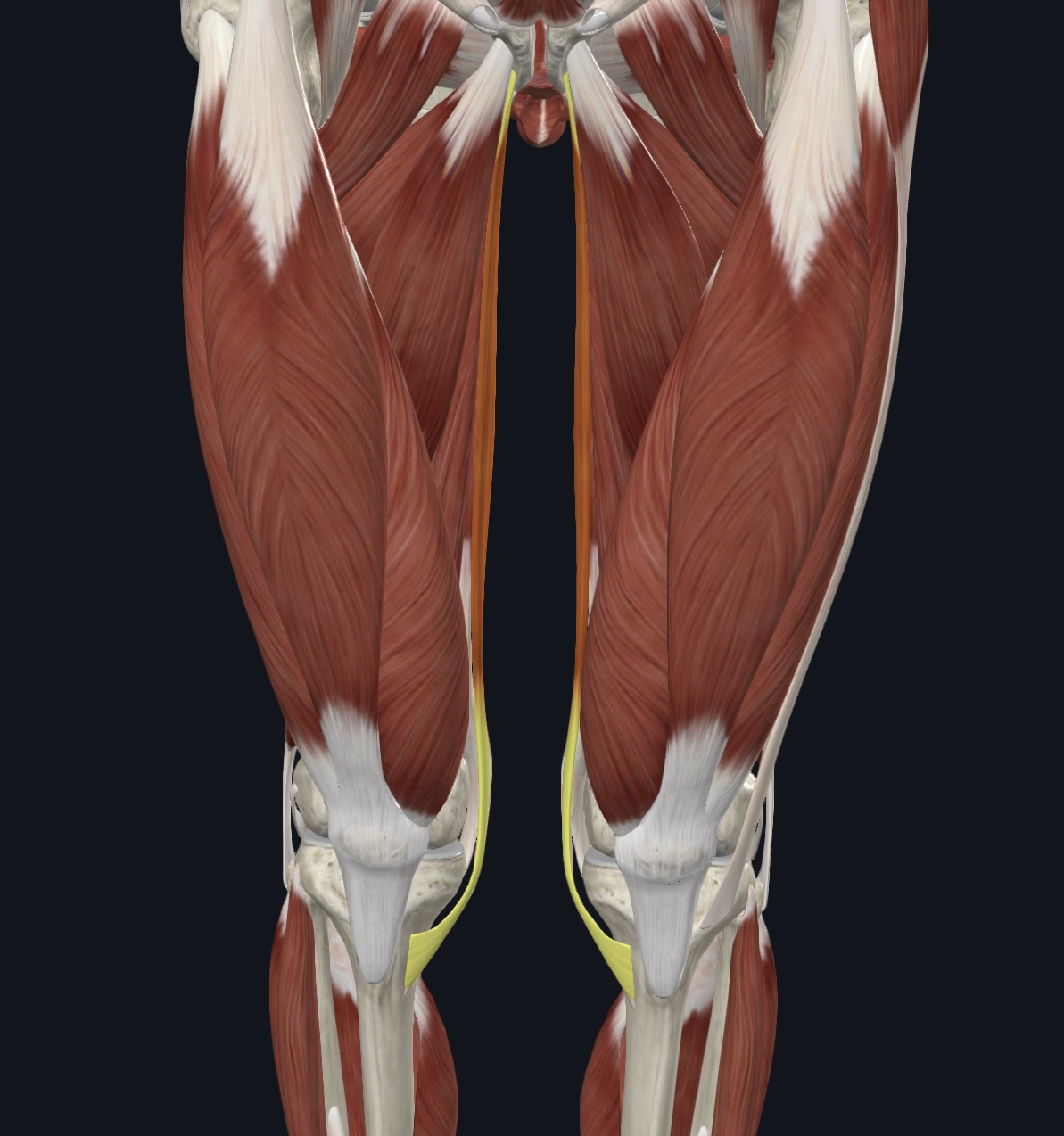
Gracilis,
O = ramus and body of pubis of the os coxa
I = medial proximal tibial shaft
A = adducts thigh; flexes and medially rotates lower leg
N = Obturator Nerve (L2 and L3)
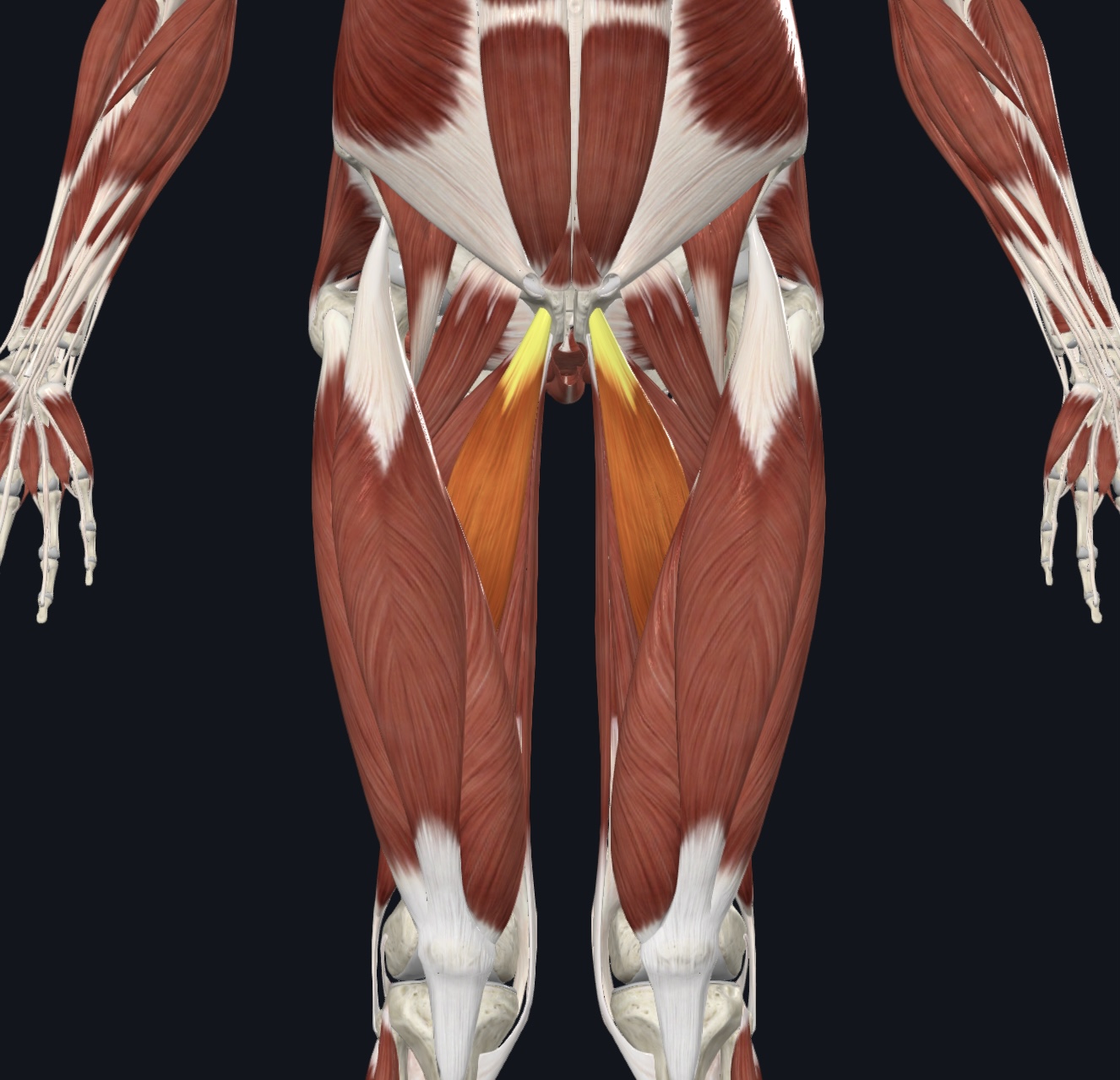
Adductor longus, (note adductor brevis also present-you will not be required to identify it)
O = pubis of the os coxa
I = linea aspera of femur
A = adducts, flexes, and medially rotates thigh
N = Obturator Nerve
Adductor magnus,
O = ischial and pubic rami and ischial tuberosity of the os coxa
I = linea aspera of femur
A = extends, adducts, flexes, and medially rotates thigh
N = Obturator Nerve and Sciatic Nerve (tibial division)
Muscles of the Anterior Compartment: Movement of the Ankle and Toes
5
(All are innervated by the Deep Peroneal Nerve)
Tibialis anterior
Extensor hallucis longus
Extensor digitorum longus
Peroneus tertius, (fused with extensor digitorum longus-often considered it’s fifth tendon)
Extensor retinaculum (dense fascia: superior and inferior, I.D. only)
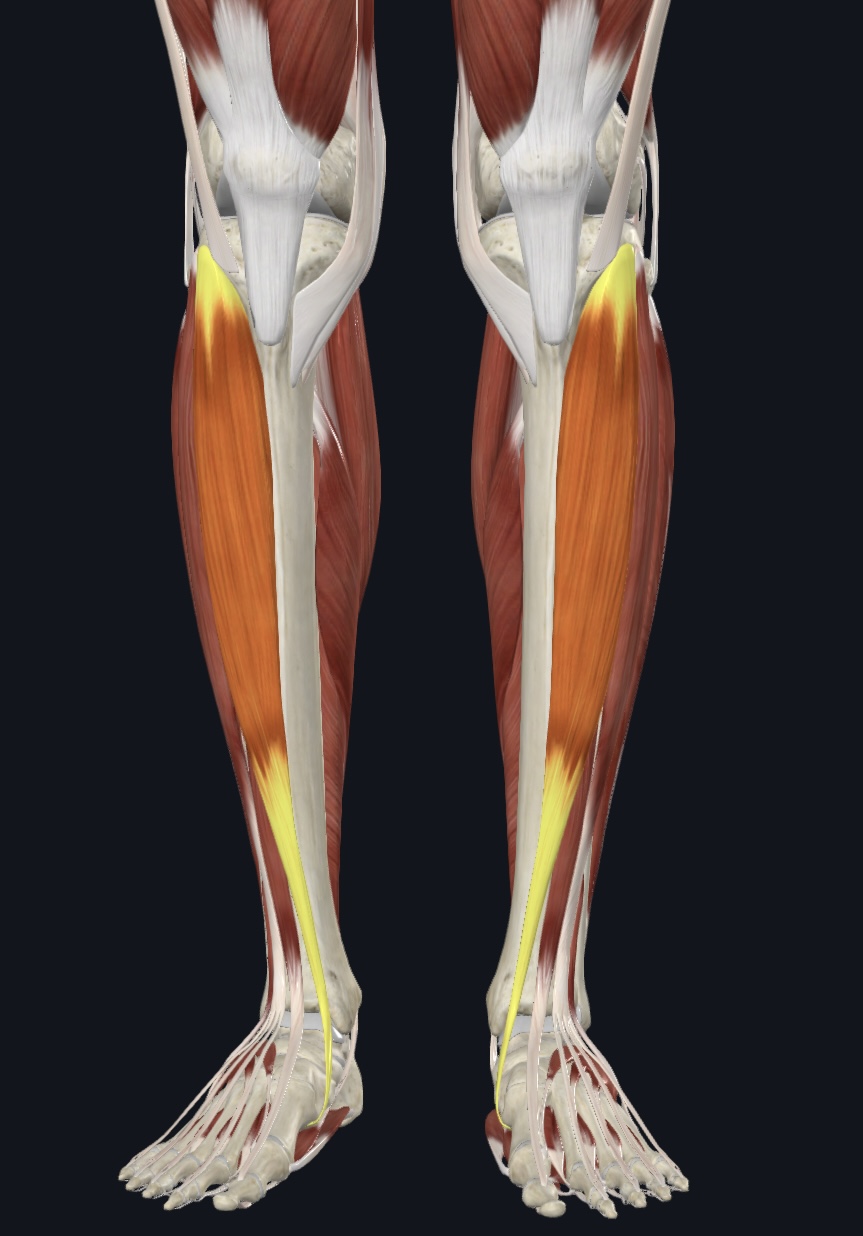
Tibialis anterior,
O = lateral condyle and proximal shaft of tibia
I = medial cuneiform and metatarsal 1
A = prime dorsiflexor; inversion
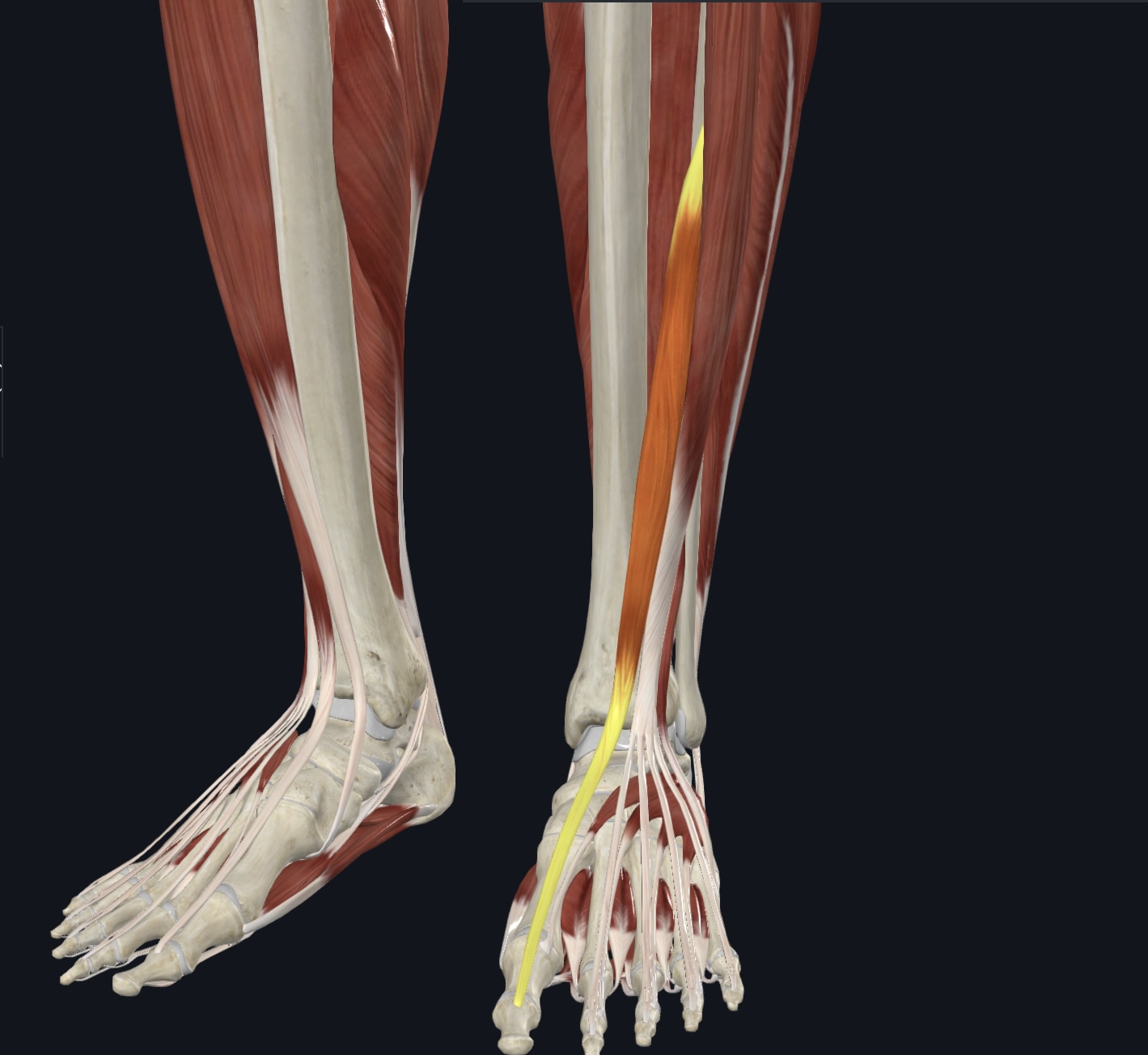
Extensor hallucis longus,
O = anteromedial fibular shaft and interosseous membrane
I = distal phalanx 1
A = dorsiflexion; extends hallux
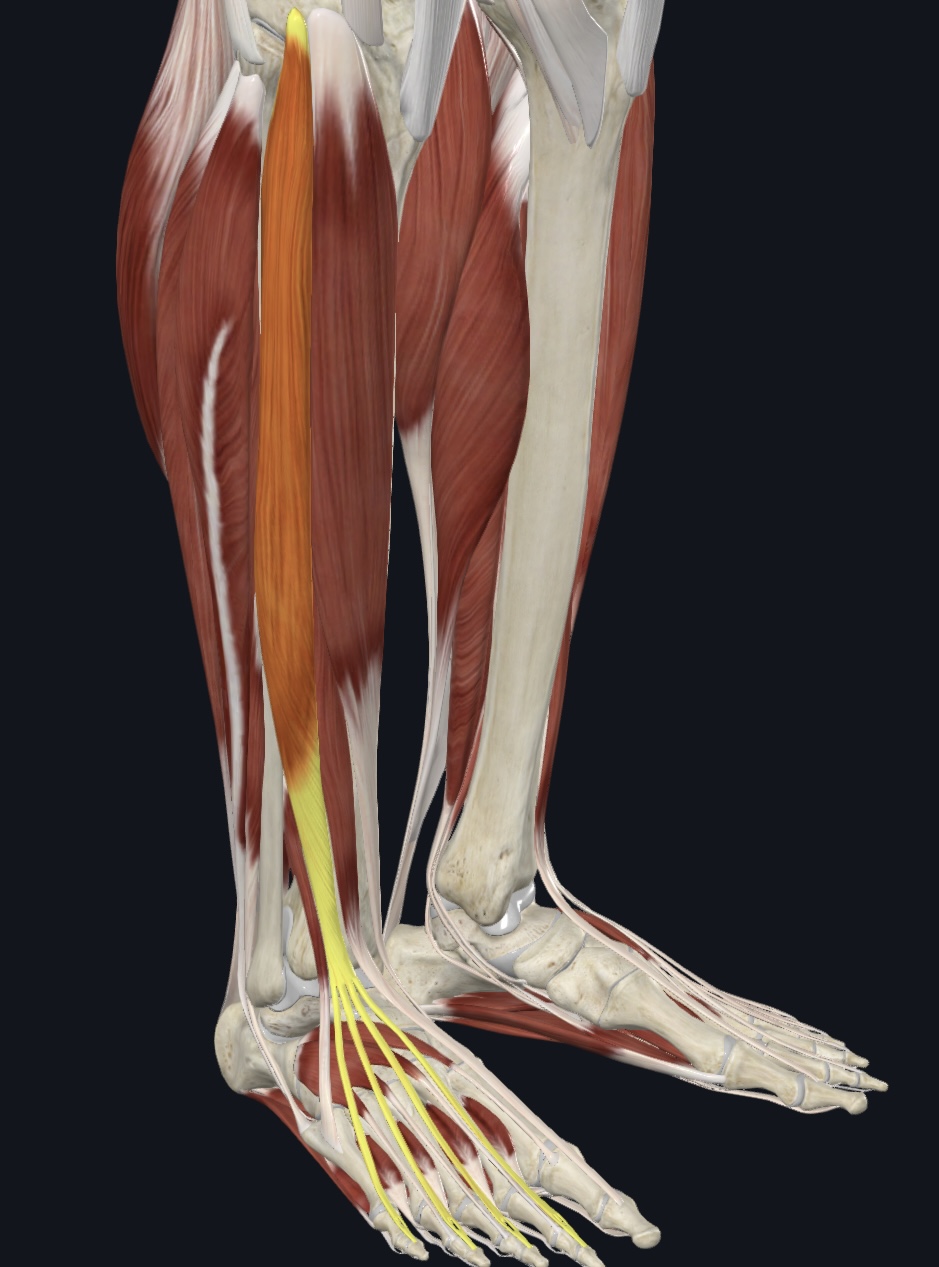
Extensor digitorum longus,
O = lateral condyle of tibia and proximal 3/4 of fibula and interosseous membrane
I = middle and distal phalanges of digits 2-5
A = dorsiflexion; prime toe extensors (2-5)
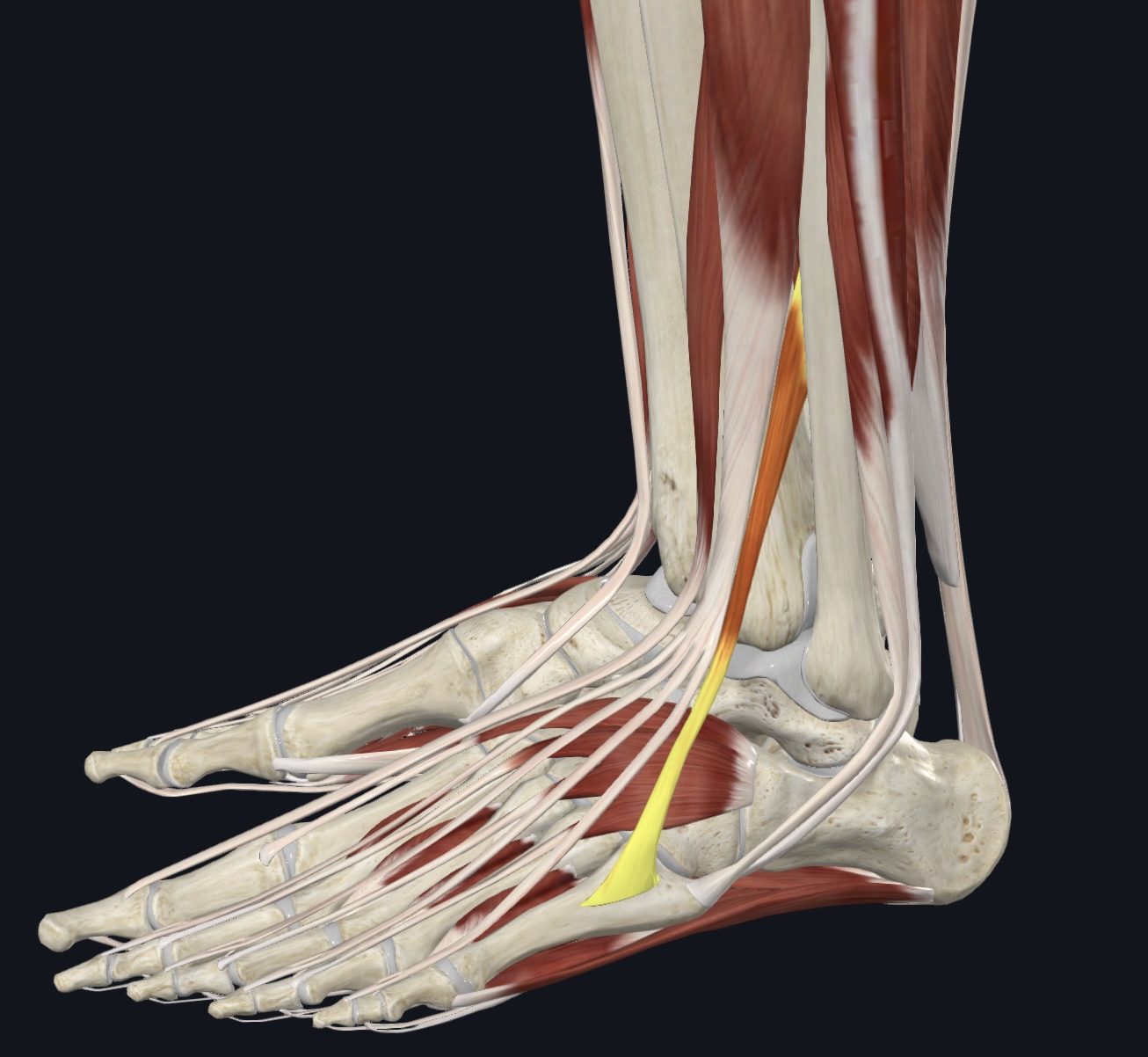
Peroneus tertius, (fused with extensor digitorum longus-often considered it’s fifth tendon)
O = distal anterior fibular shaft and interosseous membrane
I = dorsum of metatarsal 5
A = eversion and dorsiflexion
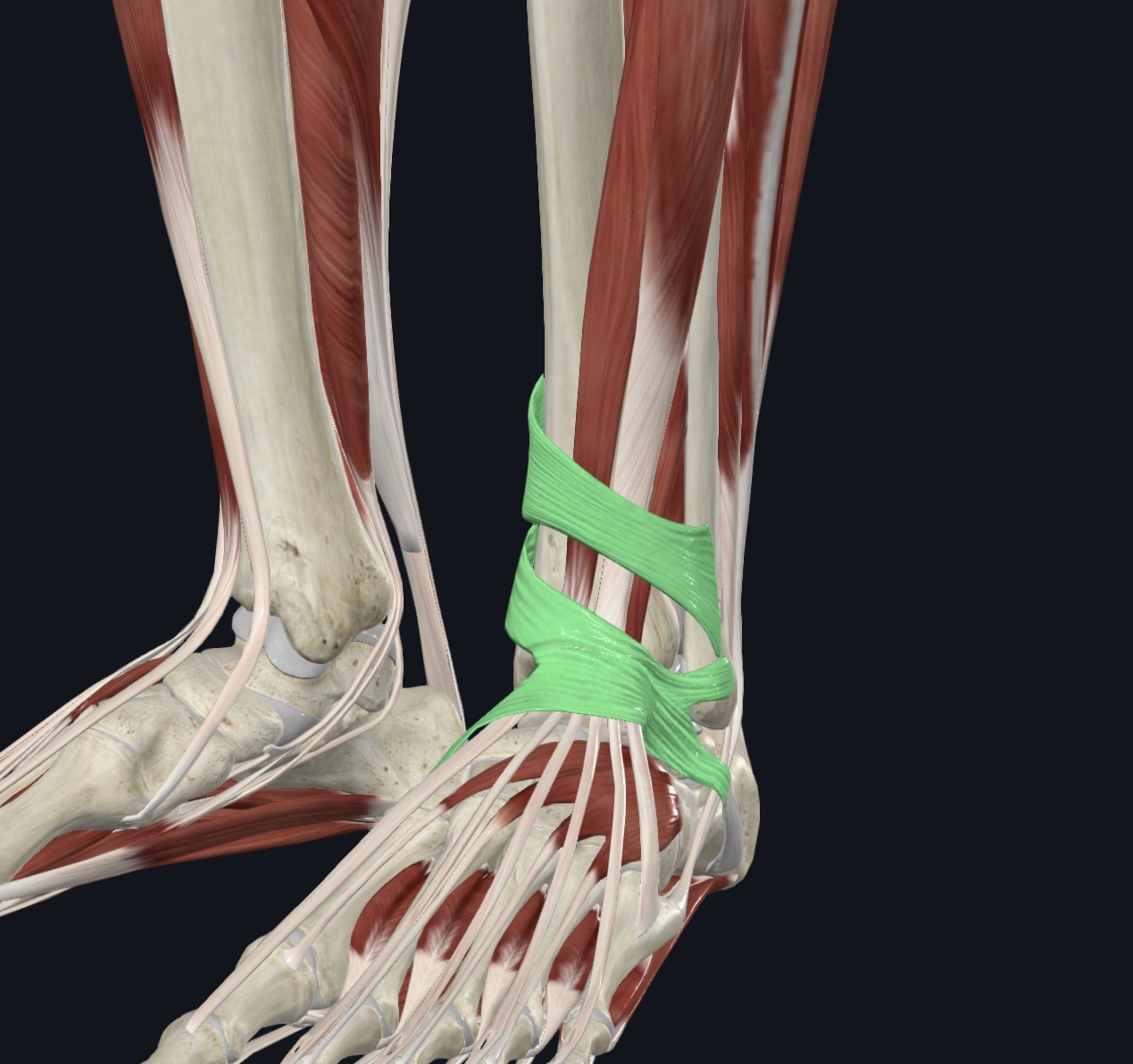
Extensor retinaculum (dense fascia: superior and inferior, I.D. only),
Muscles of the Lateral Compartment: Movement of Ankle
(Both are innervated by the superficial peroneal nerve)
Peroneus longus/Fibularis longus
Peroneus brevis
Peroneal retinaculum (dense fascia, I.D. only)
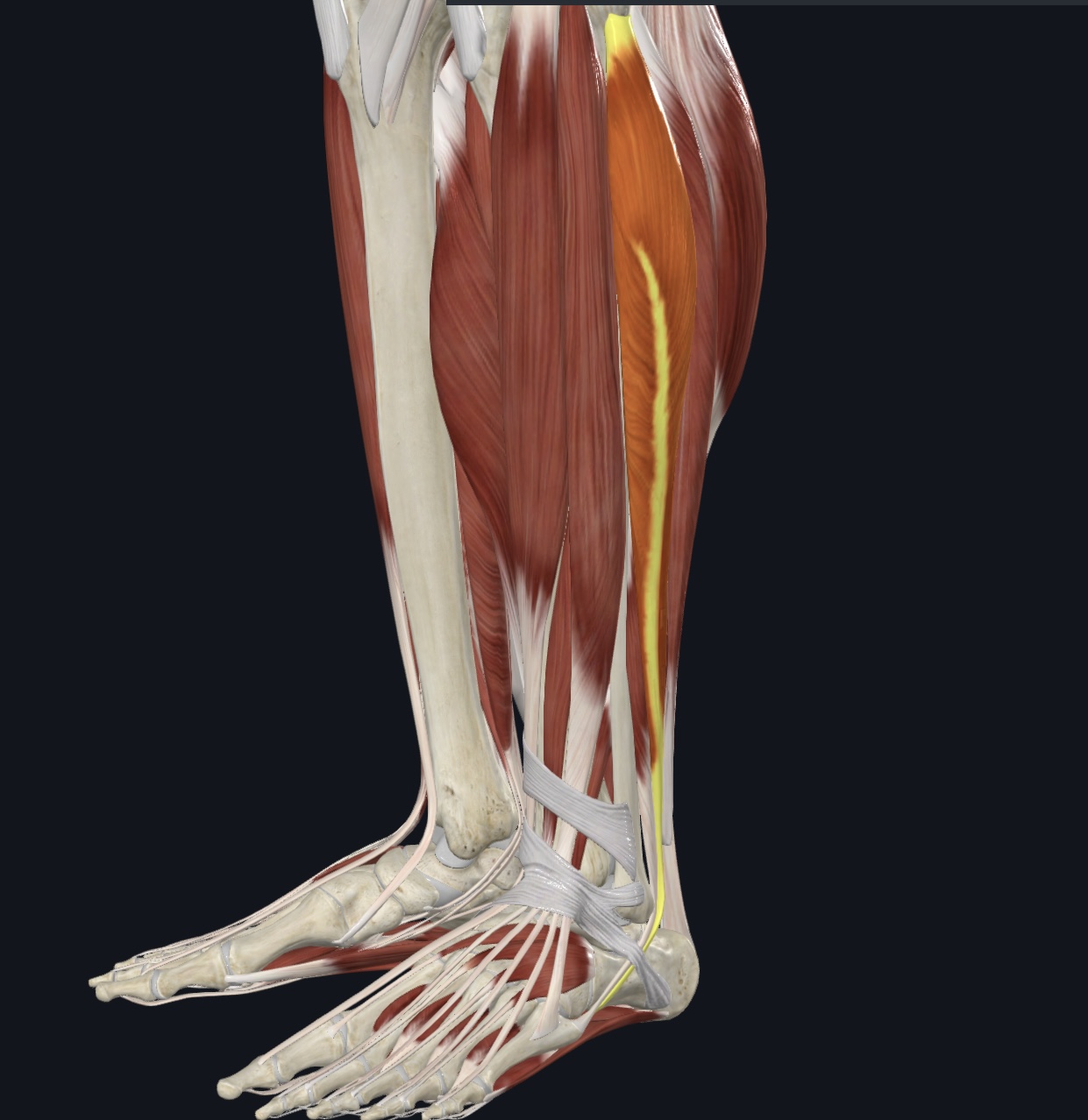
Peroneus longus/Fibularis longus
O = head and proximal fibula, lateral condyle of tibia
I = tendon travels under foot to the medial cuneiform and metatarsal 1
A = plantarflexion and eversion; supports longitudinal and transverse arches
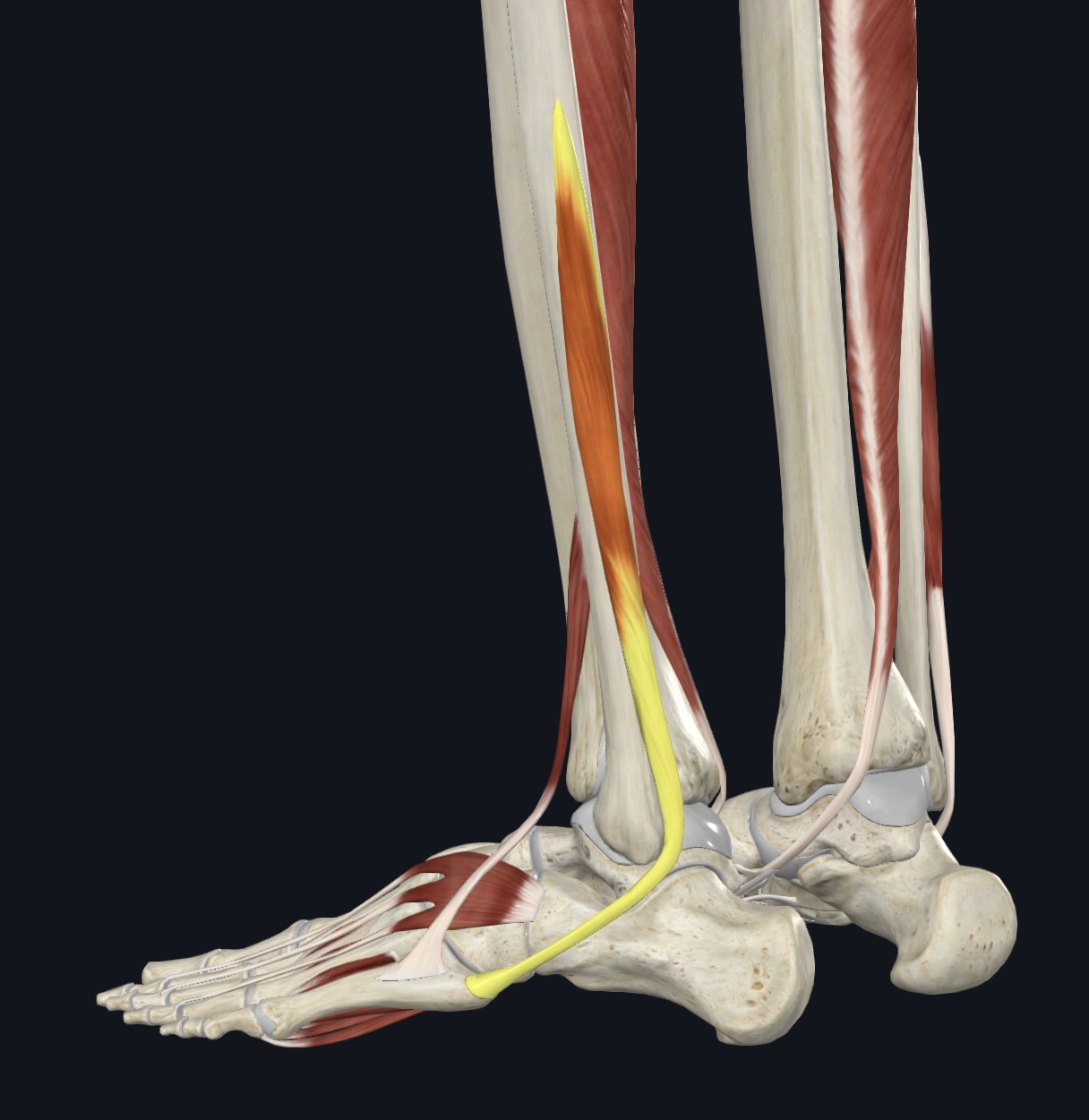
Peroneus brevis,
O = distal midlateral fibular shaft
I = proximal end of metatarsal 5
A = plantarflexion and eversion