Psychology 2000 Final Study cards
1/142
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Han
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
Operant Conditioning
A type of learning where behavior is controlled by consequences (rewards or punishments).
Skinner Box
A controlled environment where animals (like rats or pigeons) are trained to perform tasks (e.g., press a lever) in exchange for rewards (like food) or to avoid punishments (like a mild shock).
Case Study
In-depth study of one person or a very small group, often with rare traits.
Longitudinal Survey
A research method that involves repeated observations of the same variables over long periods. This method is often used to study changes over time in a population or individual, allowing researchers to observe trends and developments.
Naturalistic Observation
Observes behavior in a natural setting without manipulation or control (e.g., watching kids at recess).
Negative Correlation
A relationship between two variables in which one variable increases while the other decreases, indicating an inverse association.
Positive Correlation
A relationship between two variables where both variables move in the same direction, meaning that as one variable increases, the other also increases.
No Correlation
A relationship between two variables where changes in one variable do not predict changes in the other variable, indicating no association.
Control group
A group in an experiment that does not receive the treatment or intervention and is used as a benchmark to measure the effects of the treatment on the experimental group.
Experimental group
A group in an experiment that receives the treatment or intervention being tested, allowing for comparison with the control group.
Independent Variable
The variable that is manipulated or changed in an experiment to observe its effects on the dependent variable.
Dependent Variable
The variable that is measured or observed in an experiment, which is affected by changes in the independent variable.
cross-sectional study
compares different groups (or segments) of people at a single point in time.
A school wants to see if the amount of sleep students get impacts their test performance
This is an example of a study that examines the relationship between sleep (independent variable) and test performance (dependent variable) by comparing outcomes among students.
A fitness coach compares the effects of two workout programs on weight loss over a month.
This is an example of a study that evaluates the impact of different workout programs (independent variable) on weight loss (dependent variable) over a specific time frame.
somatic nervous system
a part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movements and sensory information transmission. controls voluntary muscle movements. “Soma" = body → Somatic = voluntary body movements
Autonomic Nervous System
a part of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. Auto = automatic → Autonomic = automatic body functions.
Sympathetic Nervous System
a division of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for stressful or emergency situations, often referred to as the 'fight or flight' response.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
a division of the autonomic nervous system that promotes rest and recovery, often referred to as the 'rest and digest' response. calms the body down, rest-and-digest mode.
Dendrites
branch-like structures on neurons that receive signals from other neurons and transmit them to the cell body.
Soma
Also called the cell body — it processes the signal but doesn’t receive it directly from other neurons.
Terminal Buttons (Axon Terminals)
These are the "senders" — they release neurotransmitters to pass the message to the next neuron.
Myelin Sheath
A fatty covering around the axon that speeds up signal transmission — it doesn’t send or receive signals directly.
The order of neural flow
Dendrites → Soma → Axon → Terminal Buttons→ Synapse
Wernicke’s Area
responsible for language comprehension — understanding spoken or written language. Wernicke = Word Meaning (comprehension)
Broca’s Area
responsible for language production — planning and creating speech. Broca = Broken speech (production problem)
Amygdala
Handles emotions, especially fear and aggression - not language.
Occipital Lobe
Processes visual information, not language
Thalamus
is the brain’s main sensory relay station. It receives sensory signals (except smell) and routes them to the appropriate areas of the cortex for processing. (“Traffic Cop” of the brain for sensory info)
Hippocampus
Handles memory formation, especially converting short-term memory to long-term.
Hypothalamus
Regulates homeostasis — controls body temperature, hunger, thirst, and links the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of tissues and organs — especially useful for the brain and spinal cord. (Magnetic + detailed images)
EEG (Electroencephalogram)
Measures electrical activity in the brain — great for studying sleep or seizures, not for imaging structures. (Electricity (brain waves))
PET Scan (Positron Emission Tomography)
Shows activity/function by tracking a radioactive tracer — used to see what part of the brain is active, not detailed tissue structure. (Position of brain activity)
CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
Uses X-rays to take images — faster but less detailed than MRI; good for detecting bleeding or fractures. (Cheaper quick scan (X-ray)
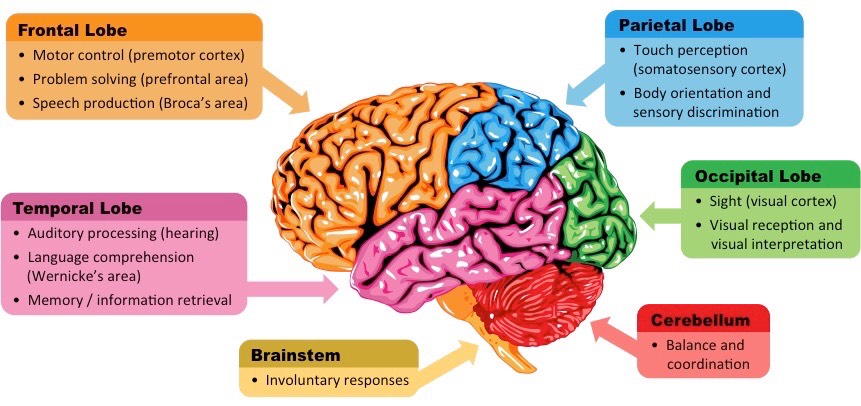
Frontal Lobe (Orange)
Motor control (premotor cortex)
Problem solving (prefrontal area)
Speech production (Broca’s area)
Also linked to decision-making, impulse control, and personality
thinking & speaking
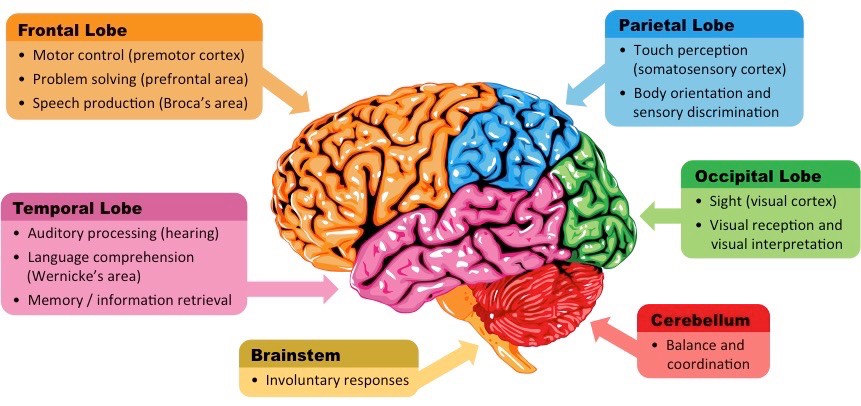
Temporal Lobe (Pink)
Hearing (auditory processing)
Language comprehension (Wernicke’s area)
Memory and information retrieval
hearing & understanding
Parietal Lobe (Blue)
Touch perception (somatosensory cortex)
Body orientation and spatial awareness
Helps you know where your body is in space
touch & space
Occipital Lobe (Green)
Sight (visual cortex)
Visual processing and interpretation
vision
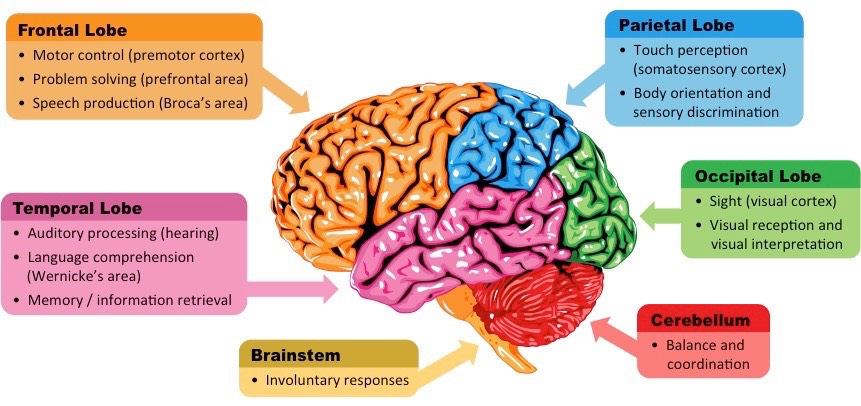
Cerebellum (red)
Balance and coordination
Helps fine-tune movements
balance
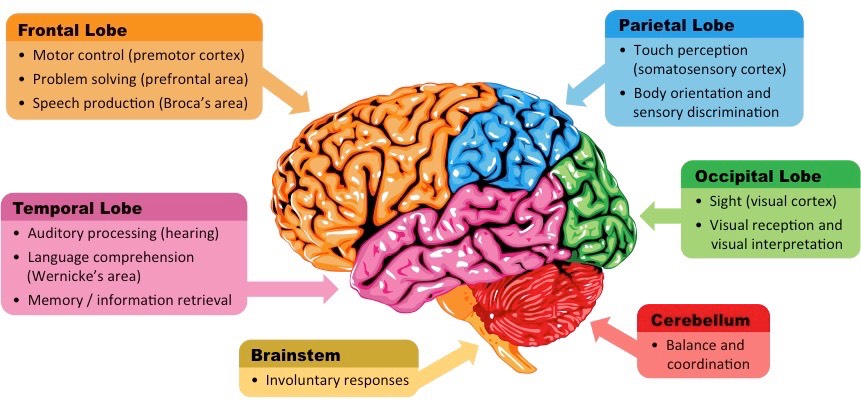
Brainstem (yellow)
Involuntary responses (breathing, heartbeat, digestion)
Connects the brain to the spinal cord
survival
Activation-Synthesis Theory
Dreams are the brain’s way of making sense of random neural activity during REM sleep.
(Key Word Trick:
Activation (brain activity) + Synthesis (making sense of it))
Wish-Fulfillment Theory (Freud)
Dreams are a way to satisfy unconscious desires and wishes.
Psychoanalytic Theory
A theory of psychology developed by Sigmund Freud that emphasizes the influence of the unconscious mind on behavior and the importance of childhood experiences.
Important Life Events Hypothesis
more like an informal idea that dreams reflect things going on in our daily lives.
Latent Content
the hidden, symbolic meaning of the dream — often representing unconscious thoughts, desires, or conflicts. (discovered by freud)
You dream of falling →
Manifest content = literally falling off a cliff.
Latent content = anxiety about losing control in real life.
Latent = Hidden (what it means)
Manifest Content
The actual events/images you remember from the dream (surface storyline).
Manifest = Memory (what you recall)
Collective Unconscious
shared symbols and memories across cultures
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD)
A sleep disorder where muscle paralysis doesn’t occur during REM sleep, causing the person to physically act out their dreams — sometimes violently
In normal REM, you're paralyzed. In RBD, you're not
Narcolepsy
A chronic sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep episodes, often accompanied by cataplexy.
Insomnia
A sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, leading to daytime fatigue and impaired functioning.
Sleep Apnea
A disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep — leads to fatigue but not dream reenactment.
Light Waves
Shorter wavelength = higher frequency = colors like blue/violet
Longer wavelength = lower frequency = colors like red
So, wavelength determines color
Sound Waves
Higher frequency = higher pitch (e.g., a whistle)
Lower frequency = lower pitch (e.g., a bass drum)
Frequency
the number of times a wave cycles in a second, determining the pitch of sound or color of light.
length (or wavelength)
the distance between consecutive peaks of a wave, affecting the color of light and pitch of sound.
Length = Frequency = Color (light), Pitch (sound)
Retina
retina is the layer at the back of the eye that contains photoreceptor cells — rods and cones — responsible for transduction, which is the process of converting light into neural signals.
Lens
Focuses light onto the retina but doesn’t handle sensory conversion
Iris
the colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil and controls the amount of light entering the eye.
Pupil
the opening in the center of the iris that allows light to enter the eye.
Rods
night/black & white vision
Cones
color/daytime vision
Proximity
the principle that objects close together are perceived as a group.
Similarity
the principle that objects that are similar in appearance are perceived as a group.
Good Continuation
the principle that elements arranged in a line or curve are perceived to be more related than elements not on the line or curve.
Closure
the principle that a broken or incomplete figure is perceived as a complete shape. (like seeing a triangle even if part of it is missing)
The Gestalt principle of closure says we tend to mentally fill in gaps in a visual image to perceive a whole, complete object, even when parts are missing.
What is the unconditioned stimulus in the Little Albert study?
A loud noise that scared Albert.
Term | Example |
|---|---|
UCS | Loud noise |
UCR | Fear to loud noise |
CS | White rat |
CR | Fear to white rat |
Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS)
A stimulus that naturally and automatically triggers a response without prior conditioning.
Unconditioned Response (UCR)
The unlearned, naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus, such as fear or distress in response to a loud noise.
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
A previously neutral stimulus that, after being paired with an unconditioned stimulus, becomes associated with a conditioned response.
Conditioned Response (CR)
The learned response to a previously neutral stimulus that has been conditioned to elicit a response after association with an unconditioned stimulus.
After Little Albert was conditioned to fear white rats, he also showed fear to a white bunny. What is this an example of?
Stimulus generalization
Stimulus Generalization happens when a subject responds the same way to stimuli that are similar to the conditioned stimulus (CS)
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates the concept of negative punishment?
Taking away a teenager's phone for breaking curfew.
Negative punishment means removing something pleasant to decrease a behavior.
_____ is when we reward successive approximations toward a target behavior, which is helpful to use when teaching a complex set of behaviors.
Shaping
Shaping
involves reinforcing behaviors that are incrementally closer to the desired behavior.
Teaching a dog to roll over by first rewarding it for lying down, then for turning slightly, and finally for a full roll.
Slot machines reward gamblers with money according to which reinforcement schedule?
Variable ratio schedule.
variable ratio schedule
provides reinforcement after an unpredictable number of responses.
Which is the correct order of steps in the modeling process?
Attention → Retention → Reproduction → Motivation
Attention
You must notice the behavior.
Retention
You must remember the behavior after observing it.
Reproduction
You must be able to reproduce the observed behavior.
Motivation
You must have a reason or desire to perform the behavior.
Bandura’s social learning theory
is a theory that explains how individuals learn behaviors through observation, imitation, and modeling, emphasizing the roles of retention, reproduction, and motivation.
What is a schema?
A mental construct consisting of a cluster or collection of related concepts.
______ is when you stereotype someone or something without a valid basis for your judgment.
Representative bias
Representative bias
occurs when we judge or stereotype something based on how closely it matches a prototype we have in mind, rather than on logical reasoning or actual probability.
Example: Assuming someone is a librarian because they’re quiet and wear glasses, even if it's statistically unlikely.
Which type of bias involves becoming fixated on a single trait of a problem?
Anchoring bias
Anchoring bias
occurs when individuals rely too heavily on the first piece of information (the “anchor”) when making decisions.
Example: If you're told a shirt was originally $200 and is now $100, it seems like a great deal—even if the shirt isn't actually worth $100.
In order for a test to be normed and standardized it must be tested on ______.
A representative sample
representative sample
accurately reflects the demographics of the larger population for which the test is intended.
Example: If you're creating a math test for all 8th graders, your sample should include 8th graders from different regions, backgrounds, and abilities — not just one specific type.
Fluid intelligence is characterized by ______.
Being able to see complex relationships and solve problems
Fluid intelligence
your ability to think quickly and abstractly, solve novel problems, and recognize patterns — without relying on prior knowledge or experience.
crystallized intelligence
which is based on accumulated knowledge (like facts and vocabulary)
The three functions of memory are ______.
Encoding, storage, and retrieval.
Encoding
The process of taking in information and converting it into a form that can be stored in the brain.
Storage
The process of maintaining encoded information over time for later retrieval.
Retrieval
The process of accessing and bringing into consciousness the stored information from memory.
Answering essay questions requires what type of retrieval?
Recall
According to the Atkinson-Shiffrin model, the three stages of memory are:
sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
Sensory Memory
Briefly holds incoming sensory information (like sights and sounds).