HOA 3 - Chinese Architecture
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Characteristics of Chinese Architecture
Palaces and temples are the chief building type.
System of wood frame construction
Bilateral Symmetry
Hierarchy of buildings based on placement in a property or complex.
Cosmological concepts (Feng Shui or Geonmancy).
China’s vast and diverse geography has played a crucial role in shaping its architectural styles. From the mountainous regions in the west to the fertile plains in the east, different landscapes influenced building techniques and materials:
Geographical Influence
Due to colder climates and proximity to the steppes in Northern China, buildings often used ____ and _____ and were built to withstand harsh winters.
thicker walls and courtyards
What are the lighter materials used in Southern China that promote ventilation?
wood and bamboo
What part of China integrate elevated floors to avoid flooding.
Southern China
The mountainous ares in China resulted to what form of structures to accommodate uneven ground?
tiered structures
stilted building
The natural resources available in different regions determined construction materials.
Geological Influence
What are the abundant materials in Northern Region that led to construction of buildings with rammed earth walls?
stone
earth resources
In this region, wood was more plentiful, and timber-frame structures became dominant. The use of bamboo was also common in these areas.
Southern Region
A technique for constructing foundations, floors, and walls using compacted natural raw materials such as earth, chalk, lime, or gravel.
Rammed Earth
The climate of a region dictated the architectural solutions for comfort.
Climatic Influence
An elevated heated platform
Kang
In this area, hot and humid weather led to large eaves in structures to provide shade and encourage air flow.
Southern China
These areas had to deal with typhoons, so homes were designed with steep roofs to allow rain to quickly run off and avoid damage.
Eastern Coastal Region
Chinese architecture evolved through several dynasties, with each era contributing to the stylistic and structural development of buildings.
Historical Influence
Marked the beginning of many typical Chinese architectural elements like courtyards and symmetry. This period also saw the construction of defensive structures like the Great Wall.
Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE)
A golden age of Chinese architecture, known for Buddhist temples and the development of multi-storied pagodas.
Tang Dynasty (618 – 907 CE)
Innovations in construction techniques, such as bracket systems that allowed for larger buildings with broader, curving roofs.
Song Dynasty (960 – 1279 CE)
Known for grandiose palatial architecture, such as the Forbidden City, with an emphasis on balance, harmony, and symbolism.
Ming Dynasty (1368 – 1644 CE)
Saw further refinement of traditional Chinese elements and an increase in Western influence, especially in port cities like Shanghai.
Qing Dynasty (1644 – 1912 CE)
What are the 3 religions and philosophies that deeply influenced Chinese architecture?
Confucianism
Buddhism
Taoism/Daoism
This religion focused on hierarchy and harmony influencing the symmetrical layout of imperial palaces, administrative buildings, and temples.
Confucianism
What did Confucian architecture focused on?
order
formality, and
a sense of hierarchy in space.
This religion introduced pagodas, stupas, and monasteries.
Buddhism
became prominent with tiered towers that were spiritual as well as practical spaces for meditation and worship.
Buddhist architecture
According to buddhist religion, the pagoda design was symbolic and represents?
the connection between heaven and earth
This religion advocated for harmony with nature, which is reflected in gardens, pavilions, and temples that blend seamlessly with the natural landscape.
Taoism/Daoism
It is visible in the undulating roofs and use of natural materials.
Daoist influence
Determine which religion.
General the least noisy, colorful, and lively of all Chinese temples.
Confucianism
Determine which religion.
Usually contain the same combination of fairly recognizable important deities
Buddhism
Determine which religion.
Courtyards are usually filled with stelae (stone tablets) dedicated to various local scholars.
Confucianism
Determine which religion.
Tend to be the most colorful and snazzy.
Taoist
Determine which religion
The main gates are painted with fierce-looking mythical heroes to scare off evil spirits. The halls can contain any number of different deities, the many-armed Guan Yin among them.
Taoist
Color of columns in Buddhist temples
Red
Color of columns in Taoist temples
Black
Some key types of ancient structures in China.
Palaces
Temples and Monasteries
Tombs and Mausoleums
Pagodas
Residential Courtyards
City Walls and Fortification
These grand complexes, like the Forbidden City, were designed with strict adherence to hierarchical and symbolic principles. Symmetry, central axes, and the use of open courtyards were essential.
Palaces
The palace of the son of heaven and the conceptual center of the empire.
Palace of Heavenly Purity
Emperor's throne room and also wehere he met daily with his officials.
Hall of Supreme Harmony
A palace complex including temples, reception halls, residences, and service buildings.
Forbidden City
Multi-tiered roofs, beautifully designed archways and magnificent temples and residences
Kaohsiung Confucius Temple in Taiwan
Bright Hall
A ritual structure that serves as the symbolic center of imperial power
Designated as the intersection of heaven and earth oriented around the four cardinal direction.
Mingtang
A jade ring moat
Biyong
Religious buildings, such as Buddhist temples, Daoist temples, and Confucian academies, were built with spiritual significance. Structures like pagodas (e.g., Big Wild Goose Pagoda) were often part of temple complexes.
Temples and Monasteries
In its overall layout, it symbolizes the relationship between heaven and earth.
It is the most complete existing imperial sacrificial building complex in China.
World's largest existing building complex for offering sacrifice to heaven.
Temple of Heaven
The most famous of these is the Mausoleum of the First Qin Emperor, which includes the Terracotta Army. Ancient Chinese tombs were typically large, mound-like structures reflecting the belief in the afterlife.
Tombs and Mausoleums
Tall, multi-storied towers introduced from India through Buddhism. Examples include the Songyue Pagoda (Henan) and the Iron Pagoda (Kaifeng).
Pagodas
These were traditional residential compounds designed around a central courtyard, prevalent among wealthy families and officials. They are a hallmark of Beijing’s hutongs.
Residential Courtyards (Siheyuan)
The Great Wall of China, spanning thousands of miles, and city walls (like those of Xi'an) were built as defense structures, often using rammed earth and brick.
City Walls and Fortifications
Name for a Chinese pagoda
Ta
World's largest military structure
Great Wall of China
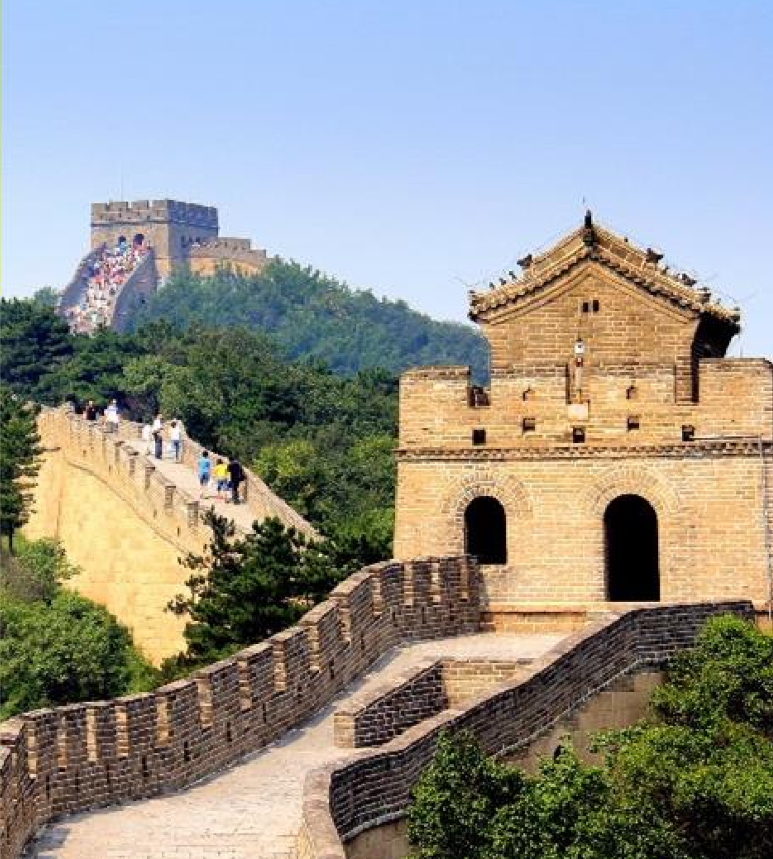

Identify the structure
The Great Wall of China
It has an incomparable significance in the history of China.
Its purpose was to protect China from outside aggressions, but also to preserve culture from the customs of foreign barbarian.
The Great Wall of China
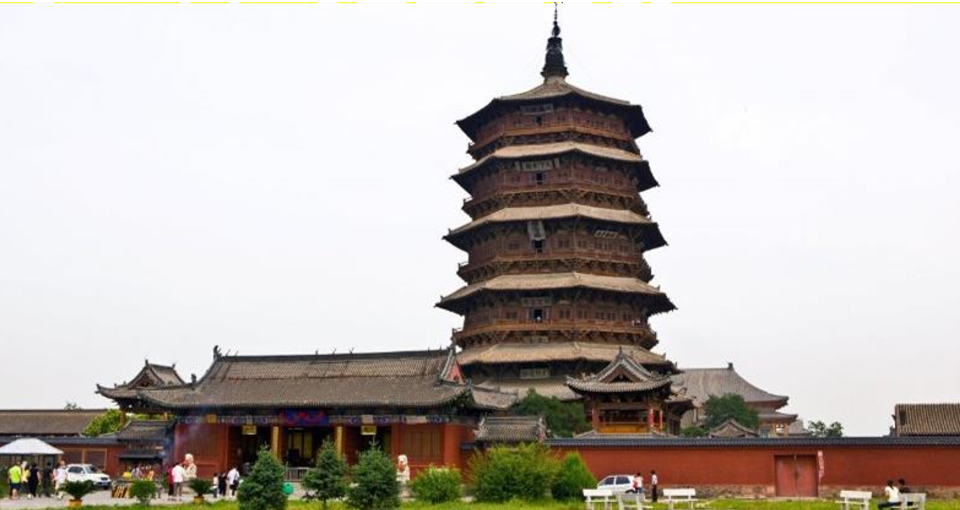

It is a 200-foot-high tower built entirely out of wood.
Fogong Pagoda
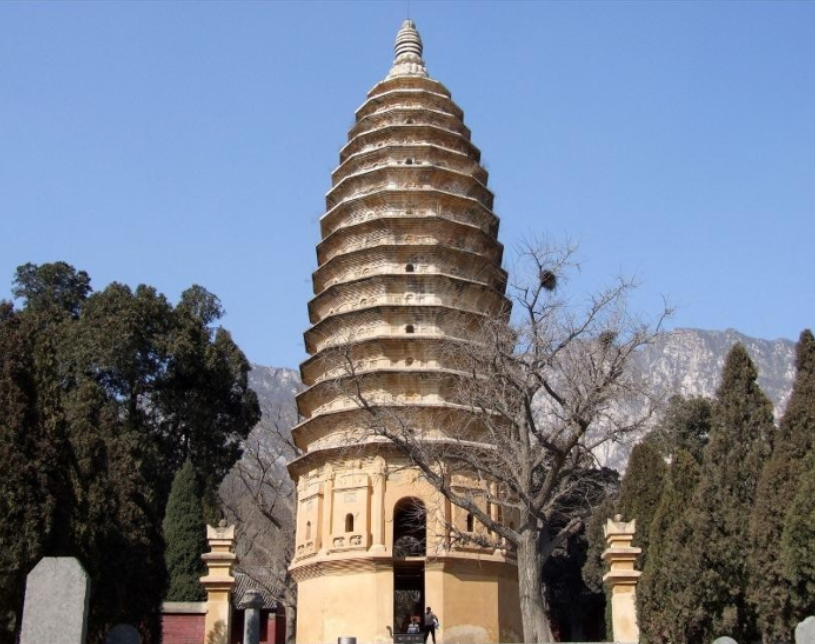

China's oldest surviving Ta.
The Songyue Temple Ta (Dengfeng, Henan Province)
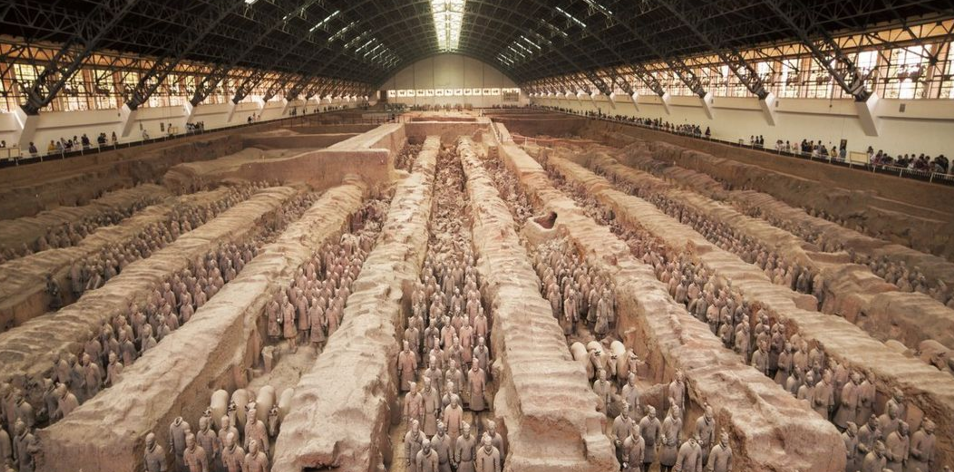

Tomb of the First Qin Emperor
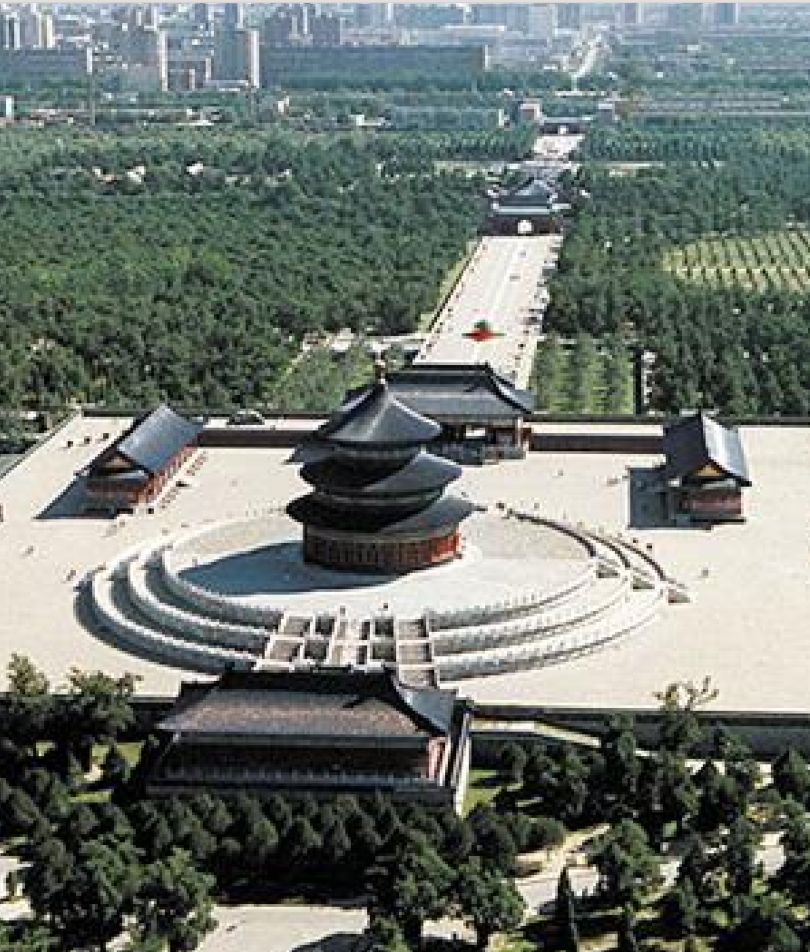

Identify the structure
Temple of Heaven
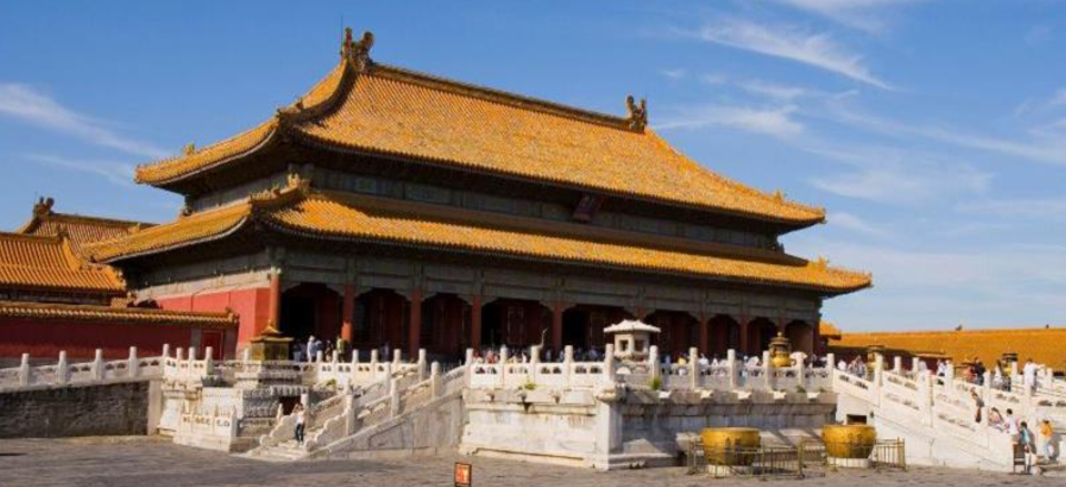

Best preserved imperial palace in China built by Emperor Zhu Di
Palace of Heavenly Purity
Monumental gateway to a palace, tomb, or sacred place.
Pailou
Bell tower or pavilion at the right side of a city gate, palace entrance, or forecourt of a temple.
Zhonglou
Left side counterpart of a Zhonglou
Guluo
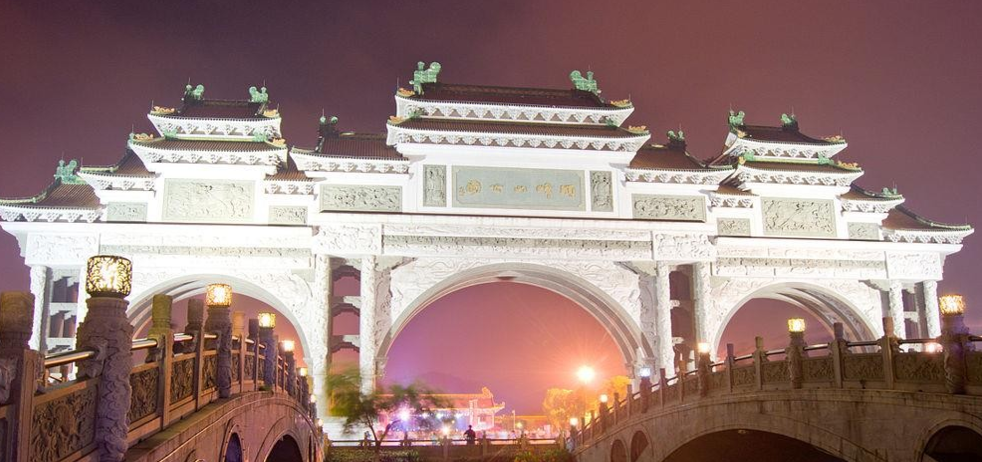

Identify the structure
Pailou or Paifang
List down particular method of construction used in ancient Chinese.
Timber Frame Construction (Post and Beam)
Rammed Earth and Brick Walls
Roofing System - Curved Roof
Use of Symmetry
Court Designs
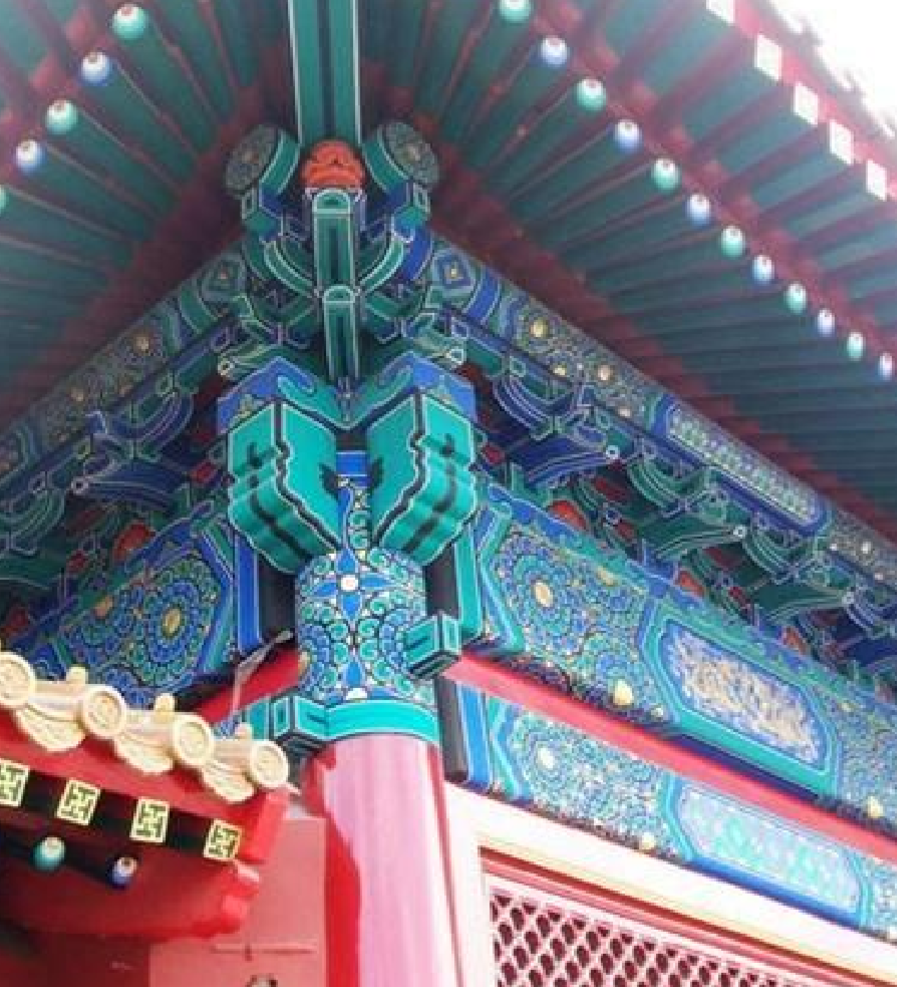

Interlocking bracket system used in traditional Chinese construction to support roof beams.
Has both structural and decorative purpose.
Dougong
It is the basic measure in construction.
Jian
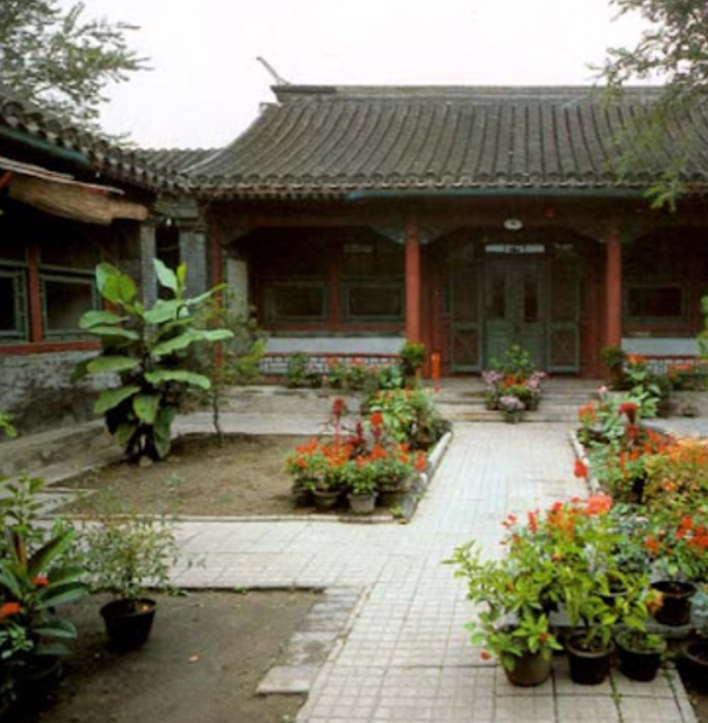

Courtyard Housing
Siheyuan
Characteristics of Ancient Architecture
Hierarchy and Symbolism
Curved Roof and Eaves
Axial Layout
Color Symbolism
Use of Wood
Color Connotations:
color of wood
green
Color Connotations:
color of the earth
yellow
Color Connotations:
color of water
blue and black
Color Connotations:
color of metal
white and gray
Color Connotations:
color of fire
red
What are the ornamental details in Chinese Architecture?
Carved and Painted Beams and Ceiling
Roof Ornament
Glazed Roof Tiles
Stone Lions (Shishi)
Windows and Doors
Calligraphy and Inscriptions
Relief and Sculptures
Intricate carvings and paintings on beams, ceilings, and eaves were common in temples and palaces.
The designs often included dragons, phoenixes, and other mythical creatures, symbolizing imperial power or auspiciousness.
Carved and Painted Beams and Ceiling
A mythical fish often placed at the roof's edge, was believed to ward off fires.
Chiwen
Many ancient buildings feature small figurines and animals (like dragons, phoenixes, and lions) perched on the corners of the roof. These decorations were meant to protect the building and its inhabitants from evil spirits.
Roof Ornaments
The use of glazed ceramic tiles, often in yellow, green, and blue, was common in palaces and temples.
The yellow-glazed tile was exclusively reserved for the emperor's use in buildings like the Forbidden City
Glazed Roof Tiles
Color of glazed roof tile that was exclusively reserved for the emperor's use in buildings like the Forbidden City.
Yellow
Pairs of stone lions were placed in front of important buildings to symbolize strength and protection.
These guardian lions are iconic and widely replicated.
Stone Lions (Shishi)
Lattice windows, typically made from wood, were decorated with geometric or floral patterns.
These were often designed with spiritual significance, symbolizing harmony between humans and nature.
Windows and Doors
Buildings often featured plaques and inscriptions in Chinese calligraphy, especially in temples and palaces, adding a layer of cultural and historical significance.
Calligraphy and Inscriptions
Stone carvings depicting dragons, cranes, and other auspicious animals were common in both palaces and tombs.
These sculptures were not only decorative but often held spiritual meaning, intended to bring good fortune or safeguard against evil.
Reliefs and Sculptures
What are the Manners of Design that is followed by Chinese Architecture?
Feng Shui
Modular Design
Blending with Nature
What are the chief building type?
Palaces and Temples
Ancient Chinese architecture often sought to harmonize with the natural environment, especially in garden designs.
Blending with Nature
The buildings were often composed of modular units, allowing flexibility and ease of expansion or reconstruction.
Modular Design
The most important annex halls in Chinese Buddhist temples and mainly for enshrining Guanyin.
Hall of Guanyin
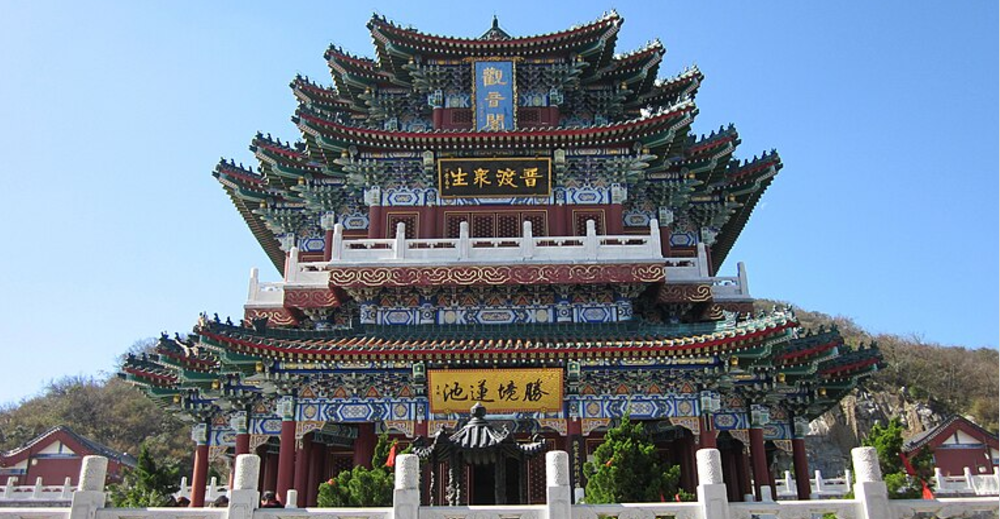

Identify the structure
Hall of Guanyin
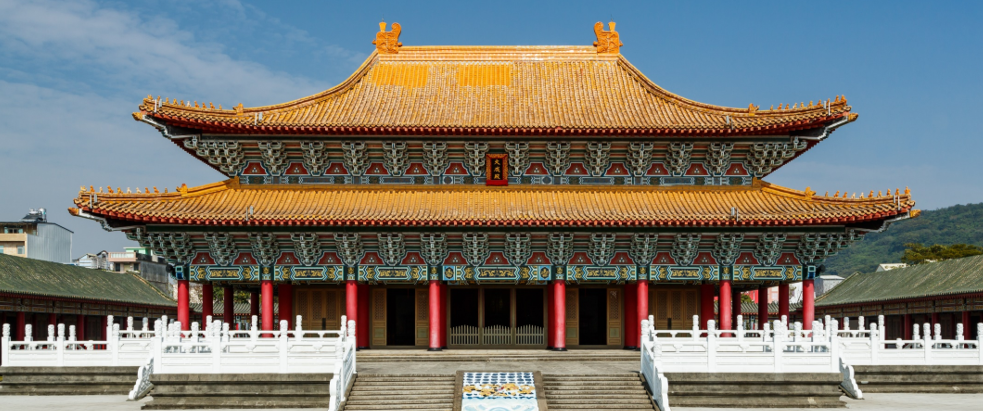

Identify the structure
Kaohsiung Confucius Temple in Taiwan
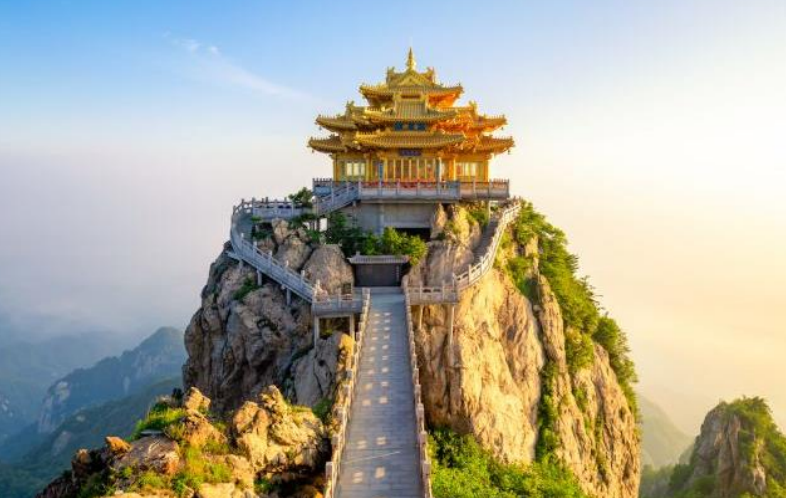

Mount Laojun in Luoyan
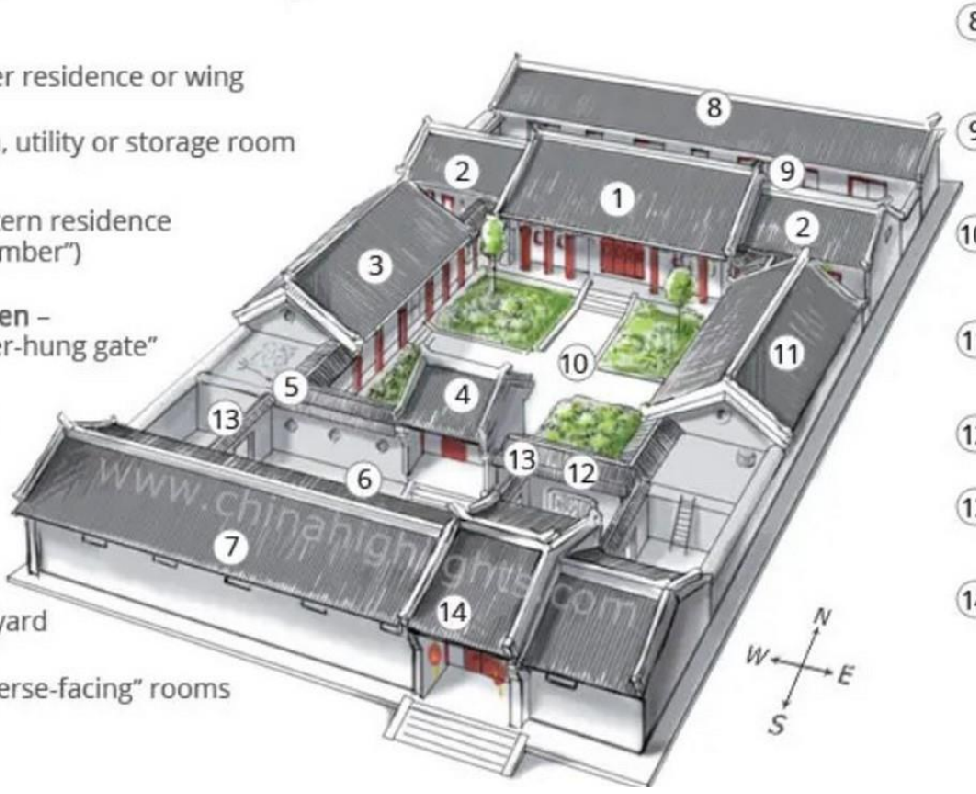
ZhengfangHoudhaji
Erfang
Xixiangfang
Ermen, Chuihuamen
Zoulang
Waiyuan
Daozuofang
Houzhaoifang
Disanjinyuan
Neiyuan
Dongxiangfang
Yingbi
Pingmen
Damen