chem exam 2
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
steam reforming
methane and catalyst forming hydrogen
bayer
bauxite and sodium hydroxide forming alumina
hall
alumina forming aluminum metal
haber
nitrogen and hydrogen forming ammonia
wet method
fluoride apatite and sulfuric acid forming phosphoric acid
ostwald
ammonia forming nitric acid
claus
hydrogen sulfide to sulfur
contact
sulfur forming sulfuric acid
chlor-alkali
sodium chloride and water forming chlorine, hydrogen, and sodium hydroxide
blast furnace
iron ore, coke, and hot air forming iron
alkali metals properties
large radius
low ionization energy and electronegativity
+1 cations
OH basic in water
groups 1 and 2 with water
very reactive
displaces in water
Be
forms covalent bonds because they are small and attract electrons
oxidize to form emeralds
Mg+2
in chlorophyll making it more rigid for electron transport rather than losing energy
Ca
building material
F inserts instead of OH- in tooth enamel
B
forms unusual bonds for octet
boric acid kills ants
borax as detergent
Al
commercial
oxidizes to form ruby, sapphaire, topaz
C
three forms
C60- is tubular and spherical sp3
graphite- sp2
diamond- sp3
CO3- greenhouse gas, CO2, diprotic acid, limestone,CaCO3
Si
found everywhere
glass, transistors, silicone, lubricants
quartz and amethyst
N
many oxidation states
explosives, fertilizers, laughing gas, viagra, smog, preservatives
P
found in common materials
soaps, toothpaste, fertilizer, pesticides, DNA
extracted from calcium phosphate rock
cause algae bloom and is discouraged
H2SO4
sulfuric acid
manufactures in large quantities
Claus and contact
strong acid, oxidizing agent, and dehydrating agent
extraction of phosphate, production of paper, and reactant
Halides
small radius
small radii, high ionization energy and electronegativity
form -1 anions
chlorine
strong oxidizing agent
disinfection and sanitation
PVC
Noble gases
inert
2-8 filled shell electrons
cryogens (He), inert gases (Ar), lights (Ne)
transition metals
metallic character?
atomic radius?
lanthanide contraction?
oxidation?
group 11 and 12?
metallurgy?
metallic character: increases down a group, decreases across a period
good conductors w high melting points
atomic radius: Decreases across the period due to increasing nuclear charge
Lanthanide contraction and density: poor shielding by f-electrons causes smaller atomic radii for 3rd row
oxidation states and acidity: higher oxidation states tens to be oxidizing agents
group 11 and 12 inertness: filled d-orbitals, inert, act like main group elements
metallurgy: extracting, refining, and processing metals form their natural sources into pure, usable forms
Scandium
strong lewis acid
titanium
white pigmentv
vanadium
catalyst in sulfuric acid production
chromium
corrosion resistant, makes stainless steel
manganese
alloys, redox demos
iron
abundant
strong
hemoglobin
cobalt
harden steel
magnets
nickels
battery
steel
cooper
conductive
found in nature
buildings and coins
silver
tarnishes to AG2S
coins
gold
inert
nature
dissolves in aqua regia
zinc
galvanization of iron
rust
mercury
liquid at room temp
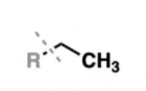
alkane
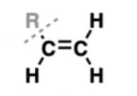
alkene
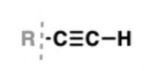
alkyne
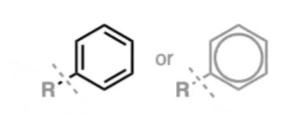
benzene ring

amine

alcohol

ether

alkyl halide

thiol

aldehyde
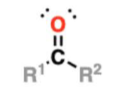
ketone
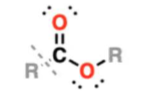
ester
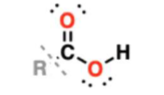
carboxylic acid
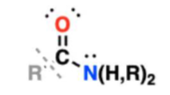
amide
CH4
meth
CH3CH3
eth
CH3CH2CH3
prop
CH3(CH2)2CH3
but
CH3(CH2)3CH3
pent
CH3(CH2)4CH3
hex
CH3(CH2)5CH3
hept
CH3(CH2)6CH3
oct
CH3(CH2)7CH3
non
CH3(CH2)8CH3
dec
CH3(CH2)9CH3
undec
CH3(CH2)10CH3
dodec
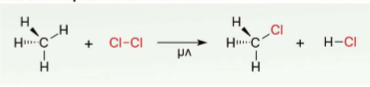
substitution
a substituent is replaced with another
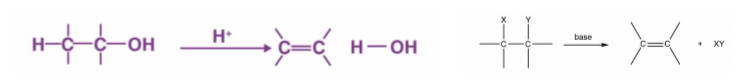
elimination
process in which a substituent is removed from a molecule
polymer condensation reactions are an example
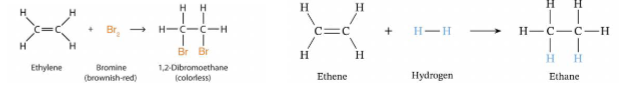
addition
process in which a substituent is added to a molecule
polymer addition reactions are an extreme example
polyester
alcohol
polyamide
amine
triglycerides
glycerol
sugars
alcohol
proteins
amine
carboxylic acid
ester
amide
ester
amide
alcohol
ether
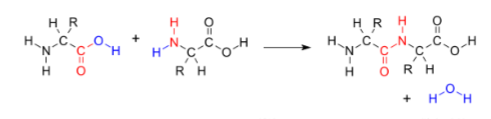
protein amide linkage
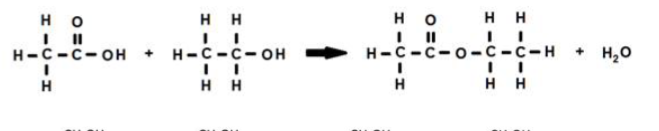
ester linkage
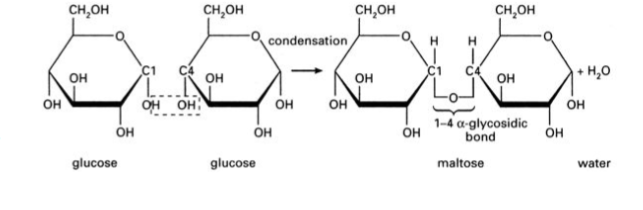
sugar ether linkage
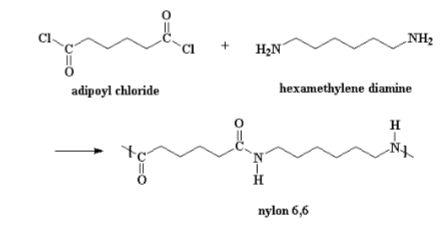
nylon amide linkage

polyethylene addition
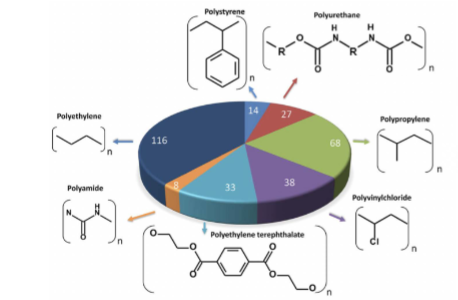
organic polymers
PET and PA are condensation- form esters (-COO-) and amides (-CONH-)
addition is everything else
Carbohydrates
polysaccharides
disaccharides
monosaccharides
lipids
triglycerides
fatty acids
glycerol
proteins
peptides
amino acids
nucleic acids
RNA
DNA
nucleotides
nuclear fission
splitting of a heavy atomic nucleus into smaller nuclei
nuclear fusion
process in which two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus
binding energy
energy required to break a nucleus into its constituent nucleons
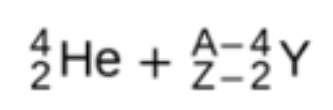
alpha decay
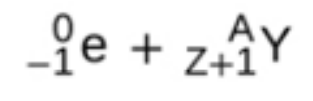
beta decay
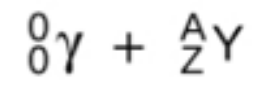
gamma decay
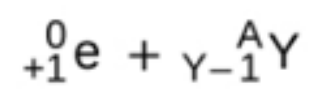
positron emission
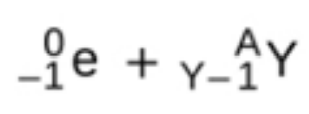
electron caputre
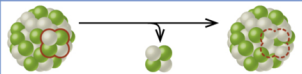
alpha decay
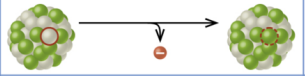
beta decay
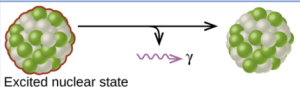
gamma decay
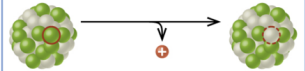
positron emission
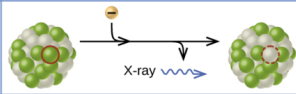
electron capture